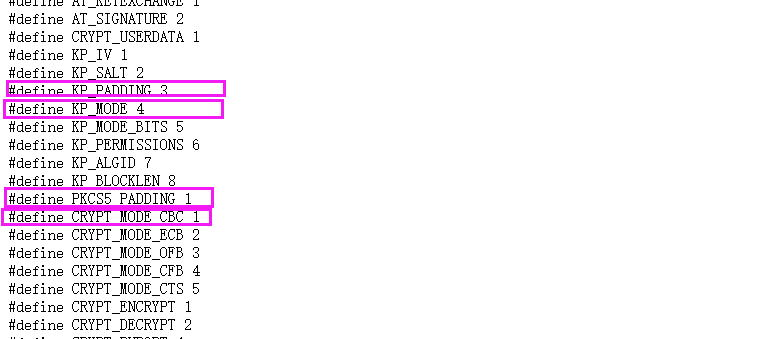Rev_Dizzy
因为main函数太大,ida默认反编译函数的大小只有64K,所以这里会反编译会失败。
这个问题可以通过修改反编译插件的配置文件\cfg\hexrays.cfg中MAX_FUNCSIZE,改为1024就好了。
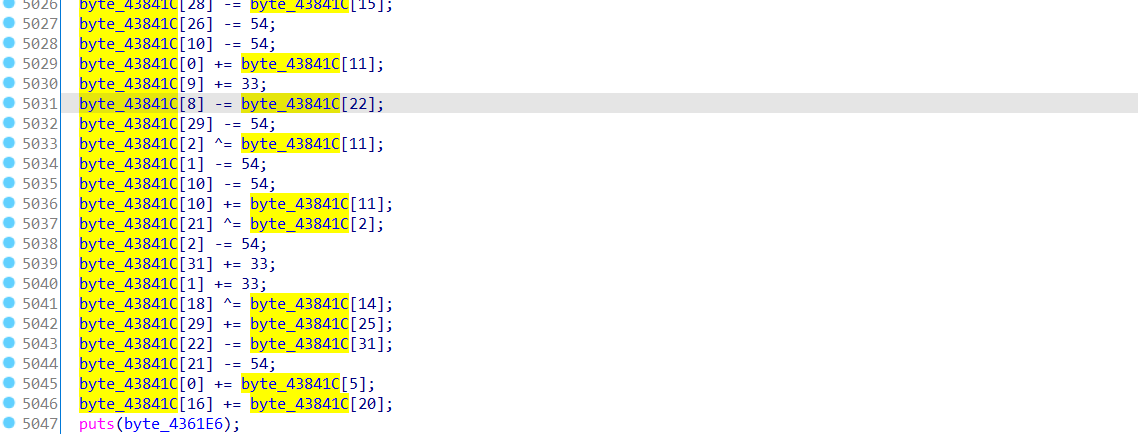
然后观察反编译后的伪代码,对输入进行了5000多行代码的运算且不是线性运算。
首先想到的是用z3来解,但刚复制完代码准备跑脚本的时候发现运算其实只有加,减,异或,那这就很好办了,直接把密文用程序中的运算加法改成减法,减法改成加法,然后倒着跑一遍就解密了,。
用python处理运算表达式:
fp = open("1.py", "rb")
fp1 = open("ans.txt", "w")
data = fp.read()
data = data.split(b'\n')
for i in data[::-1]:
tmp = i.decode()
tmp = tmp.replace('\r', '')
if '+' in tmp:
tmp = tmp.replace('+', '-')
elif '-' in tmp:
tmp = tmp.replace('-', '+')
fp1.write(tmp+'\n')
fp1.close()
fp.close()
最后在在头部补上密文,运行得到flag:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
char flag[] = {0x27, 0x3c, 0xe3, 0xfc, 0x2e, 0x41, 0x7, 0x5e, 0x62, 0xcf, 0xe8, 0xf2, 0x92, 0x80, 0xe2, 0x36, 0xb4, 0xb2, 0x67, 0x77, 0xf, 0xf6, 0xd, 0xb6, 0xed, 0x1c, 0x65, 0x8a, 0x7, 0x53, 0xa6, 0x66, 0};
flag[16] -= flag[20];
flag[0] -= flag[5];
flag[21] += 54;
flag[22] += flag[31];
flag[29] -= flag[25];
flag[18] ^= flag[14];
flag[1] -= 33;
...
...
...
