作者:o0xmuhe
预估稿费:300RMB
投稿方式:发送邮件至linwei#360.cn,或登陆网页版在线投稿
传送门
【系列分享】Linux 内核漏洞利用教程(二):两个Demo
0x00: 前言
一直想入门linux kernel exploit,但是网络上比较成熟的资料很少,只能找到一些slide和零碎的文档,对于入门选手来说真的很困难。还好在自己瞎摸索的过程中上了joker师傅的装甲车,师傅说:要有开源精神,要给大家学习的机会。
所以就有了这个系列的文章,第一篇记录是环境配置篇,包含了linux内核编译、添加系统调用并测试的过程。在这个过程中我还是遇到很多坑点的,踩了一段时间才把这些坑填好,成功搞定,希望我的经历能给大家一点帮助。
0x01: 环境说明
ubuntu 14.04 x86
qemu使用的内核版本2.6.32.1
busybox版本1.19.4
使用busybox是因为文件添加方便.
0x02: 内核编译并测试
1. 下载内核源码
$ wget https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v2.6/linux-2.6.32.1.tar.gz -O linux-2.6.32.1.tar.gz
$ tar -xjvf linux-2.6.32.1.tar.gz2. 编译过程
首先要安装一些依赖库以及qemu。
$ cd linux-2.6.32.1/
$ sudo apt-get install libncurses5-dev
$ sudo apt-get install qemu qemu-system
$ make menuconfig
$ make
$ make all
$ make modules3. 编译的时候遇到的问题以及解决方案
3.1 问题1
问题
Can't use 'defined(@array)' (Maybe you should just omit the defined()?) at kernel/timeconst.pl line 373.
/home/muhe/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/linux-2.6.32.1/kernel/Makefile:129: recipe for target 'kernel/timeconst.h' failed
make[1]: *** [kernel/timeconst.h] Error 255
Makefile:878: recipe for target 'kernel' failed
make: *** [kernel] Error 2解决方案: 尝试修改这个文件
@val = @{$canned_values{$hz}};
- if (!defined(@val)) {
+ if (!@val) {
@val = compute_values($hz);
}
output($hz, @val);
--3.2 问题2
问题描述
....
arch/x86/kernel/ptrace.c:1472:17: error: conflicting types for ‘syscall_trace_enter’
asmregparm long syscall_trace_enter(struct pt_regs *regs)
^
In file included from /home/muhe/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/arch/x86/include/asm/vm86.h:130:0,
from /home/muhe/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/arch/x86/include/asm/processor.h:10,
from /home/muhe/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/arch/x86/include/asm/thread_info.h:22,
from include/linux/thread_info.h:56,
from include/linux/preempt.h:9,
from include/linux/spinlock.h:50,
from include/linux/seqlock.h:29,
from include/linux/time.h:8,
from include/linux/timex.h:56,
from include/linux/sched.h:56,
from arch/x86/kernel/ptrace.c:11:
/home/muhe/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/arch/x86/include/asm/ptrace.h:145:13: note: previous declaration of ‘syscall_trace_enter’ was here
extern long syscall_trace_enter(struct pt_regs *);
^
arch/x86/kernel/ptrace.c:1517:17: error: conflicting types for ‘syscall_trace_leave’
