缘起
疑问
- HTTPS的证书过期是谁来判断?
- HTTPS的证书过期是谁来判断?
- 证书的合法性又是谁检查的呢?
- 什么时候触发?
- 影响性能吗?
- 如何吊销证书?
- HTTPS的请求是客户端(浏览器)发起的,他是如何知道证书被吊销的?
- 验证HTTPS证书的过程是什么样的?
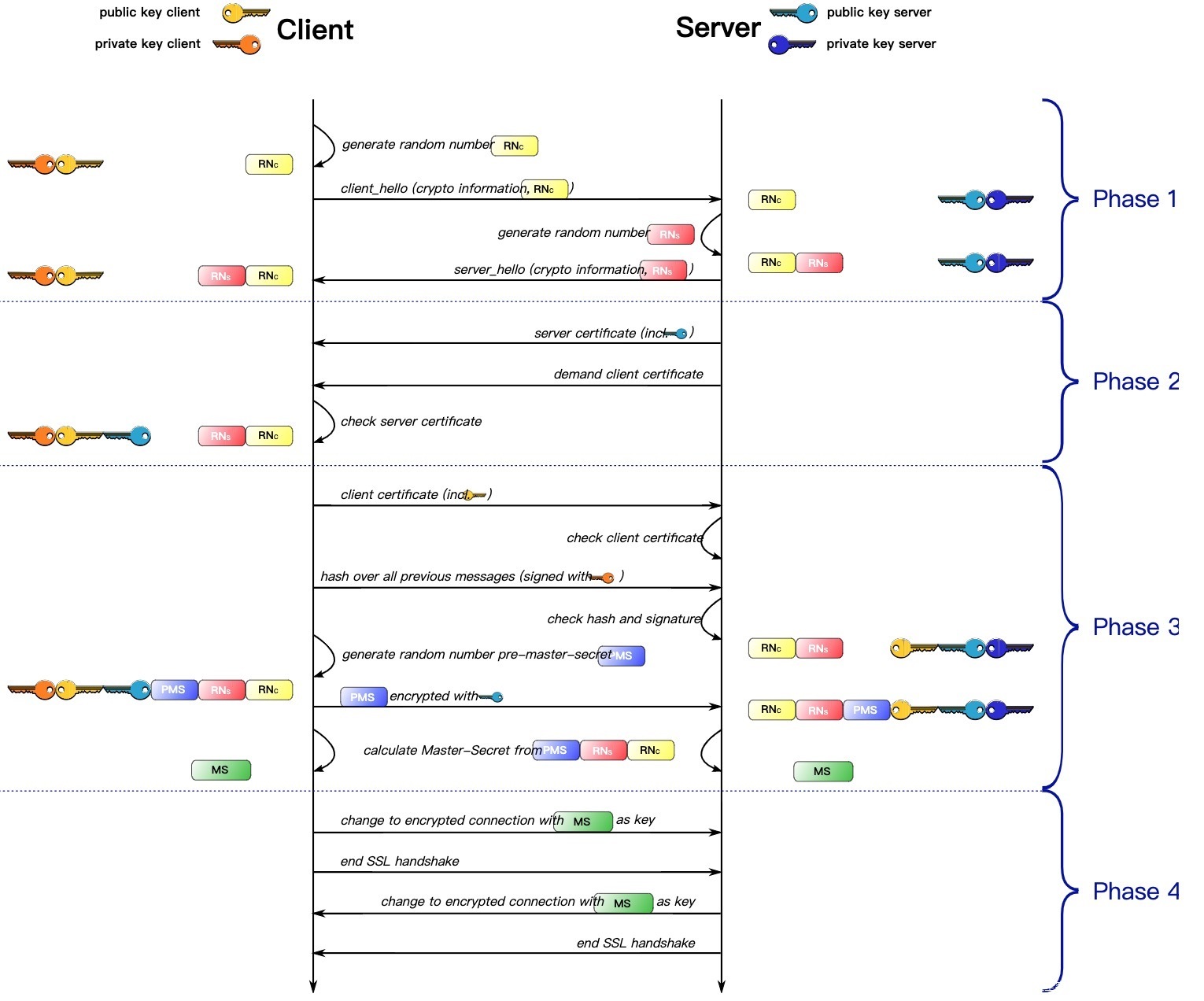
HTTPS通讯过程
(简称解释:RN: Random Number;PMS: Pre Master Secret;MS: Master Secret)
