一.原理
国外友人发表的一篇文章https://p4xon.blog/hooking-all-system-calls-in-windows-10-20h1/ 中提到了如何在20h1版本的Windows进行inf hook. 然而我发现在19041上存在不兼容.因此阅读原作者文章对其源码进行修改来学习infinity hook原理.
简单来说原来的inf hook. 它是通过修改WMI_LOGGER_CONTEXT结构的GetCpuClock函数为自己的代理函数. 当用户层程序进行系统调用时,会先调用PerfInfoLogSysCallEntry函数来对此次系统调用进行记录.然后才调用系统调用函数.PerfInfoLogSysCallEntry内部又会调用驱动注册的WMI_LOGGER_CONTEXT结构中的GetCpuClock指向的函数. 于是就可以通过修改GetCpuClock指针为自己的代理函数,而且系统调用函数被存放在栈上,因此在该函数中能从栈中获取系统调用函数的值并进行修改为自己的hook函数.具体原理已有文章讲解和源码不再赘述.
然而在20h1的更新中,GetCpuClock不再是函数指针,而是一个索引值,当该值为1时会调用KeQueryPerformanceCounter函数:
__int64 __fastcall EtwpGetLoggerTimeStamp(struct _WMI_LOGGER_CONTEXT *a1)
{
unsigned __int64 v1; // rax
int v2; // eax
int v3; // eax
__int64 result; // rax
__int64 v5; // [rsp+30h] [rbp+8h]
v1 = a1->GetCpuClock;
if ( v1 > 3 )
goto LABEL_10;
if ( !(_DWORD)v1 )
return RtlGetSystemTimePrecise();
v2 = v1 - 1;
if ( v2 )
{
v3 = v2 - 1;
if ( v3 )
{
if ( v3 == 1 )
return __rdtsc();
LABEL_10:
__fastfail(0x3Du);
}
v5 = 0i64;
off_140C00A30(&v5);
result = v5;
}
else
{
result = KeQueryPerformanceCounter(0i64).QuadPart;
}
return result;
}
当GetCpuClock 大于3时调用__fastfail(0x3Du)报错.
当GetCpuClock 等于3时调用__rdtsc()
当GetCpuClock 等于2时调用off_140C00A30
当GetCpuClock 等于1时调用KeQueryPerformanceCounter
当GetCpuClock 等于0时调用RtlGetSystemTimePrecise()
这里主要关注KeQueryPerformanceCounter()函数,因为只有这个函数里面存在通过函数指针调用函数.
在1903系统上,该函数是HAL的函数.但是在19041中,该函数在ntoskrnl中实现:
LARGE_INTEGER __stdcall KeQueryPerformanceCounter(PLARGE_INTEGER PerformanceFrequency)
{
// [COLLAPSED LOCAL DECLARATIONS. PRESS KEYPAD CTRL-"+" TO EXPAND]
v1 = HalpPerformanceCounter;
v2 = PerformanceFrequency;
...........................................
v36 = *(_QWORD *)(HalpPerformanceCounter + 0xC0);
if ( *(_DWORD *)(HalpPerformanceCounter + 0xDC) == 0x40 )
{
v5 = HalpTimerGetInternalData(HalpPerformanceCounter);
v6 = (*(__int64 (__fastcall **)(__int64))(v1 + 0x70))(v5);//调用函数指针
v7 = *(_QWORD *)(v1 + 0xD0);
...........................................
在KeQueryPerformanceCounter函数中,会调用HalpPerformanceCounter+0x70指向的函数:v6 = (*(__int64 (__fastcall **)(__int64))(v1 + 0x70))(v5)
该函数指针本来指向 HalpHvCounterQueryCounter函数. 根据p4xon所说,HalpPerformanceCounter处于.data不被pg保护,因此可以变换思路将这个函数指针指向代理函数,然后修改栈上的系统调用值的思路和以前的一样.
