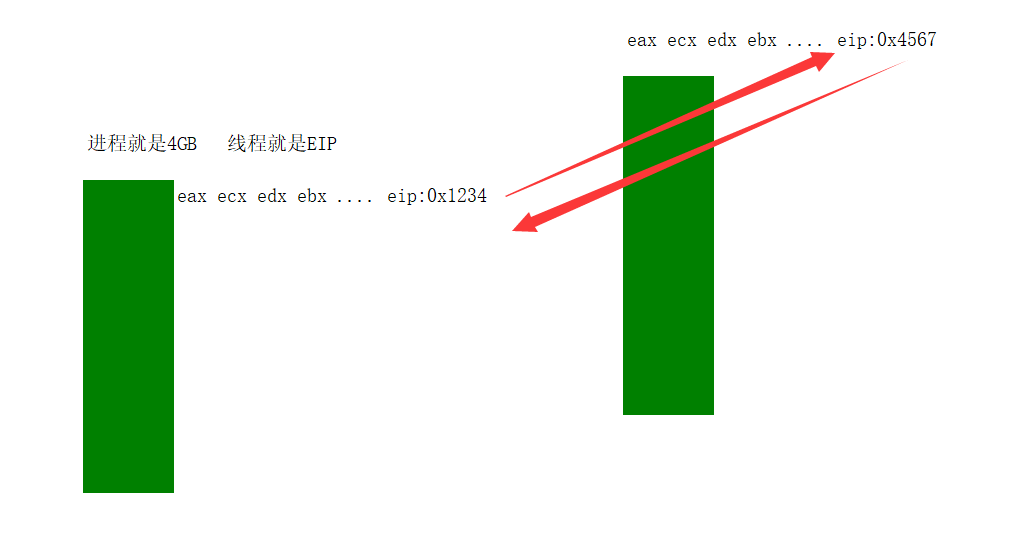前言
在上一节里面我们实现了进程的遍历以及初步了解了线程,在这一节里面我们继续来对线程控制来进行探究。
线程控制
我们首先来看两个api
SuspendThread
用来挂起线程,如果函数成功, 传回线程目前的挂起次数。如果失败, 则传回0xFFFFFFFF
case IDC_BUTTON2:
{
::SuspendThread(hThread);
return TRUE;
}
ResumeThread
用来恢复线程,如果函数成功, 则传回线程的前一个挂起次数。如果失败, 则传回0xFFFFFFFF。这个函数允许调用端指定一个线程睡眠(挂起)。直到又有人调用了ResumeThread(), 线程才会醒来。因此,睡眠中的线程不可能唤醒自己。
case IDC_BUTTON3:
{
::ResumeThread(hThread);
return TRUE;
}
这里我们编写一个win32程序并设置两个按钮,一个按钮为挂起线程,另一个按钮为恢复线程进行测试,实现代码如下
// thread CONTEXT.cpp : Defines the entry point for the application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
HWND hEdit;
HANDLE hThread;
DWORD WINAPI ThreadProc1(LPVOID lpParameter)
{
TCHAR szBuffer[10];
DWORD dwIndex = 0;
DWORD dwCount;
while(dwIndex<1000)
{
GetWindowText(hEdit,szBuffer,10);
sscanf( szBuffer, "%d", &dwCount );
dwCount++;
Sleep(200);
memset(szBuffer,0,10);
sprintf(szBuffer,"%d",dwCount);
SetWindowText(hEdit,szBuffer);
dwIndex++;
}
return 0;
}
BOOL CALLBACK MainDlgProc(HWND hDlg,UINT uMsg,WPARAM wParam,LPARAM lParam)
{
BOOL bRet = FALSE;
switch(uMsg)
{
case WM_CLOSE:
{
EndDialog(hDlg,0);
break;
}
case WM_INITDIALOG:
{
hEdit = GetDlgItem(hDlg,IDC_EDIT);
SetWindowText(hEdit,"0");
break;
}
case WM_COMMAND:
switch (LOWORD (wParam))
{
case IDC_BUTTON1:
{
//创建线程
hThread = ::CreateThread(NULL, 0, ThreadProc1, NULL, 0, NULL);
return TRUE;
}
case IDC_BUTTON2:
{
//挂起线程
::SuspendThread(hThread);
return TRUE;
}
case IDC_BUTTON3:
{
//恢复线程
::ResumeThread(hThread);
return TRUE;
}
}
break ;
}
return bRet;
}
int APIENTRY WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance,
HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
LPSTR lpCmdLine,
int nCmdShow)
{
// TODO: Place code here.
DialogBox(hInstance,MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_DIALOG_MAIN),NULL,MainDlgProc);
return 0;
}
演示效果如下
终止线程
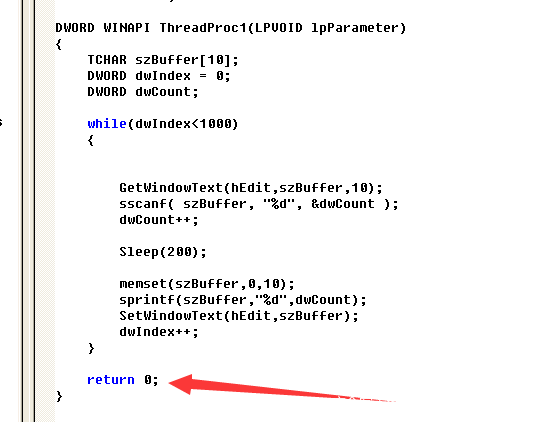
我们知道在线程结束的时候是有一个返回值的,在正常结束线程的情况下,返回值为0
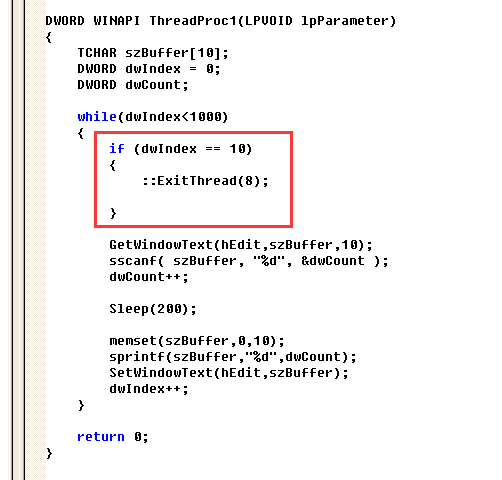
那在这里我们加一段代码,这里为终止线程的第一种方法,使用到ExitThread这个api,这种方法终止线程的同时会清理堆栈
ExitThread
void ExitThread(
[in] DWORD dwExitCode
);
::ExitThread(DWORD dwExitCode);
这里相当于如果手动中止线程的话就会返回8
同步调用&异步调用
同步调用的通俗理解就是比如有三个程序要执行,必须第一个程序被触发,执行结束了之后,才轮到其他程序执行
异步调用则是所有程序的执行不需要同步,可以多个触发,互相独立的执行相应的指令
在同步调用中关闭线程之后会得到操作系统的返回值,在往下执行代码
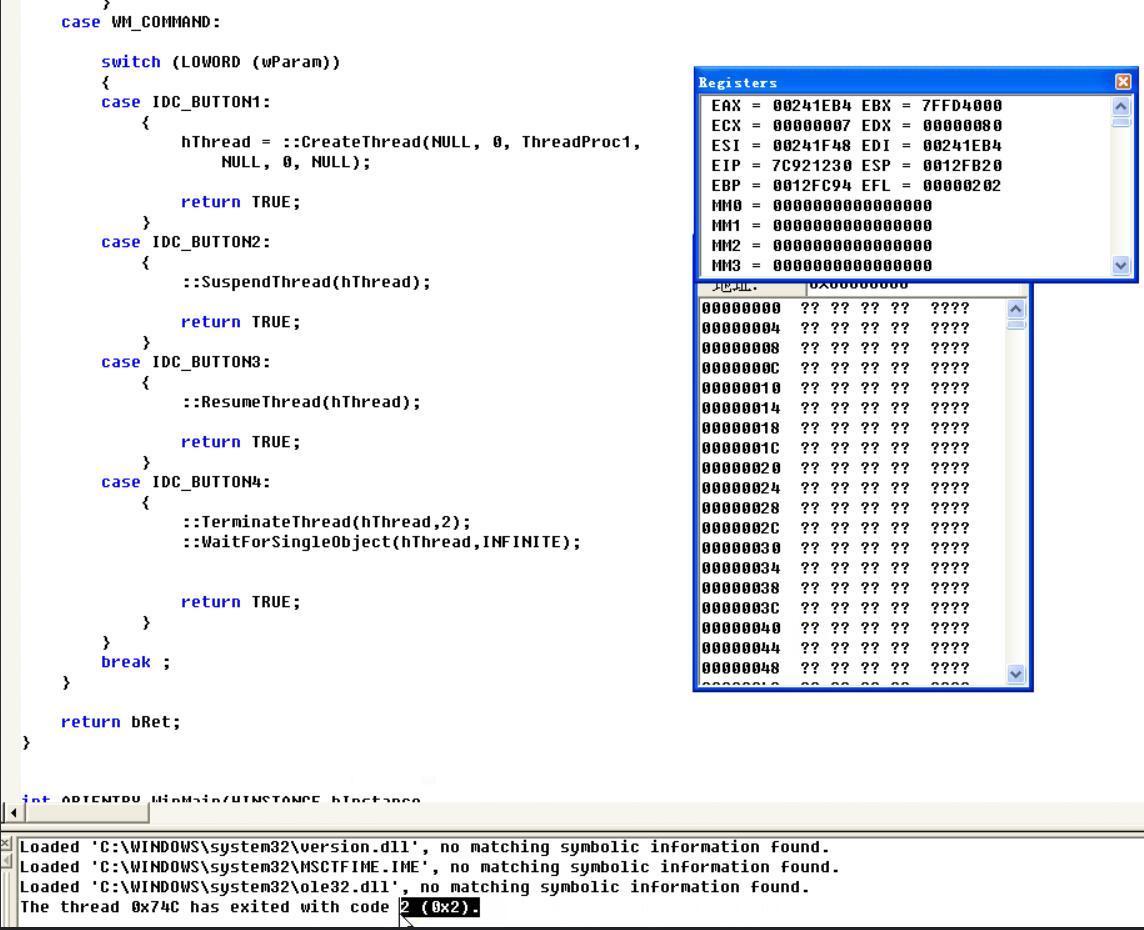
这里终止线程的第二种方法就是使用TerninateThread这个api,结构如下
TerninateThread
BOOL TerminateThread(
[in, out] HANDLE hThread,
[in] DWORD dwExitCode
);
在异步调用中如果光使用如下代码,在得到关闭线程指令后不会等待线程关闭的消息返回,而是直接往下执行
::TerminateThread(hThread,2);
所以这里就需要再加上一行等待的代码
::WaitForSingleObject(hThread,INFINITE);
这里使用的异步调用是不清理堆栈的
CONTEXT结构
每个线程在执行的时候,都会独自占用一个CPU,当系统中的线程数量 > CPU的数量时,就会存在多个线程共用一个CPU的情况。但CPU每次只能运行一个线程,Windows每隔20毫秒会进行线程的切换,那比如线程A执行到地址:0x2345678 eax:1 ecx:2 edx:3 ebx:4…还有eflag标志寄存器中的值等等
此时,线程执行时间到了,被切换到了线程B。当线程B的时间片也到了,再切换会线程A时,系统是如何知道该从哪个地址开始执行呢?被切换前用到的各种寄存器的值该如何恢复呢?
