概述
曾经我一直以为 iOS 第三方 App 在 pc 指针指向 dyldbootstrap::start(app_mh, argc, argv, dyld_mh, &startGlue) 函数返回地址前,App 并没有代码会被执行,直到遇到了一个闪退的程序。经过分析知道其实很久以前就很有多文章分析了初始化过程中会优先调用 + load函数,这篇文章基于此展开,结合源码和 Mach-O 文件结构聊一聊初始化过程中在进入程序入口前哪些代码会被执行,以及如何对其进行动静态分析。
作者水平有限,如有错误评论区请雅正。
初始化顺序
先看官方文档:
https://developer.apple.com/documentation/objectivec/nsobject/1418815-load?preferredLanguage=occ
这里也就是说无论是动态还是静态链接,类和category会收到一个load message(也就是调用 +load 函数),前提当然需要实现了+load
文档随后也说明了初始化的顺序
- All initializers in any framework you link to.
- All +load methods in your image.
- All C++ static initializers and C/C++ __attribute__(constructor) functions in your image.
- All initializers in frameworks that link to you.
(关于第一个和第四个应该是在说明 link 其他 framework 的主模块 initializers 先执行,然后再执行 framework 内的)
看到这个文档知道除了网上很多资料提到的 +load 以外,C/C++ 部分初始化代码也会优先执行。
验证 Demo:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Person.h"
@implementation Person
+(void)load
{
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
}
@end
//
// inittest.cpp
//
#include "inittest.hpp"
class inittest{
__attribute__((constructor)) void cppconstructor(void) {
printf("%s be called testfield is %d \n",__FUNCTION__,testfield);
};
public:
int static testfield ;
};
int inittest::testfield = 5;
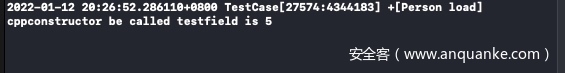
OC类和C++类仅仅做了声明(加入到工程目录),但没有进行任何new等操作,但关键函数也被执行了:
同时 static 变量也被初始化
源码分析The order of initialization
这个过程主要集中于dyld->runtime
相关源码:
https://github.com/apple-oss-distributions/dyld (github.com/opensource-apple/dyld太久没有更新了)
https://github.com/apple-oss-distributions/objc4 (github.com/opensource-apple/objc4太久没有更新+1)
+load 函数其实网上有很多文章,本文重点分析C/C++ initializers 以及一些细节
+load 函数 called
demo 中查看堆栈
(lldb) bt
* thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = breakpoint 2.1
* frame #0: 0x0000000100e518a4 TestCase`+[Person load](self=Person, _cmd="load") at Person.m:15:5
frame #1: 0x0000000187ba9e78 libobjc.A.dylib`load_images + 908
frame #2: 0x00000001011160d4 dyld`dyld::notifySingle(dyld_image_states, ImageLoader const*, ImageLoader::InitializerTimingList*) + 448
frame #3: 0x00000001011255b8 dyld`ImageLoader::recursiveInitialization(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&, unsigned int, char const*, ImageLoader::InitializerTimingList&, ImageLoader::UninitedUpwards&) + 524
frame #4: 0x0000000101124334 dyld`ImageLoader::processInitializers(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&, unsigned int, ImageLoader::InitializerTimingList&, ImageLoader::UninitedUpwards&) + 184
frame #5: 0x00000001011243fc dyld`ImageLoader::runInitializers(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&, ImageLoader::InitializerTimingList&) + 92
frame #6: 0x0000000101116420 dyld`dyld::initializeMainExecutable() + 216
frame #7: 0x000000010111adb4 dyld`dyld::_main(macho_header const*, unsigned long, int, char const**, char const**, char const**, unsigned long*) + 4616
frame #8: 0x0000000101115208 dyld`dyldbootstrap::start(dyld3::MachOLoaded const*, int, char const**, dyld3::MachOLoaded const*, unsigned long*) + 396
frame #9: 0x0000000101115038 dyld`_dyld_start + 56
通过调用栈、源码以及网上的文章相信都可以很好的理解这个流程;这里我们看一下调用细节,libobjc.A.dylib 是怎么找到那些类声明了 +load 函数呢?
