前言
由于作者水平有限如文中出现语义模糊、语法错误以及技术问题望读者斧正。上周末打了 Real World CTF ,比赛中有两道与 TEE 有关的题目,一道涉及 TEE 的 secure storage ,一道涉及 TEE TA 的漏洞利用。遗憾的是在比赛的时候并没有做出来,但是这两道题可以让做题人掌握 TEE 的 secure storage 流程以及 TA 的漏洞利用方法相关的知识,所以复现了这两道题,这也就是这篇文章的由来。这篇文章复现的是 Trust or Not ,题目与 TEE 的 secure storage 有关。
TEE
TEE 简述
TEE 全称叫做 Trust Executed Environment 可信执行系统,TEE 主要应用在手机以及 iot 设备上,比如用户的指纹识别以及支付相关的敏感操作都是在 TEE 中进行处理的,敏感的信息也是通过 TEE 加密之后存储在一个可信的位置。
TEE Feature
TEE 有几个专有的 feature ,为了读者能理解下文中的内容所以提前进行说明。
REE ,在手机上 REE 指的就是 Android ,也就是非安全系统。
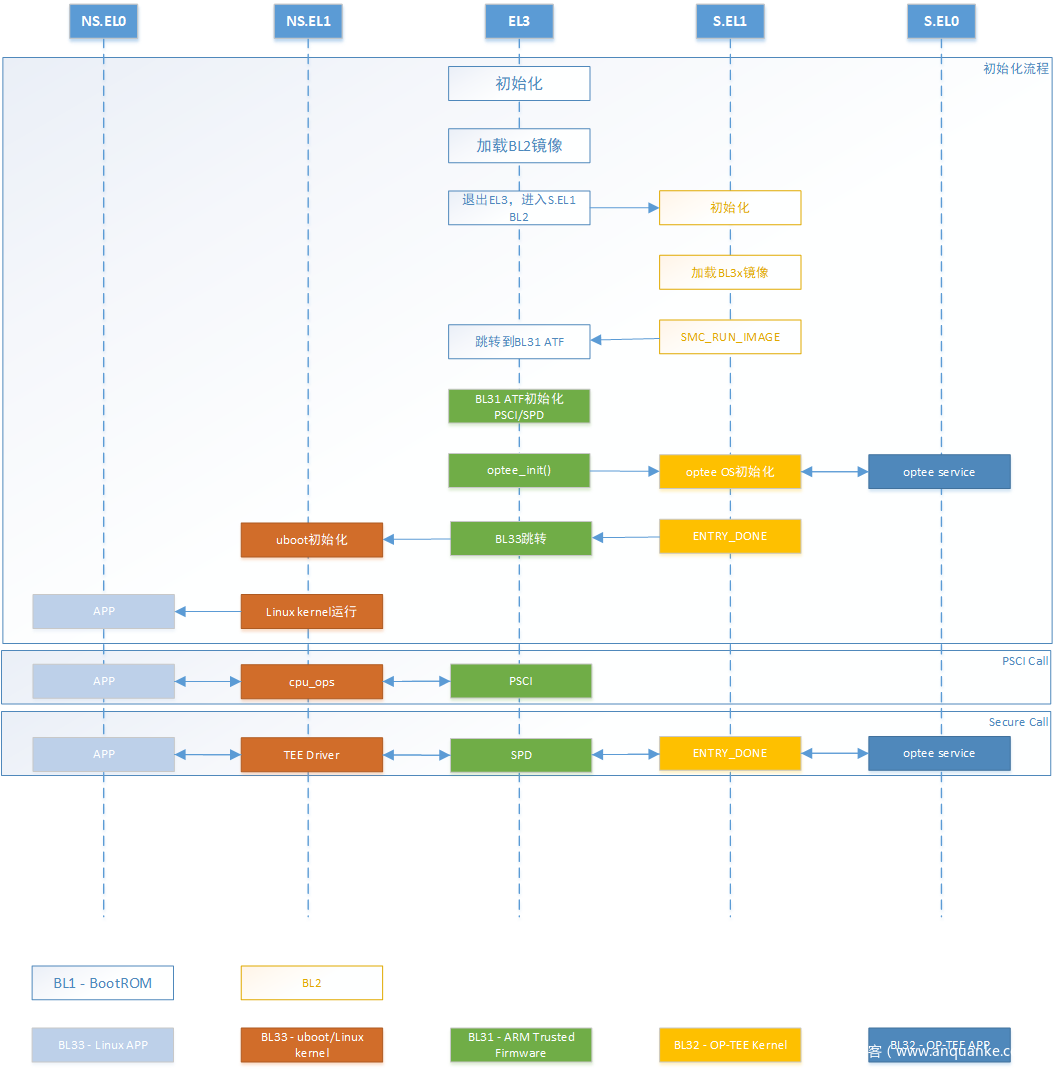
bl1.bin、bl2.bin、bl31.bin、bl32.bin、bl33.bin、前两个 bl* 主要和 boot 以及镜像加载有关,bl31 负责管理 SMC(Secure Monitor Control) 执行处理和中断,bl32 就是 TEE 系统镜像,bl33 为 REE 系统镜像也就是 Linux Kernel、uboot 之类的。调用流程如下图所示
TA 的全称是 Trusted Application 可信应用,既然有可信应用那么也就有不可信应用,不可信应用叫做 CA(Client Application) ,REE 通过调用 CA 来获取 TEE 提供的服务,每一个 CA 对应都有一个 TA ,TA 中调用 TEE 提供的 API 来满足 CA 发来的请求。每一个 TA 都被一个唯一的 UUID 标识。
TEE Secure Storage
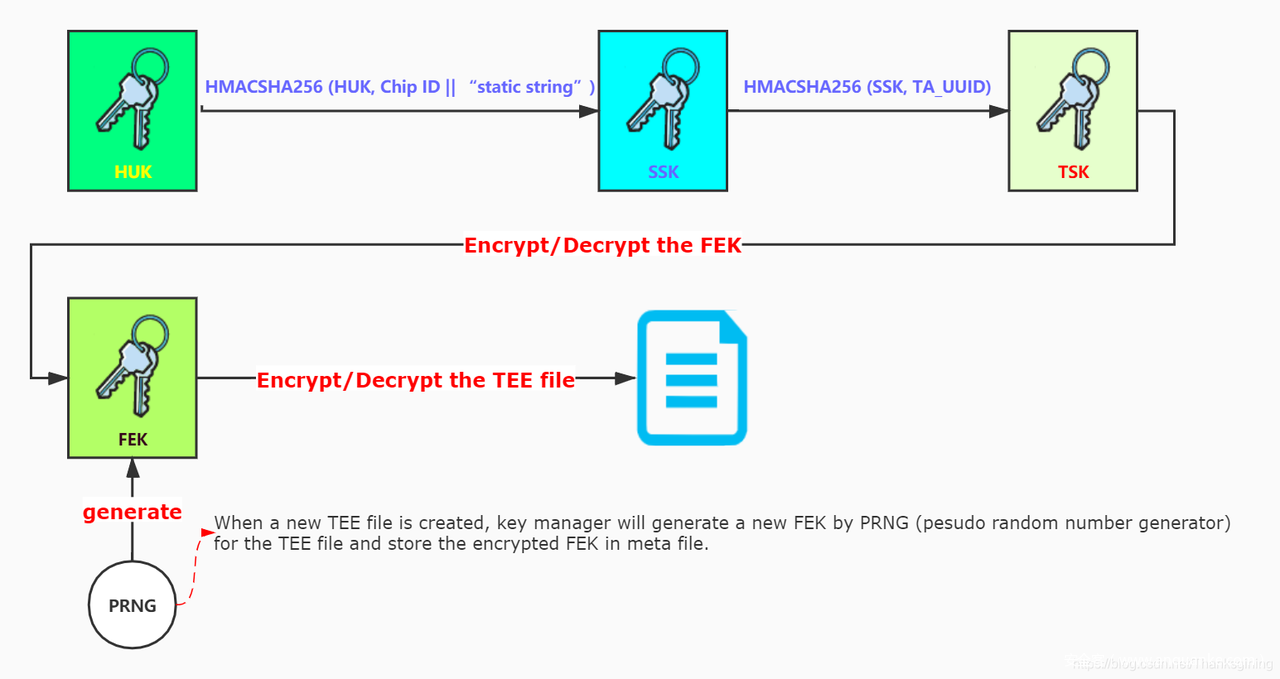
TEE Secure Storage 基本流程如下图所示:
可以看到图中有几个关键的密钥 HUK, SSK, TSK 和 FEK , SSK 是使用 HUK 和一个静态字符进行加密后得到的结果, TSK 是使用 SSK 以及 Secure Storage TA 的 UUID 加密后得到的结果,最后利用 FEK 来加密/解密文件。
解题
在对 TEE 以及 TEE Secure Storage 有了一个基本的认识之后就可以开始解题了,解题的步骤就是把 Secure Storage 中的几个密钥计算出来,最后利用 FEK 来解密安全存储的文件。
HUK
SSK is derived by:
SSK = HMACSHA256 (HUK, Chip ID || “static string”)
The functions to get Hardware Unique Key (HUK) and chip ID depend on platform implementation.
Currently, in OP-TEE OS we only have a per-device key, SSK, which is used for secure storage subsystem, but, for the future we might need to create different per-device keys for different subsystems using the same algorithm as we generate the SSK; An easy way to generate different per-device keys for different subsystems is using different static strings to generate the keys.
上面是 OPTEE 文档中的内容,其中提到 HUK 和 Chip ID 的获取都是依赖于平台实现的,不过题目是运行在 qemu 中的,这是不是就意味着即使每次重启 qemu HUK 也不会被改变。既然知道 HUK 是不会改变的那么就需要知道怎么获取 HUK 。