asmregparm void syscall_trace_leave(struct pt_regs *regs)
^
In file included from /home/muhe/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/arch/x86/include/asm/vm86.h:130:0,
from /home/muhe/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/arch/x86/include/asm/processor.h:10,
from /home/muhe/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/arch/x86/include/asm/thread_info.h:22,
from include/linux/thread_info.h:56,
from include/linux/preempt.h:9,
from include/linux/spinlock.h:50,
from include/linux/seqlock.h:29,
from include/linux/time.h:8,
from include/linux/timex.h:56,
from include/linux/sched.h:56,
from arch/x86/kernel/ptrace.c:11:
/home/muhe/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/arch/x86/include/asm/ptrace.h:146:13: note: previous declaration of ‘syscall_trace_leave’ was here
extern void syscall_trace_leave(struct pt_regs *);
^
make[2]: *** [arch/x86/kernel/ptrace.o] 错误 1
make[1]: *** [arch/x86/kernel] 错误 2
make: *** [arch/x86] 错误 2解决方案
patch patch -p1 < /tmp/1.patch
--- linux-2.6.32.59/arch/x86/include/asm/ptrace.h
+++ fix_ptrace.o_compile_error/arch/x86/include/asm/ptrace.h
@@ -130,6 +130,7 @@
ifdef KERNEL
include
+#include
struct cpuinfo_x86;
struct task_struct;
@@ -142,8 +143,8 @@
int error_code, int si_code);
void signal_fault(struct pt_regs regs, void __user frame, char *where);
-extern long syscall_trace_enter(struct pt_regs );
-extern void syscall_trace_leave(struct pt_regs );
+extern asmregparm long syscall_trace_enter(struct pt_regs );
+extern asmregparm void syscall_trace_leave(struct pt_regs );
static inline unsigned long regs_return_value(struct pt_regs *regs)
{3.3 问题3
问题描述
gcc: error: elf_i386: 没有那个文件或目录
gcc: error: unrecognized command line option ‘-m’解决方案
arch/x86/vdso/Makefile
VDSO_LDFLAGS_vdso.lds = -m elf_x86_64 -Wl,-soname=linux-vdso.so.1 -Wl,-z,max-page-size=4096 -Wl,-z,common-page-size=4096 把"-m elf_x86_64" 替换为 "-m64"
VDSO_LDFLAGS_vdso32.lds = -m elf_i386 -Wl,-soname=linux-gate.so.1中的 "-m elf_i386" 替换为 "-m32"3.4 问题4
问题描述
drivers/net/igbvf/igbvf.h15: error: duplicate member ‘page’
struct page page;
^
make[3]: ** [drivers/net/igbvf/ethtool.o] 错误 1
make[2]: [drivers/net/igbvf] 错误 2
make[1]: [drivers/net] 错误 2
make: * [drivers] 错误 2解决方案
//修改名字重复
struct {
struct page *_page;
u64 page_dma;
