本篇博文分享一篇寻找图像中灯光亮点(图像中最亮点)的教程,例如,检测图像中五个灯光的亮点并标记,项目效果如下所示:

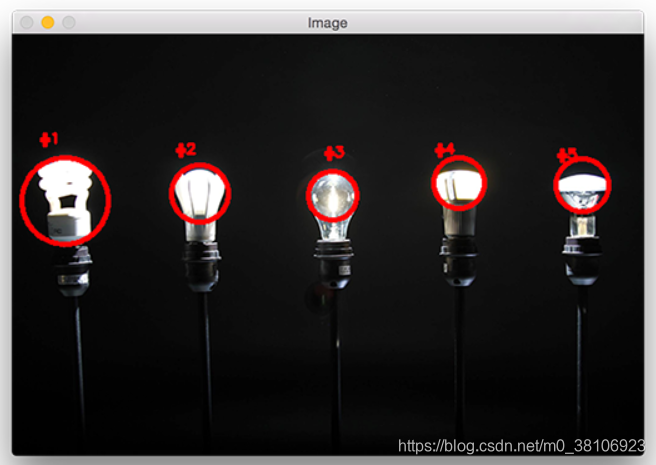
第1步:导入并打开原图像,实现代码如下所示:
-
# import the necessary packages
-
from imutils import contours
-
from skimage import measure
-
import numpy as np
-
import argparse
-
import imutils
-
import cv2
-
# construct the argument parse and parse the arguments
-
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
-
ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required=True,
-
help="path to the image file")
-
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
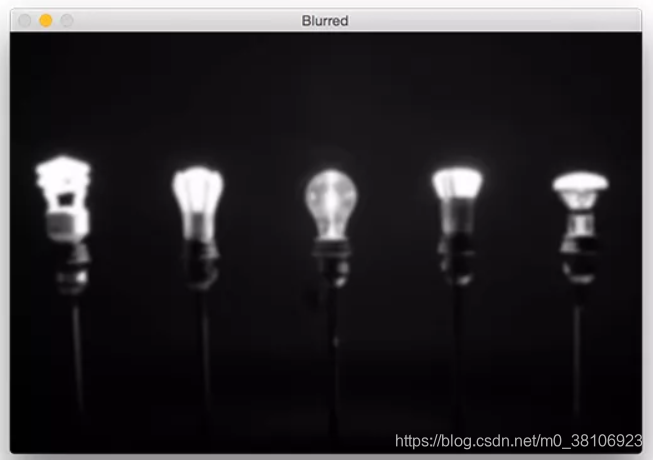
第2步:开始检测图像中最亮的区域,首先需要从磁盘加载图像,然后将其转换为灰度图并进行平滑滤波,以减少高频噪声,实现代码如下所示:
-
#load the image, convert it to grayscale, and blur it
-
image = cv2.imread(args["image"])
-
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
-
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (11, 11), 0)
导入亮灯图像,过滤后效果如下所示:
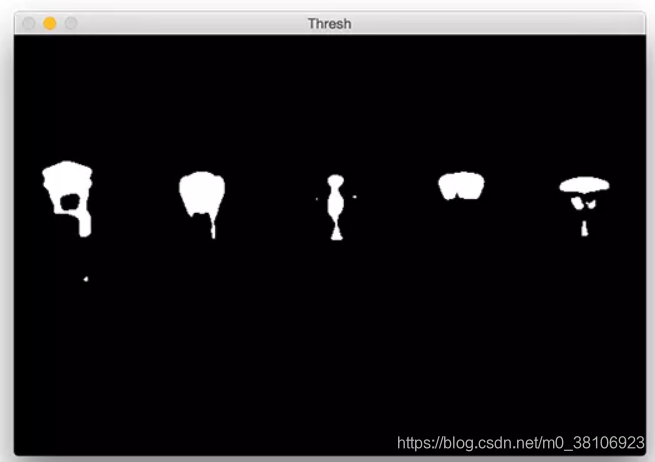
第3步:阈值化处理,为了显示模糊图像中最亮的区域,将像素值p >= 200,设置为255(白色),像素值< 200,设置为0(黑色),实现代码如下所示:
-
# threshold the image to reveal light regions in the
-
# blurred image
-
thresh = cv2.threshold(blurred, 200, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
效果如下所示:
第4步:此时可看到图像中存在噪声(小斑点),所以需要通过腐蚀和膨胀操作来清除,实现代码如下所示:
-
# perform a series of erosions and dilations to remove
-
# any small blobs of noise from the thresholded image
-
thresh = cv2.erode(thresh, None, iterations=2)
-
thresh = cv2.dilate(thresh, None, iterations=4)
此时“干净”的图像如下所示:

第5步:本项目的关键步骤是对上图中的每个区域进行标记,即使在应用了腐蚀和膨胀后,仍然想要过滤掉剩余的小块儿区域。一个很好的方法是执行连接组件分析,实现代码如下所示:
-
# perform a connected component analysis on the thresholded
-
# image, then initialize a mask to store only the "large"
-
# components
-
labels = measure.label(thresh, neighbors=8, background=0)
-
mask = np.zeros(thresh.shape, dtype="uint8")
-
# loop over the unique components
-
for label in np.unique(labels):
-
# if this is the background label, ignore it
-
if label == 0:
-
continue
-
# otherwise, construct the label mask and count the
-
# number of pixels
-
labelMask = np.zeros(thresh.shape, dtype="uint8")
-
labelMask[labels == label] = 255
-
numPixels = cv2.countNonZero(labelMask)
-
# if the number of pixels in the component is sufficiently
-
# large, then add it to our mask of "large blobs"
-
if numPixels > 300:
-
mask = cv2.add(mask, labelMask)
上述代码中,第4行使用scikit-image库执行实际的连接组件分析。measure.lable返回的label和阈值图像有相同的大小,唯一的区别就是label存储的为阈值图像每一斑点对应的正整数。
然后在第5行初始化一个掩膜来存储大的斑点。
第7行开始循环遍历每个label中的正整数标签,如果标签为零,则表示正在检测背景并可以安全的忽略它(9,10行)。否则,为当前区域构建一个掩码。
下面提供了一个GIF动画,它可视化地构建了每个标签的labelMask。使用这个动画来帮助你了解如何访问和显示每个单独的组件:

第15行对labelMask中的非零像素进行计数。如果numPixels超过了一个预先定义的阈值(在本例中,总数为300像素),那么认为这个斑点“足够大”,并将其添加到掩膜中。输出掩模如下图所示:

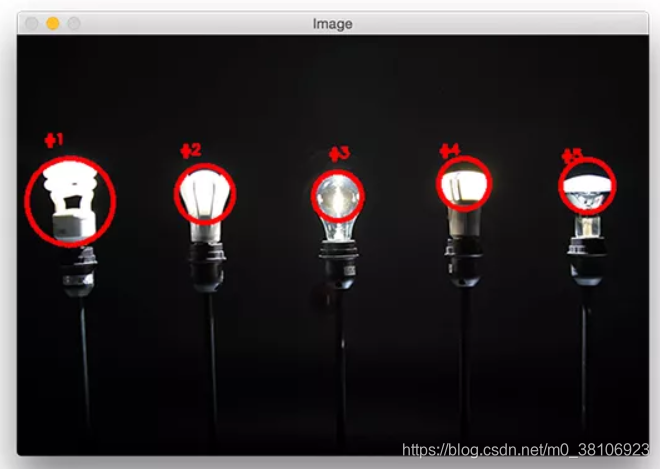
第6步:此时图像中所有小的斑点都被过滤掉了,只有大的斑点被保留了下来。最后一步是在的图像上绘制标记的斑点,实现代码如下所示:
-
# find the contours in the mask, then sort them from left to
-
# right
-
cnts = cv2.findContours(mask.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,
-
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
-
cnts = imutils.grab_contours(cnts)
-
cnts = contours.sort_contours(cnts)[0]
-
# loop over the contours
-
for (i, c) in enumerate(cnts):
-
# draw the bright spot on the image
-
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
-
((cX, cY), radius) = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(c)
-
cv2.circle(image, (int(cX), int(cY)), int(radius),
-
(0, 0, 255), 3)
-
cv2.putText(image, "#{}".format(i + 1), (x, y - 15),
-
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.45, (0, 0, 255), 2)
-
# show the output image
-
cv2.imshow("Image", image)
-
cv2.waitKey(0)
最后运行程序,可实现灯光亮点的检测和标记,每个灯泡都被独特地标上了圆圈,圆圈围绕着每个单独的明亮区域,效果如下所示:
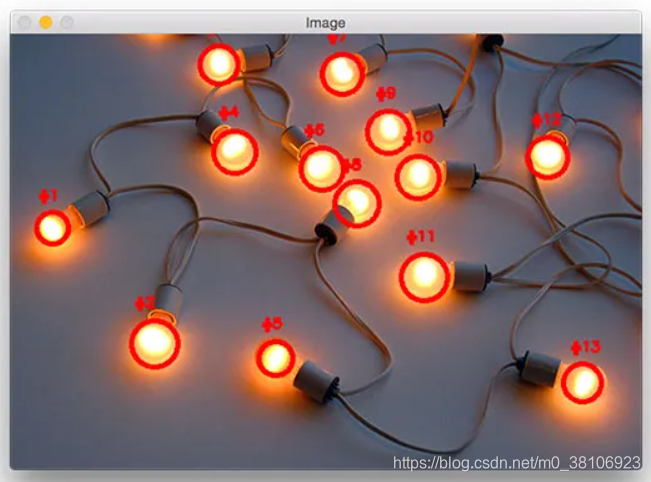
本文来源于:Detecting multiple bright spots in an image with Python and OpenCV
文章来源: handsome-man.blog.csdn.net,作者:不脱发的程序猿,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:handsome-man.blog.csdn.net/article/details/109261232