1 摘要
JavaScript是动态类型语言,数据类型具有不确定性。V8是用C++编写的,C++是强类型语言,要求类型确定。类型确定的C++是如何表达类型不确定的JS呢?解决方法是:操作JS数据前先查询类型,再操作。这又产生了新问题——性能损耗,因为类型查询是极为耗时的操作,频繁使用严重影响程序运行速度。为此,V8采用了Map机制,也称为隐藏类(Hidden Class)。注意: Map机制与JS中的map()没有关系,只是同名。Map机制可以很好地表达JS的不确定性,但它的主要作用是降低性能损耗。本文通过形象化的比喻和深入的源码分析,使大家从宏观和微观角度全面认识Map机制,本文组织结构:Map原理,它如何表达Javascript的动态类型(章节2);V8初始化阶段对Map的处理过程(章节3)。
2 Map原理
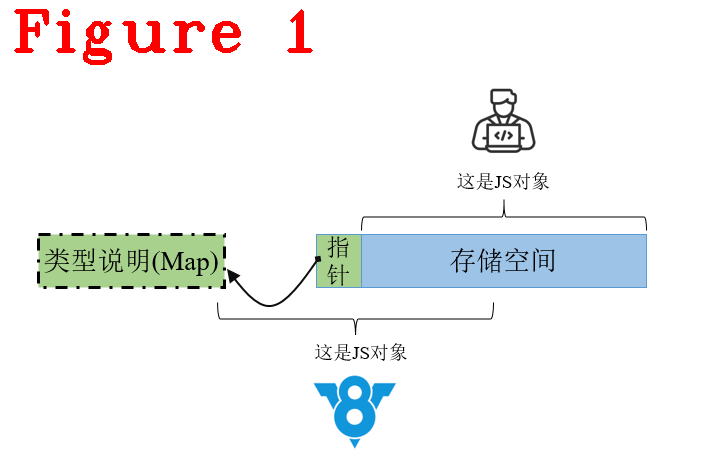
由于Javascript类型的不确定性,V8操作Javascript对象(例如:调用方法、访问对对象成员)前要先查询其类型。因此,V8引入了Map机制,它是一种用于描述类型的数据结构,可以形象地把它叫作“地图”,它的使用特点是固定的位置存储指定的内容,如图1所示。
借助图1,我们对Map机制进行概要描述:
(1) JS开发者角度,仅能看到存储空间,这段存储空间保存了开发者定义的JS对象,但V8不知道对象类型;
(2) 指针,它是存储空间的第一个位置,类型是指针,大小8byte(64位系统中),由V8维护,开发者看不到,所以叫隐藏类。它的作用是指向Map;
(3) V8角度,查询存储空间的第一个位置,就可以找到Map。这个Map大小是80byte,存储信息的格式与位置也是固定的,存储信息包括:JS对象的存储空间有哪些成员,成员类型,成员偏移地址等。所以说,Map就是地图。
V8通过查询Map,可以知道存储空间内存放了什么,怎么存放的,进而正确操作JS对象。一句话总结:V8利用类型确定的Map类(c++实现的class对象)管理JS的动态对象。其实,在V8角度看,Map类型是确定的,所以整体数据类型就是确定的。最重要是Map提高了效率,因为它代替了耗时的JS对象类型检索操作。
下面来看Map的布局:
1. Map layout:
2. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
3. // | _ Type _ | _ Description _ |
4. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
5. // | TaggedPointer | map - Always a pointer to the MetaMap root |
6. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
7. // | Int | The first int field |
8. // `---+----------+---------------------------------------------+
9. // | Byte | [instance_size] |
10. // +----------+---------------------------------------------+
11. // | Byte | If Map for a primitive type: |
12. // | | native context index for constructor fn |
13. // | | If Map for an Object type: |
14. // | | inobject properties start offset in words |
15. // +----------+---------------------------------------------+
16. // | Byte | [used_or_unused_instance_size_in_words] |
17. // | | For JSObject in fast mode this byte encodes |
18. // | | the size of the object that includes only |
19. // | | the used property fields or the slack size |
20. // | | in properties backing store. |
21. // +----------+---------------------------------------------+
22. // | Byte | [visitor_id] |
23. // +----+----------+---------------------------------------------+
24. // | Int | The second int field |
25. // `---+----------+---------------------------------------------+
26. // | Short | [instance_type] |
27. // +----------+---------------------------------------------+
28. // | Byte | [bit_field] |
29. // | | - has_non_instance_prototype (bit 0) |
30. // | | - is_callable (bit 1) |
31. // | | - has_named_interceptor (bit 2) |
32. // | | - has_indexed_interceptor (bit 3) |
33. // | | - is_undetectable (bit 4) |
34. // | | - is_access_check_needed (bit 5) |
35. // | | - is_constructor (bit 6) |
36. // | | - has_prototype_slot (bit 7) |
37. // +----------+---------------------------------------------+
38. // | Byte | [bit_field2] |
39. // | | - new_target_is_base (bit 0) |
40. // | | - is_immutable_proto (bit 1) |
41. // | | - unused bit (bit 2) |
42. // | | - elements_kind (bits 3..7) |
43. // +----+----------+---------------------------------------------+
44. // | Int | [bit_field3] |