In OP-TEE the HUK is just stubbed and you will see that in the function called tee_otp_get_hw_unique_key(…) in core/include/kernel/tee_common_otp.h. In a real secure product you must replace this with something else. If your device lacks the hardware support for a HUK, then you must at least change this to something else than just zeroes. But, remember it is not good secure practice to store a key in software, especially not the key that is the root for everything else, so this is not something we recommend that you should do.
继续看 OPTEE 的文档,在文档中提到了 core/inclue/kernel/tee_common_otp.h 中声明的 tee_otp_get_hw_unique_key(…) 函数。并且文档中说道在现实场景中开发人员必须替换掉 tee_otp_get_hw_unique_key 的实现。
在 OPTEE 的代码里寻找 tee_otp_get_hw_unqiue_key 的实现,可以看到如下代码:
/*
* Override these in your platform code to really fetch device-unique
* bits from e-fuses or whatever.
*
* The default implementation just sets it to a constant.
*/
__weak TEE_Result tee_otp_get_hw_unique_key(struct tee_hw_unique_key *hwkey)
{
memset(&hwkey->data[0], 0, sizeof(hwkey->data));
return TEE_SUCCESS;
}
代码中的注释说明默认的 tee_otp_get_hw_unique_key 的实现就是全部填充为 0 。
Chip ID 和 “Static String”
在代码中也可以直接找到 Chip ID 和 Static String 相关代码如下所示:
static TEE_Result huk_compat(void *ctx, enum huk_subkey_usage usage)
{
TEE_Result res = TEE_SUCCESS;
uint8_t chip_id[TEE_FS_KM_CHIP_ID_LENGTH] = { 0 };
static uint8_t ssk_str[] = "ONLY_FOR_tee_fs_ssk";
switch (usage) {
case HUK_SUBKEY_RPMB:
return TEE_SUCCESS;
case HUK_SUBKEY_SSK:
get_dummy_die_id(chip_id, sizeof(chip_id));
res = crypto_mac_update(ctx, chip_id, sizeof(chip_id));
if (res)
return res;
return crypto_mac_update(ctx, ssk_str, sizeof(ssk_str));
default:
return mac_usage(ctx, usage);
}
}
static void get_dummy_die_id(uint8_t *buffer, size_t len)
{
static const char pattern[4] = { 'B', 'E', 'E', 'F' };