从调用 +load 的 call_load_methods() 函数回溯逻辑(关键逻辑有注释)
void
load_images(const char *path __unused, const struct mach_header *mh)
{
if (!didInitialAttachCategories && didCallDyldNotifyRegister) {
didInitialAttachCategories = true;
loadAllCategories();
}
// Return without taking locks if there are no +load methods here.
if (!hasLoadMethods((const headerType *)mh)) return;
recursive_mutex_locker_t lock(loadMethodLock);
// Discover load methods
{
mutex_locker_t lock2(runtimeLock);
prepare_load_methods((const headerType *)mh);
}
// Call +load methods (without runtimeLock - re-entrant)
call_load_methods();
}
在call_load_methods() 之前会调用 hasLoadMethods 如果不存在就return,如果有+load 函数,还会调用 prepare_load_methods
bool hasLoadMethods(const headerType *mhdr)
{
size_t count;
if (_getObjc2NonlazyClassList(mhdr, &count) && count > 0) return true;
if (_getObjc2NonlazyCategoryList(mhdr, &count) && count > 0) return true;
return false;
}
prepare_load_methods 函数源码(关键逻辑有注释):
void prepare_load_methods(const headerType *mhdr)
{
size_t count, i;
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
classref_t const *classlist =
_getObjc2NonlazyClassList(mhdr, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
schedule_class_load(remapClass(classlist[i]));
}
category_t * const *categorylist = _getObjc2NonlazyCategoryList(mhdr, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
category_t *cat = categorylist[i];
Class cls = remapClass(cat->cls);
if (!cls) continue; // category for ignored weak-linked class
if (cls->isSwiftStable()) {
_objc_fatal("Swift class extensions and categories on Swift "
"classes are not allowed to have +load methods");
}
realizeClassWithoutSwift(cls, nil);
ASSERT(cls->ISA()->isRealized());
add_category_to_loadable_list(cat);
}
}
两个函数都用到了_getObjc2NonlazyClassList和_getObjc2NonlazyCategoryList,这个函数是什么呢?
在dyld源码内可以看到这么一段代码(关键逻辑写了注释):
// function name content type section name
GETSECT(_getObjc2SelectorRefs, SEL, "__objc_selrefs");
GETSECT(_getObjc2MessageRefs, message_ref_t, "__objc_msgrefs");
GETSECT(_getObjc2ClassRefs, Class, "__objc_classrefs");
GETSECT(_getObjc2SuperRefs, Class, "__objc_superrefs");
GETSECT(_getObjc2ClassList, classref_t, "__objc_classlist");
//下面这行
GETSECT(_getObjc2NonlazyClassList, classref_t, "__objc_nlclslist");
GETSECT(_getObjc2CategoryList, category_t *, "__objc_catlist");
//下面这行
GETSECT(_getObjc2NonlazyCategoryList, category_t *, "__objc_nlcatlist");
GETSECT(_getObjc2ProtocolList, protocol_t *, "__objc_protolist");
GETSECT(_getObjc2ProtocolRefs, protocol_t *, "__objc_protorefs");
GETSECT(getLibobjcInitializers, Initializer, "__objc_init_func");
_getObjc2NonlazyClassList和_getObjc2NonlazyCategoryList 其实是在获取 Mach-O 文 __objc_nlclslist __objc_nlcatlist 这两个 section 的内容,
通过反编译Demo 二进制程序会发现 +load 函数所在类会放在此 section 内
也就是说判断 +load 函数是否存在以及调用相关实现都用到了这些 section