这里在进行线程的切换的时候要对原线程中的寄存器的值进行保存,这时候就会用到CONTEXT这个结构体
CONTEXT的结构如下
CONTEXT:
该结构包含了特定处理器的寄存器数据。
typedef struct _CONTEXT {
//
// The flags values within this flag control the contents of
// a CONTEXT record.
//
// If the context record is used as an input parameter, then
// for each portion of the context record controlled by a flag
// whose value is set, it is assumed that that portion of the
// context record contains valid context. If the context record
// is being used to modify a threads context, then only that
// portion of the threads context will be modified.
//
// If the context record is used as an IN OUT parameter to capture
// the context of a thread, then only those portions of the thread's
// context corresponding to set flags will be returned.
//
// The context record is never used as an OUT only parameter.
//
DWORD ContextFlags;
//
// This section is specified/returned if CONTEXT_DEBUG_REGISTERS is
// set in ContextFlags. Note that CONTEXT_DEBUG_REGISTERS is NOT
// included in CONTEXT_FULL.
//
DWORD Dr0;
DWORD Dr1;
DWORD Dr2;
DWORD Dr3;
DWORD Dr6;
DWORD Dr7;
//
// This section is specified/returned if the
// ContextFlags word contians the flag CONTEXT_FLOATING_POINT.
//
FLOATING_SAVE_AREA FloatSave;
//
// This section is specified/returned if the
// ContextFlags word contians the flag CONTEXT_SEGMENTS.
//
DWORD SegGs;
DWORD SegFs;
DWORD SegEs;
DWORD SegDs;
//
// This section is specified/returned if the
// ContextFlags word contians the flag CONTEXT_INTEGER.
//
DWORD Edi;
DWORD Esi;
DWORD Ebx;
DWORD Edx;
DWORD Ecx;
DWORD Eax;
//
// This section is specified/returned if the
// ContextFlags word contians the flag CONTEXT_CONTROL.
//
DWORD Ebp;
DWORD Eip;
