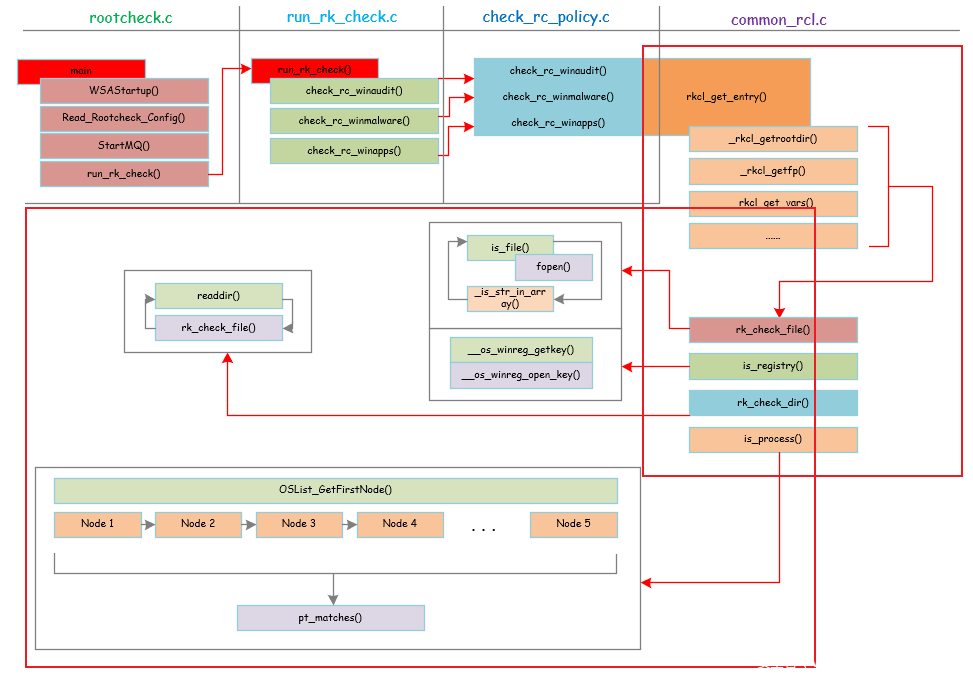
OSSEC简介
OSSEC是一个开源的多平台入侵检测系统,可以运行在Windows,Linux等多个平台之上。一般分为客户端和服务端。客户端用来收集客户机运行时消息,主要以日志为载体传送给服务端。在服务端OSSEC进行消息的解码与告警。除了告警之外,OSSEC还支持用户自定义的自主相应来抵抗入侵。
OSSEC windows客户端用来采集windows客户机运行时信息,进行一定分析后传送给服务端进行进一步的分析告警。OSSEC windows客户端同时支持rootkit检测,本文即从源码角度分析OSSEC对windows rootkit检测的实现。
整体框架
OSSEC github开源地址为:https://github.com/ossec/ossec-hids 。下载到源码之后,关于rootkit检测部分的源码位于ossec-hidssrcrootcheck目录下:
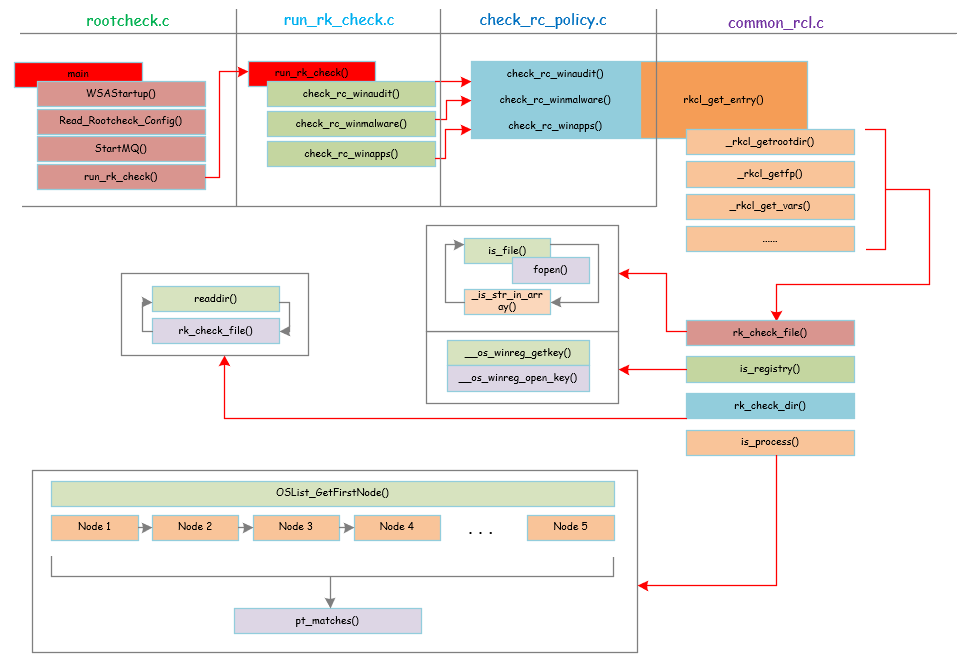
下面是OSSEC windows_rootkit检测的整体架构:
下面分部分逐一介绍。
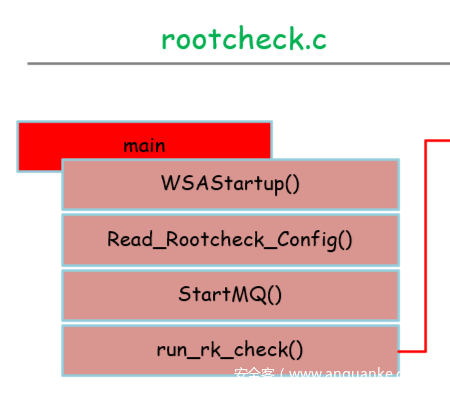
rootcheck.c
整体框架:
rootcheck.c是rootcheck功能实现的入口位置。
首先调用WSAStartup()创建socket用于和server进行通信。
然后调用Read_Rootcheck_Config()进行rootcheck功能的配置,主要包括需要检查windows相关的项的配置,这个在rootcheck.config可以配置。
然后StartMQ()用于启动和server的通信,用于传输检查结果。
最后是run_rk_check()进行最后的检查任务。
相关源码和注释:
1. int main(int argc, char **argv)
2. {
3. int test_config = 0;
4. const char *cfg = "./rootcheck.conf";
5.
6. #else
7.
8. int rootcheck_init(int test_config)
9. {
10. const char *cfg = DEFAULTCPATH;
11.
12. #endif /* OSSECHIDS */
13.
14. int c;
15.
16. /* Zero the structure, initialize default values */
17. rootcheck.workdir = NULL;
18. rootcheck.basedir = NULL;
19. rootcheck.unixaudit = NULL;
20. rootcheck.ignore = NULL;
21. rootcheck.rootkit_files = NULL;
22. rootcheck.rootkit_trojans = NULL;
23. rootcheck.winaudit = NULL;
24. rootcheck.winmalware = NULL;
25. rootcheck.winapps = NULL;
26. rootcheck.daemon = 1;
27. rootcheck.notify = QUEUE;
28. rootcheck.scanall = 0;
29. rootcheck.readall = 0;
30. rootcheck.disabled = 0;
31. rootcheck.skip_nfs = 0;
32. rootcheck.alert_msg = NULL;
33. rootcheck.time = ROOTCHECK_WAIT;
34.
35. rootcheck.checks.rc_dev = 1;
36. rootcheck.checks.rc_files = 1;
37. rootcheck.checks.rc_if = 1;
38. rootcheck.checks.rc_pids = 1;
39. rootcheck.checks.rc_ports = 1;
40. rootcheck.checks.rc_sys = 1;
41. rootcheck.checks.rc_trojans = 1;
42.
43. #ifdef OSSECHIDS
44. rootcheck.tsleep = (unsigned int) getDefine_Int("rootcheck", "sleep", 0, 64);
45. #endif
46.
47. #ifdef WIN32
48. rootcheck.checks.rc_winaudit = 1;
49. rootcheck.checks.rc_winmalware = 1;
50. rootcheck.checks.rc_winapps = 1;
51. #else
52. rootcheck.checks.rc_unixaudit = 1;
53. #endif
54.
55. /* We store up to 255 alerts in there */
56. os_calloc(256, sizeof(char *), rootcheck.alert_msg);
57. c = 0;
58. while (c <= 255) {
59. rootcheck.alert_msg[c] = NULL;
60. c++;
61. }
62.
63. #ifndef OSSECHIDS
64. rootcheck.notify = SYSLOG;
65. rootcheck.daemon = 0;
66. while ((c = getopt(argc, argv, "VstrdhD:c:")) != -1) {
67. switch (c) {
68. case 'V':
69. print_version();
70. break;
71. case 'h':
72. help_rootcheck();
73. break;
74. case 'd':
75. nowDebug();
76. break;
77. case 'D':
78. if (!optarg) {
79. ErrorExit("%s: -D needs an argument", ARGV0);
80. }
81. rootcheck.workdir = optarg;
82. break;
83. case 'c':
84. if (!optarg) {
85. ErrorExit("%s: -c needs an argument", ARGV0);
86. }
87. cfg = optarg;
88. break;
89. case 's':
90. rootcheck.scanall = 1;
91. break;
92. case 't':
93. test_config = 1;
94. break;
95. case 'r':
96. rootcheck.readall = 1;
97. break;
98. default:
99. help_rootcheck();
100. break;
101. }
102. }
103. #ifdef WIN32
104. /* Start Winsock */
105. {
106. WSADATA wsaData;
107. if (WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 0), &wsaData) != 0) {
108. ErrorExit("%s: WSAStartup() failed", ARGV0);
109. }
110. }
111. #endif /* WIN32 */
112.
113. #endif /* OSSECHIDS */
114.
115. /* Start up message */
116. debug1(STARTED_MSG, ARGV0);
117.
118. /* Check if the configuration is present */
119. if (File_DateofChange(cfg) < 0) {
120. merror("%s: Configuration file '%s' not found", ARGV0, cfg);
121. return (-1);
122. }
123.
124. /* Read configuration --function specified twice (check makefile) */
125. if (Read_Rootcheck_Config(cfg) < 0) {
126. ErrorExit(CONFIG_ERROR, ARGV0, cfg);
127. }
128.
129. /* If testing config, exit here */
130. if (test_config) {
131. return (0);
132. }
133.
134. /* Return 1 disables rootcheck */
135. if (rootcheck.disabled == 1) {
136. verbose("%s: Rootcheck disabled. Exiting.", ARGV0);
137. return (1);
138. }
139.
140. /* Check if Unix audit file is configured */
141. if (!rootcheck.unixaudit) {
142. #ifndef WIN32
143. log2file("%s: System audit file not configured.", ARGV0);
144. #endif
145. }
146.
147. /* Set default values */
148. if (rootcheck.workdir == NULL) {
149. rootcheck.workdir = DEFAULTDIR;
150. }
151.
152. #ifdef OSSECHIDS
153. /* Start up message */
154. #ifdef WIN32
155. verbose(STARTUP_MSG, "ossec-rootcheck", getpid());
156. #else
157.
158. /* Connect to the queue if configured to do so */
159. if (rootcheck.notify == QUEUE) {
160. debug1("%s: Starting queue ...", ARGV0);
161.
162. /* Start the queue */
163. if ((rootcheck.queue = StartMQ(DEFAULTQPATH, WRITE)) < 0) {
164. merror(QUEUE_ERROR, ARGV0, DEFAULTQPATH, strerror(errno));
165.
166. /* 5 seconds to see if the agent starts */
167. sleep(5);
168. if ((rootcheck.queue = StartMQ(DEFAULTQPATH, WRITE)) < 0) {
169. /* Wait 10 more seconds */
170. merror(QUEUE_ERROR, ARGV0, DEFAULTQPATH, strerror(errno));
171. sleep(10);
172. if ((rootcheck.queue = StartMQ(DEFAULTQPATH, WRITE)) < 0) {
173. ErrorExit(QUEUE_FATAL, ARGV0, DEFAULTQPATH);
174. }
175. }
176. }
177. }
178.
179. #endif /* WIN32 */
180.
181. #endif /* OSSECHIDS */
182.
183. /* Initialize rk list */
184. rk_sys_name = (char **) calloc(MAX_RK_SYS + 2, sizeof(char *));
185. rk_sys_file = (char **) calloc(MAX_RK_SYS + 2, sizeof(char *));
186. if (!rk_sys_name || !rk_sys_file) {
187. ErrorExit(MEM_ERROR, ARGV0, errno, strerror(errno));
188. }
189. rk_sys_name[0] = NULL;
190. rk_sys_file[0] = NULL;
191.
192. #ifndef OSSECHIDS
193. #ifndef WIN32
194. /* Start signal handling */
195. StartSIG(ARGV0);
196. #endif
197. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Running run_rk_check", ARGV0);
198. run_rk_check();
199.
200. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Leaving...", ARGV0);
201. #endif /* OSSECHIDS */
202. return (0);
203. }
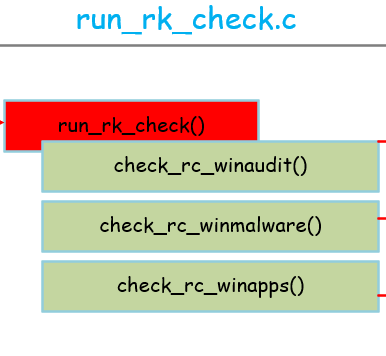
run_rk_check.c
整体框架:
run_rk_check()的源码当中包含所有平台的rootcheck检测的代码,这里只分析和windows相关的部分。
首先是check_rc_winaudit(),主要是检测windows的一些审计相关的内容,它的配置文件是在 :
用户可以进行配置来控制它的检测行为。具体如下:
1. # OSSEC Linux Audit - (C) 2018 OSSEC Project
2. #
3. # Released under the same license as OSSEC.
4. # More details at the LICENSE file included with OSSEC or online
5. # at: https://github.com/ossec/ossec-hids/blob/master/LICENSE
6. #
7. # [Application name] [any or all] [reference]
8. # type:<entry name>;
9. #
10. # Type can be:
11. # - f (for file or directory)
12. # - r (registry entry)
13. # - p (process running)
14. #
15. # Additional values:
16. # For the registry and for directories, use "->" to look for a specific entry and another
17. # "->" to look for the value.
18. # Also, use " -> r:^. -> ..." to search all files in a directory
19. # For files, use "->" to look for a specific value in the file.
20. #
21. # Values can be preceded by: =: (for equal) - default
22. # r: (for ossec regexes)
23. # >: (for strcmp greater)
24. # <: (for strcmp lower)
25. # Multiple patterns can be specified by using " && " between them.
26. # (All of them must match for it to return true).
27.
28. # http://technet2.microsoft.com/windowsserver/en/library/486896ba-dfa1-4850-9875-13764f749bba1033.mspx?mfr=true
29. [Disabled Registry tools set {PCI_DSS: 10.6.1}] [any] []
30. r:HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionPoliciesSystem -> DisableRegistryTools -> 1;
31. r:HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionPoliciesSystem -> DisableRegistryTools -> 1;
32.
33. # http://support.microsoft.com/kb/825750
34. [DCOM disabled {PCI_DSS: 10.6.1}] [any] []
35. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftOLE -> EnableDCOM -> N;
36.
37. # http://web.mit.edu/is/topics/windows/server/winmitedu/security.html
38. [LM authentication allowed (weak passwords) {PCI_DSS: 10.6.1, 11.4}] [any] []
39. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlLSA -> LMCompatibilityLevel -> 0;
40. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlLSA -> LMCompatibilityLevel -> 1;
41.
42. # http://research.eeye.com/html/alerts/AL20060813.html
43. # Disabled by some Malwares (sometimes by McAfee and Symantec
44. # security center too).
45. [Firewall/Anti Virus notification disabled {PCI_DSS: 10.6.1}] [any] []
46. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftSecurity Center -> FirewallDisableNotify -> !0;
47. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftSecurity Center -> antivirusoverride -> !0;
48. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftSecurity Center -> firewalldisablenotify -> !0;
49. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftSecurity Center -> firewalldisableoverride -> !0;
50.
51. # Checking for the microsoft firewall.
52. [Microsoft Firewall disabled {PCI_DSS: 10.6.1, 1.4}] [all] []
53. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINEsoftwarepoliciesmicrosoftwindowsfirewalldomainprofile -> enablefirewall -> 0;
54. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINEsoftwarepoliciesmicrosoftwindowsfirewallstandardprofile -> enablefirewall -> 0;
55.
56. #http://web.mit.edu/is/topics/windows/server/winmitedu/security.html
57. [Null sessions allowed {PCI_DSS: 11.4}] [any] []
58. r:HKLMSystemCurrentControlSetControlLsa -> RestrictAnonymous -> 0;
59.
60. [Error reporting disabled {PCI_DSS: 10.6.1}] [any] [http://windowsir.blogspot.com/2007/04/something-new-to-look-for.html]
61. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftPCHealthErrorReporting -> DoReport -> 0;
62. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftPCHealthErrorReporting -> IncludeKernelFaults -> 0;
63. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftPCHealthErrorReporting -> IncludeMicrosoftApps -> 0;
64. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftPCHealthErrorReporting -> IncludeWindowsApps -> 0;
65. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftPCHealthErrorReporting -> IncludeShutdownErrs -> 0;
66. r:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftPCHealthErrorReporting -> ShowUI -> 0;
67.
68. # http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=315231
69. [Automatic Logon enabled {PCI_DSS: 10.6.1}] [any] [http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=315231]
70. r:HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsNTCurrentVersionWinlogon -> DefaultPassword;
71. r:HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsNTCurrentVersionWinlogon -> AutoAdminLogon -> 1;
72.
73. [Winpcap packet filter driver found {PCI_DSS: 10.6.1}] [any] []
74. f:%WINDIR%System32driversnpf.sys;
第二个是check_rc_winmalware,用来根据配置文件检查是否存在特定的恶意软件,最后一个是check_rc_winapps,用来检查特定的windows app的特征,检查他们是否被rootkit更改等。
具体代码和注释:(只列出和windows相关的源码注释,其他的源码都已省略)
1. void run_rk_check()
2. {
3. time_t time1;
4. time_t time2;
5. FILE *fp;
6. OSList *plist;
7.
8. #ifndef WIN32
9. /* On non-Windows, always start at / */
10. size_t i;
11. char basedir[] = "/";
12.
13. /* Removing the last / from basedir */
14. i = strlen(basedir);
15. if (i > 0) {
16. if (basedir[i - 1] == '/') {
17. basedir[i - 1] = '';
18. }
19. }
20. #else
21. /* On Windows, always start at C: */
22. char basedir[] = "C:\";
23.
24. #endif
25.
26. /* Set basedir */
27. if (rootcheck.basedir == NULL) {
28. rootcheck.basedir = basedir;
29. }
30.
31. time1 = time(0);
32.
33. /* Initial message */
34. if (rootcheck.notify != QUEUE) {
35. printf("n");
36. printf("** Starting Rootcheck v0.9 by Daniel B. Cid **n");
37. printf("** http://www.ossec.net/en/about.html#dev-team **n");
38. printf("** http://www.ossec.net/rootcheck/ **nn");
39. printf("Be patient, it may take a few minutes to complete...n");
40. printf("n");
41. }
42.
43. /* Clean the global variables */
44. rk_sys_count = 0;
45. rk_sys_file[rk_sys_count] = NULL;
46. rk_sys_name[rk_sys_count] = NULL;
47.
48. /* Send scan start message */
49. notify_rk(ALERT_POLICY_VIOLATION, "Starting rootcheck scan.");
50. if (rootcheck.notify == QUEUE) {
51. merror("%s: INFO: Starting rootcheck scan.", ARGV0);
52. }
53.
54. /* Check for Rootkits */
55. /* Open rootkit_files and pass the pointer to check_rc_files */
56. if (rootcheck.checks.rc_files) {
57. if (!rootcheck.rootkit_files) {
58. #ifndef WIN32
59. merror("%s: No rootcheck_files file configured.", ARGV0);
60. #endif
61. } else {
62. fp = fopen(rootcheck.rootkit_files, "r");
63. if (!fp) {
64. merror("%s: No rootcheck_files file: '%s'", ARGV0,
65. rootcheck.rootkit_files);
66. }
67.
68. else {
69. check_rc_files(rootcheck.basedir, fp);
70.
71. fclose(fp);
72. }
73. }
74. }
75.
76. /* Check for trojan entries in common binaries */
77. if (rootcheck.checks.rc_trojans) {
78. if (!rootcheck.rootkit_trojans) {
79. #ifndef WIN32
80. merror("%s: No rootcheck_trojans file configured.", ARGV0);
81. #endif
82. } else {
83. fp = fopen(rootcheck.rootkit_trojans, "r");
84. if (!fp) {
85. merror("%s: No rootcheck_trojans file: '%s'", ARGV0,
86. rootcheck.rootkit_trojans);
87. } else {
88. #ifndef HPUX
89. check_rc_trojans(rootcheck.basedir, fp);
90. #endif
91. fclose(fp);
92. }
93. }
94. }
95.
96. #ifdef WIN32
97. /* Get process list */
98. plist = os_get_process_list();//获取每个进程的信息
99.
100. /* Windows audit check */
101. if (rootcheck.checks.rc_winaudit) {
102. if (!rootcheck.winaudit) {
103. merror("%s: No winaudit file configured.", ARGV0);
104. } else {
105. fp = fopen(rootcheck.winaudit, "r");
106. if (!fp) {
107. merror("%s: No winaudit file: '%s'", ARGV0,
108. rootcheck.winaudit);
109. } else {
110. check_rc_winaudit(fp, plist);
111. fclose(fp);
112. }
113. }
114. }
115.
116. /* Windows malware */
117. if (rootcheck.checks.rc_winmalware) {
118. if (!rootcheck.winmalware) {
119. merror("%s: No winmalware file configured.", ARGV0);
120. } else {
121. fp = fopen(rootcheck.winmalware, "r");
122. if (!fp) {
123. merror("%s: No winmalware file: '%s'", ARGV0,
124. rootcheck.winmalware);
125. } else {
126. check_rc_winmalware(fp, plist);
127. fclose(fp);
128. }
129. }
130. }
131.
132. /* Windows Apps */
133. if (rootcheck.checks.rc_winapps) {
134. if (!rootcheck.winapps) {
135. merror("%s: No winapps file configured.", ARGV0);
136. } else {
137. fp = fopen(rootcheck.winapps, "r");
138. if (!fp) {
139. merror("%s: No winapps file: '%s'", ARGV0,
140. rootcheck.winapps);
141. } else {
142. check_rc_winapps(fp, plist);
143. fclose(fp);
144. }
145. }
146. }
147.
148. /* Free the process list */
149. del_plist((void *)plist);
150.
151. #else
152. /* Checks for other non-Windows */
153.
154. /* Unix audit check ***/
155. .....
156. #endif /* !WIN32 */
157.
158. /* Check for files in the /dev filesystem */
159. if (rootcheck.checks.rc_dev) {
160. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Going into check_rc_dev", ARGV0);
161. check_rc_dev(rootcheck.basedir);
162. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Exiting check_rc_dev", ARGV0);
163. }
164.
165. /* Scan the whole system for additional issues */
166. if (rootcheck.checks.rc_sys) {
167. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Going into check_rc_sys", ARGV0);
168. check_rc_sys(rootcheck.basedir);
169. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Exiting check_rc_sys", ARGV0);
170. }
171.
172. /* Check processes */
173. if (rootcheck.checks.rc_pids) {
174. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Going into check_rc_pids", ARGV0);
175. check_rc_pids();
176. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Exiting check_rc_pids", ARGV0);
177. }
178.
179. /* Check all ports */
180. if (rootcheck.checks.rc_ports) {
181. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Going into check_rc_ports", ARGV0);
182. check_rc_ports();
183. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Exiting check_rc_ports", ARGV0);
184.
185. /* Check open ports */
186. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Going into check_open_ports", ARGV0);
187. check_open_ports();
188. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Exiting check_open_ports", ARGV0);
189. }
190.
191. /* Check interfaces */
192. if (rootcheck.checks.rc_if) {
193. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Going into check_rc_if", ARGV0);
194. check_rc_if();
195. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Exiting check_rc_if", ARGV0);
196. }
197.
198. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Completed with all checks.", ARGV0);
199.
200. /* Clean the global memory */
201. {
202. int li;
203. for (li = 0; li <= rk_sys_count; li++) {
204. if (!rk_sys_file[li] ||
205. !rk_sys_name[li]) {
206. break;
207. }
208.
209. free(rk_sys_file[li]);
210. free(rk_sys_name[li]);
211. }
212. }
213.
214. /* Final message */
215. time2 = time(0);
216.
217. if (rootcheck.notify != QUEUE) {
218. printf("n");
219. printf("- Scan completed in %d seconds.nn", (int)(time2 - time1));
220. } else {
221. sleep(5);
222. }
223.
224. /* Send scan ending message */
225. notify_rk(ALERT_POLICY_VIOLATION, "Ending rootcheck scan.");
226. if (rootcheck.notify == QUEUE) {
227. merror("%s: INFO: Ending rootcheck scan.", ARGV0);
228. }
229.
230. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Leaving run_rk_check", ARGV0);
231. return;
232. }
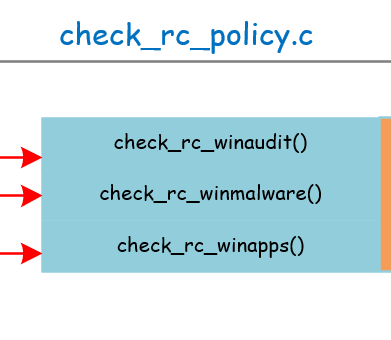
check_rc_policy.c
整体框架:
check_rc_policy只是具体功能实现过程中的一个转折点。它们在实现时都调用了rkcl_get_entry()。具体如下:
1. /* Read the file pointer specified
2. * and check if the configured file is there
3. */
4. void check_rc_winaudit(FILE *fp, OSList *p_list)
5. {
6. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Starting on check_rc_winaudit", ARGV0);
7. rkcl_get_entry(fp, "Windows Audit:", p_list);
8. }
9.
10. /* Read the file pointer specified
11. * and check if the configured file is there
12. */
13. void check_rc_winmalware(FILE *fp, OSList *p_list)
14. {
15. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Starting on check_rc_winmalware", ARGV0);
16. rkcl_get_entry(fp, "Windows Malware:", p_list);
17. }
18.
19. /* Read the file pointer specified
20. * and check if the configured file is there
21. */
22. void check_rc_winapps(FILE *fp, OSList *p_list)
23. {
24. debug1("%s: DEBUG: Starting on check_rc_winapps", ARGV0);
25. rkcl_get_entry(fp, "Application Found:", p_list);
26. }
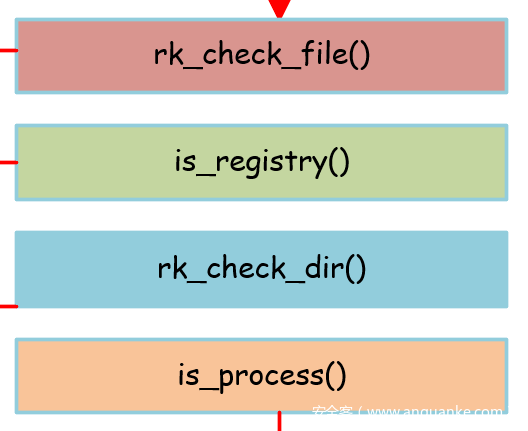
common_rcl.c
整体框架:
common_rcl.c中的rkcl_get_entry()函数是rootcheck功能实现的核心函数。
首先调用_rkcl_getrootdir()、_rkcl_getfp()、rkcl_get_vars()等函数进行一些初始化,包括设置环境变量,具体读取配置文件(read_vars)等。
然后就是与windows相关的具体检查操作,包括如下四个方面:
下面分别介绍这四个方面:
rk_check_file
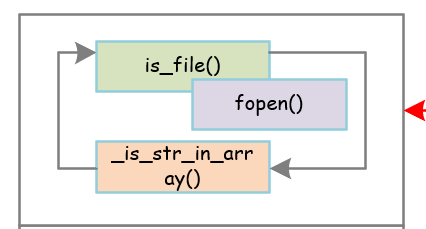
整体框架:
它的功能是检查一个文件是否存在,底层调用fopen来测试,如果打开成功则成功,否则失败:
is_file()源码如下:
1. /* Check if a file exists */
2. int is_file(char *file)
3. {
4. FILE *fp;
5. fp = fopen(file, "r");
6. if (fp) {
7. fclose(fp);
8. return (1);
9. }
10. return (0);
11. }
rk_check_file源码和注释如下:
1. int rk_check_file(char *file, char *pattern)
2. {
3. char *split_file;
4. int full_negate = 0;
5. int pt_result = 0;
6. FILE *fp;
7. char buf[OS_SIZE_2048 + 1];
8.
9. if (file == NULL) {
10. return (0);
11. }
12.
13. /* Check if the file is divided */
14. split_file = strchr(file, ',');
15. if (split_file) {
16. *split_file = '';
17. split_file++;
18. }
19.
20. /* Get each file */
21. do {
22. /* If we don't have a pattern, just check if the file/dir is there */
23. if (pattern == NULL) {
24. if (is_file(file)) {
25. int i = 0;
26. char _b_msg[OS_SIZE_1024 + 1];
27.
28. _b_msg[OS_SIZE_1024] = '';
29. snprintf(_b_msg, OS_SIZE_1024, " File: %s.",
30. file);
31.
32. /* Already present */
33. if (_is_str_in_array(rootcheck.alert_msg, _b_msg)) {
34. return (1);
35. }
36.
37. while (rootcheck.alert_msg[i] && (i < 255)) {
38. i++;
39. }
40.
41. if (!rootcheck.alert_msg[i]) {
42. os_strdup(_b_msg, rootcheck.alert_msg[i]);
43. }
44.
45. return (1);
46. }
47. } else {
48. full_negate = pt_check_negate(pattern);
49. /* Check for content in the file */
50. debug1("checking file: %s", file);
51. fp = fopen(file, "r");
52. if (fp) {
53.
54. debug1(" starting new file: %s", file);
55. buf[OS_SIZE_2048] = '';
56. while (fgets(buf, OS_SIZE_2048, fp) != NULL) {
57. char *nbuf;
58.
59. /* Remove end of line */
60. nbuf = strchr(buf, 'n');
61. if (nbuf) {
62. *nbuf = '';
63. }
64. #ifdef WIN32
65. /* Remove end of line */
66. nbuf = strchr(buf, 'r');
67. if (nbuf) {
68. *nbuf = '';
69. }
70. #endif
71. /* Matched */
72. pt_result = pt_matches(buf, pattern);
73. debug1("Buf == "%s"", buf);
74. debug1("Pattern == "%s"", pattern);
75. debug1("pt_result == %d and full_negate == %d", pt_result, full_negate);
76. if ((pt_result == 1 && full_negate == 0) ) {
77. debug1("alerting file %s on line %s", file, buf);
78. int i = 0;
79. char _b_msg[OS_SIZE_1024 + 1];
80.
81. /* Close the file before dealing with the alert */
82. fclose(fp);
83.
84. /* Generate the alert itself */
85. _b_msg[OS_SIZE_1024] = '';
86. snprintf(_b_msg, OS_SIZE_1024, " File: %s.",
87. file);
88.
89. /* Already present */
90. if (_is_str_in_array(rootcheck.alert_msg, _b_msg)) {
91. return (1);
92. }
93.
94. while (rootcheck.alert_msg[i] && (i < 255)) {
95. i++;
96. }
97.
98. if (!rootcheck.alert_msg[i]) {
99. os_strdup(_b_msg, rootcheck.alert_msg[i]);
100. }
101.
102. return (1);
103. } else if ((pt_result == 0 && full_negate == 1) ) {
104. /* Found a full+negate match so no longer need to search
105. * break out of loop and make sure the full negate does
106. * not alert.
107. */
108. debug1("found a complete match for full_negate");
109. full_negate = 0;
110. break;
111. }
112. }
113.
114. fclose(fp);
115.
116. if (full_negate == 1) {
117. debug1("full_negate alerting - file %s", file);
118. int i = 0;
119. char _b_msg[OS_SIZE_1024 + 1];
120.
121. /* Generate the alert itself */
122. _b_msg[OS_SIZE_1024] = '';
123. snprintf(_b_msg, OS_SIZE_1024, " File: %s.",
124. file);
125.
126. /* Already present */
127. if (_is_str_in_array(rootcheck.alert_msg, _b_msg)) {
128. return (1);
129. }
130.
131. while (rootcheck.alert_msg[i] && (i < 255)) {
132. i++;
133. }
134.
135. if (!rootcheck.alert_msg[i]) {
136. os_strdup(_b_msg, rootcheck.alert_msg[i]);
137. }
138.
139. return (1);
140. }
141. }
142. }
143.
144. if (split_file) {
145. file = split_file;
146. split_file = strchr(split_file, ',');
147. if (split_file) {
148. split_file++;
149. }
150. }
151.
152.
153. } while (split_file);
154.
155. return (0);
156. }
is_registry
整体框架:
is_registry函数是用来检查相应注册表是否存在的,也可以进行配置。
底层是调用RegOpenKeyEx(),RegQueryInfoKey()来进行测试:
1. int is_registry(char *entry_name, char *reg_option, char *reg_value)
2. {
3. char *rk;
4.
5. rk = __os_winreg_getkey(entry_name);
6. if (rk_sub_tree == NULL || rk == NULL) {
7. merror(SK_INV_REG, ARGV0, entry_name);
8. return (0);
9. }
10.
11. if (__os_winreg_open_key(rk, entry_name, reg_option, reg_value) == 0) {
12. return (0);
13. }
14.
15. return (1);
16. }
__os_winreg_open_key的具体实现如下:
1. int __os_winreg_open_key(char *subkey, char *full_key_name,
2. char *reg_option, char *reg_value)
3. {
4. int ret = 1;
5. HKEY oshkey;
6.
7. int REG64MASK = (KEY_READ | KEY_WOW64_64KEY);
8. int REG32MASK = (KEY_READ | KEY_WOW64_32KEY);
9.
10. if((RegOpenKeyEx(rk_sub_tree, subkey, 0, REG64MASK, &oshkey) ||
11. (RegOpenKeyEx(rk_sub_tree, subkey, 0, REG32MASK, &oshkey))
12. ) != ERROR_SUCCESS)
13. {
14. return(0);
15. }
16.
17. /* If option is set, return the value of query key */
18. if (reg_option) {
19. ret = __os_winreg_querykey(oshkey, subkey, full_key_name,
20. reg_option, reg_value);
21. }
22.
23. RegCloseKey(oshkey);
24. return (ret);
25. }
__os_winreg_querykey()具体源码和注释如下:
1. /* Query the key and get the value of a specific entry */
2. int __os_winreg_querykey(HKEY hKey,
3. __attribute__((unused))char *p_key,
4. __attribute__((unused)) char *full_key_name,
5. char *reg_option, char *reg_value)
6. {
7. int rc;
8. DWORD i, j;
9.
10. /* QueryInfo and EnumKey variables */
11. TCHAR class_name_b[MAX_PATH + 1];
12. DWORD class_name_s = MAX_PATH;
13.
14. /* Number of sub keys */
15. DWORD subkey_count = 0;
16.
17. /* Number of values */
18. DWORD value_count;
19.
20. /* Variables for RegEnumValue */
21. TCHAR value_buffer[MAX_VALUE_NAME + 1];
22. TCHAR data_buffer[MAX_VALUE_NAME + 1];
23. DWORD value_size;
24. DWORD data_size;
25.
26. /* Data type for RegEnumValue */
27. DWORD data_type = 0;
28.
29. /* Storage var */
30. char var_storage[MAX_VALUE_NAME + 1];
31.
32. /* Initialize the memory for some variables */
33. class_name_b[0] = '';
34. class_name_b[MAX_PATH] = '';
35.
36. /* We use the class_name, subkey_count and the value count */
37. rc = RegQueryInfoKey(hKey, class_name_b, &class_name_s, NULL,
38. &subkey_count, NULL, NULL, &value_count,
39. NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL);
40. if (rc != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
41. return (0);
42. }
43.
44. /* Get values (if available) */
45. if (value_count) {
46. char *mt_data;
47.
48. /* Clear the values for value_size and data_size */
49. value_buffer[MAX_VALUE_NAME] = '';
50. data_buffer[MAX_VALUE_NAME] = '';
51. var_storage[MAX_VALUE_NAME] = '';
52.
53. /* Get each value */
54. for (i = 0; i < value_count; i++) {
55. value_size = MAX_VALUE_NAME;
56. data_size = MAX_VALUE_NAME;
57.
58. value_buffer[0] = '';
59. data_buffer[0] = '';
60. var_storage[0] = '';
61.
62. rc = RegEnumValue(hKey, i, value_buffer, &value_size,
63. NULL, &data_type, (LPBYTE)data_buffer, &data_size);
64.
65. /* No more values available */
66. if (rc != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
67. break;
68. }
69.
70. /* Check if no value name is specified */
71. if (value_buffer[0] == '') {
72. value_buffer[0] = '@';
73. value_buffer[1] = '';
74. }
75.
76. /* Check if the entry name matches the reg_option */
77. if (strcasecmp(value_buffer, reg_option) != 0) {
78. continue;
79. }
80.
81. /* If a value is not present and the option matches,
82. * we can return ok
83. */
84. if (!reg_value) {
85. return (1);
86. }
87.
88. /* Write value into a string */
89. switch (data_type) {
90. int size_available;
91.
92. case REG_SZ:
93. case REG_EXPAND_SZ:
94. snprintf(var_storage, MAX_VALUE_NAME, "%s", data_buffer);
95. break;
96. case REG_MULTI_SZ:
97. /* Printing multiple strings */
98. size_available = MAX_VALUE_NAME - 3;
99. mt_data = data_buffer;
100.
101. while (*mt_data) {
102. if (size_available > 2) {
103. strncat(var_storage, mt_data, size_available);
104. strncat(var_storage, " ", 2);
105. size_available = MAX_VALUE_NAME -
106. (strlen(var_storage) + 2);
107. }
108. mt_data += strlen(mt_data) + 1;
109. }
110.
111. break;
112. case REG_DWORD:
113. snprintf(var_storage, MAX_VALUE_NAME,
114. "%x", (unsigned int)*data_buffer);
115. break;
116. default:
117. size_available = MAX_VALUE_NAME - 2;
118. for (j = 0; j < data_size; j++) {
119. char tmp_c[12];
120.
121. snprintf(tmp_c, 12, "%02x",
122. (unsigned int)data_buffer[j]);
123.
124. if (size_available > 2) {
125. strncat(var_storage, tmp_c, size_available);
126. size_available = MAX_VALUE_NAME -
127. (strlen(var_storage) + 2);
128. }
129. }
130. break;
131. }
132.
133. /* Check if value matches */
134. if (pt_matches(var_storage, reg_value)) {
135. return (1);
136. }
137.
138. return (0);
139. }
140. }
141.
142. return (0);
143. }
rk_check_dir
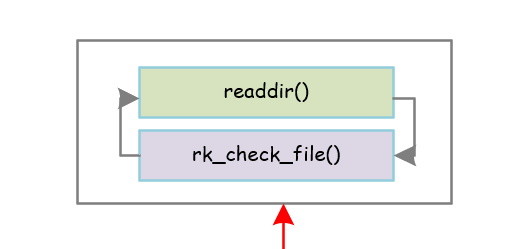
整体框架:
递归遍历目录,具体调用rk_check_file()来检查文件目录是否存在。
具体代码和注释如下:
1. int rk_check_dir(const char *dir, const char *file, char *pattern)
2. {
3. int ret_code = 0;
4. char f_name[PATH_MAX + 2];
5. struct dirent *entry;
6. struct stat statbuf_local;
7. DIR *dp = NULL;
8.
9. f_name[PATH_MAX + 1] = '';
10.
11. dp = opendir(dir);
12. if (!dp) {
13. return (0);
14. }
15.
16. while ((entry = readdir(dp)) != NULL) {
17. /* Ignore . and .. */
18. if ((strcmp(entry->d_name, ".") == 0) ||
19. (strcmp(entry->d_name, "..") == 0)) {
20. continue;
21. }
22.
23. /* Create new file + path string */
24. snprintf(f_name, PATH_MAX + 1, "%s/%s", dir, entry->d_name);
25.
26. /* Check if the read entry matches the provided file name */
27. if (strncasecmp(file, "r:", 2) == 0) {
28. if (OS_Regex(file + 2, entry->d_name)) {
29. if (rk_check_file(f_name, pattern)) {
30. ret_code = 1;
31. }
32. }
33. } else {
34. /* ... otherwise try without regex */
35. if (OS_Match2(file, entry->d_name)) {
36. if (rk_check_file(f_name, pattern)) {
37. ret_code = 1;
38. }
39. }
40. }
41.
42. /* Check if file is a directory */
43. if (lstat(f_name, &statbuf_local) == 0) {
44. if (S_ISDIR(statbuf_local.st_mode)) {
45. if (rk_check_dir(f_name, file, pattern)) {
46. ret_code = 1;
47. }
48. }
49. }
50. }
51.
52. closedir(dp);
53. return (ret_code);
54.
55. }
is_process
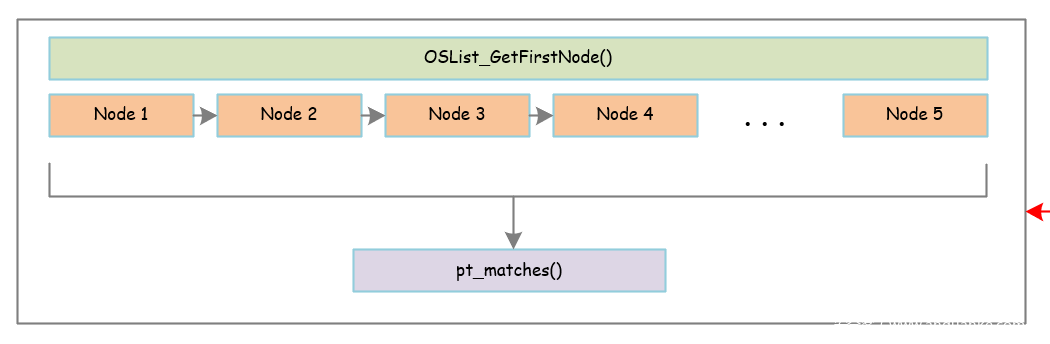
整体框架:
这个函数是用来检查相应的进程是否存在的。
具体是先调用OSList_GetFirstNode()获取第一个进程的信息,进程是以链表的形式进行链接的,所以循环进行检查即可,中间调用pt_matches()进行匹配。
具体源码和注释如下:
1. int is_process(char *value, OSList *p_list)
2. {
3. OSListNode *l_node;
4. if (p_list == NULL) {
5. return (0);
6. }
7. if (!value) {
8. return (0);
9. }
10.
11. l_node = OSList_GetFirstNode(p_list);
12. while (l_node) {
13. Proc_Info *pinfo;
14.
15. pinfo = (Proc_Info *)l_node->data;
16.
17. /* Check if value matches */
18. if (pt_matches(pinfo->p_path, value)) {
19. int i = 0;
20. char _b_msg[OS_SIZE_1024 + 1];
21.
22. _b_msg[OS_SIZE_1024] = '';
23.
24. snprintf(_b_msg, OS_SIZE_1024, " Process: %s.",
25. pinfo->p_path);
26.
27. /* Already present */
28. if (_is_str_in_array(rootcheck.alert_msg, _b_msg)) {
29. return (1);
30. }
31.
32. while (rootcheck.alert_msg[i] && (i < 255)) {
33. i++;
34. }
35.
36. if (!rootcheck.alert_msg[i]) {
37. os_strdup(_b_msg, rootcheck.alert_msg[i]);
38. }
39.
40. return (1);
41. }
42.
43. l_node = OSList_GetNextNode(p_list);
44. }
45.
46. return (0);
47. }
功能测试
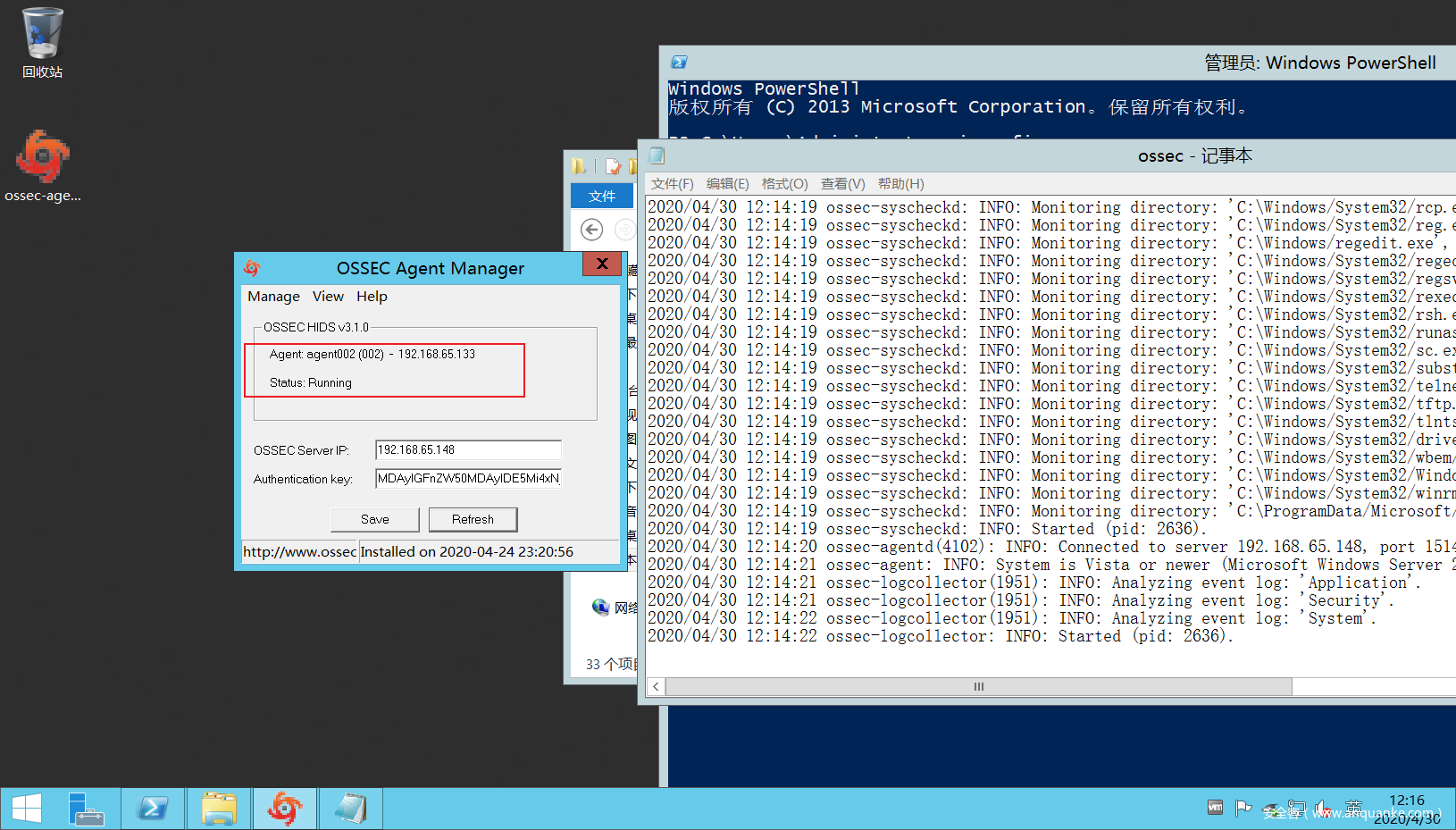
首先windows客户端和用户端建立连接:
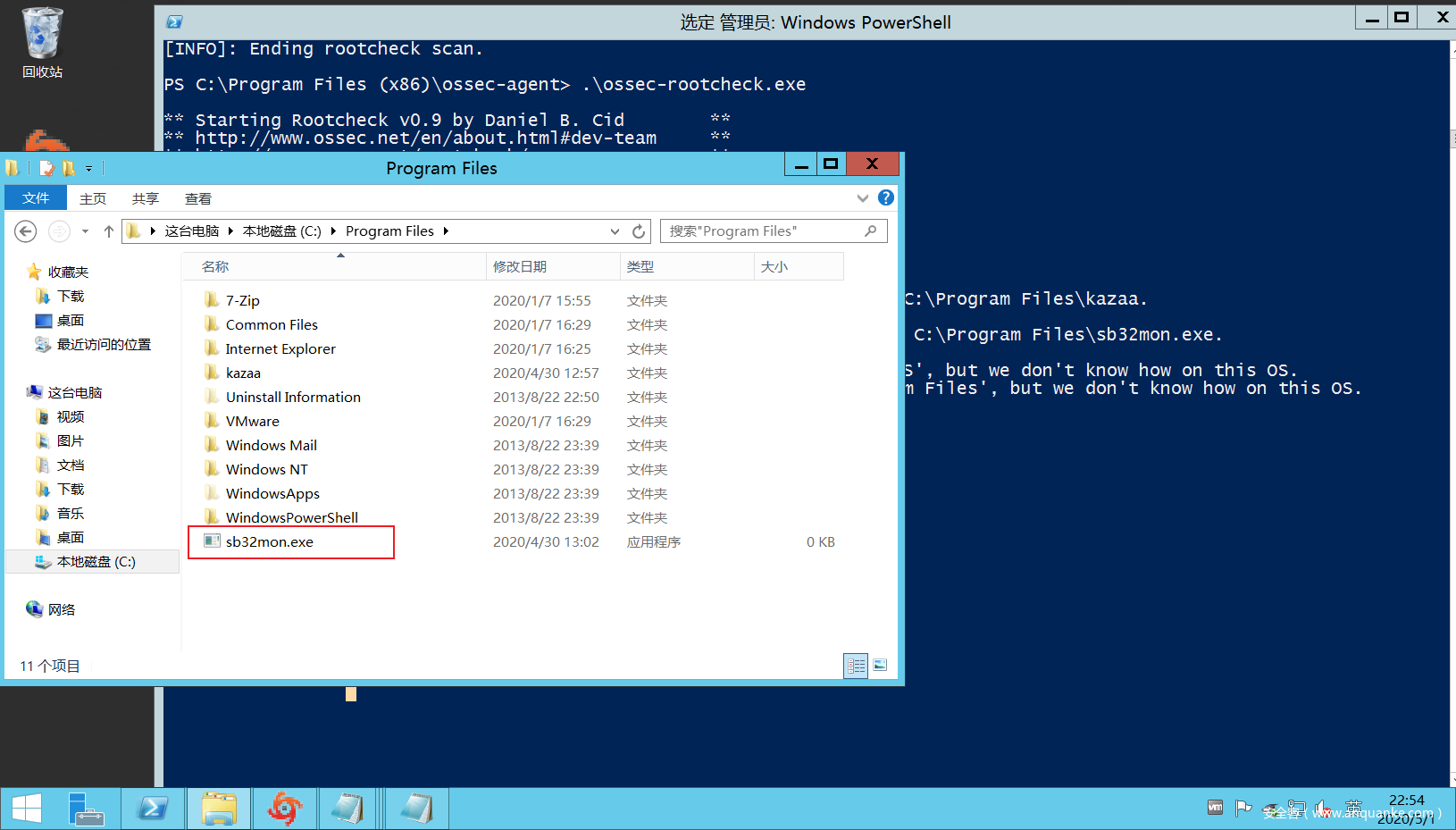
然后为了测试,我们故意在C:Program Files文件夹下放一个sb32mon.exe文件(伪造的rootkit文件),然后运行rootkit_check进行检测。
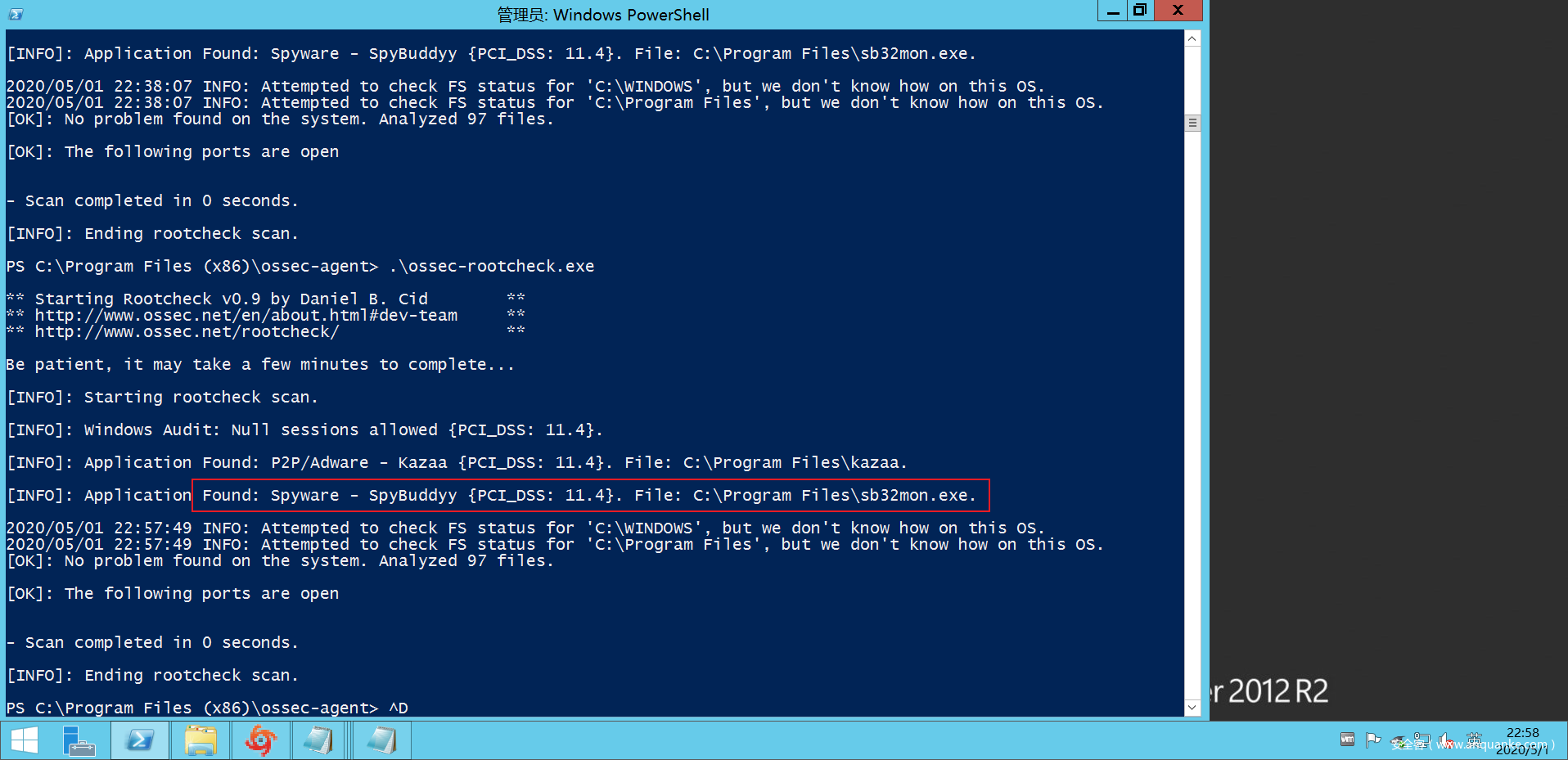
可以看到成功检测到root_kit文件。
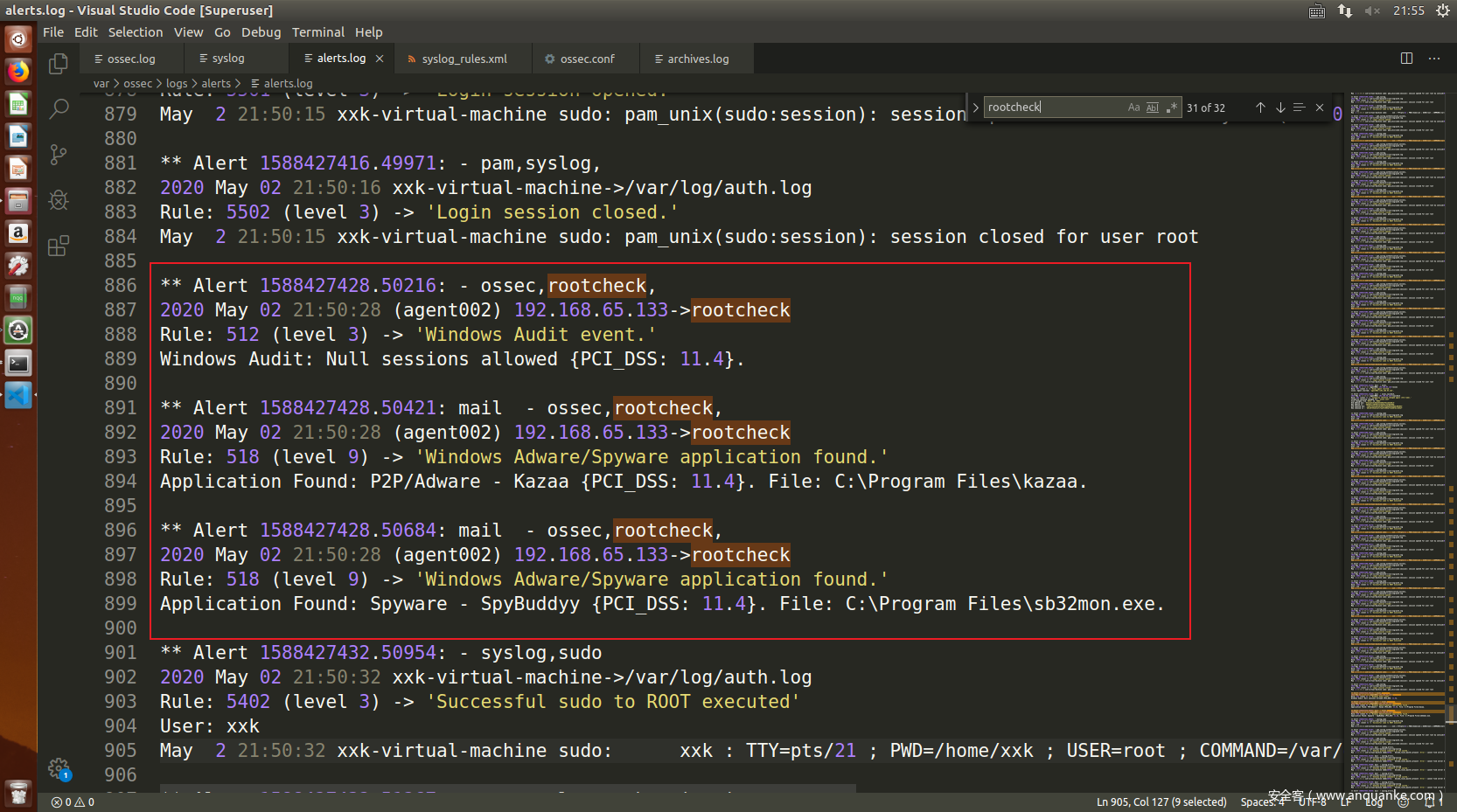
同时在server端也可以看到成功检测的日志:
总结
本文从源码角度分析OSSEC windows rootkit的实现。在具体使用OSSEC进行入侵检测时,知其然,知其所以然才可以在出现故障时更快更好的进行修复与响应。