其他相关文章:
1. 前言
ViewModel 的作用是专门存放与界面相关的数据,分担 Activity/Fragment 的逻辑,同时会维护自己独立的生命周期。如当系统配置发生变更(如切换语言等)、横竖屏切换等,可能会导致 Activity 销毁重建,假设要被销毁是 Activity A,需要被重新创建的是 Activity B,虽然他们都属于同一类型,但是是两个不同的实例对象。因此在 Activity 销毁重建的过程中,就涉及 A 在销毁时,其内部维护的数据要过渡到重建的 B 中,这就依赖于 ViewModel。
ViewModel is a class that is responsible for preparing and managing the data for an
Activityor aFragment. It also handles the communication of the Activity / Fragment with the rest of the application (e.g. calling the business logic classes).
.
A ViewModel is always created in association with a scope (an fragment or an activity) and will be retained as long as the scope is alive. E.g. if it is an Activity, until it is finished.
.
In other words, this means that a ViewModel will not be destroyed if its owner is destroyed for a configuration change (e.g. rotation). The new instance of the owner will just re-connected to the existing ViewModel.
.
引用自 https://developer.android.com/reference/android/arch/lifecycle/ViewModel
ViewModel 一般在 MVVM 模式中协同 Jetpack 的其他组件一起使用。另外,ViewModel 的使用需要引入:androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel (本文涉及的版本为 2.2.0)。
2. ViewModel 常用的创建方式
由于 ViewModel 的生命周期是由系统维护的,因此不能直接在代码中通过 new 的方式创建。
另外 androidx.lifecycle.ViewModelProviders 在高版本中已经被废弃。
(1)直接基于 ViewModelProvider 获取
ViewModelProvider(activity/fragment).get(XXXViewModel::class.java)
- 1
(2)通过 ViewModelFactory 创建
class TestViewModelFactory(private val param: Int) : ViewModelProvider.Factory { override fun <T : ViewModel> create(modelClass: Class<T>): T { return TestViewModel(param) as T }
}
// 实例代码
ViewModelProvider(activity/fragment, TestViewModelFactory(0)).get(TestViewModel::class.java)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
其实,上述两种方式最终都是基于 ViewModelProvider.Factory 来生成 ViewModel 实例,只不过第一种方式如果不传 Factory,内部会使用默认的 Factory。
另外:
- 当需要在
androidx.fragment.app.Fragment中获取 ViewModel 实例时,可以基于androidx.fragment:fragment-ktx的FragmentViewModelLazyKt的扩展方法来实现懒加载。具体可以参考 Google architecture-samples TaskDetailFragment 的实现。 - 当需要在
androidx.activity.ComponentActivity中获取 ViewModel 实例时,可以基于androidx.activity:activity-ktx的ActivityViewModelLazyKt的扩展方法来实现懒加载。具体可以参考 Google architecture-samples TaskDetailFragment 的实现。
3. ViewModel 的生命周期
ViewModel 目前只有一个生命周期方法 onCleared(),是在 ViewModel 实例对象被清除的时候回调。
4. 关于 ViewModel 的架构规范
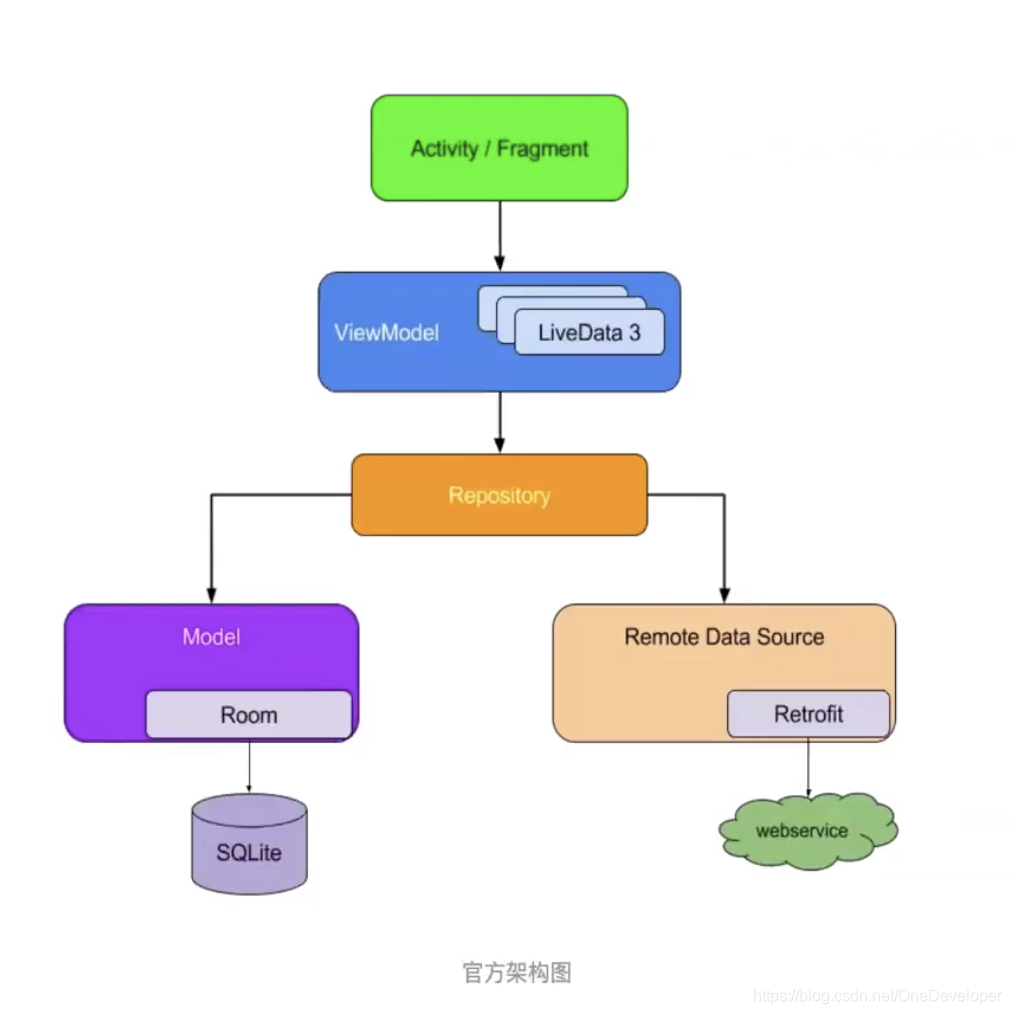
在 Google 的 architecture-samples(main 分支)Demo 中,在创建 ViewModel 实例时,会传递以 Repository 为后缀的接口实现实例。这其实是实现 MVVM 模式时的一种规范。
以 Repository 为后缀的接口,用于连接数据层,定义数据操作的约束与规范,然后由具体的实现类去实现(如去数据库加载数据、从网络获取数据)。从而 ViewModel 与数据层的操作逻辑解耦,只需要关注业务逻辑。参考:TasksRepository。
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:OneDeveloper,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/OneDeveloper/article/details/115049221