unsigned int page_offset;
};
};
struct page *page;
0x03:增加syscall
增加syscall的方式和之前文章写的差不多,只是这次内核版本更低,所以更简单一点。我这里添加了两个系统调用进去。
1. 在syscall table中添加信息
文件 arch/x86/kernel/syscall_table_32.S中添加自己的调用
.long sys_muhe_test
.long sys_hello2. 定义syscall的宏
文件arch/x86/include/asm/unistd_32.h中添加
#define __NR_hello 337
#define __NR_muhe_test 338
#ifdef __KERNEL__
#define NR_syscalls 339要注意NR_syscalls要修改成现有的调用数目,比如原来有0~336一共337个调用,现在增加了两个,那就改成339。
3. 添加函数定义
文件include/linux/syscalls.h
asmlinkage long sys_muhe_test(int arg0);
asmlinkage long sys_hello(void);4. 编写syscall代码
新建目录放自定义syscall的代码
# muhe @ ubuntu in ~/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/linux-2.6.32.1/muhe_test [2:43:06]
$ cat muhe_test.c
#include <linux/kernel.h>
asmlinkage long sys_muhe_test(int arg0){
printk("I am syscall");
printk("syscall arg %d",arg0);
return ((long)arg0);
}
asmlinkage long sys_hello(void){
printk("hello my kernel worldn");
return 0;
}
# muhe @ ubuntu in ~/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/linux-2.6.32.1/muhe_test [2:43:12]
$ cat Makefile
obj-y := muhe_test.o5. 修改Makefile
# muhe @ ubuntu in ~/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/linux-2.6.32.1 [2:44:59]
$ cat Makefile| grep muhe
core-y += kernel/ mm/ fs/ ipc/ security/ crypto/ block/ muhe_test/6. 编译
make -j2我虚拟机分配了两个核,所以使用-j2 这样能稍微快一点。
0x04: busybox编译配置
1. 编译步骤
$ make menuconfig
$ make
$ make install2. 遇到的问题
2.1 问题一以及解决方案
错误
loginutils/passwd.c:188:12: error: ‘RLIMIT_FSIZE’ undeclared (first use in this function)
setrlimit(RLIMIT_FSIZE, &rlimit_fsize);解决
$ vim include/libbb.h
$ add a line #include <sys/resource.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/resource.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>2.2 问题二以及解决方案
错误
linux/ext2_fs.h: 没有那个文件或目录解决
Linux System Utilities --->
[ ] mkfs_ext2
[ ] mkfs_vfat3. 编译完成之后如下配置
1. 方案1
$ cd _install
$ mkdir -pv {bin,sbin,etc,proc,sys,usr/{bin,sbin}}
$ cat init
#!/bin/sh
echo "INIT SCRIPT"
mount -t proc none /proc
mount -t sysfs none /sys
mount -t debugfs none /sys/kernel/debug
mkdir /tmp
mount -t tmpfs none /tmp
mdev -s # We need this to find /dev/sda later
echo -e "nBoot took $(cut -d' ' -f1 /proc/uptime) secondsn"
exec /bin/sh
$ chmod +x init
$ find . -print0
| cpio --null -ov --format=newc
| gzip -9 > /tmp/initramfs-busybox-x86.cpio.gz