HalpHvCounterQueryCounter函数:
__int64 HalpHvCounterQueryCounter()
{
__int64 result; // rax
if ( HalpHvTimerApi )
result = HalpHvTimerApi();
else
result = __readmsr(0x40000020u);
return result;
}
二.关键源码解析
bool hookSystemCall(std::uintptr_t hookFunction, std::uintptr_t systemFunction) {
systemCallHookFunction = hookFunction;
targetSystemCallFunction = systemFunction;
// Get the Circular Kernel Context Logger WMI_LOGGER_CONTEXT structure
circularKernelContextLogger = getCKCLContext();
if (!circularKernelContextLogger)
return false;
// Get the service descriptor table which is used for resolving system call numbers
keServiceDescriptorTable = Native::getServiceDescriptorTable();
if (!keServiceDescriptorTable)
return false;
// Try to enable system call logging for the Circular Kernel Context Logger
// In the case that the logger is not started, try to start it up
if(!NT_SUCCESS(modifyCKCL(EtwUpdateLoggerCode, EVENT_TRACE_FLAG_SYSTEMCALL)))
if(!NT_SUCCESS(modifyCKCL(EtwStartLoggerCode, EVENT_TRACE_FLAG_SYSTEMCALL)))
return false;
else
{
if (!NT_SUCCESS(modifyCKCL(EtwUpdateLoggerCode, EVENT_TRACE_FLAG_SYSTEMCALL)))
{
return false;
}
}
// Set the GetCpuClock member of WMI_LOGGER_CONTEXT to 1 so KeQueryPerformanceCounter is called
*reinterpret_cast<std::uint64_t*>(circularKernelContextLogger + Offsets::wmiGetCpuClock) = 1;
// Hook HalpPerformanceCounter so we can actually intercept system calls
if (!NT_SUCCESS(hookPerformanceCounterRoutine(reinterpret_cast<std::uintptr_t>(&checkLogger), &halCounterQueryRoutine)))
return false;
return true;
}
首先获取WMI_LOGGER_CONTEXT结构指针:circularKernelContextLogger = getCKCLContext();,该变量通过搜索特征码得到.当然也可以通过解析pdb符号来得到.
然后开启对系统调用的日志记录:modifyCKCL(EtwStartLoggerCode, EVENT_TRACE_FLAG_SYSTEMCALL)
成功后,将GetCpuClock改为1:*reinterpret_cast<std::uint64_t*>(circularKernelContextLogger + Offsets::wmiGetCpuClock) = 1;
之后调用hookPerformanceCounterRoutine修改HalpPerformanceCounter+0x70指针:
NTSTATUS hookPerformanceCounterRoutine(std::uintptr_t hookFunction, std::uintptr_t* oldFunction) {
UNICODE_STRING keQueryPerformanceCounterUnicode = RTL_CONSTANT_STRING(L"KeQueryPerformanceCounter");
const auto keQueryPerformanceCounter = reinterpret_cast<std::uintptr_t>(
MmGetSystemRoutineAddress(&keQueryPerformanceCounterUnicode));
if (!keQueryPerformanceCounter)
return STATUS_NOT_FOUND;
// Find HalpPerformanceCounter from KeQueryPerformanceCounter
//auto halpPerformanceCounter = Scanner::scanPattern(reinterpret_cast<std::uint8_t*>(keQueryPerformanceCounter),
// 0x100, "x80x96x98x00", "xxxx");
//halpPerformanceCounter += 7;
//halpPerformanceCounter += *reinterpret_cast<std::int32_t*>(halpPerformanceCounter) + sizeof(std::int32_t);
//halpPerformanceCounter = *reinterpret_cast<std::uintptr_t*>(halpPerformanceCounter);
//首先找到HalpPerformanceCounter变量
halpPerformanceCounter = Scanner::scanPattern(reinterpret_cast<std::uint8_t*>(keQueryPerformanceCounter),
0x100, "x56x57x41x56", "xxxx");
halpPerformanceCounter += 8;
auto saddr = halpPerformanceCounter;
halpPerformanceCounter += 3;
halpPerformanceCounter = saddr +*reinterpret_cast<std::int32_t*>(halpPerformanceCounter) + 7;
halpPerformanceCounter = *reinterpret_cast<std::uintptr_t*>(halpPerformanceCounter);
// Swap the function pointers for the QueryCounter routine
//将HalpPerformanceCounter+0x70指向改为自己的代理函数
*oldFunction = *reinterpret_cast<std::uintptr_t*>(halpPerformanceCounter + Offsets::counterQueryRoutine);
*reinterpret_cast<std::uintptr_t*>(halpPerformanceCounter + Offsets::counterQueryRoutine) = hookFunction;
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
通过特征码搜索得到将HalpPerformanceCounter后,直接对+0x70处指针进行修改即可.