size_t i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
buffer[i] = pattern[i % 4];
}
SSK
现在已经知道了 HUK、 Chip ID 和 Static String 那我们就可以计算出 SSK 的值是多少了。
import os
import struct
from hashlib import sha256
from hmac import HMAC
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import binascii
def bytesToHexString(bs):
return ''.join(['%02X ' % b for b in bs])
HUK = b'\x00'*0x10
chip_id = b'BEEF'*8
static_string = b'ONLY_FOR_tee_fs_ssk'
message = chip_id + static_string
SSK = HMAC(HUK, message, digestmod=sha256).digest()
print ("SSK: " + bytesToHexString(SSK))
可以得到 SSK 的值为
SSK: D0 23 CE 37 07 F6 CF 82 5E 2F 7C 1C 6A F8 2A 8B F1 E8 CF 9D E7 17 3D 74 31 2A A0 E2 77 6F 93 41
TSK
TSK 的值是根据 SSK 和 TA 的 UUID 计算得到的,目前已经有了 SSK 只需要再得到 UUID 就可以了,根据下图中的内容我们可以得到 UUID 的值为 “\xbb\x50\xe7\xf4\x37\x14\xbf\x4f\x87\x85\x8d\x35\x80\xc3\x49\x94” , 这个值是通过 f4e750bb-1437-4fbf-8785-8d3580c34994.ta 文件得到的,在 TA 中找到对应的位置将 UUID dump 下来就可以了。
利用下面的脚本可以计算出 TSK 的值为多少。
import os
import struct
from hashlib import sha256
from hmac import HMAC
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import binascii
def bytesToHexString(bs):
return ''.join(['%02X ' % b for b in bs])
HUK = b'\x00'*0x10
chip_id = b'BEEF'*8
static_string = b'ONLY_FOR_tee_fs_ssk'
message = chip_id + static_string
SSK = HMAC(HUK, message, digestmod=sha256).digest()
print ("SSK: " + bytesToHexString(SSK))
ta_uuid = b'\xbb\x50\xe7\xf4\x37\x14\xbf\x4f\x87\x85\x8d\x35\x80\xc3\x49\x94'
TSK = HMAC(SSK, ta_uuid, digestmod=sha256).digest()
print ("TSK: " + bytesToHexString(TSK))
可以得到 TSK 的值为
TSK: 7E BE 82 6A A4 F4 57 AE FB EA EA 6E 34 BC D6 AA 14 A6 DD C7 EE 90 4C E4 9F 8F 20 71 3F 40 E6 CC
FEK
根据 010 的模板我们可以得到被加密的文件的格式如下所示:
//------------------------------------------------
//--- 010 Editor v10.0.2 Binary Template
//
// File:
// Authors:
// Version:
// Purpose:
// Category:
// File Mask:
// ID Bytes:
// History:
//------------------------------------------------
#define TEE_FS_HTREE_IV_SIZE 16
#define TEE_FS_HTREE_TAG_SIZE 16
#define TEE_FS_HTREE_FEK_SIZE 16
typedef struct _tee_fs_htree_meta {
UINT64 length;
}tee_fs_htree_meta;
typedef struct _tee_fs_htree_imeta {
struct tee_fs_htree_meta meta;
UINT32 max_node_id;
UINT32 nop;
}tee_fs_htree_imeta;
typedef struct _tee_fs_htree_image {
UCHAR iv[TEE_FS_HTREE_IV_SIZE];
UCHAR tag[TEE_FS_HTREE_TAG_SIZE];
UCHAR enc_fek[TEE_FS_HTREE_FEK_SIZE];
UCHAR imeta[sizeof(struct tee_fs_htree_imeta)];
UINT32 counter;
}tee_fs_htree_image;
#define TEE_FS_HTREE_HASH_SIZE 32
#define TEE_FS_HTREE_IV_SIZE 16
#define TEE_FS_HTREE_TAG_SIZE 16
typedef struct _tee_fs_htree_node_image {
/* Note that calc_node_hash() depends on hash first in struct */
UCHAR hash[TEE_FS_HTREE_HASH_SIZE];
UCHAR iv[TEE_FS_HTREE_IV_SIZE];
UCHAR tag[TEE_FS_HTREE_TAG_SIZE];
USHORT flags;
}tee_fs_htree_node_image;
//--------------------------------------
LittleEndian();
tee_fs_htree_image ver0_head;
tee_fs_htree_image ver1_head;
FSeek(0x1000);
tee_fs_htree_node_image ver0_root_node;
tee_fs_htree_node_image ver1_root_node;
FSeek(0x2000);
在上面的结构中我们可以看到 enc_fek 是存在 ver0_head 和 ver1_head 中的,对应的我们将存储 flag 的文件中对应部分读取出来。
0000000 5e8e 9760 37e9 9170 a110 7f2f 4ef2 3b89
0000010 f90c 165b 6c1e 0c5d 3421 2aa0 910c 770f
0000020 9ae4 f295 f4b5 049c 07f6 fb9f 2ef0 efd2
0000030 2c73 5363 58f7 3774 07a1 4c4f 846f 3035
0000040 0002 0000 707f 7ba1 2738 1add e4b5 e4e0
0000050 3e7d a3e5 fcbe 2384 440e 0ac1 2f7c c4aa
0000060 d51f 6f9f 9ae4 f295 f4b5 049c 07f6 fb9f
0000070 2ef0 efd2 3963 d3ef c803 0dca 36f5 178c
0000080 5e15 7fed 0003 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000090 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
再通过偏移计算可以计算出 enc_fek 的值为 “\xe4\x9a\x95\xf2\xb5\xf4\x9c\x04\xf6\x07\x9f\xfb\xf0\x2e\xd2\xef” (ver0_head 和 ver1_head 中的 enc_fek 的值是相同的)