对于第二阶段中的证书检验这块,相信很多人都不太了解,甚至都不知道会检验什么内容,那么下面我们就来了解一下。
证书完整性验证
证书有效性验证
证书吊销状态检测
验证发行者
- 证书发行方issuer,有签名密钥的私钥。
- 证书申请方subject,使用证书公钥进行身份验证的用户 浏览器检查证书的发行者字段与证书路径中上级证书的subject字段相同。
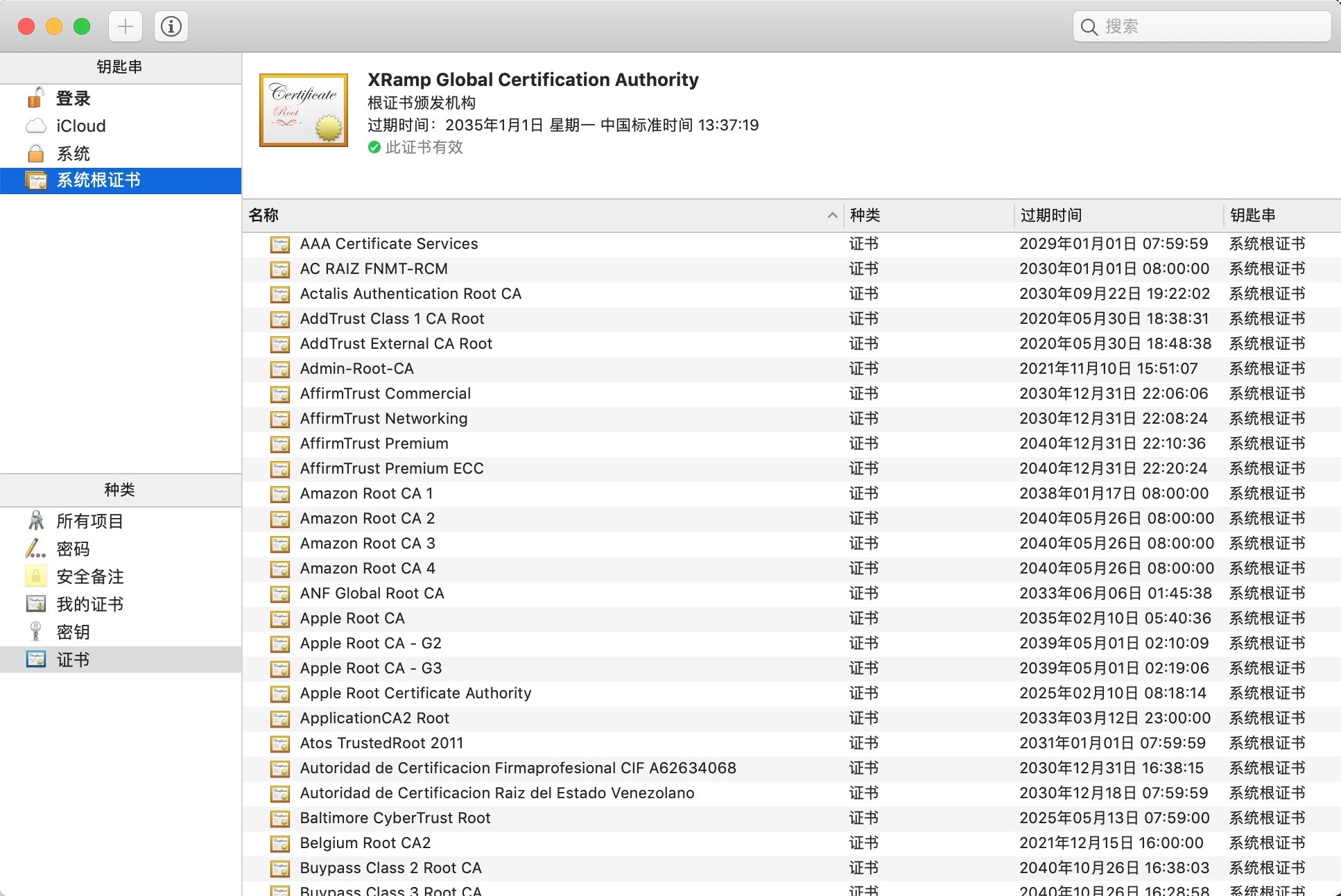
为了增加安全性,PKI在实现时,多数都验证了发型方的密钥、签名等信息是否跟当前证书的密钥相同。但对于信任链来说,根证书自己签发的,也就是说它们的issuer和subject是一样的。
同时,这些CA根证书都是被操作系统、浏览器等直接打入系统的。比如:
检查域名(IP)规范
检查策略约束
证书的吊销状态检测方式
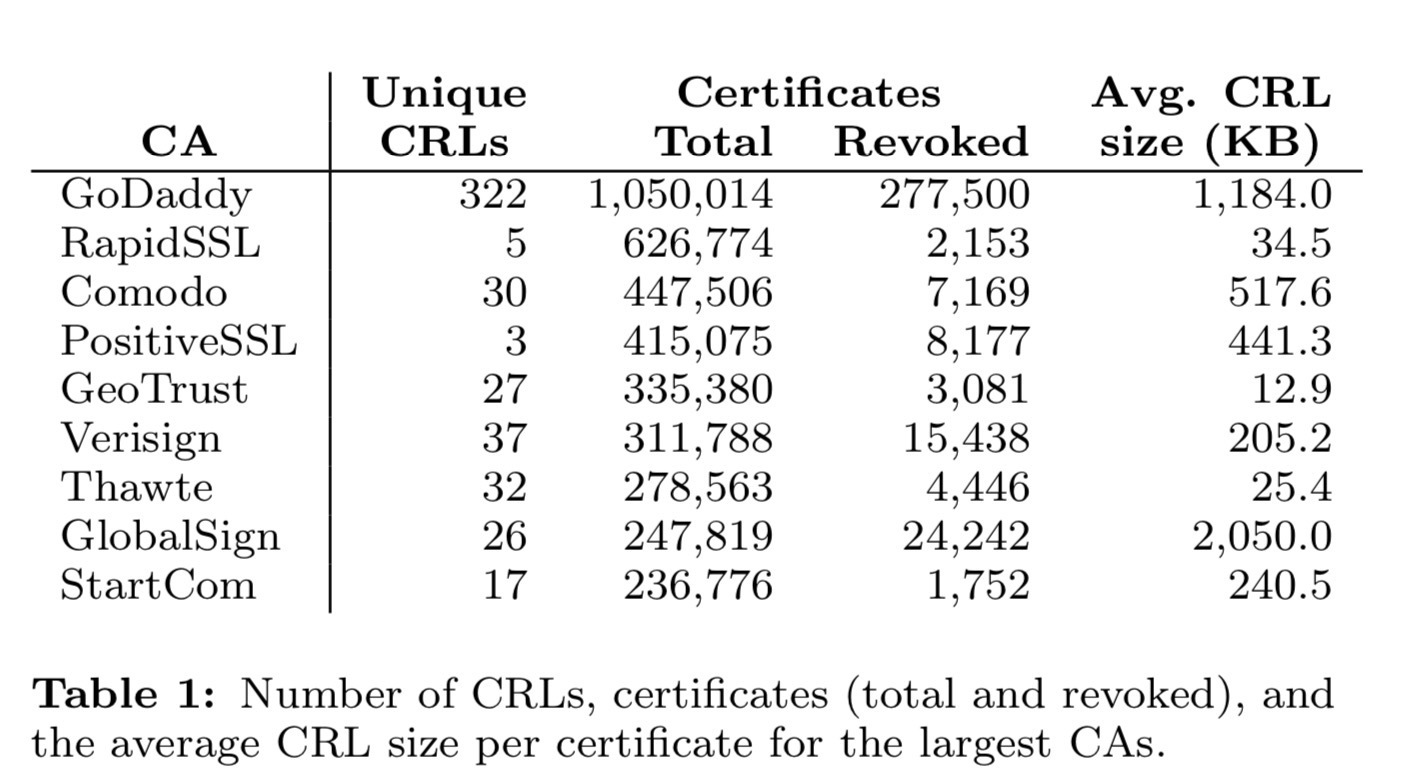
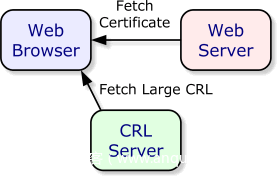
1. Certificate Revocation Lists (CRL)
-
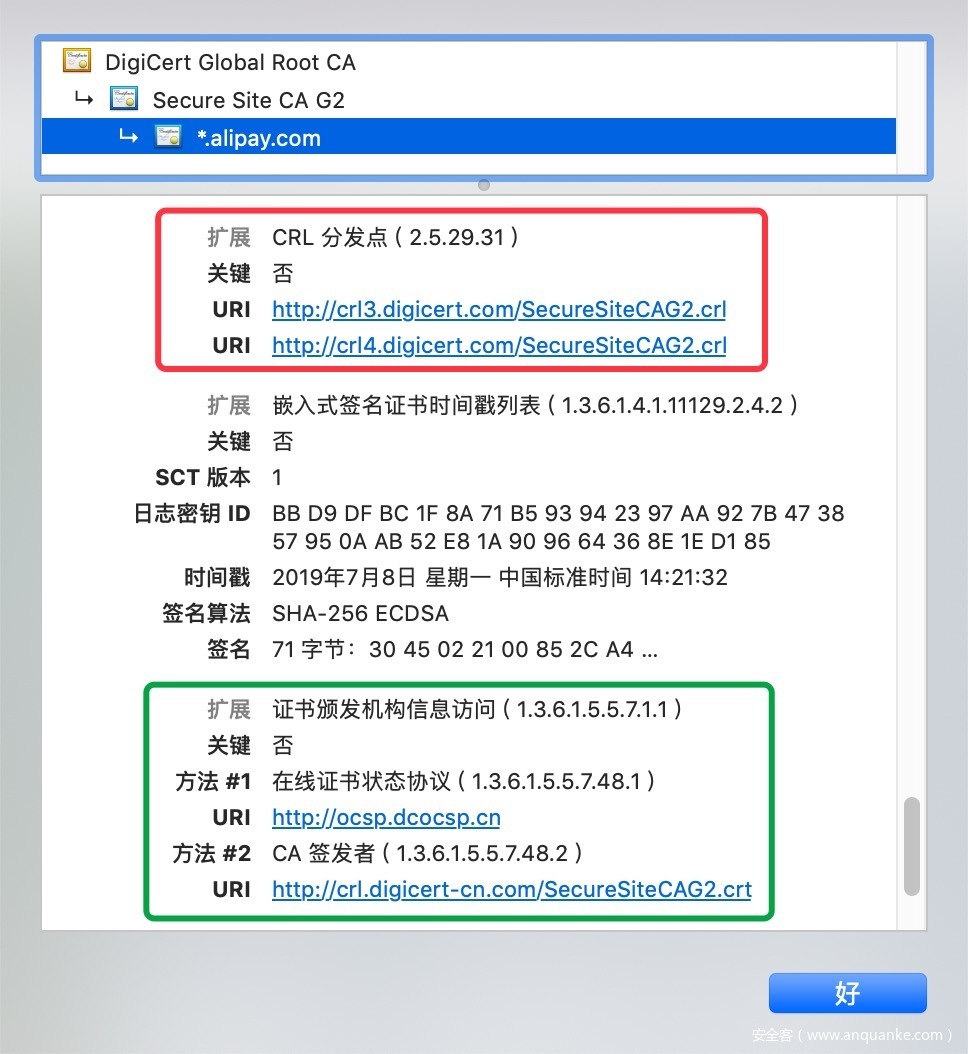
证书的CRL信息
-
CRL 检测流程
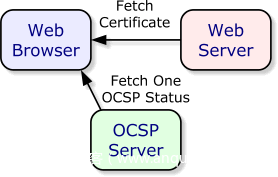
2. Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP)
-
OCSP 检测流程
-
OCSP的优点
-
OCSP的缺点
第一个缺点:浏览器的每次HTTPS请求创建,都需要连接CA OCSP Server进行验证,有的浏览器所在IP与CA OCSP Server的网络并不是通畅的,比如我们村。而且,OCSP的验证有网络IO,花费了很长的时间,严重影响了浏览器访问服务器的用户体验。
-
OCSP机制衍生出来的问题
-
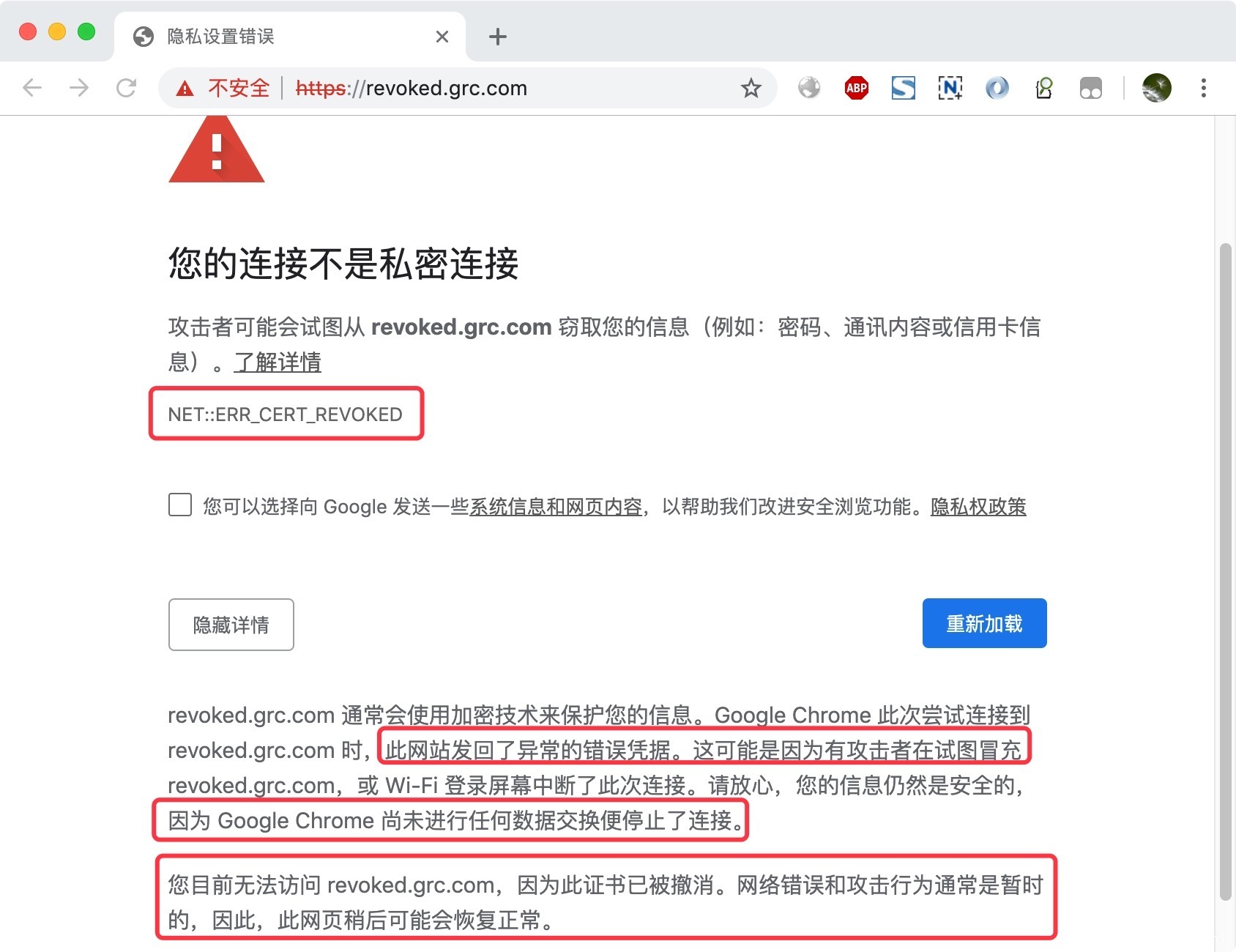
如果你选择拒绝该证书信息,并且拒绝后续的HTTPS通讯,那么这个方式称之为Hard-fail -
如果你选择信任该证书,认为没有被吊销,那么这个方式称之为Soft-fail
如果是hard-fail模式,那浏览器对任何HTTPS服务器访问的先决条件都取决于OCSP Server,这将是一个致命的单点故障,对于具有资深架构设计经验的你来说,你会这么选择吗?
如果是soft-fail模式,取不到OCSP Server的响应就忽略了,那么,要这个机制还有啥意义呢?要你有何用?
-
OCSP Stapling
- 解决了访问慢的问题
-
解决了用户隐私泄露的问题

-
OCSP Must-Staple
-
CA厂商支持
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
subjectAltName = @alt_names
1.3.6.1.5.5.7.1.24 = DER:30:03:02:01:05如果是使用openssl 1.1.0或更高的版本,可以这样设置:[ v3_req ]
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
subjectAltName = @alt_names
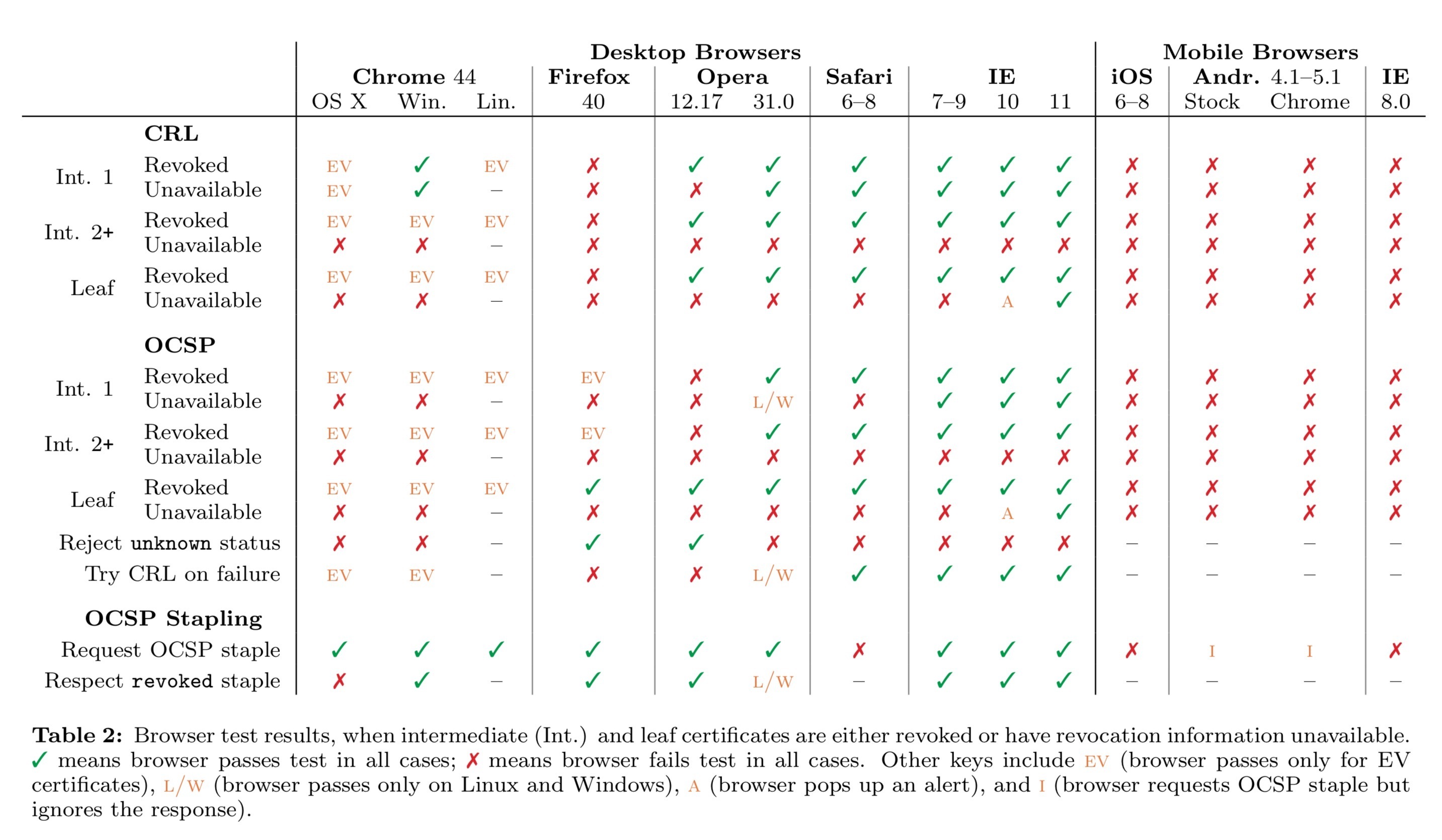
各平台上浏览器对证书吊销的支持情况
1. Mac Safari
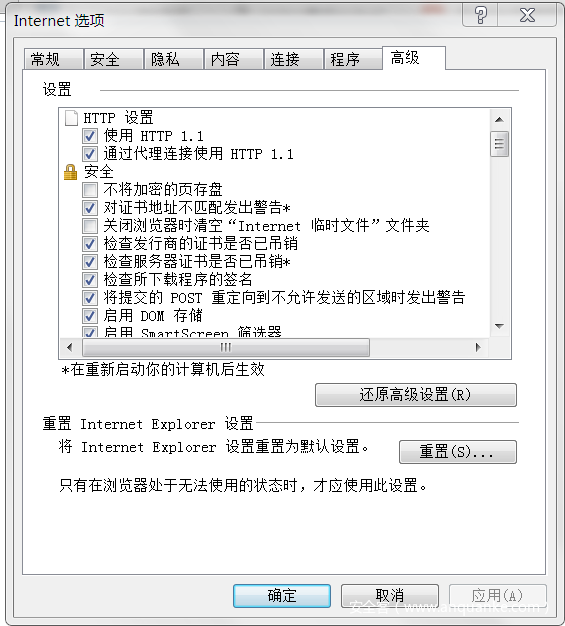
2. Windows Internet Explorer
3. Mozilla Firefox
Firefox 官方短期内并无支持Multi-staple的打算。
方案四:OCSP,跟RFC规范一样。如果OCSP的响应在2秒(EV证书是10秒)内没返回,则直接忽略。
方案五:CRLite,类似Chrome CRLSets的一种检测机制,用于OCSP、OCSP stapling失败后的机制。Firefox的官方计划把这种机制作来代替CRL方式作为主要的检测机制(OCSPOCSP stapling失败后)。
4. Chrome
2012年,Chrome禁用了CRLs、OCSP检测: Google Chrome Will No Longer Check for Revoked SSL Certificates Online ,使用了自行设计的证书校验机制 CRLSets
Stapled OCSP with the Must Staple option (hard-fail if a valid OCSP response is not stapled to the certificate) is a much better solution to the revocation problem than non-stapled OCSP. CAs and browsers are working toward that solution (see the Internet-Draft: http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-hallambaker-tlssecuritypolicy-03).
Additionally, non-stapled OCSP poses a privacy problem: in order to check the status of a certificate, the client must query an OCSP responder for the status of the certificate, thus exposing a user’s HTTPS browsing history to the responder (a third party).
That said, you can use enterprise policies to enable soft-fail OCSP (http://www.chromium.org/administrators/policy-list-3#EnableOnlineRevocationChecks) and hard-fail OCSP for local trust anchors (http://www.chromium.org/administrators/policy-list-3#RequireOnlineRevocationChecksForLocalAnchors).
Chrome performs online checking for Extended Validation certificates if it does not already have a non-expired CRLSet entry covering the domain. If Chrome does not get a response, it simply downgrades the security indicator to Domain Validated.
See also this bug for more discussion of the user-facing UX: https://crbug.com/361820.
但这也不是完美解决了这个问题,来自【An Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Chrome’s CRLSets】:
这篇文章中提到CRLSet的最大问题是包含的证书吊销数据太少,个别情况下占了主流CRL证书吊销信息的2%不到。而且,CRLSets的更新也不是那么及时,chrome为了用户体验,为了性能,为了用户隐私,牺牲了一点点安全性,也是可以理解的。但好像对不起最安全浏览器的称号了。[手动狗头]
汇总
附:WebServer的支持情况
- The Apache web server has supported OCSP stapling since v2.3.3 (ref).
- The nginx web server has supported OCSP stapling since v1.3.7 (ref).
