目录
一、题目内容
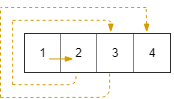
在 R 行 C 列的矩阵上,我们从 (r0, c0) 面朝东面开始
这里,网格的西北角位于第一行第一列,网格的东南角位于最后一行最后一列。
现在,我们以顺时针按螺旋状行走,访问此网格中的每个位置。
每当我们移动到网格的边界之外时,我们会继续在网格之外行走(但稍后可能会返回到网格边界)。
最终,我们到过网格的所有 R * C 个空间。
按照访问顺序返回表示网格位置的坐标列表。
示例 1:
输入:R = 1, C = 4, r0 = 0, c0 = 0
输出:[[0,0],[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]]
示例 2:
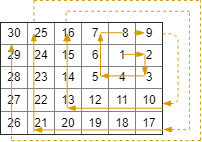
输入:R = 5, C = 6, r0 = 1, c0 = 4
输出:[[1,4],[1,5],[2,5],[2,4],[2,3],[1,3],[0,3],[0,4],[0,5],[3,5],[3,4],[3,3],[3,2],[2,2],[1,2],[0,2],[4,5],[4,4],[4,3],[4,2],[4,1],[3,1],[2,1],[1,1],[0,1],[4,0],[3,0],[2,0],[1,0],[0,0]]
提示:
1 <= R <= 100
1 <= C <= 100
0 <= r0 < R
0 <= c0 < C
二、解题思路
和leetcode_59. 螺旋矩阵 II和leetcode_54. 螺旋矩阵思想类似,四个方向逐次存储坐标即可,注意逐渐扩大的范围。
三、代码
-
class Solution:
-
def spiralMatrixIII(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int) -> list:
-
res = [[r0, c0]]
-
offset = 0
-
x = r0
-
y = c0
-
while 1:
-
if len(res) == R * C:
-
break
-
offset += 1
-
-
for i in range(1, offset + 1):
-
if 0 <= x < R and 0 <= y + i < C and len(res) < R * C:
-
res.append([x, y + i])
-
y += offset
-
-
for i in range(1, offset + 1):
-
if 0 <= x + i < R and 0 <= y < C and len(res) < R * C:
-
res.append([x + i, y])
-
x += offset
-
-
offset += 1
-
-
for i in range(1, offset + 1):
-
if 0 <= x < R and 0 <= y - i < C and len(res) < R * C:
-
res.append([x, y - i])
-
y -= offset
-
-
for i in range(1, offset + 1):
-
if 0 <= x - i < R and 0 <= y < C and len(res) < R * C:
-
res.append([x - i, y])
-
x -= offset
-
-
return res
-
-
-
if __name__ == '__main__':
-
s = Solution()
-
R = 5
-
C = 6
-
r0 = 1
-
c0 = 4
-
ans = s.spiralMatrixIII(R, C, r0, c0)
-
print(ans)
文章来源: nickhuang1996.blog.csdn.net,作者:悲恋花丶无心之人,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:nickhuang1996.blog.csdn.net/article/details/114870068