C++ initializers的调用
同样先看堆栈:
(lldb) bt
* thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = breakpoint 1.1
* frame #0: 0x0000000100e51b68 TestCase`inittest::cppconstructor(this=0x0000000000000001) at inittest.cpp:17:16
frame #1: 0x000000010112a1b8 dyld`ImageLoaderMachO::doModInitFunctions(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&) + 428
frame #2: 0x000000010112a58c dyld`ImageLoaderMachO::doInitialization(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&) + 52
frame #3: 0x00000001011255d0 dyld`ImageLoader::recursiveInitialization(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&, unsigned int, char const*, ImageLoader::InitializerTimingList&, ImageLoader::UninitedUpwards&) + 548
frame #4: 0x0000000101124334 dyld`ImageLoader::processInitializers(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&, unsigned int, ImageLoader::InitializerTimingList&, ImageLoader::UninitedUpwards&) + 184
frame #5: 0x00000001011243fc dyld`ImageLoader::runInitializers(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&, ImageLoader::InitializerTimingList&) + 92
frame #6: 0x0000000101116420 dyld`dyld::initializeMainExecutable() + 216
frame #7: 0x000000010111adb4 dyld`dyld::_main(macho_header const*, unsigned long, int, char const**, char const**, char const**, unsigned long*) + 4616
frame #8: 0x0000000101115208 dyld`dyldbootstrap::start(dyld3::MachOLoaded const*, int, char const**, dyld3::MachOLoaded const*, unsigned long*) + 396
frame #9: 0x0000000101115038 dyld`_dyld_start + 56
根据调用堆栈的调用也能轻松解释为什么 C/C++ initializers为什么会晚于+load 函数,在调用 ImageLoaderMachO::doInitialization 之前 +load 函数的调用就已经完成。这里重点看一下 doModInitFunctions(关键逻辑写了注释)
void ImageLoaderMachO::doModInitFunctions(const LinkContext& context)
{
if ( fHasInitializers ) {
const uint32_t cmd_count = ((macho_header*)fMachOData)->ncmds;
const struct load_command* const cmds = (struct load_command*)&fMachOData[sizeof(macho_header)];
const struct load_command* cmd = cmds;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < cmd_count; ++i) {
if ( cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT_COMMAND ) {
const struct macho_segment_command* seg = (struct macho_segment_command*)cmd;
const struct macho_section* const sectionsStart = (struct macho_section*)((char*)seg + sizeof(struct macho_segment_command));
const struct macho_section* const sectionsEnd = §ionsStart[seg->nsects];
for (const struct macho_section* sect=sectionsStart; sect < sectionsEnd; ++sect) {
const uint8_t type = sect->flags & SECTION_TYPE;
// 获取 section
if ( type == S_MOD_INIT_FUNC_POINTERS ) {
Initializer* inits = (Initializer*)(sect->addr + fSlide);
const size_t count = sect->size / sizeof(uintptr_t);
for (size_t i=0; i < count; ++i) {
// 获取函数指针
Initializer func = inits[i];
// <rdar://problem/8543820&9228031> verify initializers are in image
if ( ! this->containsAddress((void*)func) ) {
dyld::throwf("initializer function %p not in mapped image for %s\n", func, this->getPath());
}
if ( context.verboseInit )
dyld::log("dyld: calling initializer function %p in %s\n", func, this->getPath());
// 调用
func(context.argc, context.argv, context.envp, context.apple, &context.programVars);
}
}
}
}
cmd = (const struct load_command*)(((char*)cmd)+cmd->cmdsize);
}
}
}
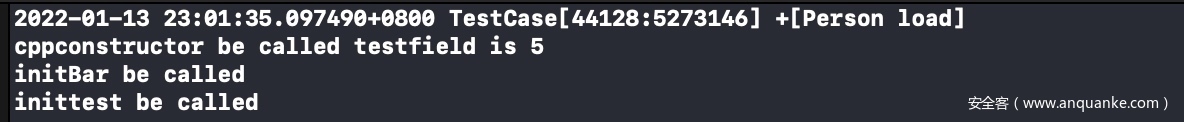
与前文提到的类似,根据代码可知C/C++ 的 Initializer 函数也是通过遍历 section 获取再调用,当然 section 不同,此处是 __mod_init_func。Demo 二进制也很清楚
其他因为C++ initializers 产生自动执行的情况(一些变形,本文重点关注代码的执行忽略变量的赋值
全局变量的初始化如果涉及以下情况,则会在 __mod_init_func 中产生对应的条目:
- 需要执行C函数
bool initBar(){ int i = 0; ++i; return i == 1; } static bool globalBar = initBar(); bool globalBar2 = initBar(); - 需要执行C++类的构造函数
class FooObject{ public: FooObject(){ // do somthing NSLog(@"in fooobject"); } }; static FooObject globalObj = FooObject(); FooObject globalObj2 = FooObject(); - 其他姿势
这一部分参考了 https://everettjf.github.io/2017/02/06/a-method-of-hook-static-initializers/ 在此表示感谢
加入上述情况的demo代码变为:
bool initBar(){
int i = 0;
printf("%s be called \n",__FUNCTION__);
return ++i;
}
class inittest{
__attribute__((constructor)) void cppconstructor(void) {
printf("%s be called testfield is %d \n",__FUNCTION__,testfield);
};
public:
int static testfield ;
static bool globalBar;
inittest(){
// do somthing
printf("%s be called \n",__FUNCTION__);
}
};
int inittest::testfield = 5;
bool inittest::globalBar = initBar();
static inittest i = inittest();
执行新的 Demo:
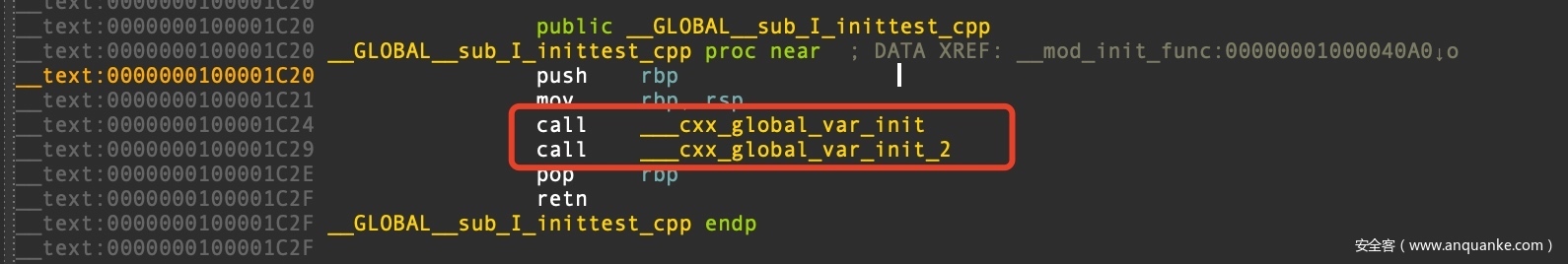
二进制分析,这里其实也并不是把新增的两个函数直接加入到 __mod_init_func section 中,而是加入一个函数
新增的函数又 call 相应的初始化函数(实体机当然就是bl了
___cxx_global_var_init
___cxx_global_var_init_2
对应了两个全局变量赋值所调用的函数
动态分析优先被调用的初始化函数
除了刚刚提到的静态分析,还需要必要的动态调试,这部分主要说一下如何动态调试。
根据 Mach-O section 可以获取到相对地址,那么还需要获取ASLR的偏移,回到源码(关键逻辑写了注释):
uintptr_t start(const dyld3::MachOLoaded* appsMachHeader, int argc, const char* argv[],
const dyld3::MachOLoaded* dyldsMachHeader, uintptr_t* startGlue)
{
...
_subsystem_init(apple);
// now that we are done bootstrapping dyld, call dyld's main
// 这里根据函数名即可判断是获取 ASLR 的 slide值的函数,在此处下断即可
uintptr_t appsSlide = appsMachHeader->getSlide();
return dyld::_main((macho_header*)appsMachHeader, appsSlide, argc, argv, envp, apple, startGlue);
}
验证一下:
# debugserver -x backboard 127.0.0.1:port /var/containers/Bundle/Application/xxx/yyy.app/yyy
默认断点位置:
(lldb) connect port
Process 4987 stopped
* thread #1, stop reason = signal SIGSTOP
frame #0: 0x0000000104f29000 dyld`_dyld_start
dyld`_dyld_start:
-> 0x104f29000: 0x910003fc mov x28, sp
0x104f29004: 0x927cef9f and sp, x28, #0xfffffffffffffff0
0x104f29008: 0xd2800000 mov x0, #0x0
0x104f2900c: 0xd2800001 mov x1, #0x0
0x104f29010: 0xa9bf03e1 stp x1, x0, [sp, #-0x10]!
0x104f29014: 0x910003fd mov x29, sp
0x104f29018: 0xd10043ff sub sp, sp, #0x10 ; =0x10
0x104f2901c: 0xf9400380 ldr x0, [x28]
0x104f29020: 0xf9400781 ldr x1, [x28, #0x8]
0x104f29024: 0x91004382 add x2, x28, #0x10 ; =0x10
0x104f29028: 0xf0ffffe3 adrp x3, -1
0x104f2902c: 0x91000063 add x3, x3, #0x0 ; =0x0
0x104f29030: 0x910003e4 mov x4, sp
;这里
0x104f29034: 0x94000012 bl 0x104f2907c ; dyldbootstrap::start(dyld3::MachOLoaded const*, int, char const**, dyld3::MachOLoaded const*, unsigned long*)
0x104f29038: 0xaa0003f0 mov x16, x0
0x104f2903c: 0xf94003e1 ldr x1, [sp]
0x104f29040: 0xf100003f cmp x1, #0x0 ; =0x0
0x104f29044: 0x54000061 b.ne 0x104f29050 ; <+80>
0x104f29048: 0x9100239f add sp, x28, #0x8 ; =0x8
0x104f2904c: 0xd61f0200 br x16
直接在0x104f29034 下断后si,dis -a $pc后即可查看当前函数的汇编,其实这部分是有符号的
0x104f291c0 <+324>: bl 0x104f47264 ; Diagnostics::~Diagnostics()
0x104f291c4 <+328>: add w8, w22, #0x1 ; =0x1
0x104f291c8 <+332>: add x23, x20, w8, sxtw #3
0x104f291cc <+336>: mov x24, x23
0x104f291d0 <+340>: ldr x8, [x24], #0x8
0x104f291d4 <+344>: cbnz x8, 0x104f291d0 ; <+340>
0x104f291d8 <+348>: mov x0, x24
0x104f291dc <+352>: bl 0x104f36560 ; __guard_setup
0x104f291e0 <+356>: mov x0, x21
;这里
0x104f291e4 <+360>: bl 0x104f4a0f4 ; dyld3::MachOLoaded::getSlide() const
0x104f291e8 <+364>: mov x1, x0
0x104f291ec <+368>: mov x2, x22
0x104f291f0 <+372>: mov x0, x21
0x104f291f4 <+376>: mov x3, x20
0x104f291f8 <+380>: mov x4, x23
0x104f291fc <+384>: mov x5, x24
0x104f29200 <+388>: mov x6, x19
0x104f29204 <+392>: bl 0x104f2dbac ; dyld::_main(macho_header const*, unsigned long, int, char const**, char const**, char const**, unsigned long*)
0x104f29208 <+396>: ldp x29, x30, [sp, #0xe0]
0x104f2920c <+400>: ldp x20, x19, [sp, #0xd0]
0x104f29210 <+404>: ldp x22, x21, [sp, #0xc0]
0x104f29214 <+408>: ldp x24, x23, [sp, #0xb0]
0x104f29218 <+412>: ldp x26, x25, [sp, #0xa0]
0x104f2921c <+416>: add sp, sp, #0xf0 ; =0xf0
0x104f29220 <+420>: ret
根据符号所以直接在0x104f291e4下断即可,获取返回值
(lldb) re r $x0
x0 = 0x0000000004cc0000
(lldb) br s -a 0x0000000004cc0000+0x100005778
0x100005778 是静态反编译获取 +load 函数的偏移地址
c 以后即可成功下断
(lldb) c
Process 4987 resuming
Process 4987 stopped
* thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = breakpoint 3.1
frame #0: 0x0000000104cc5778 TestCase`+[Person load](self=0x0000000104f942a8, _cmd=<no value available>) at Person.m:13
10 #import "Person.h"
11
12 @implementation Person
-> 13 +(void)load
14 {
15 NSLog(@"%s dics is ",__FUNCTION__);
16 }
Target 0: (TestCase) stopped.
(lldb) dis -a $pc
TestCase`+[Person load]:
-> 0x104cc5778 <+0>: sub sp, sp, #0x30 ; =0x30
0x104cc577c <+4>: stp x29, x30, [sp, #0x20]
0x104cc5780 <+8>: add x29, sp, #0x20 ; =0x20
0x104cc5784 <+12>: stur x0, [x29, #-0x8]
0x104cc5788 <+16>: str x1, [sp, #0x10]
至此,动静态分析就都可以实现了。