通过以下脚本计算出 fek 的值
import os
import struct
from hashlib import sha256
from hmac import HMAC
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import binascii
def bytesToHexString(bs):
return ''.join(['%02X ' % b for b in bs])
def AES_Decrypt_ECB(key, data):
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
text_decrypted = cipher.decrypt(data)
return text_decrypted
HUK = b'\x00'*0x10
chip_id = b'BEEF'*8
static_string = b'ONLY_FOR_tee_fs_ssk'
message = chip_id + static_string
SSK = HMAC(HUK, message, digestmod=sha256).digest()
print ("SSK: " + bytesToHexString(SSK))
ta_uuid = b'\xbb\x50\xe7\xf4\x37\x14\xbf\x4f\x87\x85\x8d\x35\x80\xc3\x49\x94'
TSK = HMAC(SSK, ta_uuid, digestmod=sha256).digest()
print ("TSK: " + bytesToHexString(TSK))
Enc_FEK = b'\xe4\x9a\x95\xf2\xb5\xf4\x9c\x04\xf6\x07\x9f\xfb\xf0\x2e\xd2\xef'
FEK = AES_Decrypt_ECB(TSK, Enc_FEK)
print ("FEK: " + bytesToHexString(FEK))
可以得到 FEK 的值为
FEK: 9C 83 DB 49 07 2D BE CB E9 9C 8D 70 AA 91 2C 6E
解密
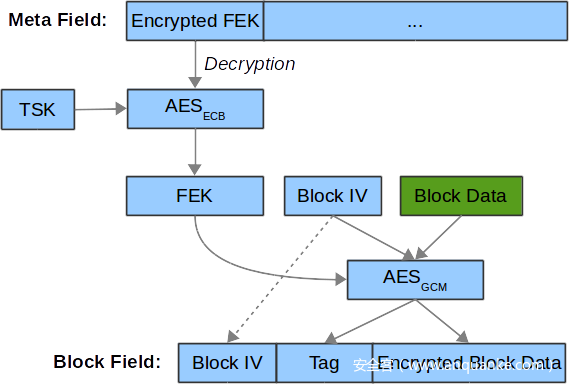
现在所有的密钥的值我们都得到了,只需要进行最后一步解密就可以了。按照下图的步骤进行解密即可:
首先现将 iv 和 tag 提取出来
0001000 d563 3c8b be23 9f8d 0874 6deb 6caa 3f30
0001010 37df 5faa 0498 3153 cbd6 c372 260b 6847
0001020 1d81 5649 4a30 cb52 518a 7f9c 4354 cc00
0001030 e272 8fd9 4820 3d76 4c1c 7578 a58f 56cf
0001040 0001 be9b bb08 b8a6 601a a293 8320 a977
0001050 f935 cb11 5410 f54e 1643 0a7c 7531 5bb9
0001060 8334 c9b4 226a 36e6 cf72 446a 108f 11a3
0001070 6844 65ce 73de f908 0921 d2f2 9f99 b4a4
0001080 51e7 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0001090 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
通过 010 的模板我们可以得到
iv:
B4 C9 6A 22 E6 36 72 CF 6A 44 8F 10 A3 11 44 68
tag:
CE 65 DE 73 08 F9 21 09 F2 D2 99 9F A4 B4 E7 51
现在所有未知的内容我们都已经获得到了,那么就可以开始进行解密了,解密脚本如下:
import os
import struct
from hashlib import sha256
from hmac import HMAC