flag[14] -= flag[3];
flag[10] -= flag[6];
flag[10] += flag[27];
flag[6] -= flag[3];
puts(flag);
}
勒索解密
程序加密了一个bmp图片,让我们逆向程序得到加密算法进而解密还原图片得到flag。
开始我通过自己创建文件加密后看密文与明文的关系,发现16字节一组加密,每次加密结果都不一样,且明文的最后一组会被填充到32字节,接着会在密文后填充128字节数据加末尾的0x80。
接着分析程序,来到main函数,代码有点繁琐,调试辅助分析,开始就是去取C:\XX_CTF_XX\目录下的文件,得到文件内容然后对其加密。
定位到main函数中加密开始的逻辑:
注意到它是用的wincrypt.h库中的加密函数,官方文档。
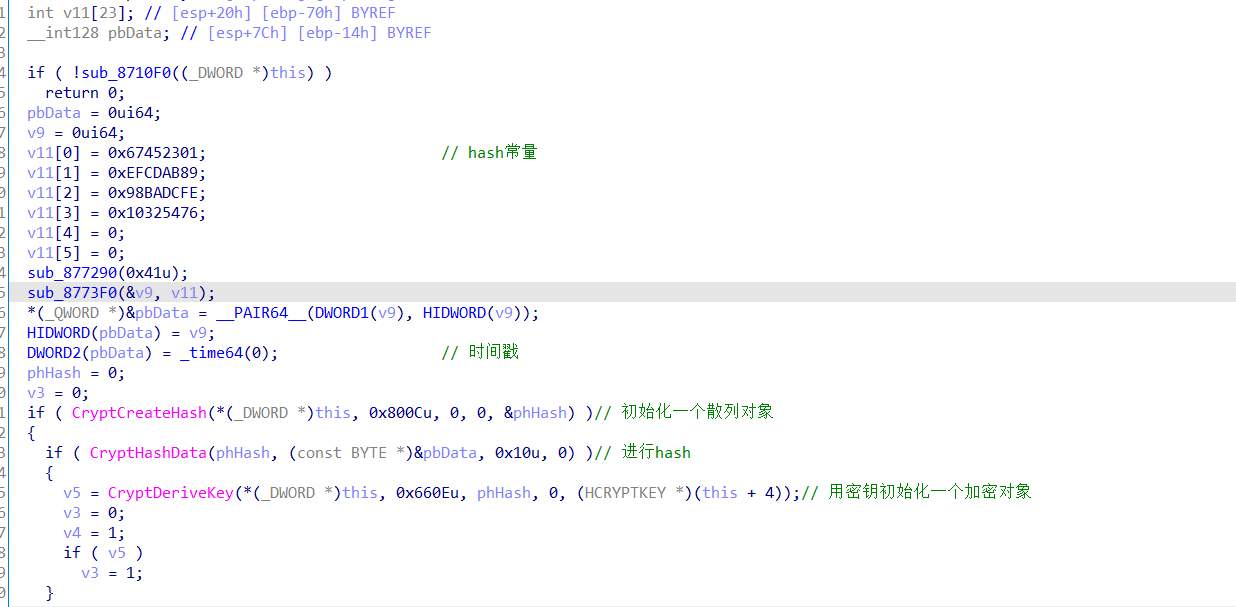
来看关键的加密函数,看到加密前的初始化工作:
因为使用的wincrypt,通过alg_id来区分使用的加密算法,查看文档:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/seccrypto/alg-id
所以说就是先用得到pdata进行了sha256然后作为aes_128的初始化密钥。
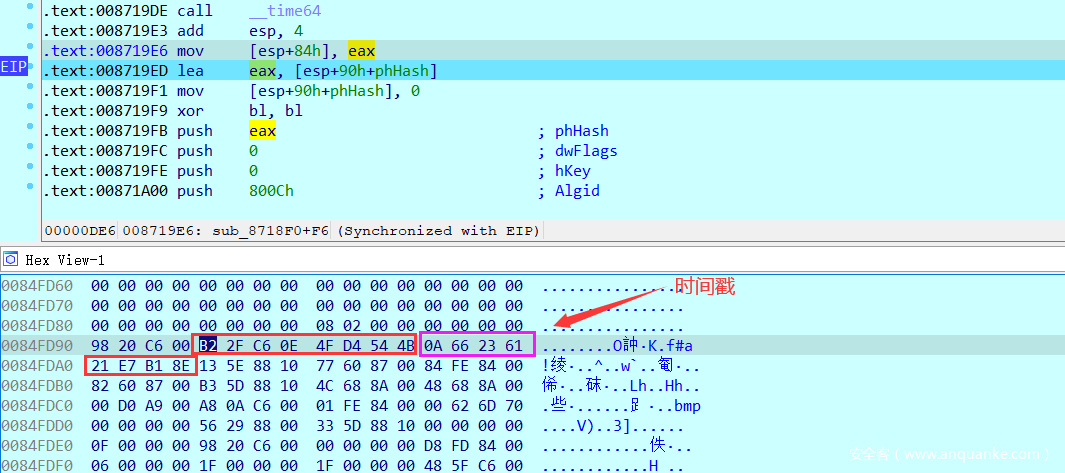
调试得到pdata是通过一些算出的固定值和时间戳组成的16字节:
然后直接在最后加密的函数下断点,看加密数据是否是我们的输入,确定输入在之前没有变化操作。
自己用数据测试了本地aes解密经过程序加密的数据正确后开始解密工作。
先得到pdata进而得到key:
1.通过文件最后修改的时间,然后在线转换一下得到对应的时间戳。
2.通过bmp文件的魔术字段爆破出时间戳。
这里我2个方法都试了下,得到同样的结果:
爆破pdata,进而得到key:
#coding:utf-8
import base64
from hashlib import *
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
def decrypt(data, key):
cryptos = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
decrpytBytes = list(base64.b64decode(data))
decrpytBytes = bytes(decrpytBytes)
meg = cryptos.decrypt(decrpytBytes)
return meg
enc = 'sgL4CWqLPyWU7eexyfw6pw=='