45. // | | - enum_length (bit 0..9) |
46. // | | - number_of_own_descriptors (bit 10..19) |
47. // | | - is_prototype_map (bit 20) |
48. // | | - is_dictionary_map (bit 21) |
49. // | | - owns_descriptors (bit 22) |
50. // | | - is_in_retained_map_list (bit 23) |
51. // | | - is_deprecated (bit 24) |
52. // | | - is_unstable (bit 25) |
53. // | | - is_migration_target (bit 26) |
54. // | | - is_extensible (bit 28) |
55. // | | - may_have_interesting_symbols (bit 28) |
56. // | | - construction_counter (bit 29..31) |
57. // | | |
58. // +*************************************************************+
59. // | Int | On systems with 64bit pointer types, there |
60. // | | is an unused 32bits after bit_field3 |
61. // +*************************************************************+
62. // | TaggedPointer | [prototype] |
63. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
64. // | TaggedPointer | [constructor_or_backpointer] |
65. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
66. // | TaggedPointer | [instance_descriptors] |
67. // +*************************************************************+
68. // ! TaggedPointer ! [layout_descriptors] !
69. // ! ! Field is only present if compile-time flag !
70. // ! ! FLAG_unbox_double_fields is enabled !
71. // ! ! (basically on 64 bit architectures) !
72. // +*************************************************************+
73. // | TaggedPointer | [dependent_code] |
74. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
75. // | TaggedPointer | [prototype_validity_cell] |
76. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
77. // | TaggedPointer | If Map is a prototype map: |
78. // | | [prototype_info] |
79. // | | Else: |
80. // | | [raw_transitions] |
81. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
前面提到Map是格式统一、大小固定的数据结构,即规定的位置代表指定的含义。上面代码是它的格式,它大小是80个字节,代码9行,instance_size代表图1中的存储空间的大小;代码24行,instance_type代表图1中的存储空间内的JS数据类型,例如:JS数组、JSFunction等。代码66行,instance_descriptors对JS数据的详细描述,例如:每个成员都是什么,存在哪里等。
注意:每一个JavaScript对象的存储空间的第一个位置都是一个Map指针,也就是每个js对象都有Map,Map大小不因js对象不同而改变,始终是80字节,存储内容也如上所示,保持不变。它用来描述JS对象的形状,相同形状的不同js对象共同一个Map。“形状相同”是类型一样,内部成员存储布局也一样,如下面代码:
function Point(x,y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
var fun1 = new Point(1,2);
var fun2 = new Point(3,4);
fun1和fun2共用一个Map,因为他们的形状一样。执行fun2.z=80;之后,fun2的形状发生了变,随之会有新的Map产生,叫Map迁移,后续文章会讲解。
下面来看是Map类的核心代码:
1. class Map : public HeapObject {
2. public:
3. //...............省略很多..................
4. DECL_PRIMITIVE_ACCESSORS(bit_field, byte)
5. DECL_PRIMITIVE_ACCESSORS(relaxed_bit_field, byte)
6. // Bit positions for |bit_field|.
7. #define MAP_BIT_FIELD_FIELDS(V, _) \
8. V(HasNonInstancePrototypeBit, bool, 1, _) \
9. V(IsCallableBit, bool, 1, _) \
10. V(HasNamedInterceptorBit, bool, 1, _) \
11. V(HasIndexedInterceptorBit, bool, 1, _) \
12. V(IsUndetectableBit, bool, 1, _) \
13. V(IsAccessCheckNeededBit, bool, 1, _) \
14. V(IsConstructorBit, bool, 1, _) \
15. V(HasPrototypeSlotBit, bool, 1, _)
16. DEFINE_BIT_FIELDS(MAP_BIT_FIELD_FIELDS)
17. #undef MAP_BIT_FIELD_FIELDS
18. // Bit field 2.