hookFunction:
checkLogger PROC
push rcx
mov rcx,rsp
call keQueryPerformanceCounterHook
pop rcx
mov rax, halCounterQueryRoutine
jmp rax
checkLogger ENDP
end
因为HalpHvCounterQueryCounter函数存在一个参数,需要保存rcx.然后把rsp传入keQueryPerformanceCounterHook:
//代理函数. 在汇编中将栈pStack传过来
void keQueryPerformanceCounterHook(ULONG_PTR* pStack) {
if (ExGetPreviousMode() == KernelMode)
{
return;
}
//往上遍历,看是否能发现WMI_LOGGER_CONTEXT指针,因为该函数不仅仅在ETW中被调用.在ETW调用时,会把WMI_LOGGER_CONTEXT
//指针压栈.经过测试,发现pStack[7]==circularKernelContextLogger.
//pStack[7]== circularKernelContextLogger
for (size_t i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if (pStack[i]== circularKernelContextLogger)
{
std::uintptr_t currentThread = reinterpret_cast<std::uintptr_t>(KeGetCurrentThread());
std::uint32_t syscallNumber = *reinterpret_cast<std::uint32_t*>(currentThread + Offsets::kthreadSystemCallNumber);
if (!syscallNumber)
return;
// Determine whether it's a win32k or nt syscall and resolve the system routine address
const auto syscallType = (syscallNumber >> 7) & 0x20;
const auto serviceTable = *reinterpret_cast<std::int32_t**>(keServiceDescriptorTable + syscallType);
const auto systemRoutine = reinterpret_cast<std::uintptr_t>(serviceTable) + (serviceTable[syscallNumber & 0xFFF] >> 4);
//获取栈顶
std::uintptr_t stackLowLimit, stackHighLimit;
IoGetStackLimits(&stackLowLimit, &stackHighLimit);
int j = 0;
//auto stack = (ULONG_PTR)pStack + 0x228;
//auto stack = (ULONG_PTR)pStack + 0x250;
auto stack = (ULONG_PTR)pStack + 0x2c0;
//从当前rsp往上遍历栈,直到找到存储系统调用的地址,经过测试发现栈上有3个地址都可能存储了函数指针
//因此把他们都打印出来后,依次修改为hook函数,看哪个生效,结果是(ULONG_PTR)pStack + 0x2c0有效
for (auto stack = (ULONG_PTR)pStack; stack <= stackHighLimit-8; stack+=8) {
if (*reinterpret_cast<std::uint64_t*>(stack) == systemRoutine) {
if (systemRoutine == targetSystemCallFunction)
{
DbgPrintEx(0, 0, "%d %08x %d,%s %d %p n", i, stack - (ULONG_PTR)pStack, j,
PsGetProcessImageFileName(PsGetCurrentProcess()),
syscallNumber, systemRoutine);
//修改栈数据
*reinterpret_cast<std::uint64_t*>(stack) = systemCallHookFunction;
//return;
j++;
}
}
}
return;
}
}
}
第4行首先排除内核代码(非从用户层来的系统调用代码)的调用.
第13行,由于在调用KeQueryPerformanceCounter时,WMI_LOGGER_CONTEXT结构指针被保存在栈中,因此可以根据这点判断是否是监控系统调用而调用的KeQueryPerformanceCounter.
然后获取系统调用号后,根据SSDT计算要调用的函数值,用于在栈中寻找保存的系统调用指针.找到目标指针后,即可替换成自己的hook函数.
NTSTATUS ntCreateFileHook(PHANDLE fileHandle, ACCESS_MASK desiredAccess, POBJECT_ATTRIBUTES objectAttributes,
PIO_STATUS_BLOCK ioStatusBlock, PLARGE_INTEGER allocationSize, ULONG fileAttributes,
ULONG shareAccess, ULONG createDisposition, ULONG createOptions, PVOID eaBuffer,
ULONG eaLength) {
kprintf("%s call NtCreateFile: %wsn", PsGetProcessImageFileName(PsGetCurrentProcess()),objectAttributes->ObjectName->Buffer);
if (wcsstr(objectAttributes->ObjectName->Buffer,L"1.txt"))
{
kprintf("已拦截n");
return STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED;
}
return NtCreateFile(fileHandle, desiredAccess, objectAttributes, ioStatusBlock, allocationSize, fileAttributes,
shareAccess, createDisposition, createOptions, eaBuffer, eaLength);
}
到此,可以根据自己系统版本对源码做针对性修改.