DWORD SegCs; // MUST BE SANITIZED
DWORD EFlags; // MUST BE SANITIZED
DWORD Esp;
DWORD SegSs;
//
// This section is specified/returned if the ContextFlags word
// contains the flag CONTEXT_EXTENDED_REGISTERS.
// The format and contexts are processor specific
//
BYTE ExtendedRegisters[MAXIMUM_SUPPORTED_EXTENSION];
} CONTEXT;
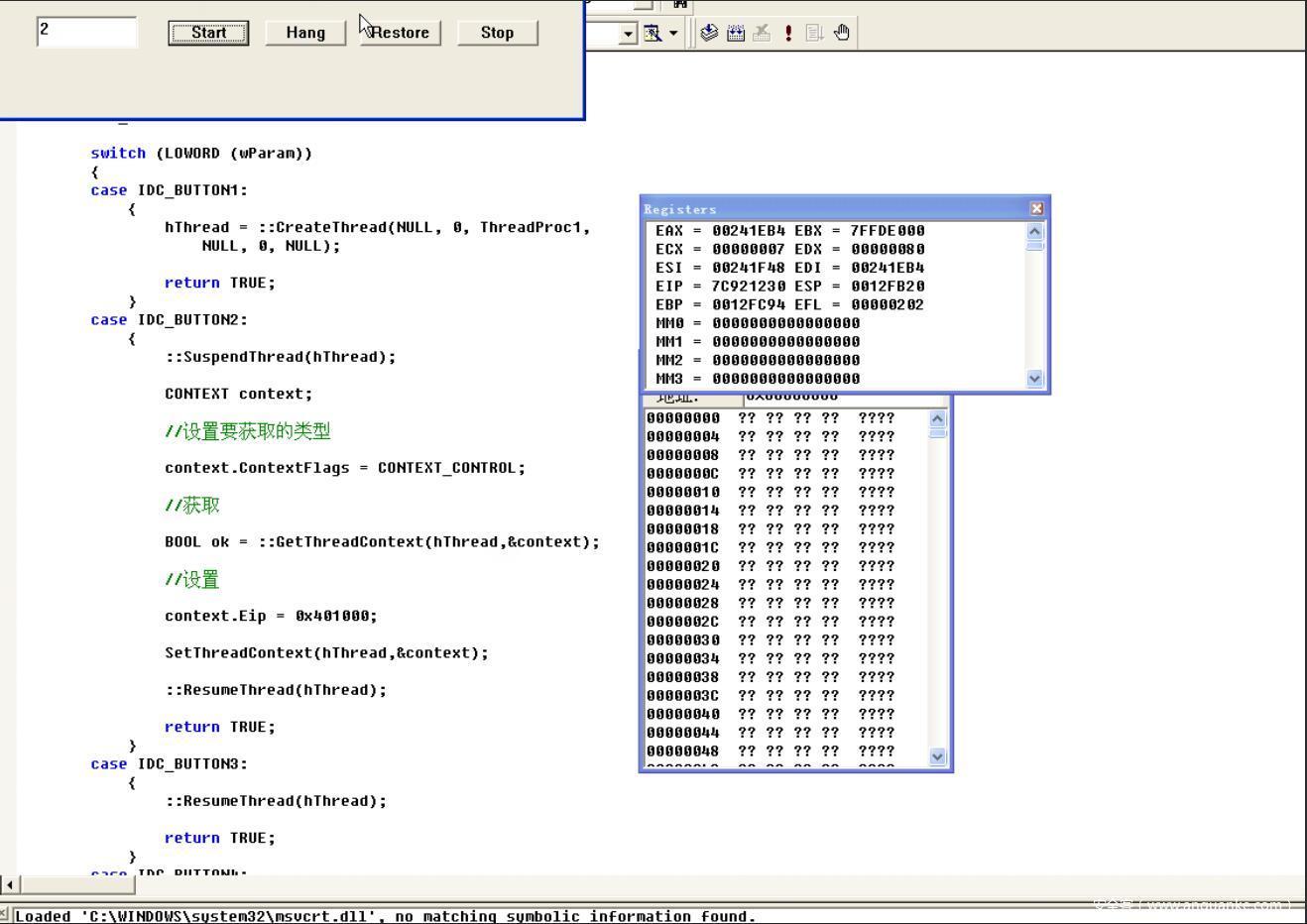
那么这里测试一下,代码如下
case IDC_BUTTON2:
{
::SuspendThread(hThread);
CONTEXT context;
//设置要获取的类型
context.ContextFlags = CONTEXT_CONTROL;
//获取
BOOL ok = ::GetThreadContext(hThread,&context);
//设置
context.Eip = 0x401000;
SetThreadContext(hThread,&context);
::ResumeThread(hThread);
return TRUE;
}
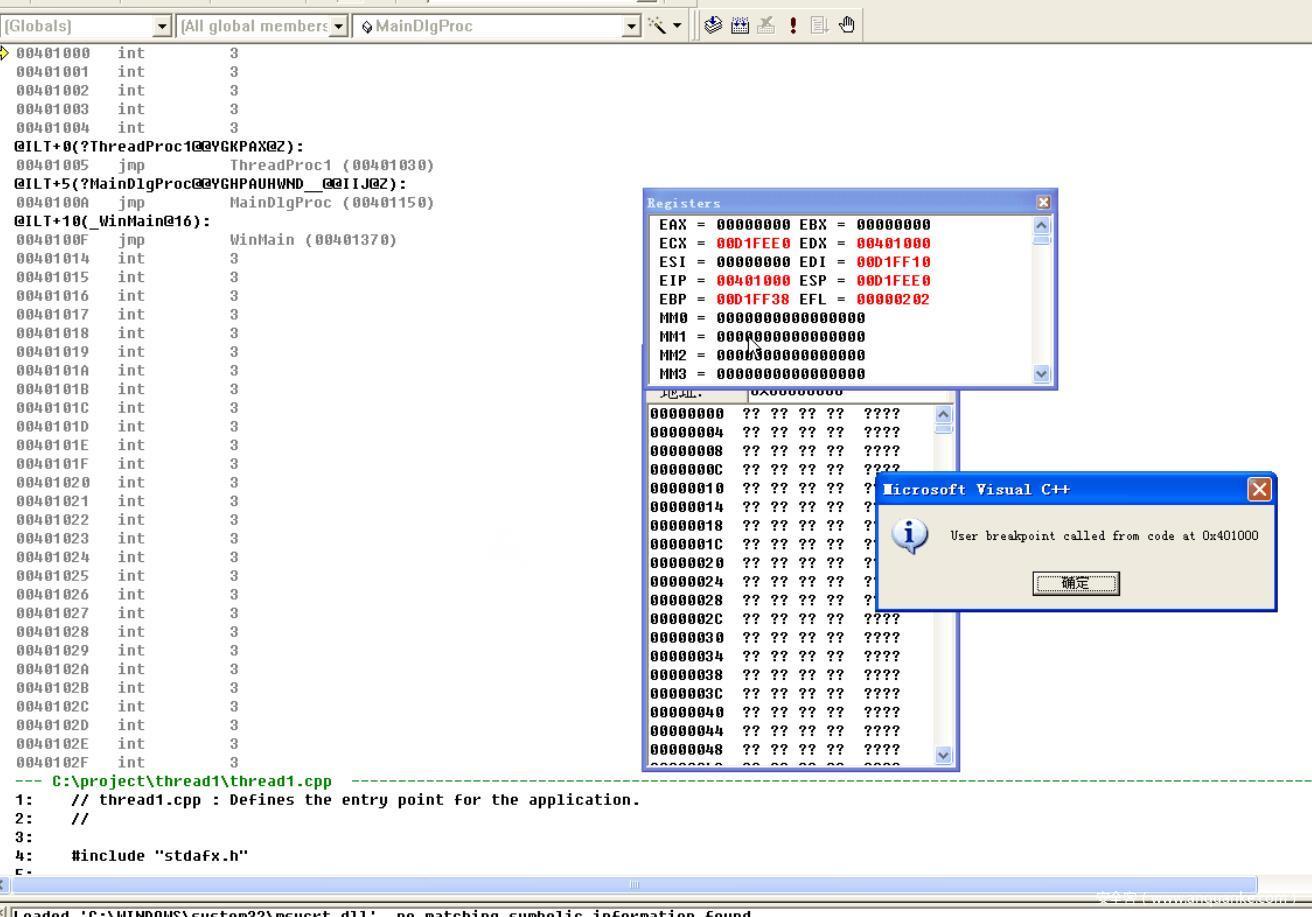
演示效果如下,这里因为eip的值是随便设置的所以挂掉了
GetExitCodeThread
用来判断判断线程是否结束,此函数调用成功返回TRUE,失败返回FALSE,只表示这个函数是否调用成功而己。不能根据返回值来判断一个线程是否结束,而要根据 lpExitCode的值来确定,lpExitCode为STILL_ACTIVE时表示线程正在运行。若线程己经结束,则lpExitCode中存储指定线程的返回值,结构如下
BOOL GetExitCodeThread(
HANDLE hThread,
LPDWORD lpExitCode
);
- hThread[in] Handle to the thread. Windows NT/2000/XP: The handle must have THREAD_QUERY_INFORMATION access. For more information, see Thread Security and Access Rights.
- lpExitCode[out] Pointer to a variable to receive the thread termination status.
其中返回值为一个指针,实现代码如下
case IDC_BUTTON5:
{
DWORD dwExitCode = 0;
::GetExitCodeThread(hThread, &dwExitCode);
OutputDebugStringF("The process ID is:%d",dwExitCode);
return TRUE;
}
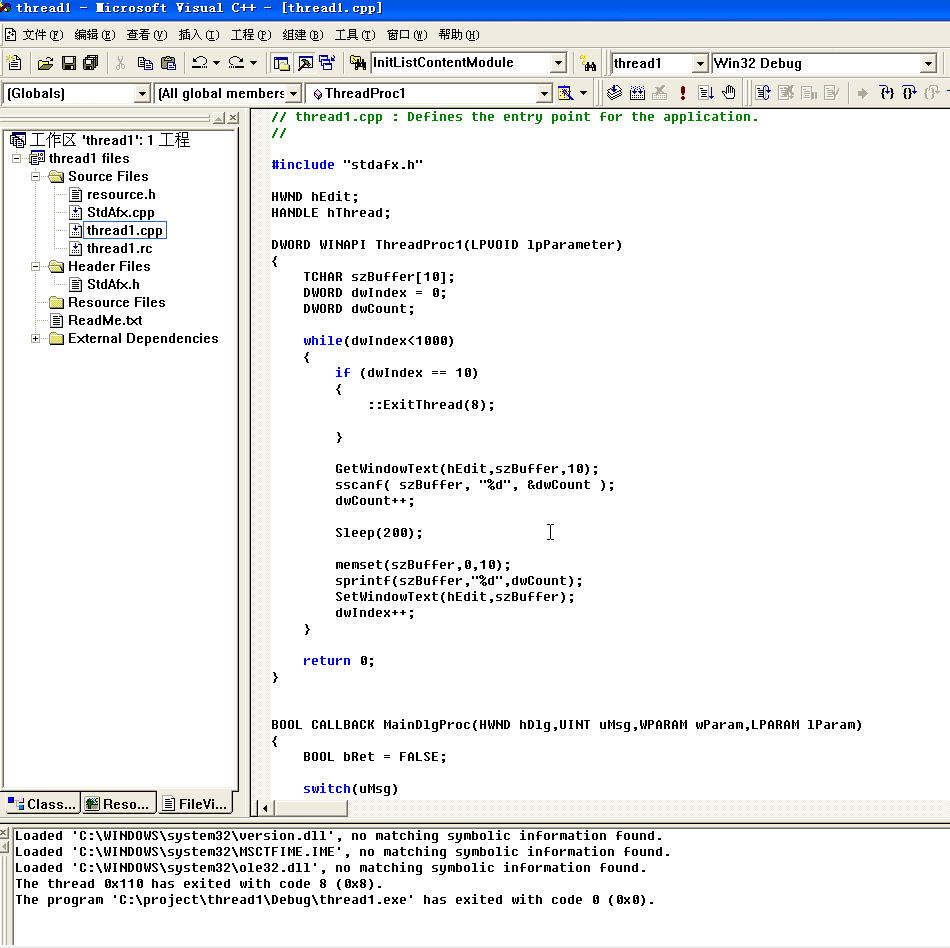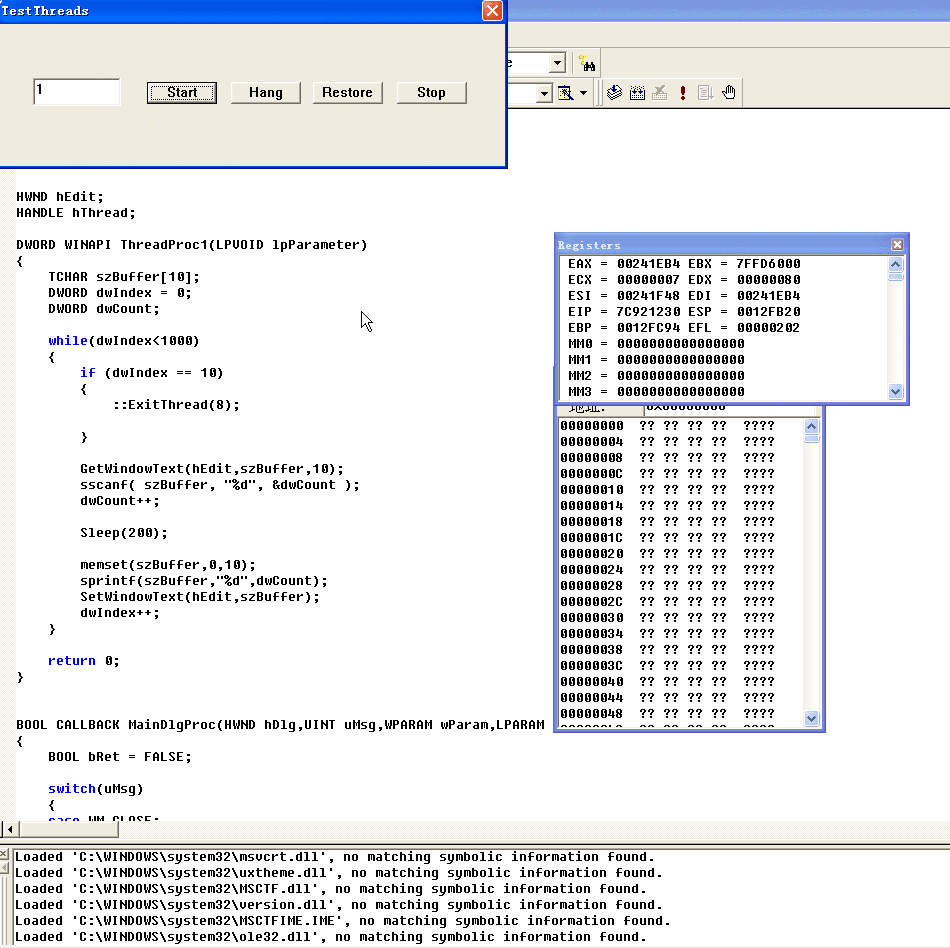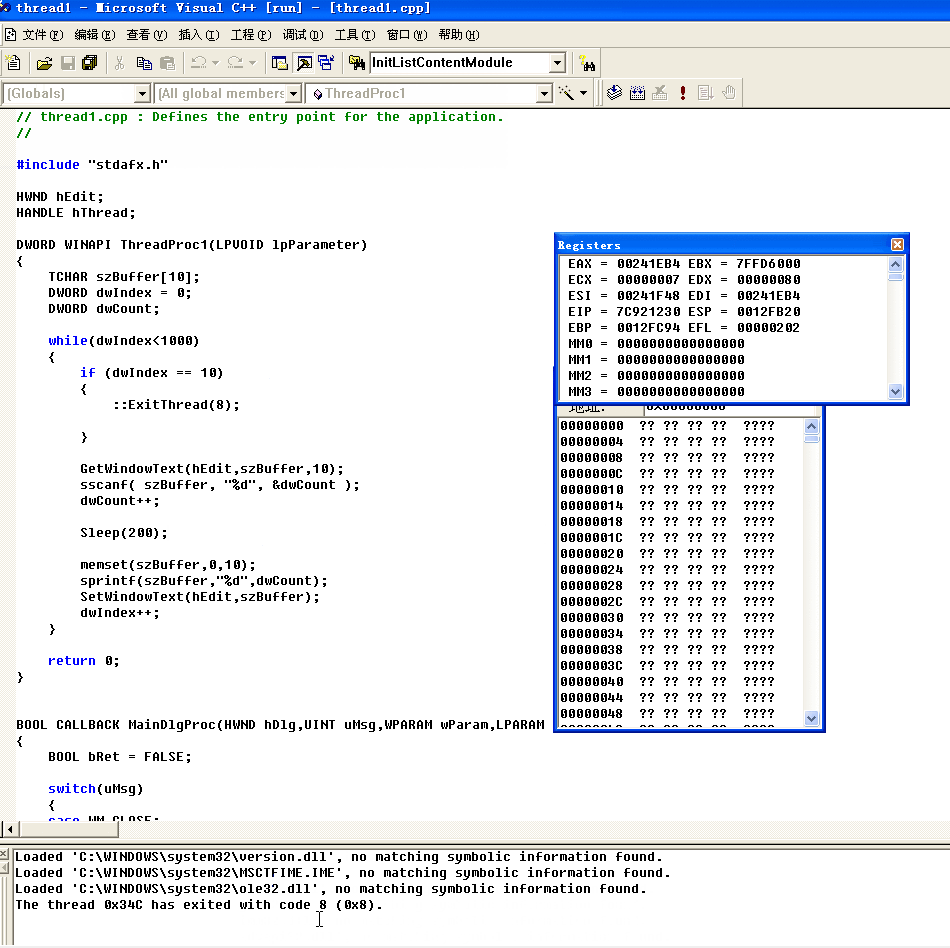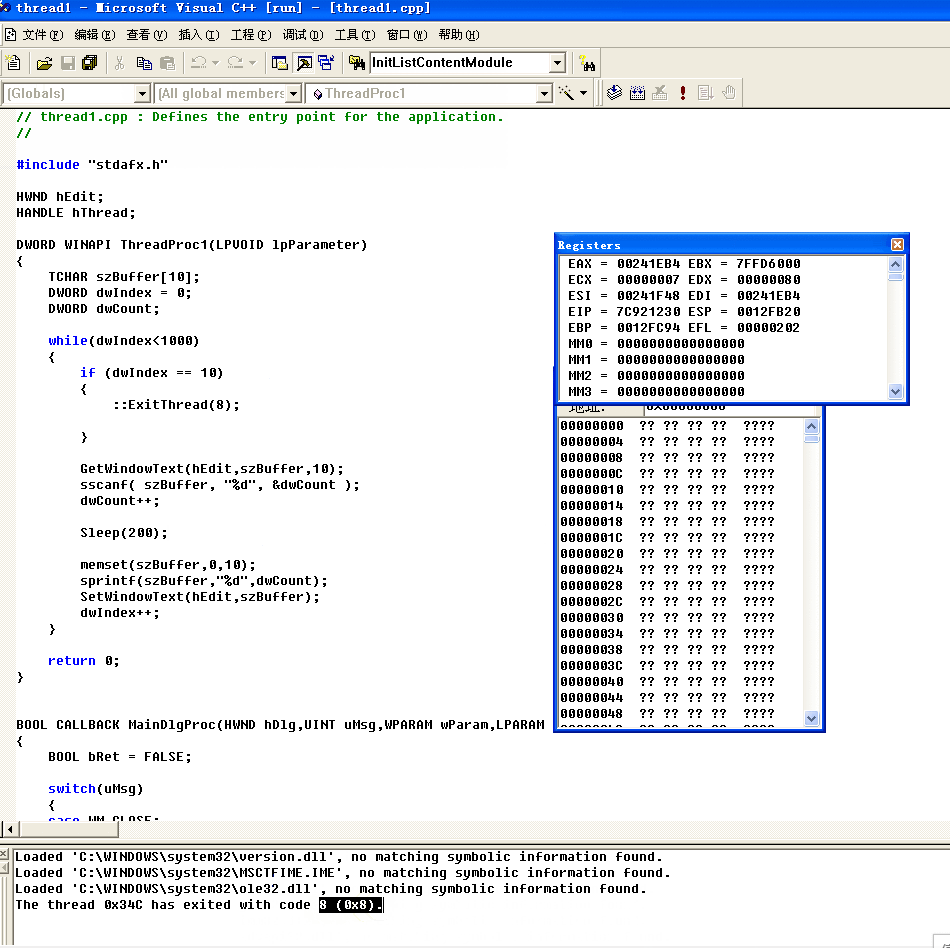
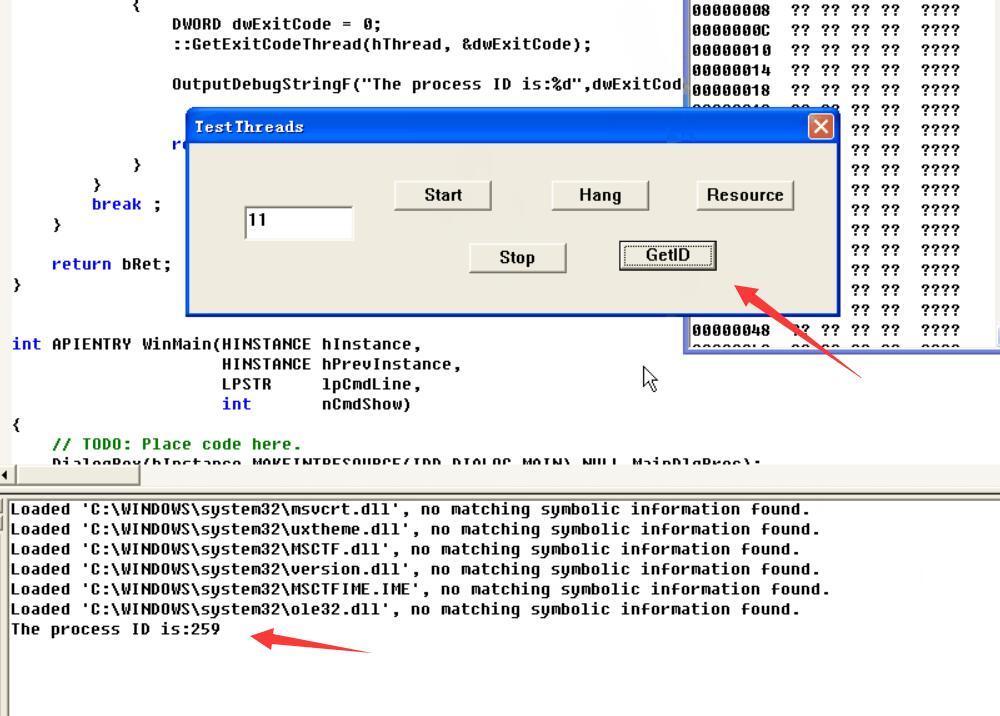
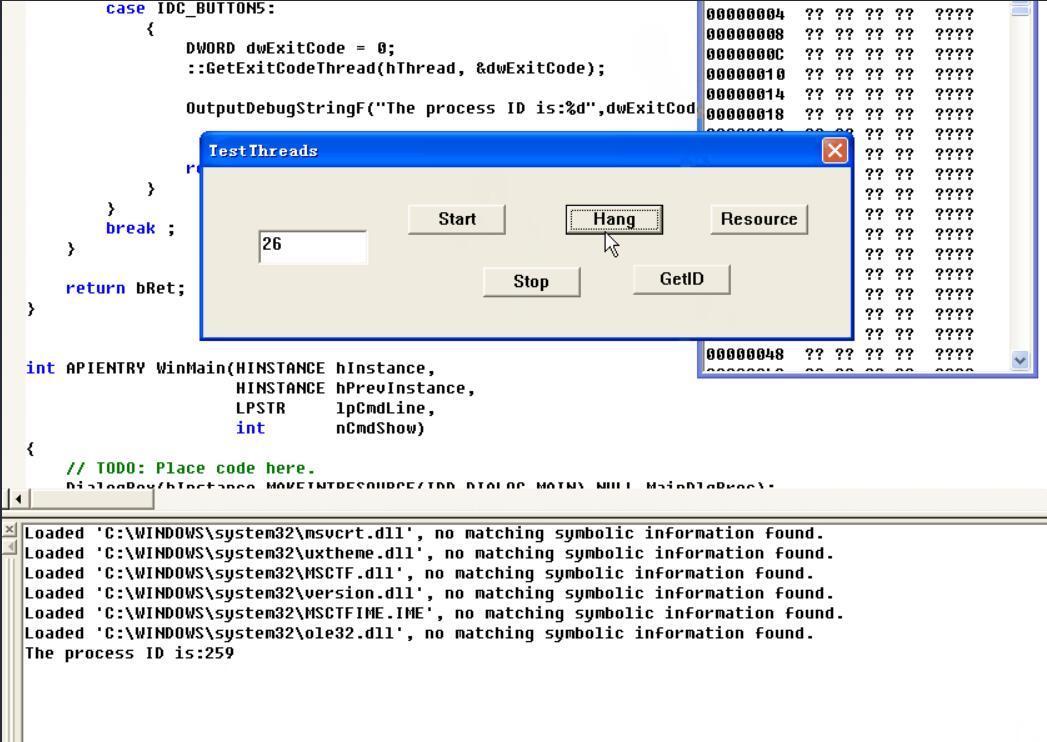
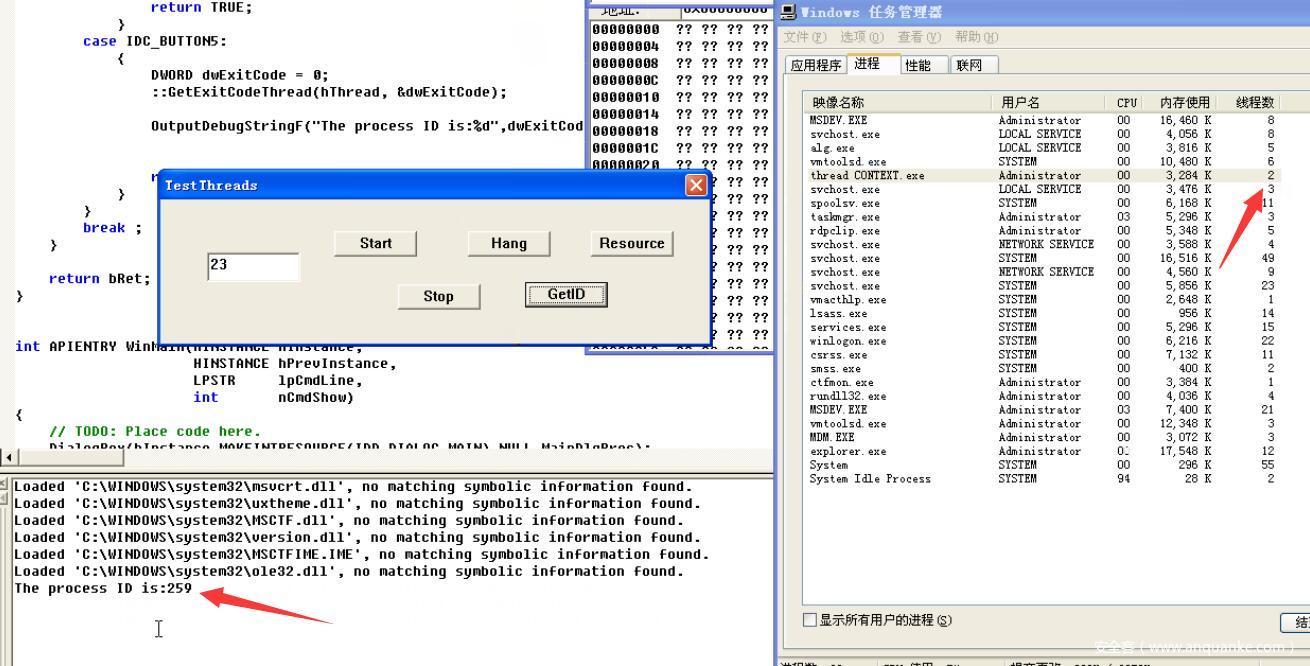
实现效果如下,这里的259就是16进制103,STILL_ACTIVE,证明线程还存在没有终止