$ qemu-system-i386 -kernel arch/i386/boot/bzImage -initrd /tmp/initramfs-busybox-x86.cpio.gz2. 方案2
后面为了方便,使用了另一种方式:
目录结构和之前差不多,添加inittab文件:
$ cat etc/inittab
::sysinit:/etc/init.d/rcS
::askfirst:/bin/ash
::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/reboot
::shutdown:/sbin/swapoff -a
::shutdown:/bin/umount -a -r
::restart:/sbin/init添加rcS文件
$ cat etc/init.d/rcS
#!/bin/sh
#!/bin/sh
mount -t proc none /proc
mount -t sys none /sys
/bin/mount -n -t sysfs none /sys
/bin/mount -t ramfs none /dev
/sbin/mdev -
$ chmod +x ./etc/init.d/rcS配置下dev目录
mkdir dev
sudo mknod dev/ttyAMA0 c 204 64
sudo mknod dev/null c 1 3
sudo mknod dev/console c 5 1
$ find . | cpio -o --format=newc > ../rootfs.img
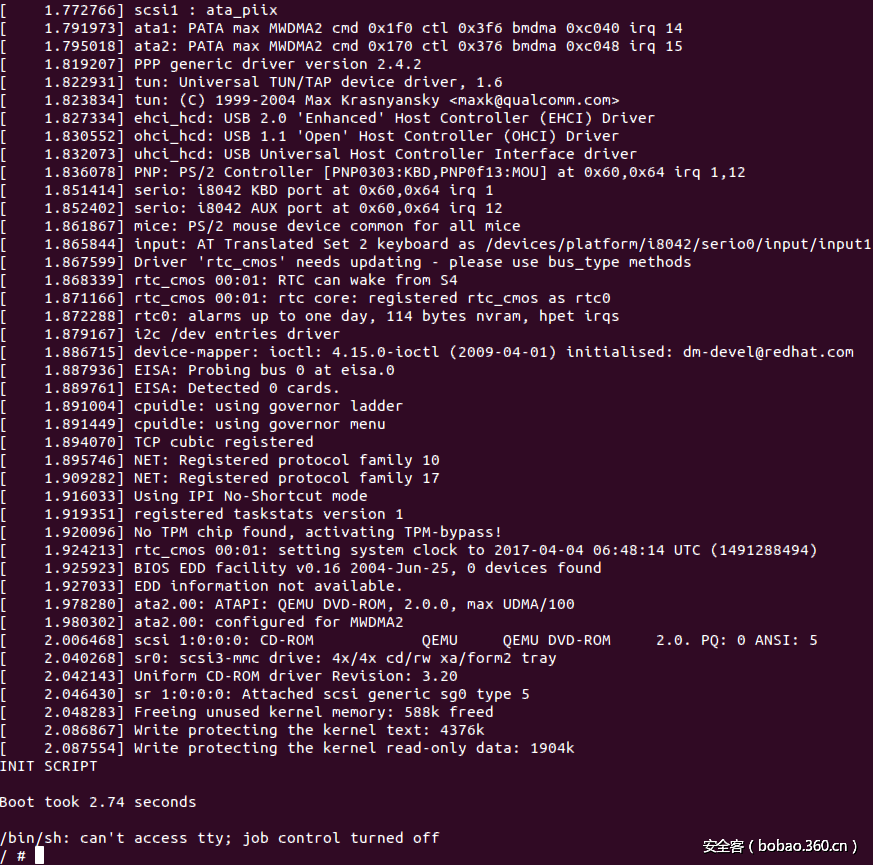
$ qemu-system-i386 -kernel arch/i386/boot/bzImage -initrd ../busybox-1.19.4/rootfs.img -append "root=/dev/ram rdinit=/sbin/init"0x05: 测试系统调用
# muhe @ ubuntu in ~/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/linux-2.6.32.1 [2:45:04]
$ cd muhe_test_syscall_lib
# muhe @ ubuntu in ~/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/linux-2.6.32.1/muhe_test_syscall_lib [2:51:48]
$ cat muhe_test_syscall_lib.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <linux/unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
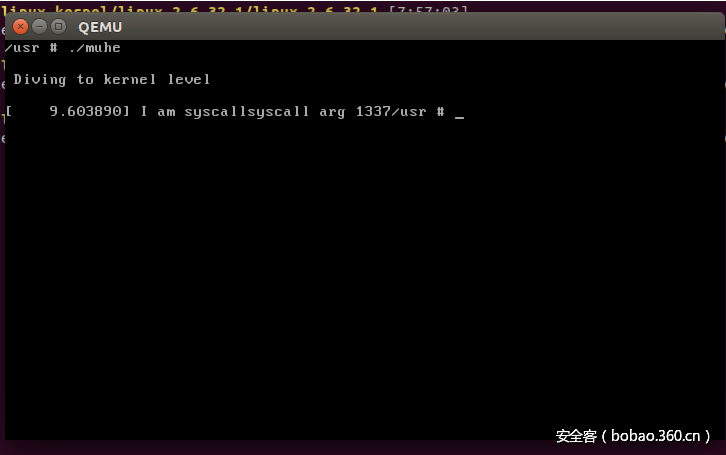
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
printf("n Diving to kernel levelnn");
syscall(337,1337);
return 0;
}
# muhe @ ubuntu in ~/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/linux-2.6.32.1/muhe_test_syscall_lib [2:51:51]
$ gcc muhe_test_syscall_lib.c -o muhe -static一定要静态链接,因为你进busybox链接库那些是没有的。
# muhe @ ubuntu in ~/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/linux-2.6.32.1/muhe_test_syscall_lib [2:52:20]
$ cp muhe_test_syscall_lib/muhe ../busybox-1.19.4/_install/usr/muhe这里要注意,每次拷贝新文件到busybox的文件系统中去,都要执行find . | cpio -o –format=newc > ../rootfs.img去生成新的rootfs。
然后qemu起系统
# muhe @ ubuntu in ~/linux_kernel/linux-2.6.32.1/linux-2.6.32.1 [2:53:33]
$ qemu-system-i386 -kernel arch/i386/boot/bzImage -initrd ../busybox-1.19.4/rootfs.img -append "root=/dev/ram rdinit=/sbin/init"0x06:引用与参考
adding-hello-world-system-call-to-linux
Adding a new system call to the Linux kernel
Adding a system call in X86 QEMU Environment
Setup for linux kernel dev using qemu
root-file-system-for-embedded-system
传送门