19. DECL_PRIMITIVE_ACCESSORS(bit_field2, byte)
20. // Bit positions for |bit_field2|.
21. #define MAP_BIT_FIELD2_FIELDS(V, _) \
22. V(NewTargetIsBaseBit, bool, 1, _) \
23. V(IsImmutablePrototypeBit, bool, 1, _) \
24. V(UnusedBit, bool, 1, _) \
25. V(ElementsKindBits, ElementsKind, 5, _)
26. DEFINE_BIT_FIELDS(MAP_BIT_FIELD2_FIELDS)
27. #undef MAP_BIT_FIELD2_FIELDS
28. DECL_PRIMITIVE_ACCESSORS(bit_field3, uint32_t)
29. V8_INLINE void clear_padding();
30. // Bit positions for |bit_field3|.
31. #define MAP_BIT_FIELD3_FIELDS(V, _) \
32. V(EnumLengthBits, int, kDescriptorIndexBitCount, _) \
33. V(NumberOfOwnDescriptorsBits, int, kDescriptorIndexBitCount, _) \
34. V(IsPrototypeMapBit, bool, 1, _) \
35. V(IsDictionaryMapBit, bool, 1, _) \
36. V(OwnsDescriptorsBit, bool, 1, _) \
37. V(IsInRetainedMapListBit, bool, 1, _) \
38. V(IsDeprecatedBit, bool, 1, _) \
39. V(IsUnstableBit, bool, 1, _) \
40. V(IsMigrationTargetBit, bool, 1, _) \
41. V(IsExtensibleBit, bool, 1, _) \
42. V(MayHaveInterestingSymbolsBit, bool, 1, _) \
43. V(ConstructionCounterBits, int, 3, _)
44. DEFINE_BIT_FIELDS(MAP_BIT_FIELD3_FIELDS)
45. #undef MAP_BIT_FIELD3_FIELDS
46. DEFINE_FIELD_OFFSET_CONSTANTS(HeapObject::kHeaderSize,
47. TORQUE_GENERATED_MAP_FIELDS)
48. //...............省略很多..................
49. OBJECT_CONSTRUCTORS(Map, HeapObject);
50. };
上述代码中,只保留了MAP格式的定义,我们对DEFINE_FIELD_OFFSET_CONSTANTS做展开,如下:
1. enum {
2. TORQUE_GENERATED_MAP_FIELDS_StartOffset= 7,
3. kInstanceSizeInWordsOffset=8, kInstanceSizeInWordsOffsetEnd = 8,
4. kInObjectPropertiesStartOrConstructorFunctionIndexOffset=9, kInObjectPropertiesStartOrConstructorFunctionIndexOffsetEnd = 9,
5. kUsedOrUnusedInstanceSizeInWordsOffset=10, kUsedOrUnusedInstanceSizeInWordsOffsetEnd = 10,
6. kVisitorIdOffset=11, kVisitorIdOffsetEnd = 11,
7. kInstanceTypeOffset=12, kInstanceTypeOffsetEnd = 13,
8. kBitFieldOffset=14, kBitFieldOffsetEnd = 14,
9. kBitField2Offset=15, kBitField2OffsetEnd = 15,
10. kBitField3Offset=16, kBitField3OffsetEnd = 19,
11. kOptionalPaddingOffset=20, kOptionalPaddingOffsetEnd = 23,
12. kStartOfStrongFieldsOffset=24, kStartOfStrongFieldsOffsetEnd = 23,
13. kPrototypeOffset=24, kPrototypeOffsetEnd = 31,
14. kConstructorOrBackPointerOffset=32, kConstructorOrBackPointerOffsetEnd = 39,
15. kInstanceDescriptorsOffset=40, kInstanceDescriptorsOffsetEnd = 47,
16. kLayoutDescriptorOffset=48, kLayoutDescriptorOffsetEnd = 55,
17. kDependentCodeOffset=56, kDependentCodeOffsetEnd = 63,
18. kPrototypeValidityCellOffset=64, kPrototypeValidityCellOffsetEnd = 71,
19. kEndOfStrongFieldsOffset=72, kEndOfStrongFieldsOffsetEnd = 71,
20. kStartOfWeakFieldsOffset=72, kStartOfWeakFieldsOffsetEnd = 71,
21. kTransitionsOrPrototypeInfoOffset=72, kTransitionsOrPrototypeInfoOffsetEnd = 79,
22. kEndOfWeakFieldsOffset=80, kEndOfWeakFieldsOffsetEnd = 79,
23. kSize=80, kSizeEnd = 79,
24. }
代码2行TORQUE_GENERATED_MAP_FIELDS_StartOffset说明了Map的起始偏移是7(从0算起),也就是第8个字节,前面提到一个Map的大小是80个字节,由于Map继承Heap对象,这80个字节中的前8个字节是Heap对象,所以它的实际可用的字节是72个,每个成员的偏移和大小与前述第一段代码(Map Layout)对应。Map的创建和回收由V8的Heap负责管理,下面是创建Map的源码位置:
1. AllocationResult Heap::AllocateRaw(int size_in_bytes, AllocationType type,
2. AllocationOrigin origin,
3. AllocationAlignment alignment) {
4. //.....省略很多.......