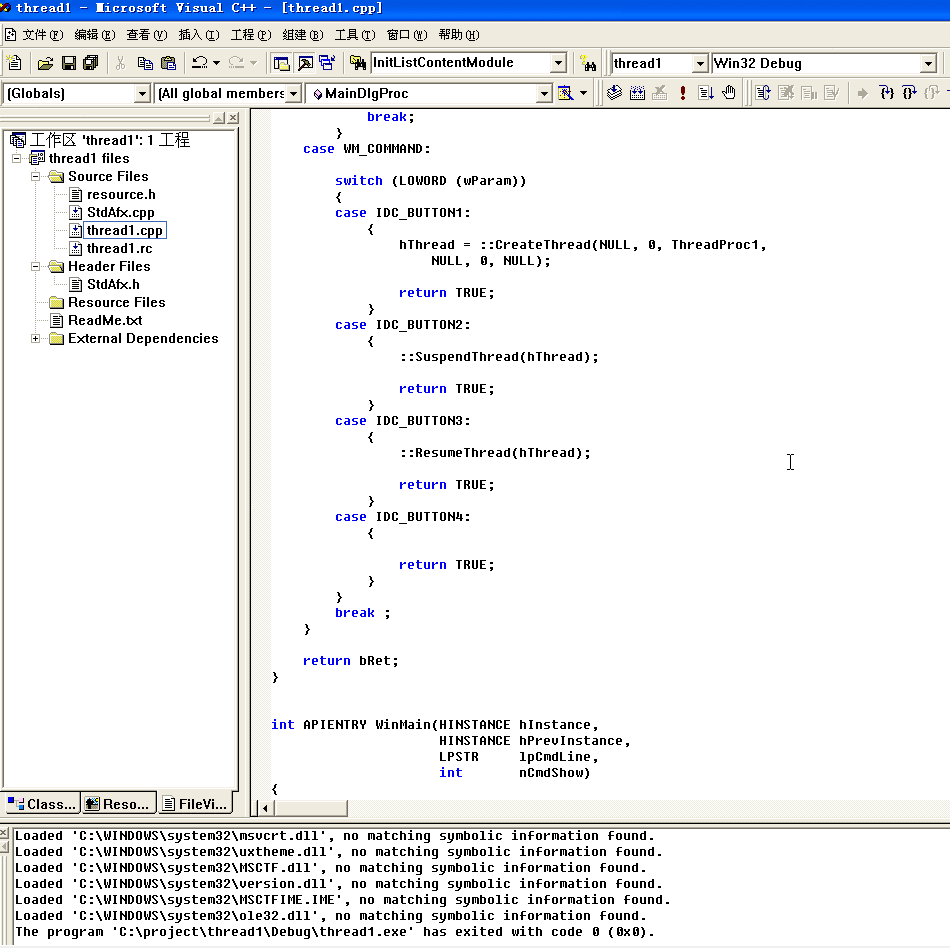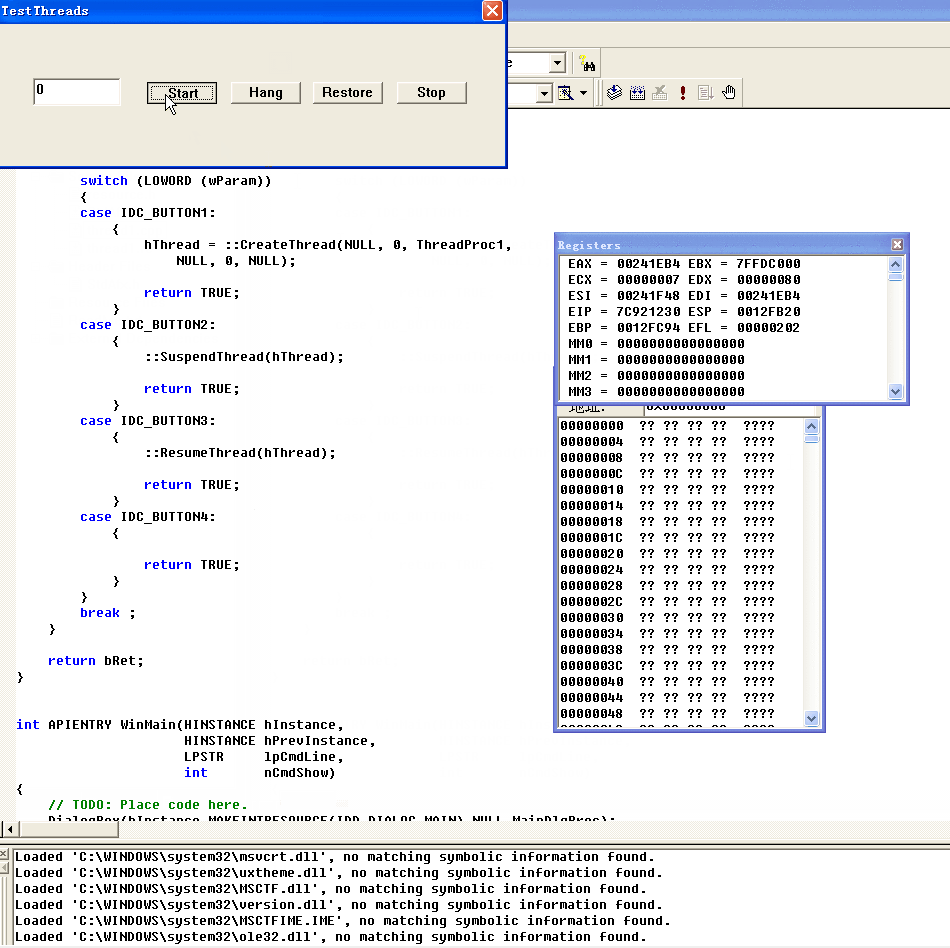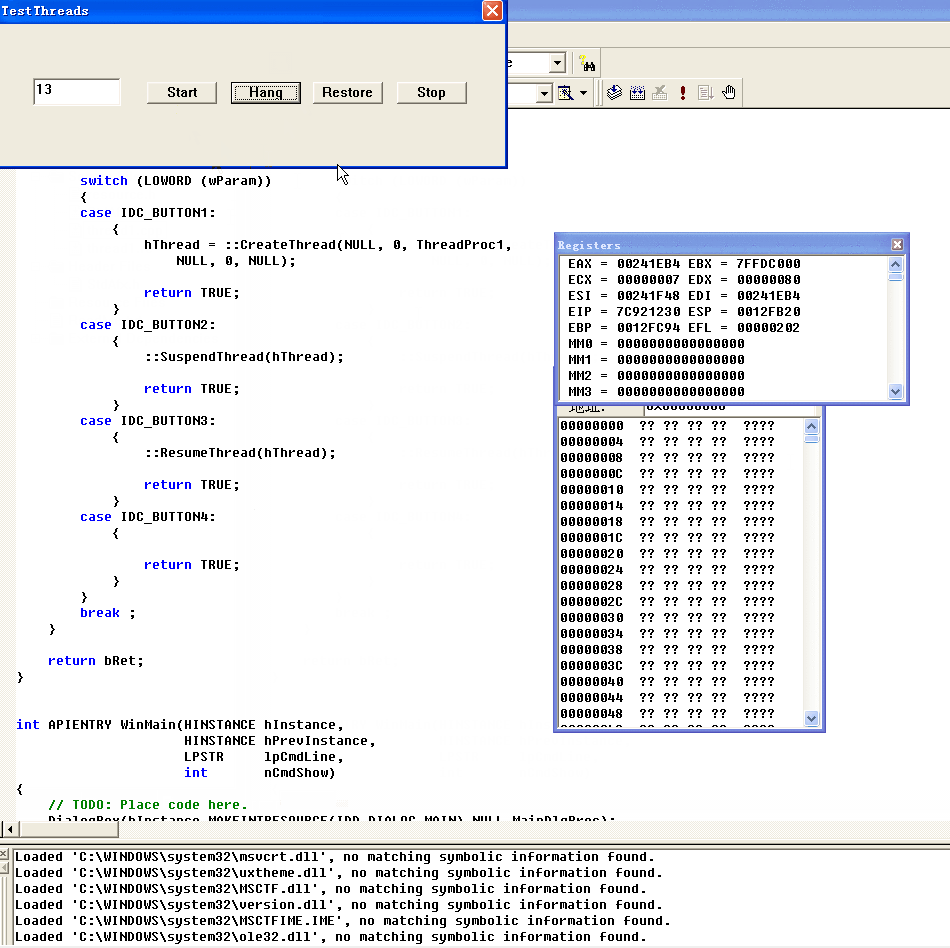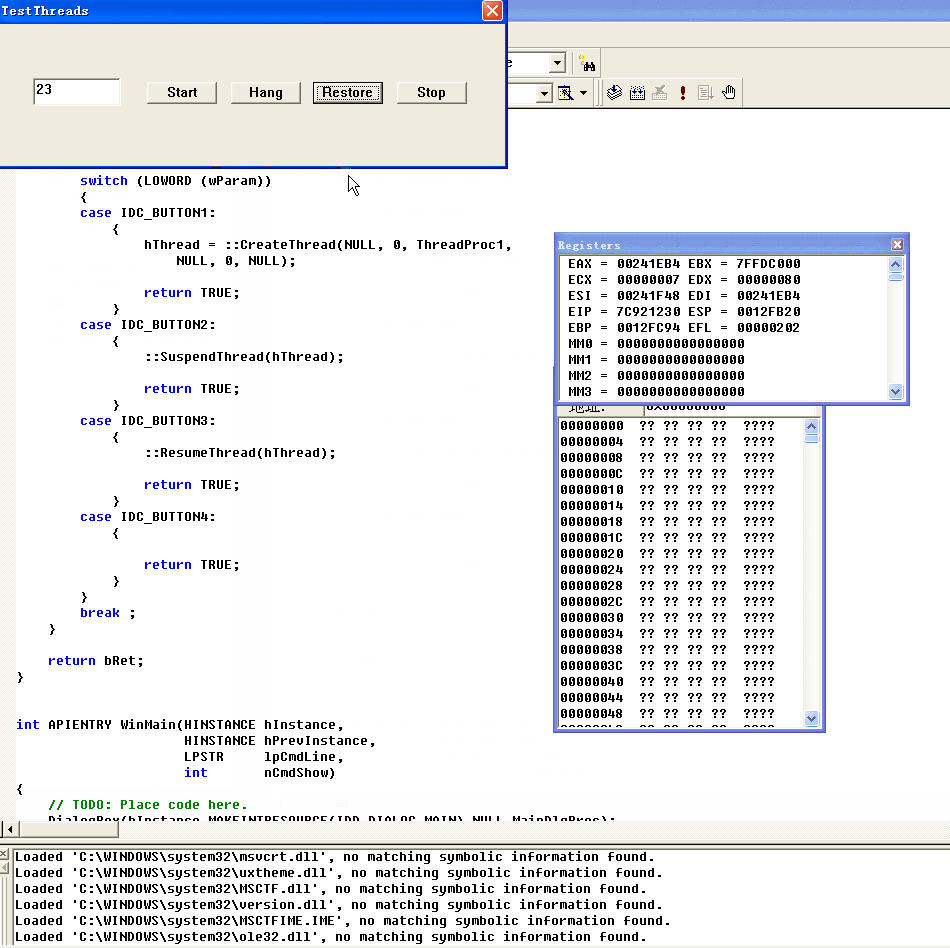
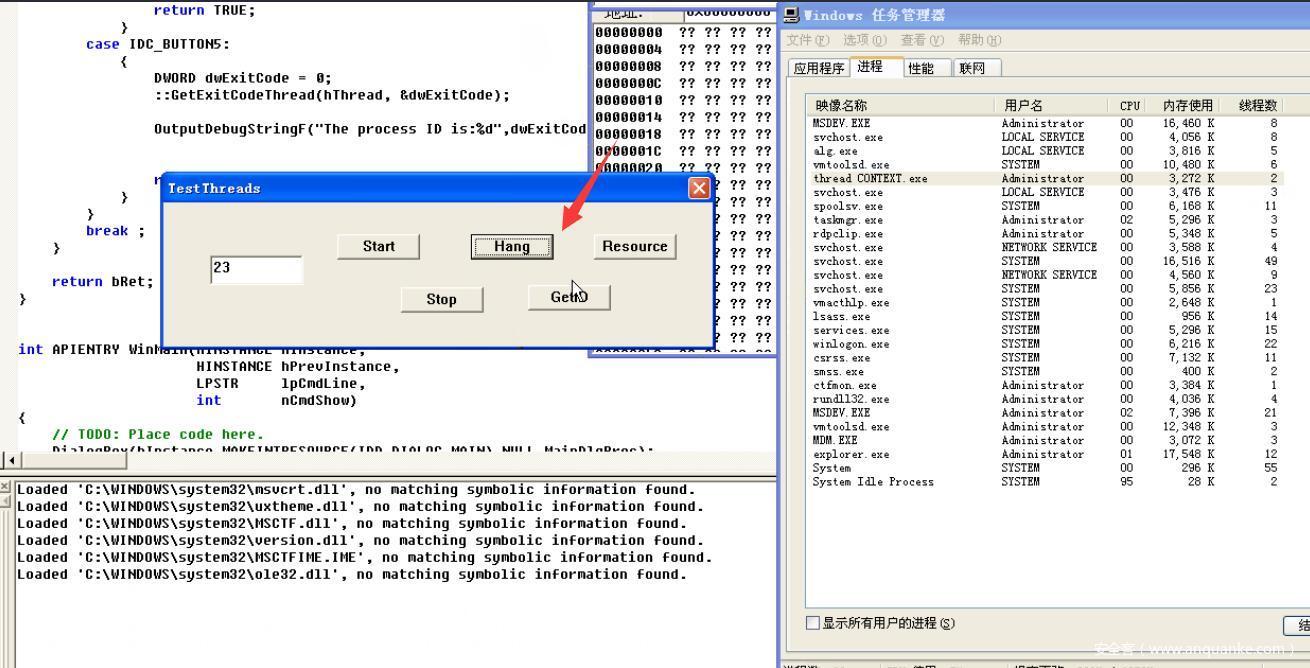
首先点击Start,然后GetID为259
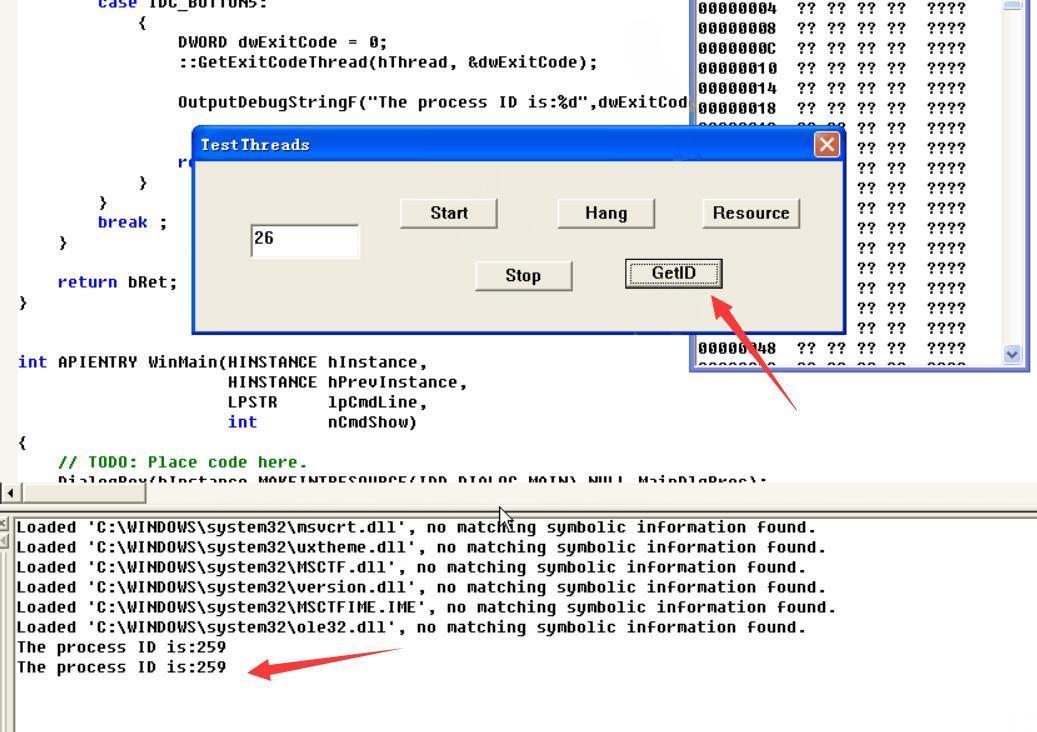
点击Hang即挂起,GetID还是259证明还是线程还是处于STILL_ACTIVE状态
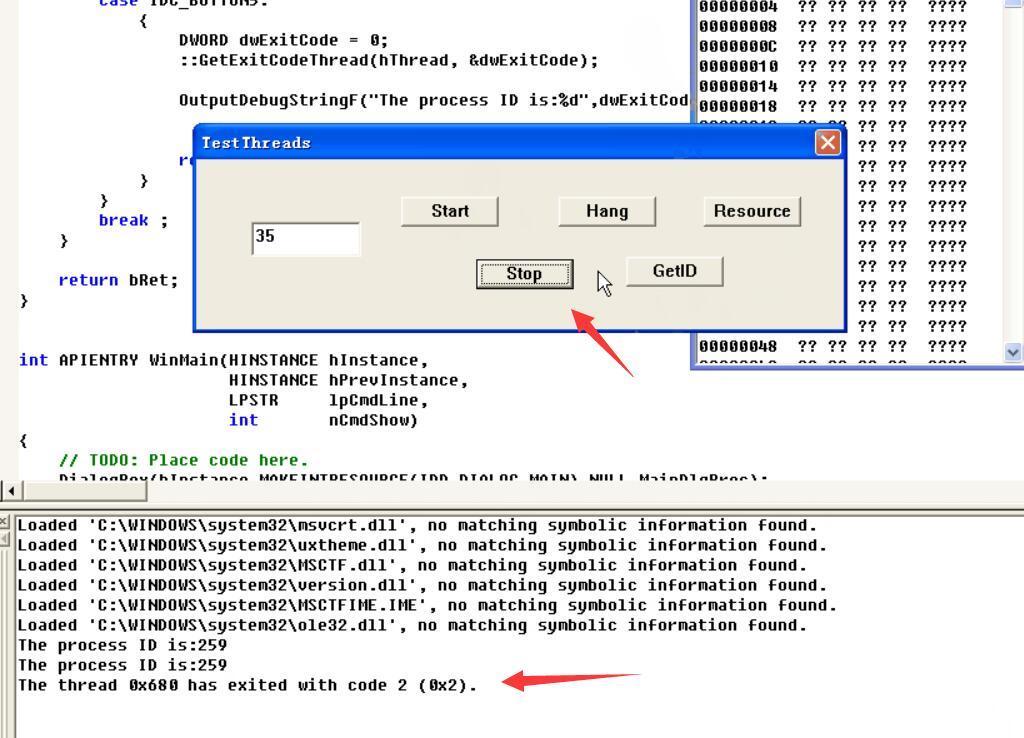
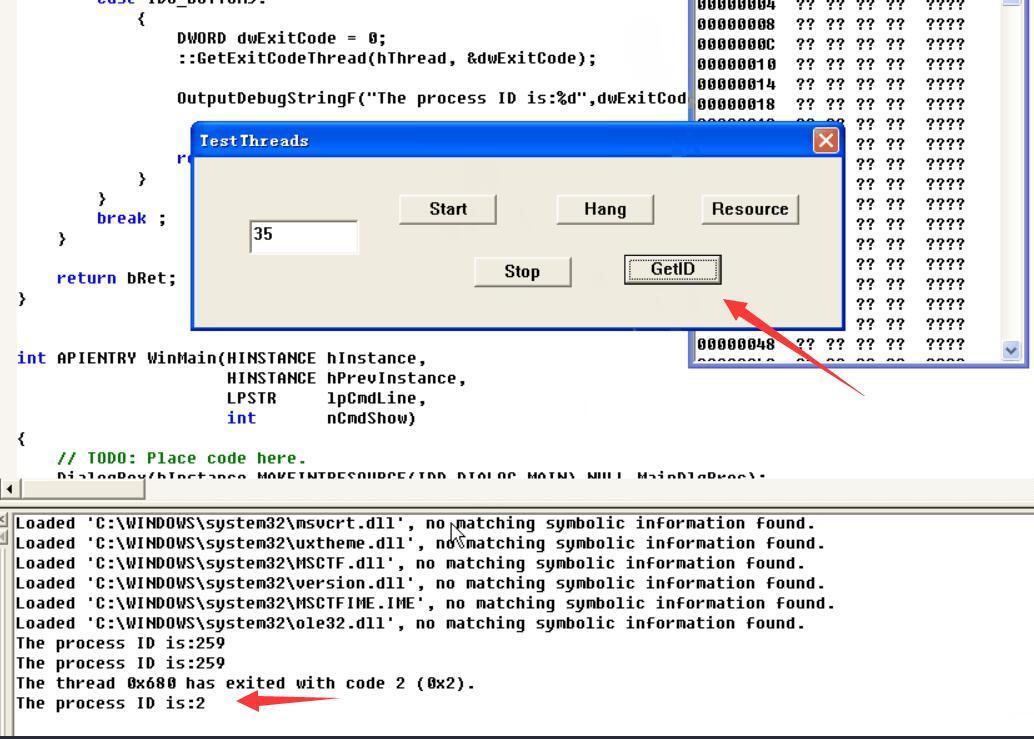
点击Stop即终止线程,GetID为2证明线程已经终止
这里再测试一下最终效果,代码如下
// thread CONTEXT.cpp : Defines the entry point for the application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
HWND hEdit;
HANDLE hThread;
DWORD WINAPI ThreadProc1(LPVOID lpParameter)
{
TCHAR szBuffer[10];
DWORD dwIndex = 0;
DWORD dwCount;
while(dwIndex<1000)
{
GetWindowText(hEdit,szBuffer,10);
sscanf( szBuffer, "%d", &dwCount );
dwCount++;
Sleep(200);
memset(szBuffer,0,10);
sprintf(szBuffer,"%d",dwCount);
