前言
最近在学习基于机器学习的入侵检测系统,需要用到大量得网络安全数据集。了解到由加拿大网络安全研究室基于java开发的开源工具Cicflowmeter。该工具输入pcap文件,输出pcap文件中包含的数据包的特征信息,共80多维,以csv表格的形式输出。非常好用,但是网上相关的资料太少了,我需要对Cicflowmeter进行修改增加新的特征提取功能,所以分析了工具的执行流程,这里做一个分享,方便其他用到这个工具的同学快速上手。
Cicflowmeter开源地址https://github.com/ahlashkari/CICFlowMeter
实际运行效果
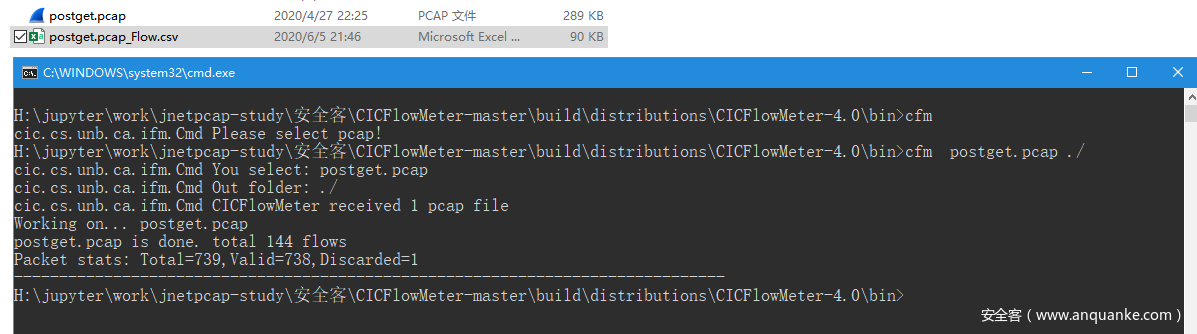
命令行模式:
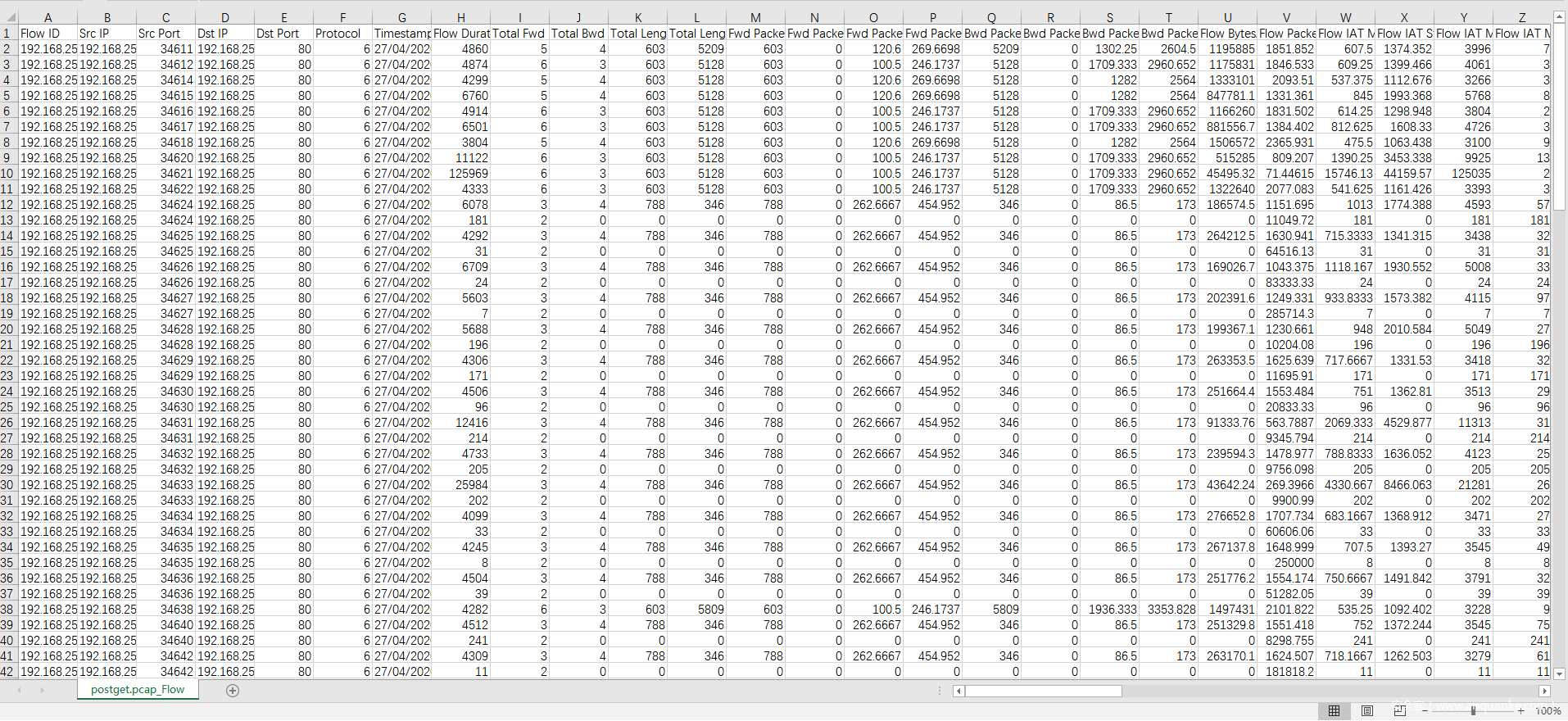
比如这里选择gpostget.pcap, 命令行模式运行就得到postget.pcap_flow.csv
postget.pcap_flow.csv内容为:
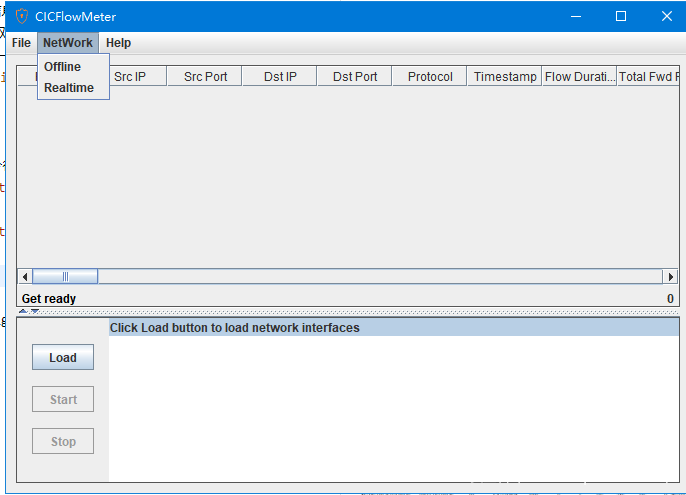
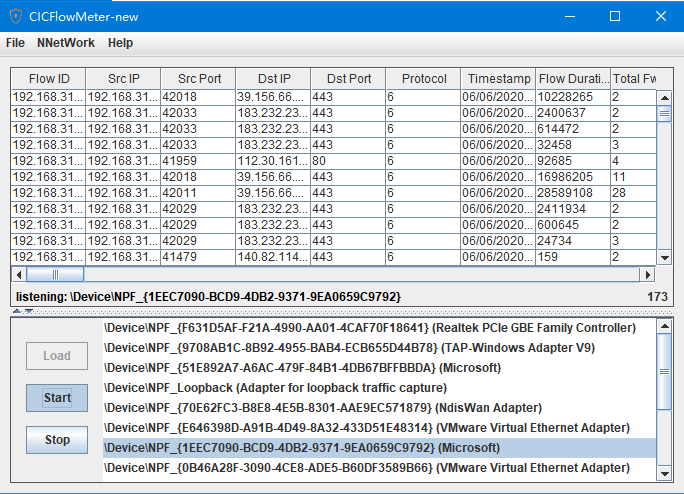
gui界面
可以选择离线模式和实时模式。离线模式与命令行模式相同,选择pcap包,展示抓取的特征。实时模式则实时抓取流量展示抓取的特征。如图所示:
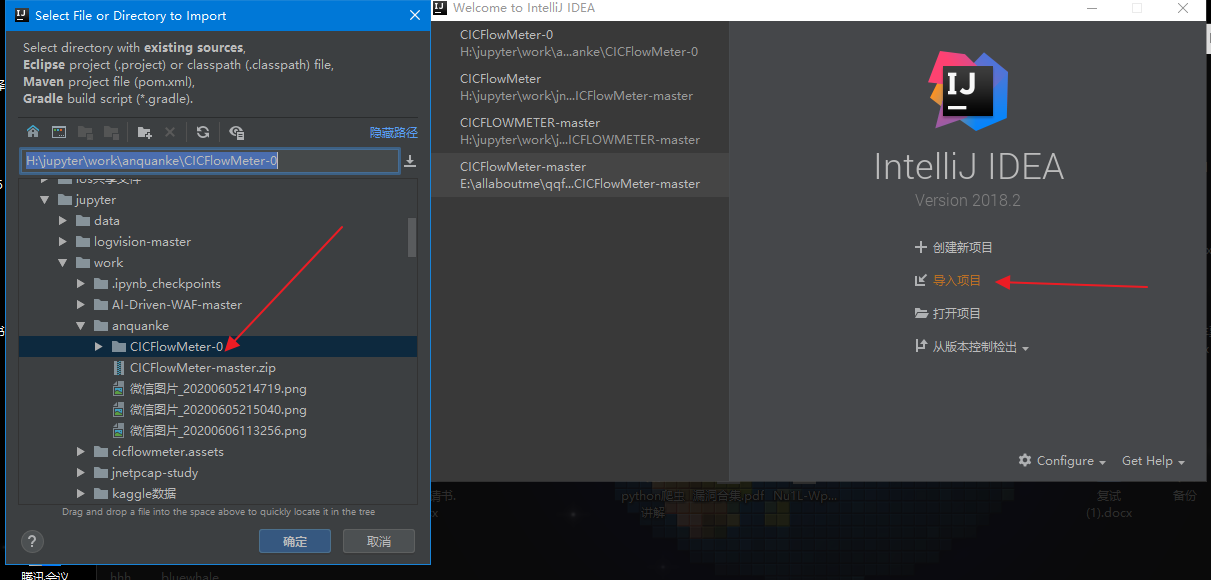
环境安装
我采用的是IntelliJ IDEA,首先从github下载项目文件,然后打开IntelliJ导入项目,导入时选择Gradle,之后运行下面命令即可。
//linux :at the pathtoproject/jnetpcap/linux/jnetpcap-1.4.r1425
//windows: at the pathtoproject/jnetpcap/win/jnetpcap-1.4.r1425
mvn install:install-file -Dfile=jnetpcap.jar -DgroupId=org.jnetpcap -DartifactId=jnetpcap -Dversion=1.4.1 -Dpackaging=jar
环境配好之后:
工具分析
首先介绍一下Cicflowmeter整体的工作逻辑。
提取的80多维特征举例如以下几种:
提取的都是传输层的一些统计信息,以一个TCP流或一个UDP流为一个单位。TCP流以FIN标志为结束,UDP以设置的flowtimeout时间为限制,超过时间就判为结束。在一个TCP流中有很多个数据包,先三次握手而后传输信息再四次挥手。统计一个流中的统计信息作为提取的特征。且统计的特征都分前后向,规定由源地址到目的地址为正向,目的地址到源地址为反向,为每个流构建一个标志叫Flow ID:192.168.31.100-183.232.231.174-46927-443-6,由源地址、目的地址、协议号组成。
由加拿大网络安全研究所公开的网络安全数据集CICIDS2017/2018就是由这个工具从实际网络流量中提取得到的。
下门分析一下代码的工作逻辑:
App,Cmd,CICflowmeter分别是入口文件。Cmd对应命令行模式,App对应gui模式。
首先从Cmd分析起:
public static void main(String[] args) {
long flowTimeout = 120000000L;
long activityTimeout = 5000000L;
String rootPath = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String pcapPath;
String outPath;
/* Select path for reading all .pcap files */
/*if(args.length<1 || args[0]==null) {
pcapPath = rootPath+"/data/in/";
}else {
}*/
/* Select path for writing all .csv files */
/*if(args.length<2 || args[1]==null) {
outPath = rootPath+"/data/out/";
}else {
}*/
if (args.length < 1) {
logger.info("Please select pcap!");
return;
}
pcapPath = args[0];
File in = new File(pcapPath);