s = [0xB2, 0x2F, 0xC6, 0x0E, 0x4F, 0xD4, 0x54, 0x4B, 0x4E, 0x31, 0x21, 0x61, 0x21, 0xE7, 0xB1, 0x8E]
for i in range(0xff):
for j in range(0xff):
for k in range(0xff):
s[8:11] = [i, j, k]
key = sha256(bytes(s)).hexdigest()[:32]
key = bytes.fromhex(key)
ans = decrypt(enc, key)
if ans[:2] == b'BM' and ans[15] == 0 and ans[5] == 0:
print(key)
然后写脚本解密,但发现只有第一组解密正确。
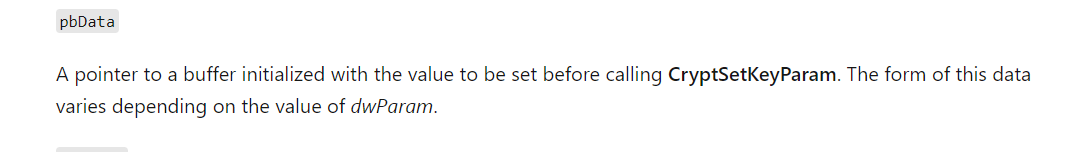
其实这里是我忽略了上面的CryptSetKeyParam:
BOOL CryptSetKeyParam(
HCRYPTKEY hKey,
DWORD dwParam,
const BYTE *pbData,
DWORD dwFlags
);
其中参数2我们可以从wincrypt.h中找到:
从以上我看可以了解到,程序是使用了PKCS5_PADDING与cbc模式加密。
然后从第一组能解密成功可以推测出使用了默认的iv:0。
最后解密还原bmp图片:
#coding:utf-8
import base64
from hashlib import *
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
def decrypt(data, key):
cryptos = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
decrpytBytes = list(base64.b64decode(data))
decrpytBytes = bytes(decrpytBytes)
meg = cryptos.decrypt(decrpytBytes)
return meg
key = "f4b6bb19108b56fc60a61fc967c0afbe71d2d9048ac0ffe931c901e75689eb46"[:32]
key = bytes.fromhex(key)
f = open("1.bmp.ctf_crypter", "rb")
fp = open("1", "wb")
data = f.read()
def xor(a, b):
res = []
for i in range(len(a)):
#print(i)
res += [a[i]^b[i]]
return bytes(res)
for i in range(len(data)//16):
#print(data[16*i:16*(i+1)].hex())
enc = base64.b64encode(data[16*i:16*(i+1)])
if i > 0:
ans = xor(decrypt(enc, key), data[16*(i-1):16*i])
else:
ans = decrypt(enc, key)
fp.write(ans)
f.close()
fp.close()
print('*'*100)
至于最后一块的填充数据,从解密结果来看是10。
Rev_APC
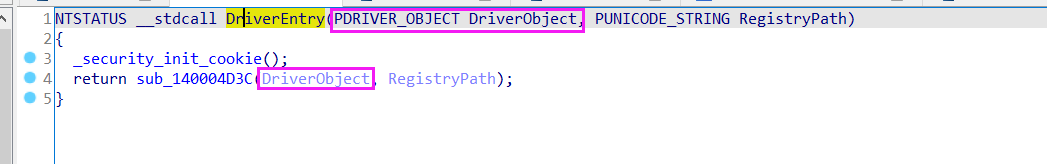
首先定位到DriverEntry:
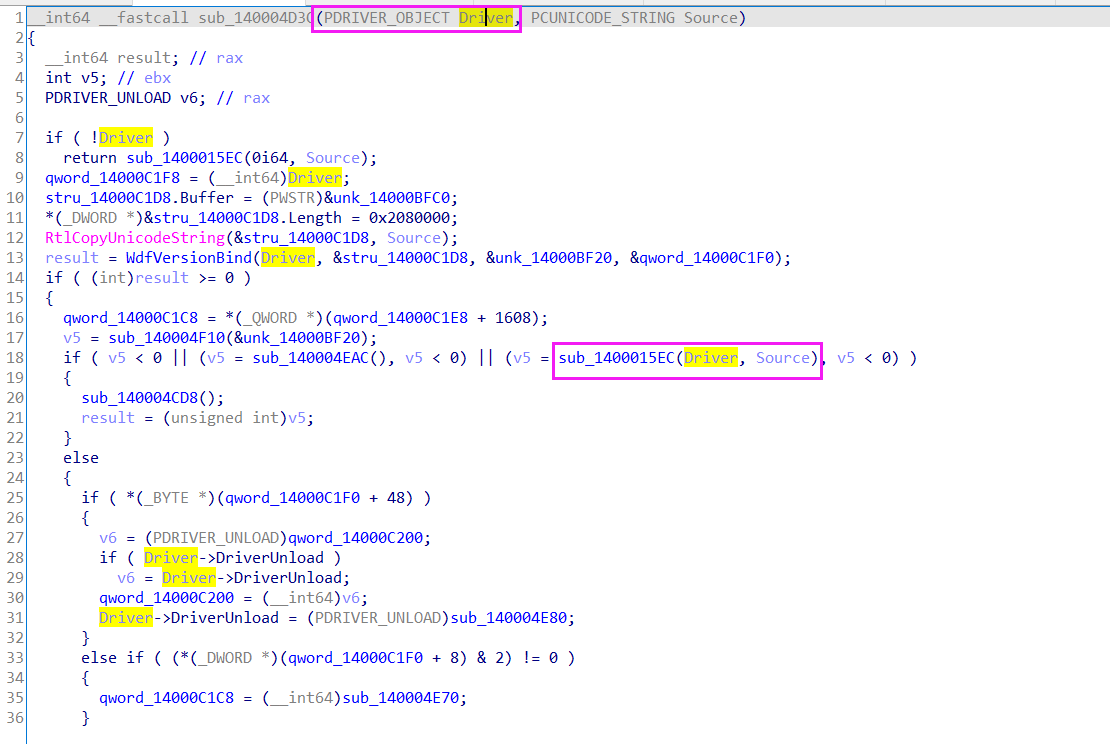
再看sub_140004D3C:
我们知道DriverEntry的第一个参数是驱动对象指针(PDRIVER_OBJECT Driver)。驱动对象用DRIVER_OBJECT Driver数据结构表示,它做为驱动的一个实例被内核加载,并且内核中一个驱动只加载一个实例,也就是一个驱动最多只有一个驱动对象。
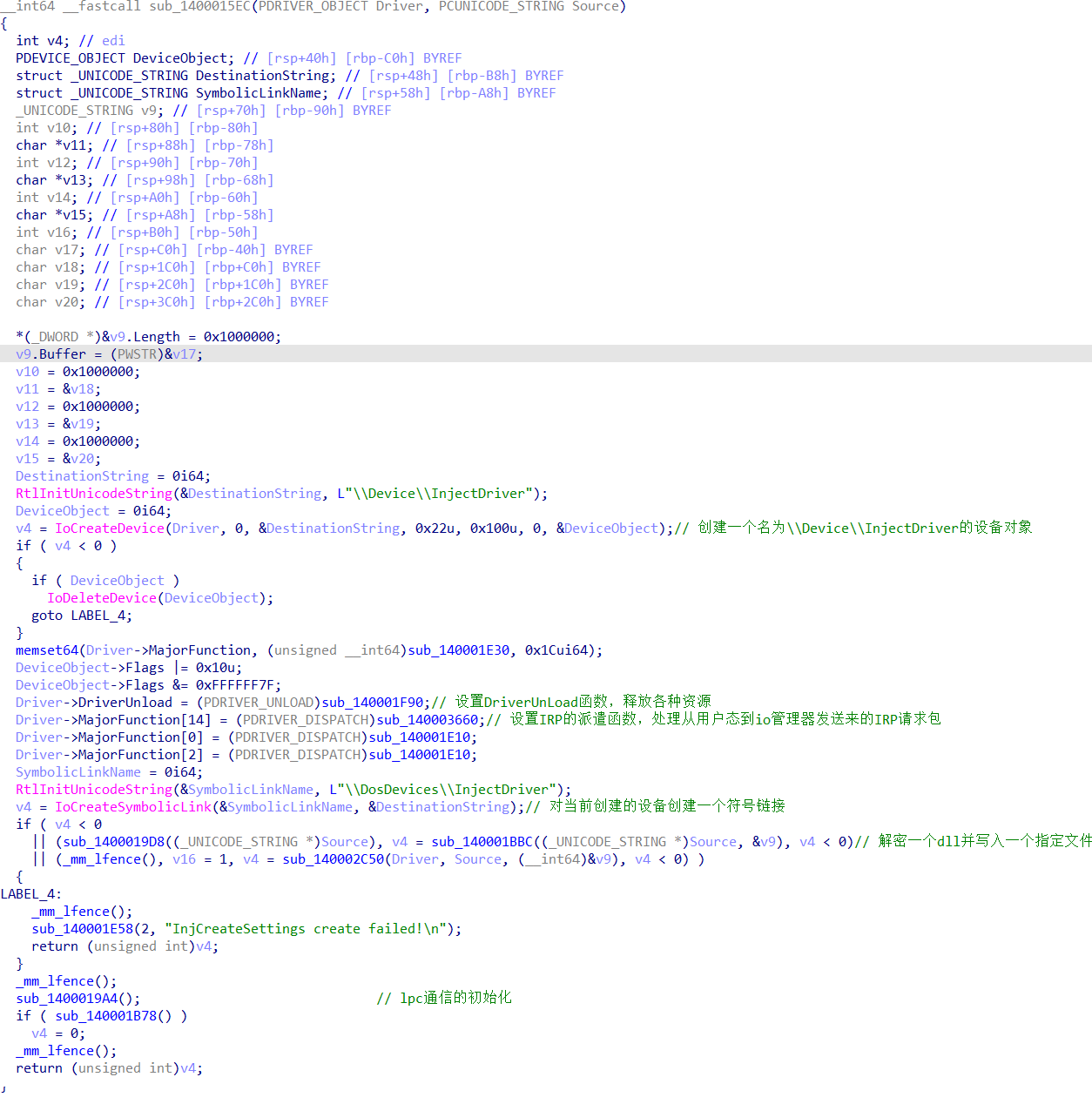
驱动程序的关键是要去分析AddDevice函数,而设备对象结构体中的一个成员:struct _DRIVER_OBJECT *DriverObject; 它也是一个驱动对象指针,且它与DriverEntry中的一个参数都是同一个驱动对象指针,依据这个我们就能快速的从DriverEntry中找到设备创建相关关键函数了。其实也就是定位DriverEntry的第一个参数Driver,看那个函数把它作为了第一个参数。(如上图演示,找到了sub_1400015EC函数。
看到sub_1400015EC函数:
其中IoCreateSymbolicLink创建符号链接是为了给设备对象起个别名,为了让用户模式下的程序识别这个设备对象;
Driver->DriverUnload是设置驱动卸载时要调用的回调函数,一般负责删除在DriverEntry中创建的设备对象,并把设备对象所关联的符号链接删除;
Driver->MajorFunction记录的是一个函数指针数组,函数是处理IRP的派遣函数,是用户模式发出请求,然后由用户态与内核态之间的桥梁I/O管理器发出。
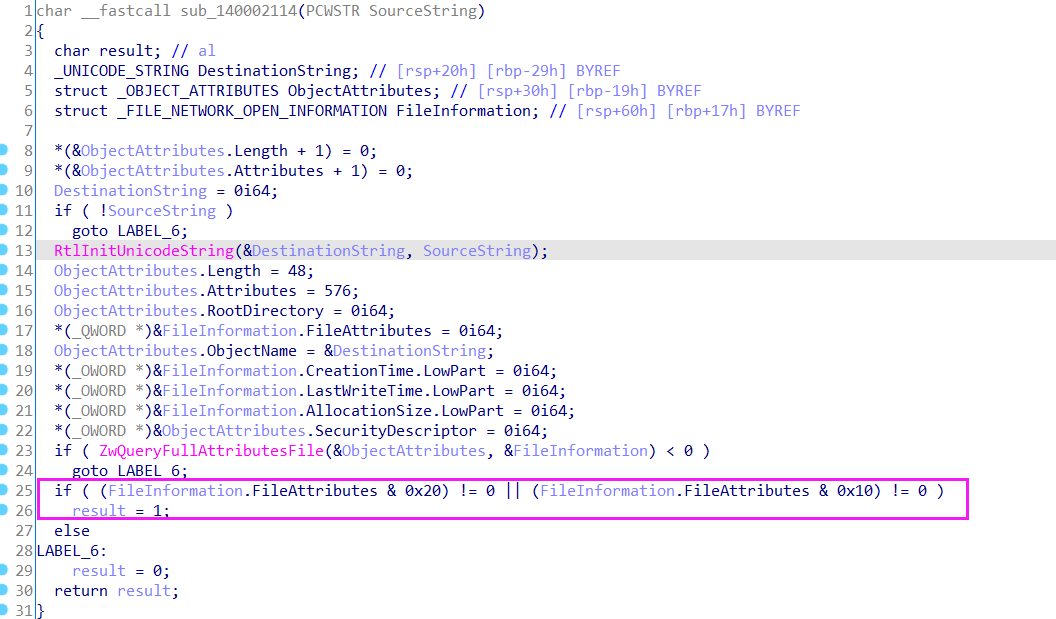
再看到里面的sub_1400019D8函数:判断指定的dll是否存在,如果不存在就从编码的数据中异或解密出一个dll写入文件。
判断dll是否存在代码:
找到FileAttributes的枚举值:
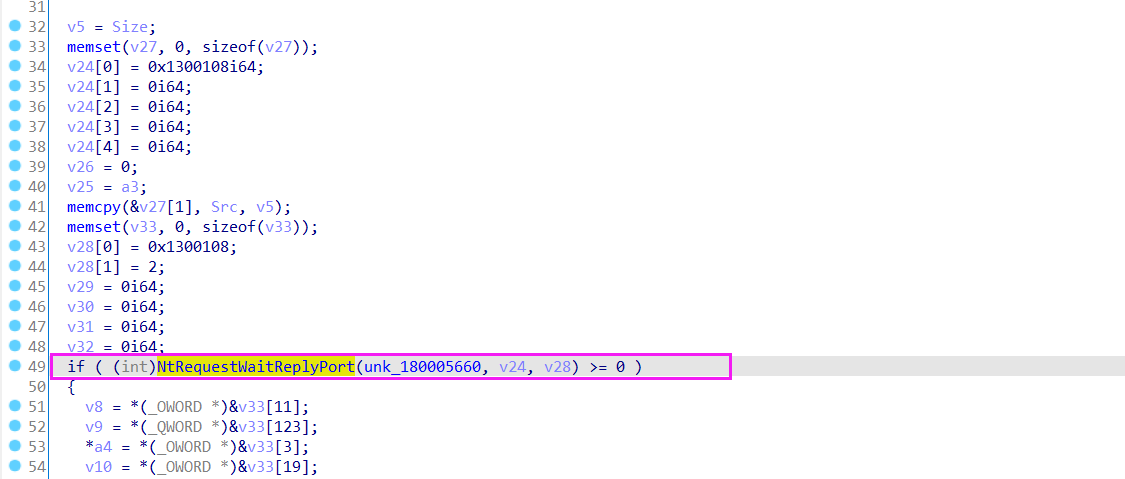
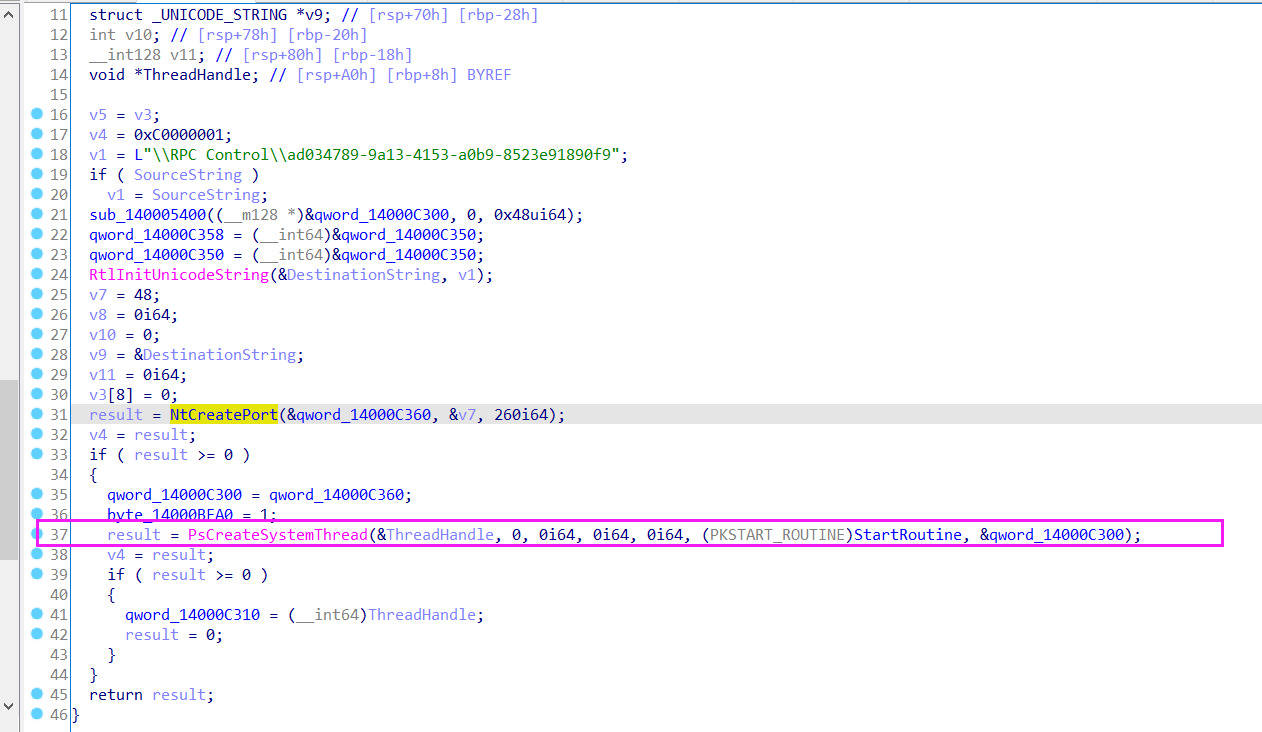
接着sub_1400019A4函数进行了lpc通信的初始化,监听端口等。
最后sub_140001B78函数设置了一个进程创建的监控函数,本题是监控新创建的进程,用md5值判断该进程是否是explorer.exe。
上面我们对整个创建设备对象的函数整体上梳理了一遍,下面开始提取出要解密的dll。
idapython提取解密dll:
from ida_bytes import *
addr = 0x140007000
fp = open("InjectDLL.dll", "wb")
for i in range(0x3c00):
fp.write(bytes([get_byte(addr+i)]))
fp.close()
print('*'*100)
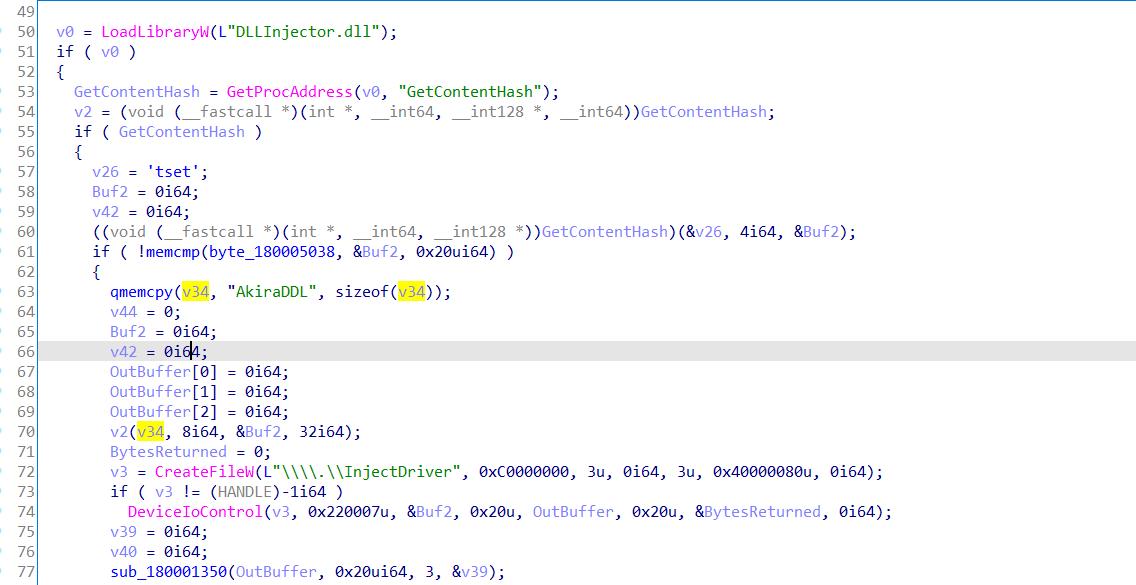
从字符串信息定位到dll中的关键函数sub_1800015C0,上半部分:使用sha3-256加密AkiraDDL字符串,将32字节的结果通过DeviceIoControl函数发送到CreateFileW函数创建的驱动对象,让驱动对象相应的设备执行相应的操作(也就是驱动程序中设置的Driver->MajorFunction。
接着就是本题解题的关键了:找到正确的用于后面和flag明文加密的32字节数据。
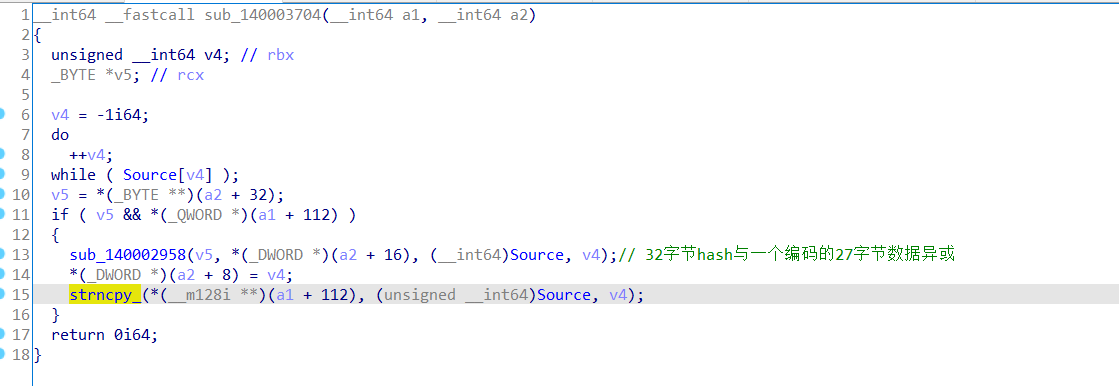
上面我们知道计算的32字节hash值发送到了驱动对象,看到驱动对象中对应的处理函数:可以看到32字节hash经过的异或的数据并没有传出到dll中,而是直接把编码的数据复制到了*(__m128i **)(a1 + 112),所以说我们的hash值根本没有使用的。
接着是后面的sub_180001350函数:处理从驱动对象发送回的数据,使用了lpc通信向服务方发送报文,请求得到LPC服务。
回到驱动程序中找到lpc通信初始化的地方,用StartRoutine函数处理lpc通信请求。
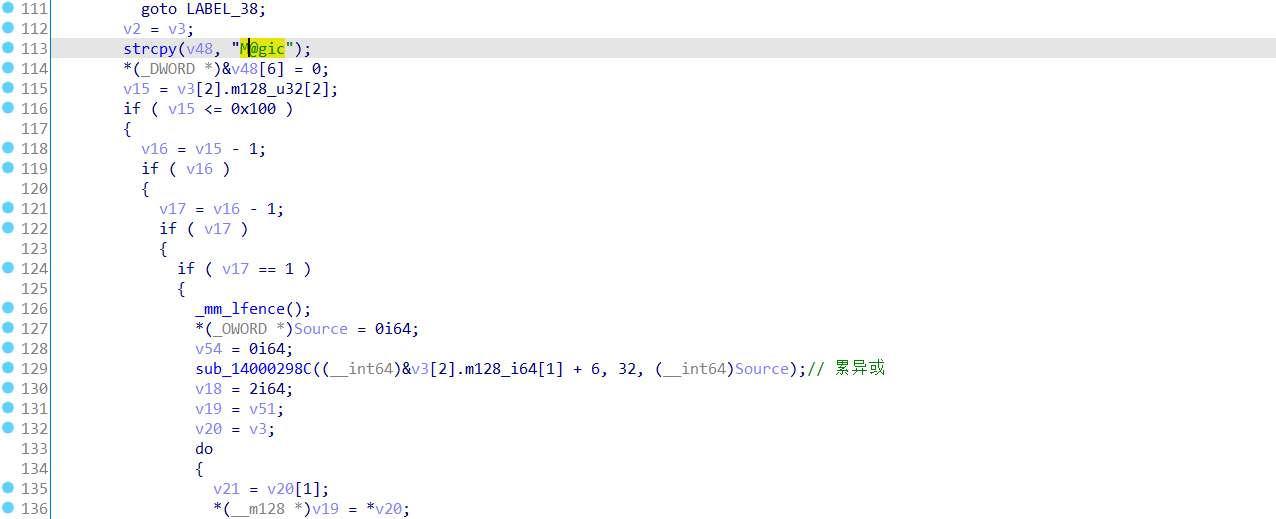
从StartRoutine函数找到处理从dll发送的数据的地方,这里的if else分支中,一个是累异或:每个字节与它之前的所有字节异或;另外一个是将M@gic字符串添加到本来有的27字节数据后面正好组成32字节数据。
剩下就是最后的加密,32轮加密,每轮加密函数用随机数确定。因为这里没有使用srand()初始化种子,那使用的就是默认的种子:1。
上面也说了在我分析来,有2种用于和flag明文加密的数据,这里我在解密时两种结果都试了一下,从第一种累异或得到正确结果。
