以下三种排序的时间复杂度 都是 O(N^ 2)
冒泡排序
排序原理
1、比较相邻的元素。如果前一个元素比后一个元素大,就交换这两个元素的位置
2、对每一对相邻元素做同样的工作,从开始第一对元素到结尾的最后一对元素。最终最后元素就是最大
排序图解
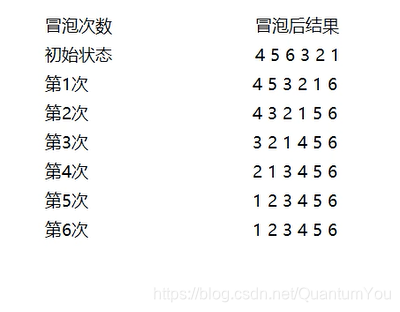
解法
API 设计

package Sort;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author LZH.create
* Date : 2021.3.11
* API 设计思想实现 与传统实现(方式二)
*
*/
public class BubbleSort { public static void sort(int [] arr) { for(int i = arr.length - 1 ; i > 0 ;i-- ) { for(int j = 0 ; j < i ; j++) { if(greater(arr[j],arr[j+1])) { exch(arr,j,j+1) ; } } }
} private static boolean greater(int v ,int w) { return v > w ; } private static void exch(int[] a, int i , int j) {
int temp = a[i] ;
a[i] = a[j] ;
a[j] = temp ;
} }
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) { int [] arr = {4,5,6,3,2,1} ; BubbleSort.sort(arr);
System.out.println(arr); //数组地址 System.out.println("=========");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // 返回数组的字符串形式 System.out.println("===== 方式二 ===="); int a [] = {4,2,5,8,1} ; for (int i = 0; i <=a.length-1 ; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <a.length-i-1 ; j++) { if(a[j]>a[j+1]){ //升序 int t = a[j] ; a[j] = a[j+1] ; a[j+1] = t ; } } } for (int i = 0; i <a.length ; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " "); } }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
选择排序
排序原理
1、每一次遍历的过程中,都假定第一个索引处的元素是最小值,和其他索引处的值依次进行比较,如果当前索引处的值大于其他某个索引处的值,则假定其他某个索引出的值为最小值,最后可以找到最小值所在的索引
2、交换第一个索引处和最小值所在的索引处的值
排序图解
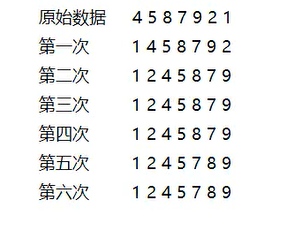
解法
package Sort;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SelectionSort { public static void sort(int [] arr) { for(int i = 0 ; i <= arr.length - 1 ; i++ ) { int Minindex = i ; for (int j = i + 1 ; j <= arr.length-1 ; j++) { if(greater(arr[Minindex] ,arr[j])) { Minindex = j ; } } exch(arr,i, Minindex) ;
} } private static boolean greater(int v ,int w) { return v > w ; } private static void exch(int[] a, int i , int j) {
int temp = a[i] ;
a[i] = a[j] ;
a[j] = temp ;
}
}
class Test2{ public static void main(String [] args) { int a [] = {4,5,8,7,9,2,1} ; SelectionSort.sort(a) ; // 注意外层有 主函数 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); System.out.println("=======方法二======"); for(int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {// 做第i趟排序 int k = i; for(int j = k + 1; j < a.length; j++){// 选最小的记录 if(a[j] < a[k]){ k = j; //记下目前找到的最小值所在的位置 } } //在内层循环结束,也就是找到本轮循环的最小的数以后,再进行交换 if(i != k){ //交换a[i]和a[k] int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[k]; a[k] = temp; } } for(int num:a){ System.out.print(num+" "); }
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
插入排序
排序原理
1把所有的元素分为两组,已经排序的和未排序的
2找到未排序的组中的第一个元素,向已经排序的组中进行插入
3倒叙遍历已经排序的元素,依次和待插入的元素进行比较,直到找到一个元素小于等于待插入元素,那么就把待
插入元素放到这个位置,其他的元素向后移动一位
排序图解
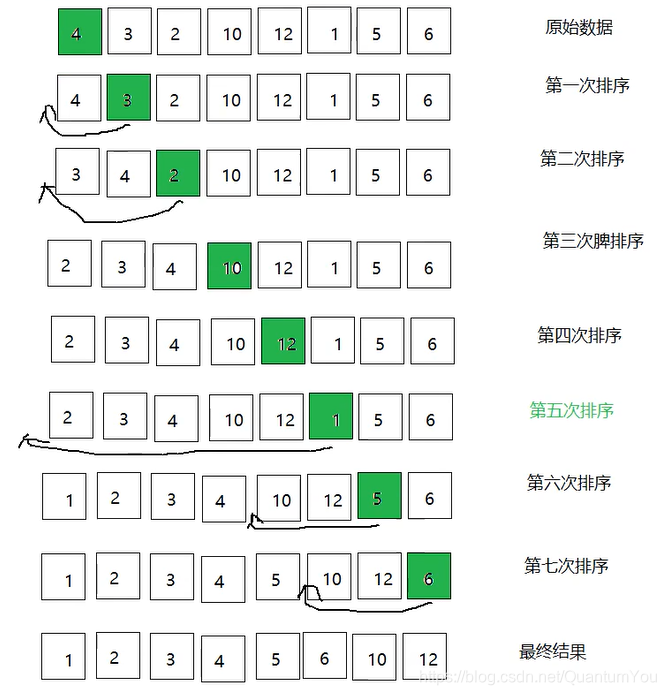
解法
Java 代码
package Sort;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class InsertSort { public static void sort(int [] arr) {
for (int i = 1 ; i < arr.length ; i++) { for(int j = i ; j> 0 ; j--){ if(greater(arr[j-1],arr[j])) { exch(arr,j-1,j) ; } else { break ; } }
} } private static boolean greater(int v ,int w) { return v > w ; } private static void exch(int[] a, int i , int j) {
int temp = a[i] ;
a[i] = a[j] ;
a[j] = temp ;
}
}
class Test3{ public static void main(String [] args) { int a [] = {4,5,8,7,9,2,1} ; SelectionSort.sort(a) ; // 注意外层有 主函数 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:QuantumYou,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/QuantumYou/article/details/114693600