if(in==null || !in.exists()){
logger.info("The pcap file or folder does not exist! -> {}",pcapPath);
return;
}
if (args.length < 2) {
logger.info("Please select output folder!");
return;
}
outPath = args[1];
File out = new File(outPath);
if (out == null || out.isFile()) {
logger.info("The out folder does not exist! -> {}",outPath);
return;
}
logger.info("You select: {}",pcapPath);
logger.info("Out folder: {}",outPath);
if (in.isDirectory()) {
readPcapDir(in,outPath,flowTimeout,activityTimeout);
} else {
if (!SwingUtils.isPcapFile(in)) {
logger.info("Please select pcap file!");
} else {
logger.info("CICFlowMeter received 1 pcap file");
readPcapFile(in.getPath(), outPath,flowTimeout,activityTimeout);
}
}
}
共输入两个参数,分别对应pcap文件路径及输出路径。后续处理pcap文件主要使用的是readPcapFile函数:
private static void readPcapFile(String inputFile, String outPath, long flowTimeout, long activityTimeout) {
if(inputFile==null ||outPath==null ) {
return;
}
String fileName = FilenameUtils.getName(inputFile);
if(!outPath.endsWith(FILE_SEP)){
outPath += FILE_SEP;
}
File saveFileFullPath = new File(outPath+fileName+FlowMgr.FLOW_SUFFIX);
if (saveFileFullPath.exists()) {
if (!saveFileFullPath.delete()) {
System.out.println("Save file can not be deleted");
}
}
FlowGenerator flowGen = new FlowGenerator(true, flowTimeout, activityTimeout);
flowGen.addFlowListener(new FlowListener(fileName,outPath));
boolean readIP6 = false;
boolean readIP4 = true;
PacketReader packetReader = new PacketReader(inputFile, readIP4, readIP6);
System.out.println(String.format("Working on... %s",fileName));
int nValid=0;
int nTotal=0;
int nDiscarded = 0;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int i=0;
while(true) {
/*i = (i)%animationChars.length;
System.out.print("Working on "+ inputFile+" "+ animationChars[i] +"r");*/
try{
BasicPacketInfo basicPacket = packetReader.nextPacket();
nTotal++;
if(basicPacket !=null){
flowGen.addPacket(basicPacket);
nValid++;
}else{
nDiscarded++;
}
}catch(PcapClosedException e){
break;
}
i++;