SetWindowText(hEdit,szBuffer);
dwIndex++;
}
return 0;
}
BOOL CALLBACK MainDlgProc(HWND hDlg,UINT uMsg,WPARAM wParam,LPARAM lParam)
{
BOOL bRet = FALSE;
switch(uMsg)
{
case WM_CLOSE:
{
EndDialog(hDlg,0);
break;
}
case WM_INITDIALOG:
{
hEdit = GetDlgItem(hDlg,IDC_EDIT);
SetWindowText(hEdit,"0");
break;
}
case WM_COMMAND:
switch (LOWORD (wParam))
{
case IDC_BUTTON1:
{
//创建线程
hThread = ::CreateThread(NULL, 0, ThreadProc1, NULL, 0, NULL);
return TRUE;
}
case IDC_BUTTON2:
{
//挂起线程
::SuspendThread(hThread);
/*CONTEXT context;
//设置要获取的类型
context.ContextFlags = CONTEXT_CONTROL;
//获取
BOOL ok = ::GetThreadContext(hThread,&context);
//设置
context.Eip = 0x401000;
SetThreadContext(hThread,&context);
::ResumeThread(hThread);*/
return TRUE;
}
case IDC_BUTTON3:
{
//恢复线程
::ResumeThread(hThread);
return TRUE;
}
case IDC_BUTTON4:
{
::TerminateThread(hThread,2);