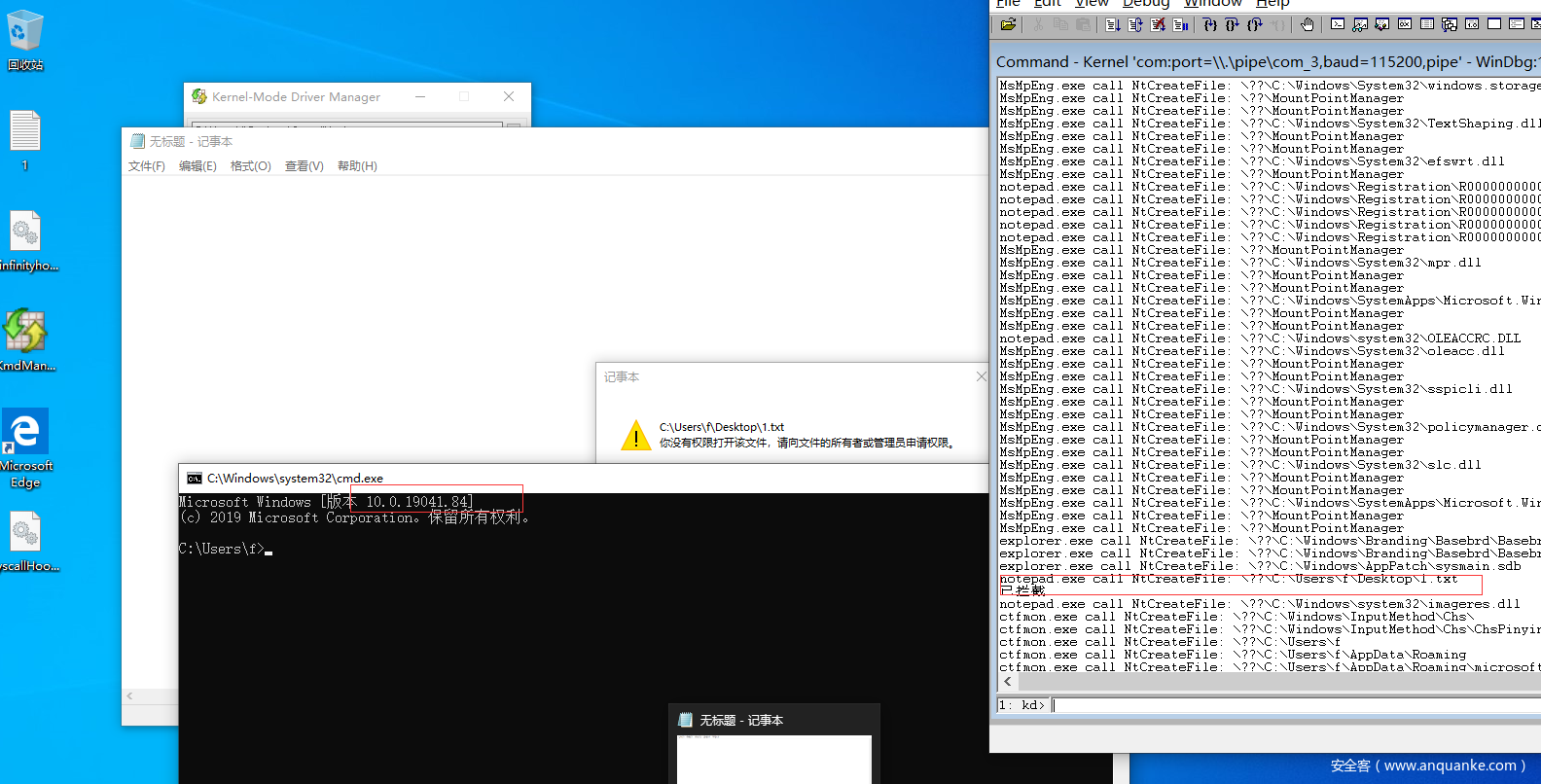
完整代码见:https://github.com/fIappy/InfinityHook
最终效果图: