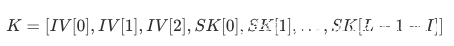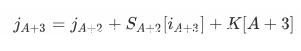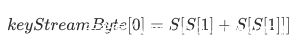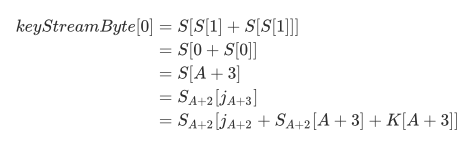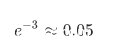简介
FMS attack是针对广泛使用的RC4流密码和WEP的攻击,本人将简单介绍一下该攻击。
RC4
RC4(Rivest Cipher 4)是一种流加密算法,密码长度可变,是有线等效加密(WEP)中采用的加密算法。其原理比较简单,包括密钥调度算法(KSA)和伪随机子密码生成算法(PRGA)两大部分:
KSA
RC4初始化的时候会先对state进行初始化,如下所示:
def __init__(self):
self.state = [i for i in range(256)]
self.i = 0
self.j = 0
然后将使用key来对state进行更新,每一步都会将两个状态的值互换:
def __swap_state(self, a, b):
self.state[a], self.state[b] = self.state[b], self.state[a]
def ksa(self, key):
j = 0
for i in range(256):
j = (j + self.state[i] + key[i % len(key)]) % 256
self.__swap_state(i, j)
PRGA
当要产生密钥流的时候,进行如下操作。在生成密钥流的同时,也会对状态进行实时的更新,以保证其安全性:
def prna(self):
self.i = (self.i + 1) % 256
self.j = (self.j + self.state[self.i]) % 256
self.__swap_state(self.i, self.j)
return self.state[(self.state[self.i] + self.state[self.j]) % 256]
FMS攻击
FMS(Fluhrer, Mantin and Shamir))attack是一种针对RC4的攻击,这种攻击方式在2001年的论文Weaknesses in the Key Scheduling Algorithm of RC4中被提到。该攻击利用RC4中的密钥调度算法(KSA)的弱点来从加密消息中重构出密钥。FMS攻击在一些网络工具(例如AirSnort、weplab和aircrack)中得到了普及应用,这些工具使用该攻击来恢复受WEP保护的无线网络的密钥。
攻击描述
在WEP中,不仅仅有用户所输入的key,同时也有设置好的iv(initialization vector),WEP会将它俩拼在一起作为RC4的密钥调度算法中所输入的key,即inputKey = iv + key,这样可以防止key复用所导致的一些问题,但是这也并不是安全的。
现在我们来重点关注密钥调度算法。我们将经过了t次迭代的state记为St,这时的index分别记为it和jt。同时我们设所使用的IV的长度为I(假设I = 3),用户所输入的key为SK,inputKey的长度为L,则inputKey(记为K)表示为:
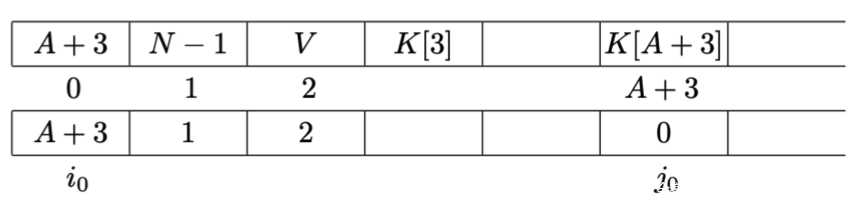
假设我们知道IV、加密过的密文和明文的第一个字节(在WEP中固定为aa),我们尝试从第一个我们不知道的key开始着手,设它在SK中的索引为A,则在K中的索引为A+3。当我们的IV都是诸如(A+3,N-1=255,V)的形式(其中V可以是任何值),我们可以有如下结论:
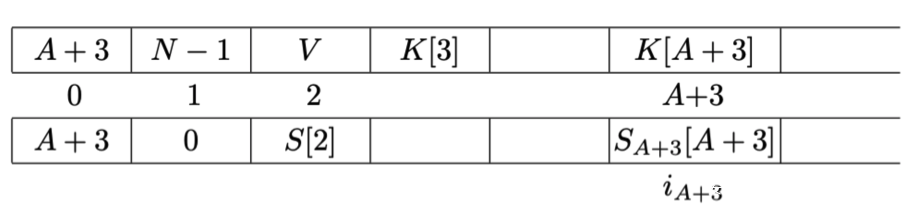
在经过了第一轮密钥调度算法中的迭代后,status如下所示:
其中上方的第一行是K,中间的数字是每个元素的索引值,最下方的一行是status。
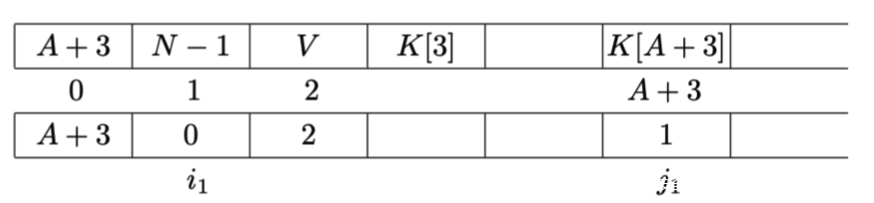
在经过了第二轮密钥调度算法中的迭代后,status如下所示:
在取到K[A+3],即攻击者不知道的第一个key的字节之前,status都是可以被攻击者所计算出来的(即S(A+3)之前的状态),如果在第二轮迭代后的S[0]和S[1]有受到更改,则攻击者可以丢弃使用该IV的情形
如果S[0]和S[1]没有受到更改,则在S(A+2)到S(A+3)的更新过程中,j会进行如下变化:
然后会进行self.__swap_state(i, j),这个时候的status如下所示:
因为攻击者知道S(A+2)和j(A+2),如果攻击者知道S(A+3)[A+3]的值,则攻击者可以知道它在S(A+2)中的位置(即j(A+3)的值),那么攻击者就可以计算出来K[A+3]的值。
为什么这样就可以计算出K[A+3]的值了呢?让我们关注伪随机子密码生成算法的部分,在对第一个明文字节进行加密的时候,密钥流(设为keyStreamByte)中的第一个字节的格式为:
则我们可以推出如下公式:
由于这里面除了K[A+3]我们都是知道的,那么我们就可以很容易地推出K[A+3]的值
上述公式中所使用到的states的值在S(A+2)到S(L-1)的更新过程中都没有受到更改的概率为:
在有足够的信息的时候,这个攻击是很容易实现并使用的
2020蓝帽杯决赛-infinite_game
这道题目的主要代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import binascii
import os
import sys
FLAG = "flag{XXXXXX}"
KEY = os.urandom(9)
def enhex(s):
return binascii.hexlify(s.strip()).decode()
def unhex(s):
return binascii.unhexlify(s.strip())
def echo(msg):
sys.stdout.write(msg)
sys.stdout.flush()
class PRNG:
def __init__(self):
self.state = [i for i in range(256)]
self.i = 0
self.j = 0
def __swap_state(self, a, b):
self.state[a], self.state[b] = self.state[b], self.state[a]
def ksa(self, key):
j = 0
for i in range(256):
j = (j + self.state[i] + key[i % len(key)]) % 256
self.__swap_state(i, j)
def prng(self):
self.i = (self.i + 1) % 256
self.j = (self.j + self.state[self.i]) % 256
self.__swap_state(self.i, self.j)
return self.state[(self.state[self.i] + self.state[self.j]) % 256]
def do_typing():
echo("iv > ")
iv = unhex(input())
if len(iv) != 3:
echo("ERROR: The length of IV must be 3.\n")
return
prng = PRNG()
prng.ksa(iv + KEY)
plaintext = b"The Big Monkey is now typing...:" + os.urandom(128)
ciphertext = b''
for i in range(len(plaintext)):
ciphertext += bytes([plaintext[i] ^ prng.prng()])
echo("Tac, tac, tac... The monkey is typing: " + enhex(ciphertext) + "\n")
def do_pay_flag():
echo("iv > ")
iv = unhex(input())
if len(iv) != 3:
echo("The length of IV must be 3.\n")
return
echo("input > ")
ciphertext = unhex(input())
prng = PRNG()
prng.ksa(iv + KEY)
plaintext = b''
for i in range(len(ciphertext)):
plaintext += bytes([ciphertext[i] ^ prng.prng()])
if b"There is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so." in plaintext:
echo("The infinite monkey theorem is true. " + FLAG + "\n")
echo("Done.\n")
def main():
echo("""\
__,__
.--. .-" "-. .--.
/ .. \/ .-. .-. \/ .. \\
| | '| / Y \ |' | |
| \ \ \ 0 | 0 / / / |
\ '- ,\.-"`` ``"-./, -' / T H E I N F I N I T E M O N K E Y G A M E
`'-' /_ ^ ^ _\ '-'`
.--'| \._ _ _./ |'--.
/` \ \.-. / / `\\ 0> Start typing
/ '._/ |-' _.' \\
/ ; /--~' | \\ 1> Pay flag
/ .'\|.-\--. \ \\
/ .'-. /.-.;\ |\|'~'-.|\ \\ 2> Exit
\ `-./`|_\_/ ` `\\'. \\
'. ; ___) '.`; /
'-.,_ ; ___) \/ /
\ ``'------'\ \ ` /
'. \ '. | ;/_
jgs ___> '. \_ _ _/ , '--.
.' '. .-~~~~~-. / |--'`~~-. \\
// / .---'/ .-~~-._/ / / /---..__.' /
((_(_/ / / (_(_(_(---.__ .'
| | _ `~~`
| | \\'.