5. if (AllocationType::kYoung == type) {
6. //.....省略很多.......
7. } else if (AllocationType::kOld == type) {
8. //.....省略很多.......
9. } else if (AllocationType::kCode == type) {
10. if (size_in_bytes <= code_space()->AreaSize() && !large_object) {
11. allocation = code_space_->AllocateRawUnaligned(size_in_bytes);
12. } else {
13. allocation = code_lo_space_->AllocateRaw(size_in_bytes);
14. }
15. } else if (AllocationType::kMap == type) {
16. allocation = map_space_->AllocateRawUnaligned(size_in_bytes);
17. } else if (AllocationType::kReadOnly == type) {
18. #ifdef V8_USE_SNAPSHOT
19. DCHECK(isolate_->serializer_enabled());
20. #endif
21. DCHECK(!large_object);
22. DCHECK(CanAllocateInReadOnlySpace());
23. DCHECK_EQ(AllocationOrigin::kRuntime, origin);
24. allocation =
25. read_only_space_->AllocateRaw(size_in_bytes, alignment, origin);
26. } else {
27. UNREACHABLE();
28. }
29. return allocation;
30. }
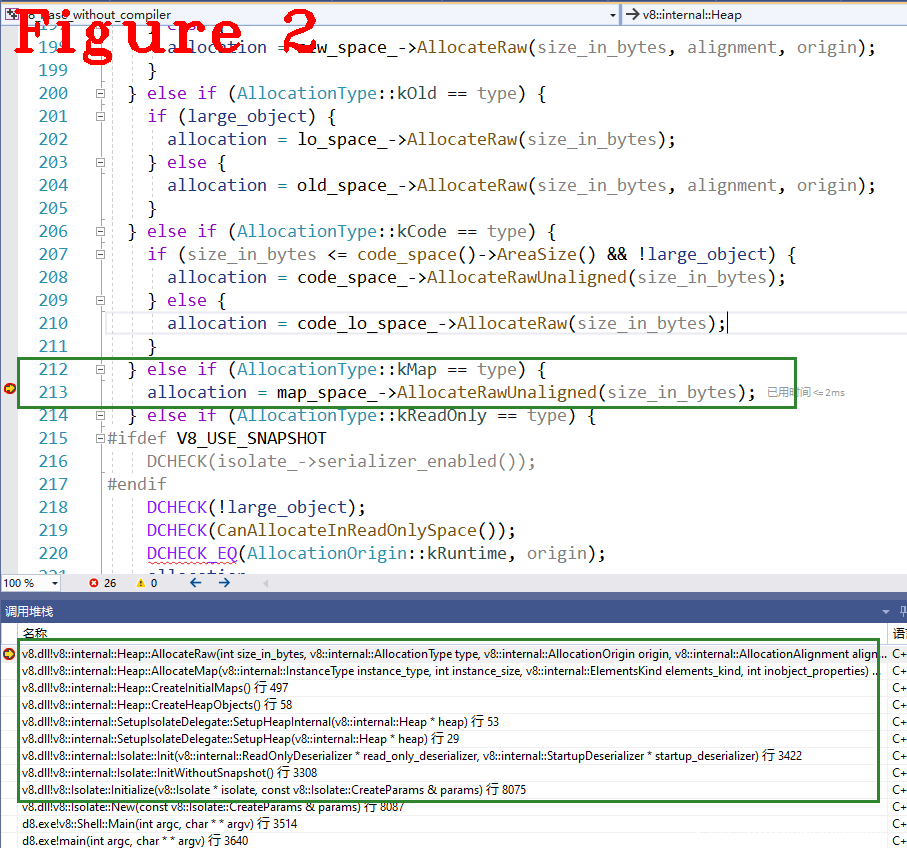
代码15行,type=KMap时size_in_bytes是80,进入代码16行分配内存,图2给出了执行代码16的调用堆栈。
AllocateRaw()分配内存后返回到AllocateMap(),对内存进行初始化,代码如下:
1. Map Factory::InitializeMap(Map map, InstanceType type, int instance_size,
2. ElementsKind elements_kind,
3. int inobject_properties) {
4. map.set_instance_type(type);
5. map.set_prototype(*null_value(), SKIP_WRITE_BARRIER);
6. map.set_constructor_or_backpointer(*null_value(), SKIP_WRITE_BARRIER);
7. map.set_instance_size(instance_size);
8. if (map.IsJSObjectMap()) {
9. DCHECK(!ReadOnlyHeap::Contains(map));
10. map.SetInObjectPropertiesStartInWords(instance_size / kTaggedSize -
11. inobject_properties);
12. DCHECK_EQ(map.GetInObjectProperties(), inobject_properties);
13. map.set_prototype_validity_cell(*invalid_prototype_validity_cell());
14. } else {
15. DCHECK_EQ(inobject_properties, 0);
16. map.set_inobject_properties_start_or_constructor_function_index(0);
17. map.set_prototype_validity_cell(Smi::FromInt(Map::kPrototypeChainValid));
18. }
19. map.set_dependent_code(DependentCode::cast(*empty_weak_fixed_array()),
20. SKIP_WRITE_BARRIER);
21. map.set_raw_transitions(MaybeObject::FromSmi(Smi::zero()));
22. map.SetInObjectUnusedPropertyFields(inobject_properties);
23. map.SetInstanceDescriptors(isolate(), *empty_descriptor_array(), 0);
24. if (FLAG_unbox_double_fields) {
25. map.set_layout_descriptor(LayoutDescriptor::FastPointerLayout());
26. }
27. //.................省略很多...............
28. return map;
29. }
上面代码是对Map的初始化,按最开始给出的May layout对每个字段(bit位、byte位、short位等)进行初始化。代码8,9,10,13行对JSObject对象中的InObject数据进行初始化,“InObject”是存储在JSObject对象内部的数据,访问这些数据更快。代码28返回Map,至此Map生成完毕,后续会通过这个Map访问图1中的存储空间,请读者自行跟踪代码,不再赘述。
3 Map初始化
在V8的启动阶段,CreateInitialMaps()对所有Javascript类型分别建立对应的空Map,“空Map”说明了创建某个JS类型数据所需的最小内存空间。这样,开发者创建javascript对象时,V8先用对应的空Map申请一段最小空间,随时开发者对JS对象添加成员,Map也会发生改变。下面给出Map初始化的源码:
1. bool Heap::CreateInitialMaps() {//....代码太长,中间省略很多........
2. HeapObject obj;
3. {
4. AllocationResult allocation = AllocatePartialMap(MAP_TYPE, Map::kSize);
5. if (!allocation.To(&obj)) return false;
6. }
7. Map new_meta_map = Map::unchecked_cast(obj);
8. set_meta_map(new_meta_map);
9. new_meta_map.set_map_after_allocation(new_meta_map);
10. //...................分隔线....................
11. ReadOnlyRoots roots(this);
12. { // Partial map allocation
13. #define ALLOCATE_PARTIAL_MAP(instance_type, size, field_name) \
14. { \
15. Map map; \
16. if (!AllocatePartialMap((instance_type), (size)).To(&map)) return false; \
17. set_##field_name##_map(map); \
18. }
19. ALLOCATE_PARTIAL_MAP(FIXED_ARRAY_TYPE, kVariableSizeSentinel, fixed_array);
20. ALLOCATE_PARTIAL_MAP(WEAK_FIXED_ARRAY_TYPE, kVariableSizeSentinel,
21. weak_fixed_array);
22. ALLOCATE_PARTIAL_MAP(WEAK_ARRAY_LIST_TYPE, kVariableSizeSentinel,
23. //...................分隔线....................
24. #undef ALLOCATE_PARTIAL_MAP
25. }
26. // Allocate the empty array.
27. {
28. AllocationResult alloc =
29. AllocateRaw(FixedArray::SizeFor(0), AllocationType::kReadOnly);
30. if (!alloc.To(&obj)) return false;
31. obj.set_map_after_allocation(roots.fixed_array_map(), SKIP_WRITE_BARRIER);
32. FixedArray::cast(obj).set_length(0);
33. }
34. set_empty_fixed_array(FixedArray::cast(obj));
35. //...................分隔线....................
36. FinalizePartialMap(roots.meta_map());
37. FinalizePartialMap(roots.fixed_array_map());
38. FinalizePartialMap(roots.weak_fixed_array_map());
39. {
40. if (!AllocateRaw(FixedArray::SizeFor(0), AllocationType::kReadOnly)
41. .To(&obj)) {
42. return false;
43. }
44. obj.set_map_after_allocation(roots.closure_feedback_cell_array_map(),
45. SKIP_WRITE_BARRIER);
46. FixedArray::cast(obj).set_length(0);
47. set_empty_closure_feedback_cell_array(ClosureFeedbackCellArray::cast(obj));
48. }
49. DCHECK(!InYoungGeneration(roots.empty_fixed_array()));
50. roots.bigint_map().SetConstructorFunctionIndex(
51. Context::BIGINT_FUNCTION_INDEX);
52. return true;
53. }
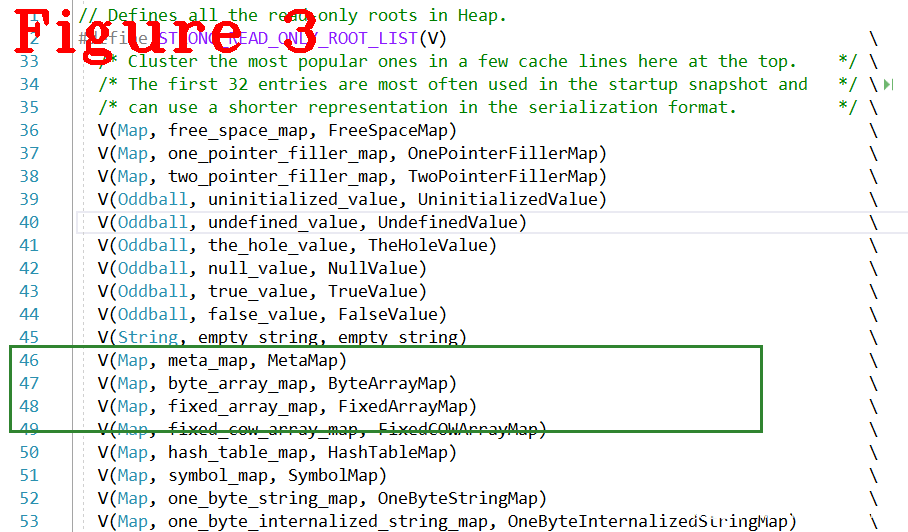
分隔线把代码分成了四部分,代码4,5,6,7,8行创建meta_data,这是所有Map都要用的元信息;代码13~22行,结合宏模板ALLOCATE_PARTIAL_MAP创建ARRAY和ARRAY_LIST类型的Map;代码27~34行创建其类型Map;分三批创建是因为后者的创建要依赖前者。最后,36开始,是完成所有Map创建的最终工作,并存储到root_table中,图3给出部分Map在root_table中的存储位置。
root_table是由下面的一系列宏板定义实现的指针类型数组,通过debug跟踪代码,可以看到meta_data在root_table中的位置下标是10,其它的下标请读者自行计算。
#define READ_ONLY_ROOT_LIST(V) \
STRONG_READ_ONLY_ROOT_LIST(V) \
INTERNALIZED_STRING_ROOT_LIST(V) \
PRIVATE_SYMBOL_ROOT_LIST(V) \
PUBLIC_SYMBOL_ROOT_LIST(V) \
WELL_KNOWN_SYMBOL_ROOT_LIST(V) \
STRUCT_MAPS_LIST(V) \
ALLOCATION_SITE_MAPS_LIST(V) \
DATA_HANDLER_MAPS_LIST(V)
#define MUTABLE_ROOT_LIST(V) \
STRONG_MUTABLE_IMMOVABLE_ROOT_LIST(V) \
STRONG_MUTABLE_MOVABLE_ROOT_LIST(V) \
V(StringTable, string_table, StringTable) \
SMI_ROOT_LIST(V)
#define ROOT_LIST(V) \
READ_ONLY_ROOT_LIST(V) \
MUTABLE_ROOT_LIST(V)
上述定义了root_table,通过宏模板的参数,可猜想出每个元素的大体功能和作用,配合debug跟踪来验证猜想是否确。
好了,今天到这里,下次见。
恳请读者批评指正、提出宝贵意见
微信:qq9123013 备注:v8交流 邮箱:v8blink@outlook.com