总结
证书泄露的危害
- 具备证书
- 具备域名
- 浏览器访问该服务器
如果几个都具备,那么你就是该网站的官方了。
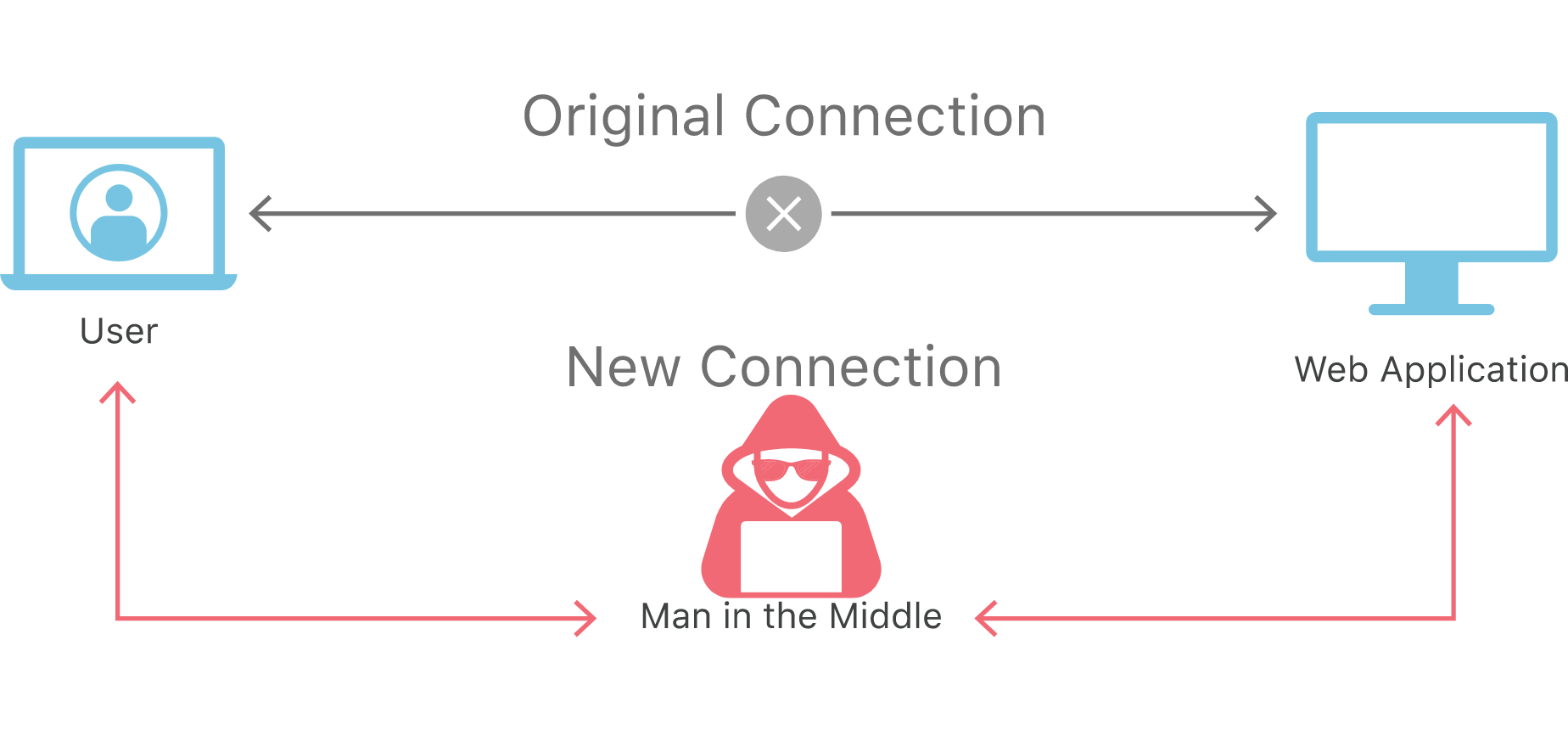
在安全界,有个攻击手段,叫Man-in-the-middle attack中间人攻击,如果证书被黑客拿到,搭建一个具备相同域名的网站,通过DNS污染的方式使得用户浏览器访问该域名,那么可以成为一个反向代理,把用户的请求解析后,伪造程客户端来跟真实的Web服务器通讯,从而获取双方通信的明文信息,达到攻击的目的。
证书泄露了怎么办?
证书泄露了怎么办?从浏览器的支持情况来看,好像及时申请吊销了证书,也不能对丢失的证书起到太大的防范作用,很多浏览器并不是很支持的嘛。
注
参考文献
- RFC3280 Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure Certificate
- High-reliability OCSP stapling and why it matters
- Security Certificate Revocation AwarenessThe case for “OCSP Must-Staple”
- Security Certificate Revocation AwarenessSpecific Implementations
- Security Sidebar: My Browser Has No Idea Your Certificate Was Just Revoked
- SSL certificate revocation and how it is broken in practice
- Revoking Intermediate Certificates: Introducing OneCRL
- Revocation doesn’t work (18 Mar 2011)
- Revocation checking and Chrome’s CRL (05 Feb 2012)
- No, don’t enable revocation checking (19 Apr 2014)
- Revocation still doesn’t work (29 Apr 2014)
- An End-to-End Measurement of Certificate Revocation in the Web’s PKI