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import binascii
def bytesToHexString(bs):
return ''.join(['%02X ' % b for b in bs])
def AES_Decrypt_ECB(key, data):
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
text_decrypted = cipher.decrypt(data)
return text_decrypted
fp = open("2","rb")
data = fp.read()
fp.close()
HUK = b'\x00'*0x10
chip_id = b'BEEF'*8
static_string = b'ONLY_FOR_tee_fs_ssk'
message = chip_id + static_string + b'\x00'
SSK = HMAC(HUK, message, digestmod=sha256).digest()
# print ("SSK: " + bytesToHexString(SSK))
ta_uuid = b'\xbb\x50\xe7\xf4\x37\x14\xbf\x4f\x87\x85\x8d\x35\x80\xc3\x49\x94'
TSK = HMAC(SSK, ta_uuid, digestmod=sha256).digest()
# print ("TSK: " + bytesToHexString(TSK))
Enc_FEK = b'\xe4\x9a\x95\xf2\xb5\xf4\x9c\x04\xf6\x07\x9f\xfb\xf0\x2e\xd2\xef'
FEK = AES_Decrypt_ECB(TSK, Enc_FEK)
# print ("FEK: " + bytesToHexString(FEK))
# print ("........ decrypt block data ...........")
block_0 = data[0x2000:0x3000]
Tee_fs_htree_node_image_1_iv = b'\xB4\xC9\x6A\x22\xE6\x36\x72\xCF\x6A\x44\x8F\x10\xA3\x11\x44\x68'
Tee_fs_htree_node_image_1_tag = b'\xCE\x65\xDE\x73\x08\xF9\x21\x09\xF2\xD2\x99\x9F\xA4\xB4\xE7\x51'
cipher = AES.new(FEK, AES.MODE_GCM, nonce = Tee_fs_htree_node_image_1_iv)
cipher.update(Enc_FEK)
cipher.update(Tee_fs_htree_node_image_1_iv)
plaintext = cipher.decrypt_and_verify(block_0, Tee_fs_htree_node_image_1_tag)
print (plaintext)
运行即可得到 flag 为 rwctf{b5f3a0b72861b4de41f854de0ea3da10} 。
总结
Real World 题目质量很不错,从比赛中也能学到新的东西,希望下次能不爆零。结尾需要说明由于本人对密码学仅有微薄的了解所以文中解题使用的脚本是参考了 r3kapig 的 wp ,希望之后能加强一下这方面的技能。自己的搜索能力以及高效阅读文档的能力也需要提升。
参考链接
https://bestwing.me/RWCTF-4th-TrustZone-challenge-Writeup.html
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42135087/article/details/119121392
https://github.com/ForgeRock/optee-os/blob/master/documentation/secure_storage.md
https://optee.readthedocs.io/en/latest/architecture/porting_guidelines.html