::WaitForSingleObject(hThread,INFINITE);
return TRUE;
}
case IDC_BUTTON5:
{
DWORD dwExitCode = 0;
::GetExitCodeThread(hThread, &dwExitCode);
OutputDebugStringF("The process ID is:%d",dwExitCode);
return TRUE;
}
}
break ;
}
return bRet;
}
int APIENTRY WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance,
HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
LPSTR lpCmdLine,
int nCmdShow)
{
// TODO: Place code here.
DialogBox(hInstance,MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_DIALOG_MAIN),NULL,MainDlgProc);
return 0;
}
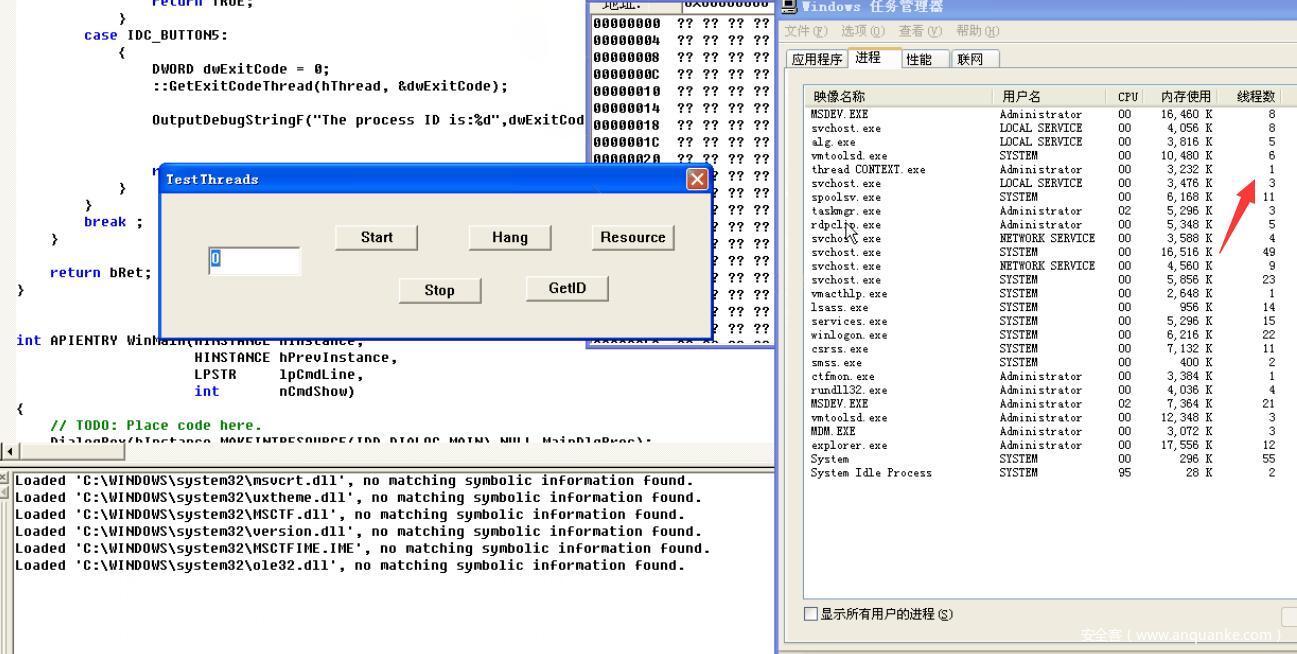
我们知道程序窗口是主线程,我们又自己创建了一个线程,观察线程返回ID和线程数的变化
首先我们启动程序,因为主程序启动了所以只有1个线程
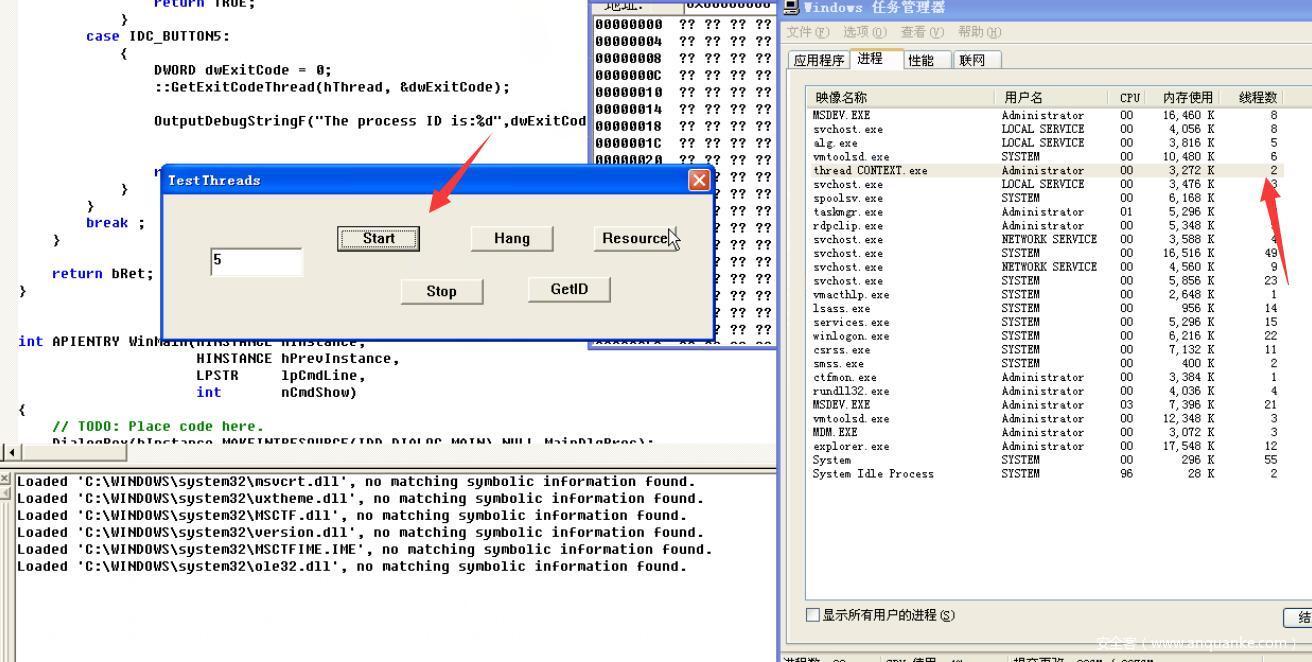
点击start之后,因为使用CreateThread又创建了一个线程,所以为两个线程
然后点击Hang即挂起,使用GetID查看为259,线程仍然存在,处于STILL_ACTIVE状态,任务管理器里面也可以看到线程仍然为2
点击Stop,使用GetID查看为2,证明线程已经终止,任务管理器里面的线程也变为了1