\ '....' |
'.,___.'
\n""")
while True:
print("key:",KEY.hex())
echo("\nInput your choice> ")
choice = input()
if not choice.strip():
continue
choice = int(choice)
if choice == 0:
do_typing()
elif choice == 1:
do_pay_flag()
elif choice == 2:
break
else:
echo("Unknown choice\n")
continue
try:
main()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
except Exception as err:
print("*** Exception:", err, "***")
该挑战首先会在每次连接的时候生成一个随机的key,然后提供了两个功能,do_typing和do_pay_flag
在do_typing中,我们可以提供任意的长度为3的iv,它会使用iv+key来进行RC4的密钥调度算法,并且使用RC4的伪随机子密码生成算法来加密一段前32个字节是已知的明文并返回加密后的密文
在do_pay_flag中,我们可以提供任意的长度为3的iv和一段密文,它也和选项do_typing一样使用相同的方法来进行RC4算法的使用,并解密我们所提供的密文,如果密文中有指定的明文段则会得到flag
这个场景就是我们上面所提到的FMS攻击的场景,那么按照上面的描述进行攻击即可:
#!/usr/bin/env python
from pwn import *
from tqdm import tqdm
from Crypto.Util.number import *
#context.log_level = "debug"
plain = b"There is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so."
key_length = 9
# Helper function, which swaps two values in the box.
def swapValueByIndex(box, i, j):
temp = box[i]
box[i] = box[j]
box[j] = temp
# Initialize S-box.
def initSBox(box):
if len(box) == 0:
for i in range(256):
box.append(i)
else:
for i in range(256):
box[i] = i
# Key schedule Algorithm (KSA) for key whose value is in unicode.
def ksa(key, box):
j = 0
for i in range(256):
j = (j + box[i] + ord(key[i % len(key)])) % 256
swapValueByIndex(box, i, j)
class PRNG:
def __init__(self):
self.state = [i for i in range(256)]
self.i = 0
self.j = 0
def __swap_state(self, a, b):
self.state[a], self.state[b] = self.state[b], self.state[a]
def ksa(self, key):
j = 0
for i in range(256):
j = (j + self.state[i] + key[i % len(key)]) % 256
self.__swap_state(i, j)
def prng(self):
self.i = (self.i + 1) % 256
self.j = (self.j + self.state[self.i]) % 256
self.__swap_state(self.i, self.j)
return self.state[(self.state[self.i] + self.state[self.j]) % 256]
def cmd(idx):
r.sendlineafter("Input your choice> ",str(idx))
def typing(iv):
cmd(0)
r.sendlineafter("iv > ",iv)
r.recvuntil("Tac, tac, tac... The monkey is typing: ")
result = int(r.recvuntil("\n",drop = True),16)
result = long_to_bytes(result)
return result
def getflag(iv,cipher):
cmd(1)
r.sendlineafter("iv > ",iv)
r.sendlineafter("input > ",cipher)
r.recvuntil("The infinite monkey theorem is true. ")
flag = r.recvuntil("\n",drop = True, timeout = 2)
return flag
r = process(argv=["python3", "chall.py"])
iv = [0,255,0]
rows = []
for A in tqdm(range(key_length)):
iv[0] = A + 3
for thirdByte in range(256):
iv[2] = thirdByte
cipherByte = typing(bytes(iv).hex())[0]
rows.append([iv[0],iv[1],iv[2],cipherByte])
box = []
plainKnown = "54"
key = [None] * 3
for A in range(key_length):
prob = [0] * 256
for row in rows:
key[0] = int(row[0])
key[1] = int(row[1])
key[2] = int(row[2])
j = 0
initSBox(box)
for i in range(A + 3):
j = (j + box[i] + key[i]) % 256
swapValueByIndex(box, i, j)
if i == 1:
original0 = box[0]
original1 = box[1]
i = A + 3
z = box[1]
if z + box[z] == A + 3:
if (original0 != box[0] or original1 != box[1]):
continue
keyStreamByte = int(row[3]) ^ int(plainKnown, 16)
keyByte = (keyStreamByte - j - box[i]) % 256
prob[keyByte] += 1
higherPossibility = prob.index(max(prob))
key.append(higherPossibility)
userInput = key[3:]
result = [format(key, 'x') for key in userInput]
rawkey = ''.join(result)
rawkey = rawkey.ljust(18,"0")
print(rawkey)
iv = "777777"
key = long_to_bytes(int(iv + rawkey,16))
prng = PRNG()
prng.ksa(key)
cipher = b''
for i in range(len(plain)):
cipher += bytes([plain[i] ^ prng.prng()])
cipher = cipher.hex()
flag = getflag(iv,cipher)
print(flag)
r.close()
Reference
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RC4
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wired_Equivalent_Privacy
https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007%2F3-540-45537-X_1.pdf
https://github.com/jackieden26/FMS-Attack