}
flowGen.dumpLabeledCurrentFlow(saveFileFullPath.getPath(), FlowFeature.getHeader());
long lines = SwingUtils.countLines(saveFileFullPath.getPath());
System.out.println(String.format("%s is done. total %d flows ",fileName,lines));
System.out.println(String.format("Packet stats: Total=%d,Valid=%d,Discarded=%d",nTotal,nValid,nDiscarded));
System.out.println(DividingLine);
}
这里flowGen是FlowGenerator类型的对象,而FlowGenerator包含以下内容:
currentFlows = new HashMap<>(); 存储当前所有还未结束的TCP、UDP流
finishedFlows = new HashMap<>();
IPAddresses = new HashMap<>();
finishedFlowCount = 0;
主要流程集中在while循环中,BasicPacketInfo basicPacket = packetReader.nextPacket();
通过这一句从pcap包不断中读取下一个数据包,存储在basicpacket中。
而后flowGen.addPacket(basicPacket);负责将每个数据包添加到对应的流中,在添加的过程中不断地更新每个流的统计特征。
addPacket函数:
public void addFlowListener(FlowGenListener listener) {
mListener = listener;
}
public void addPacket(BasicPacketInfo packet){
if(packet == null) {
return;
}
BasicFlow flow;
long currentTimestamp = packet.getTimeStamp();
String id;
if(this.currentFlows.containsKey(packet.fwdFlowId())||this.currentFlows.containsKey(packet.bwdFlowId())){
if(this.currentFlows.containsKey(packet.fwdFlowId()))
{id = packet.fwdFlowId();}
else {
id = packet.bwdFlowId();}
flow = currentFlows.get(id);
// Flow finished due flowtimeout:
// 1.- we move the flow to finished flow list
// 2.- we eliminate the flow from the current flow list
// 3.- we create a new flow with the packet-in-process
if((currentTimestamp -flow.getFlowStartTime())>flowTimeOut){
if(flow.packetCount()>1){
if (mListener != null) {
mListener.onFlowGenerated(flow);
}
else{
finishedFlows.put(getFlowCount(), flow);
}
//flow.endActiveIdleTime(currentTimestamp,this.flowActivityTimeOut, this.flowTimeOut, false);
}
currentFlows.remove(id);
currentFlows.put(id, new BasicFlow(bidirectional,packet,flow.getSrc(),flow.getDst(),flow.getSrcPort(),flow.getDstPort()));
int cfsize = currentFlows.size();
if(cfsize%50==0) {
logger.debug("Timeout current has {} flow",cfsize);
}
// Flow finished due FIN flag (tcp only):
// 1.- we add the packet-in-process to the flow (it is the last packet)
// 2.- we move the flow to finished flow list
// 3.- we eliminate the flow from the current flow list
}else if(packet.hasFlagFIN()){
logger.debug("FlagFIN current has {} flow",currentFlows.size());
flow.addPacket(packet);
if (mListener != null) {
mListener.onFlowGenerated(flow);
}
else {
finishedFlows.put(getFlowCount(), flow);
}
currentFlows.remove(id);
}else{
flow.updateActiveIdleTime(currentTimestamp,this.flowActivityTimeOut);
flow.addPacket(packet);
currentFlows.put(id,flow);
}
}else{
currentFlows.put(packet.fwdFlowId(), new BasicFlow(bidirectional,packet));
}
}
currentFlows存储当前还未结束得所有TCP、UDP流。
首先this.currentFlows.containsKey(packet.fwdFlowId())判断新加入的数据包是否属于当前所有未结束的流,如果属于当前流则判断正向还是反向,之后判断时间是否超时、不超时则判断是否含有FIN标志,如果两者都不满足,则声明一个BasicFlow对象,根据id从currentFlows中拿到与当前数据包对应的流,调用addPacket将该数据包加入到对应流中。这里addPacket与前面flowGen.addpacket二者并不相同,前者是将数据包存入到对应的流中,后者是将数据包存入到当前所有还未结束的流中,后者对前者有一个调用的关系。如果前面判断不在当前所有未结束的流中,则直接currentFlows.put(packet.fwdFlowId(), new BasicFlow(bidirectional,packet));创建一个新得流,里面只含当前数据包,存入到currentFlows中。如果属于当前某个未结束的流,且超时或存在FIN标志,则说明当前flow结束,超时则从currentFlows中移除对应流,新建flow存入currentFlows中,含FIN标志则直接从currentFlows中移除对应流。结束的flow直接调用onFlowGenerated函数:
public void onFlowGenerated(BasicFlow flow) {
String flowDump = flow.dumpFlowBasedFeaturesEx();
List<String> flowStringList = new ArrayList<>();
flowStringList.add(flowDump);
InsertCsvRow.insert(FlowFeature.getHeader(),flowStringList,outPath,fileName+ FlowMgr.FLOW_SUFFIX);
cnt++;
String console = String.format("%s -> %d flows r", fileName,cnt);
System.out.print(console);
}
onFlowGenerated函数调用dumpFlowBasedFeaturesEx函数及InsertCsvRow.insert将流打印存储起来。
接下里介绍一下将数据包加入到流中的addPacket函数,这里是读取更新数据包及流统计特征的关键函数:
public void addPacket(BasicPacketInfo packet){
updateFlowBulk(packet);
detectUpdateSubflows(packet);
checkFlags(packet);
long currentTimestamp = packet.getTimeStamp();
if(isBidirectional){
this.flowLengthStats.addValue((double)packet.getPayloadBytes());
if(Arrays.equals(this.src, packet.getSrc())){
if(packet.getPayloadBytes() >=1){
this.Act_data_pkt_forward++;
}
this.fwdPktStats.addValue((double)packet.getPayloadBytes());
this.fHeaderBytes +=packet.getHeaderBytes();
this.forward.add(packet);
this.forwardBytes+=packet.getPayloadBytes();
if (this.forward.size()>1)
this.forwardIAT.addValue(currentTimestamp -this.forwardLastSeen);
this.forwardLastSeen = currentTimestamp;
this.min_seg_size_forward = Math.min(packet.getHeaderBytes(),this.min_seg_size_forward);
}else{
this.bwdPktStats.addValue((double)packet.getPayloadBytes());
Init_Win_bytes_backward = packet.getTCPWindow();
this.bHeaderBytes+=packet.getHeaderBytes();
this.backward.add(packet);
this.backwardBytes+=packet.getPayloadBytes();
if (this.backward.size()>1)
this.backwardIAT.addValue(currentTimestamp-this.backwardLastSeen);
this.backwardLastSeen = currentTimestamp;
}
}
else{
if(packet.getPayloadBytes() >=1) {
this.Act_data_pkt_forward++;
}
this.fwdPktStats.addValue((double)packet.getPayloadBytes());
this.flowLengthStats.addValue((double)packet.getPayloadBytes());
this.fHeaderBytes +=packet.getHeaderBytes();
this.forward.add(packet);
this.forwardBytes+=packet.getPayloadBytes();
this.forwardIAT.addValue(currentTimestamp-this.forwardLastSeen);
this.forwardLastSeen = currentTimestamp;
this.min_seg_size_forward = Math.min(packet.getHeaderBytes(),this.min_seg_size_forward);
}
this.flowIAT.addValue(packet.getTimeStamp()-this.flowLastSeen);
this.flowLastSeen = packet.getTimeStamp();
}
updateFlowBulk、detectUpdateSubflows等函数负责更新当前流的统计特征信息,函数其余部分也都是在更新统计特征信息。
整体流程如下:
为工具添加其他特征提取
对于数据包具体信息的提取,主要在最开始入口文件不断获取nextPcap函数中:
public BasicPacketInfo nextPacket(){
PcapPacket packet;
BasicPacketInfo packetInfo = null;
try{
if(pcapReader.nextEx(hdr,buf) == Pcap.NEXT_EX_OK){
packet = new PcapPacket(hdr, buf);
packet.scan(Ethernet.ID);
if(this.readIP4){
packetInfo = getIpv4Info(packet);
if (packetInfo == null && this.readIP6){
packetInfo = getIpv6Info(packet);
}
}else if(this.readIP6){
packetInfo = getIpv6Info(packet);
if (packetInfo == null && this.readIP4){
packetInfo = getIpv4Info(packet);
}
}
if (packetInfo == null){
packetInfo = getVPNInfo(packet);
}
}else{
throw new PcapClosedException();
}
}catch(PcapClosedException e){
logger.debug("Read All packets on {}",file);
throw e;
}catch(Exception ex){
logger.debug(ex.getMessage());
}
return packetInfo;
}
工具可以支持IPv4包和IPv6包,所以会首先进行判断,主要的信息提取是getIpv4Info及getIpv6Info函数。
getIpv4Info:
private static BasicPacketInfo getIpv4Info(PcapPacket packet,Protocol protocol) {
BasicPacketInfo packetInfo = null;
try {
if (packet.hasHeader(protocol.getIpv4())){
packetInfo = new BasicPacketInfo(idGen);
packetInfo.setSrc(protocol.getIpv4().source());
packetInfo.setDst(protocol.getIpv4().destination());
//packetInfo.setTimeStamp(packet.getCaptureHeader().timestampInMillis());
packetInfo.setTimeStamp(packet.getCaptureHeader().timestampInMicros());
/*if(this.firstPacket == 0L)
this.firstPacket = packet.getCaptureHeader().timestampInMillis();
this.lastPacket = packet.getCaptureHeader().timestampInMillis();*/
if(packet.hasHeader(protocol.getTcp())){
packetInfo.setTCPWindow(protocol.getTcp().window());
packetInfo.setSrcPort(protocol.getTcp().source());
packetInfo.setDstPort(protocol.getTcp().destination());
packetInfo.setProtocol(6);
packetInfo.setFlagFIN(protocol.getTcp().flags_FIN());
packetInfo.setFlagPSH(protocol.getTcp().flags_PSH());
packetInfo.setFlagURG(protocol.getTcp().flags_URG());
packetInfo.setFlagSYN(protocol.getTcp().flags_SYN());
packetInfo.setFlagACK(protocol.getTcp().flags_ACK());
packetInfo.setFlagECE(protocol.getTcp().flags_ECE());
packetInfo.setFlagCWR(protocol.getTcp().flags_CWR());
packetInfo.setFlagRST(protocol.getTcp().flags_RST());
packetInfo.setPayloadBytes(protocol.getTcp().getPayloadLength());
packetInfo.setHeaderBytes(protocol.getTcp().getHeaderLength());
}else if(packet.hasHeader(protocol.getUdp())){
packetInfo.setSrcPort(protocol.getUdp().source());
packetInfo.setDstPort(protocol.getUdp().destination());