加密算法也很好逆,一是加密只有异或,加法,减法及移位。二是要和flag明文加密的数据的变化不受明文的影响。
解密脚本:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
unsigned char hash[] = {165, 106, 167, 113, 180, 119, 198, 3, 209, 8, 223, 24, 206, 3, 215, 15, 204, 119, 186, 98, 174, 109, 221, 24, 192, 9, 213, 213, 213, 213, 213, 213};
//unsigned char hash[] = {0xA5, 0xCF, 0xCD, 0xD6, 0xC5, 0xC3, 0xB1, 0xC5, 0xD2, 0xD9, 0xD7, 0xC7, 0xD6, 0xCD, 0xD4, 0xD8, 0xC3, 0xBB, 0xCD, 0xD8, 0xCC, 0xC3, 0xB0, 0xC5, 0xD8, 0xC9, 0xDC, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0};
//unsigned char hash[] = {56, 144, 185, 193, 92, 20, 87, 231, 166, 41, 206, 164, 135, 174, 194, 10, 40, 211, 69, 111, 251, 121, 0, 103, 104, 40, 171, 235, 244, 190, 95, 32};
unsigned char hashed[32][32] = {0};
char order[] = {0, 5, 5, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 3, 2, 0, 3, 0, 3, 2, 1, 5, 1, 3, 1, 5, 5, 2, 4, 0, 0, 4, 5, 4, 4, 5, 5};
unsigned char enc[32] = {87, 197, 56, 27, 58, 168, 52, 47, 57, 151, 198, 228, 4, 47, 143, 238, 94, 81, 128, 103, 36, 201, 111, 72, 91, 127, 189, 199, 176, 194, 194, 235};
//unsigned char enc[] = {145, 245, 10, 154, 15, 94, 11, 194, 194, 229, 233, 150, 87, 240, 145, 56, 1, 113, 96, 76, 163, 181, 65, 253, 1, 237, 39, 181, 137, 88, 235, 108};