packetInfo.setPayloadBytes(protocol.getUdp().getPayloadLength());
packetInfo.setHeaderBytes(protocol.getUdp().getHeaderLength());
packetInfo.setProtocol(17);
} else {
int headerCount = packet.getHeaderCount();
for(int i=0;i<headerCount;i++) {
JHeader header = JHeaderPool.getDefault().getHeader(i);
//JHeader hh = packet.getHeaderByIndex(i, header);
//logger.debug("getIpv4Info: {} --description: {} ",header.getName(),header.getDescription());
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
/*
* BufferUnderflowException while decoding header
* havn't fixed, so do not e.printStackTrace()
*/
//e.printStackTrace();
/*packet.scan(protocol.ipv4.getId());
String errormsg = "";
errormsg+=e.getMessage()+"n";
//errormsg+=packet.getHeader(new Ip4())+"n";
errormsg+="********************************************************************************"+"n";
errormsg+=packet.toHexdump()+"n";
logger.error(errormsg);
return null;*/
}
return packetInfo;
}
这里就是对数据包各层数据进行提取,如果我们要修改的话,需要在basicPacket中定义对应的变量,而后在getIpv4Info中为变量赋值。同样也需要在BasciFlow中定义对应的统计特征变量,这里是在updateFlowBulk等更新流统计特征的函数中进行赋值。
最后还需要在dumpFlowBasedFeaturesEx等最后打印统计好的流特征函数中添加打印新定义得特征。
这里对于数据包信息的提取使用的都是java下的jnetpcap库,相关资料也比较少,我也是摸索了有段时间才摸索出来,这里贴出我提取应用层url、cookie等信息的代码给大家参考:
if(packet.hasHeader(this.http)){
packetInfo.setUrl(this.http.fieldValue(Http.Request.RequestUrl));
try {
if (this.http.fieldValue(Http.Request.RequestMethod).equals("GET")) {
packetInfo.setHttp_get(true);
} else if (this.http.fieldValue(Http.Request.RequestMethod).equals("POST")) {
packetInfo.setHttp_post(true);
String post_payload = byteArrayToStr(this.http.getPayload());
packetInfo.setPost_payload(post_payload);
System.out.printf("http post payload::%s%n", post_payload);
}
}catch (Exception e) {
packetInfo.setHttp_http(true);
}
String cookies = this.http.fieldValue(Http.Request.Cookie);
packetInfo.setCookies(cookies);
最终修改完成之后,进入项目目录,执行
//linux:
$ gradle distZip
//window
$ gradlew distZip
即可在CICFlowMeter-masterbuilddistributions中找到生成的可执行文件。