unsigned char plain[32] = {0};
unsigned char fun(unsigned char a)
{
return ((a<<4)|(a>>4));
}
void fun1(unsigned char *a, unsigned char *b)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
a[i] += 16;
b[i] ^= a[i];
}
}
void fun2(unsigned char *a, unsigned char *b)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
a[i] -= 80;
b[i] ^= fun(a[i]);
}
}
void fun3(unsigned char *a, unsigned char *b)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
b[i] ^= a[i];
}
}
void fun4(unsigned char *a, unsigned char *b)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
a[i] -= 80;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i += 2)
{
b[i] ^= 16*a[i];
b[i+1] ^= a[i] >> 4;
}
}
void fun5(unsigned char *a, unsigned char *b)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
b[i] ^= a[i];
}
}
void fun6(unsigned char *a, unsigned char *b)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
if((unsigned char)(a[i]-33) > 46)
{
if((unsigned char)(a[i]-81) > 46)
{
if(a[i]>0x80)
{
a[i] = a[i]-48;
b[i] -= a[i];
}
}
else
{
a[i] = a[i]-48;
b[i] ^= a[i] >> 4;
}
}
else
{
a[i] = a[i]-80;
b[i] += a[i];
}
}
}
void defun6(unsigned char *a, unsigned char *b)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
if((unsigned char)(a[i]-33) > 46)
{
if((unsigned char)(a[i]-81) > 46)
{
if(a[i]>0x80)
{
a[i] = a[i]-48;
b[i] += a[i];
}
}
else
{
a[i] = a[i]-48;
b[i] ^= a[i] >> 4;
}
}
else
{
a[i] = a[i]-80;
b[i] -= a[i];
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
unsigned char tmp = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < i+1; j++)
tmp ^= hash[j];
}
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 32; j++)
{
hashed[i][j] = hash[j];
//printf("%d, ", hash[j]);
}
//putchar(10);
switch(rand()%6)
{
case 0: fun1(hash, plain);
break;
case 1: fun2(hash, plain);
break;
case 2: fun3(hash, plain);
break;
case 3: fun4(hash, plain);
break;
case 4: fun5(hash, plain);
break;
case 5: fun6(hash, plain);
break;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
switch(order[i])
{
case 0: fun1(hashed[31-i], enc);
break;
case 1: fun2(hashed[31-i], enc);
break;
case 2: fun3(hashed[31-i], enc);
break;
case 3: fun4(hashed[31-i], enc);
break;
case 4: fun5(hashed[31-i], enc);
break;
case 5: defun6(hashed[31-i], enc);
break;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
printf("%c", enc[i]);
}
return 0;
}