作者:唐银@涂鸦智能安全实验室
一、etcd简介
etcd是一个具有强一致性的分布式 key-value 存储组件。采用类似目录结构的方式对数据进行存储,仅在叶子结点上存储数据,叶子结点的父节点为目录,不能存储数据。
“etcd”这个名字源自两个想法:unix “/etc” 目录和 “d” istributed 分布式系统。“/etc” 目录是用于存储单个系统的配置数据的位置,而 etcd 用于存储大规模分布式的配置信息。因此,加了 “d” 的 “/etc” 就是 “etcd”。
etcd使用比较多的场景包括服务注册与发现、键值对存储、消息发布订阅等。
在kubernetes中,etcd存储集群状态和配置信息,以用于服务发现和集群管理。
二、测试环境搭建
测试环境说明:
- etcdctl在本机运行;
- etcd集群部署在虚拟机中的docker下;
- 虚拟机环境:CentOS 7;
- 虚拟机ip:192.168.126.143
首先拉取etcd镜像
docker pull quay.io/coreos/etcd:v3.3.1
# 查看镜像
docker images
创建自定义网络
docker network create --driver bridge --subnet=172.16.1.0/16 --gateway=172.16.1.1 mynet
# 查看网络
docker network ls
创建etcd节点
节点1:
docker run -d -p 23791:2379 -p 23801:2380 \
--name etcdnode1 \
--network=mynet \
--ip 172.16.2.1 \
quay.io/coreos/etcd:v3.3.1 \
etcd -name etcdnode1 \
-advertise-client-urls http://172.16.2.1:2379 \
-initial-advertise-peer-urls http://172.16.2.1:2380 \
-listen-client-urls http://0.0.0.0:2379 \
-listen-peer-urls http://0.0.0.0:2380 \
-initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster \
-initial-cluster "etcdnode1=http://172.16.2.1:2380,etcdnode2=http://172.16.2.2:2380,etcdnode3=http://172.16.2.3:2380" \
-initial-cluster-state new
节点2
docker run -d -p 23792:2379 -p 23802:2380 \
--name etcdnode2 \
--network=mynet \
--ip 172.16.2.2 \
quay.io/coreos/etcd:v3.3.1 \
etcd -name etcdnode2 \
-advertise-client-urls http://172.16.2.2:2379 \
-initial-advertise-peer-urls http://172.16.2.2:2380 \
-listen-client-urls http://0.0.0.0:2379 \
-listen-peer-urls http://0.0.0.0:2380 \
-initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster \
-initial-cluster "etcdnode1=http://172.16.2.1:2380,etcdnode2=http://172.16.2.2:2380,etcdnode3=http://172.16.2.3:2380" \
-initial-cluster-state new
节点3:
docker run -d -p 23793:2379 -p 23803:2380 \
--name etcdnode3 \
--network=mynet \
--ip 172.16.2.3 \
quay.io/coreos/etcd:v3.3.1 \
etcd -name etcdnode3 \
-advertise-client-urls http://172.16.2.3:2379 \
-initial-advertise-peer-urls http://172.16.2.3:2380 \
-listen-client-urls http://0.0.0.0:2379 \
-listen-peer-urls http://0.0.0.0:2380 \
-initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster \
-initial-cluster "etcdnode1=http://172.16.2.1:2380,etcdnode2=http://172.16.2.2:2380,etcdnode3=http://172.16.2.3:2380" \
-initial-cluster-state new
参数说明:
| 参数项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -name | etcd集群中的节点名,各节点可区分不重复即可。 |
| -advertise-client-urls | 客户端(etcdctl/curl等)与当前节点通信的URL。 |
| -initial-advertise-peer-urls | 其他节点与当前节点通信的URL。 |
| -listen-client-urls | 当前节点监听的URL,用于跟客户端通信。 |
| -listen-peer-urls | 当前节点监听的URL,用于其他节点与当前节点通信,集群内部将通过这些URL进行数据交互(如选举,数据同步等)。 |
| -initial-cluster-token | 启动集群的时候指定集群token,只有token相同的节点才能加入到同一集群。当使用相同配置再启动一个集群时,只要该 token 值不一样,etcd 集群就不会相互影响。 |
| -initial-cluster | 所有集群节点的url列表。 |
| -initial-cluster-state | 初始化集群状态,默认为new,也可以指定为existing表示要加入到一个已有集群。 |
# 查看docker进程
docker ps
更多的安装和部署方式可参考:
http://blueskykong.com/2020/05/27/etcd-2/
http://blueskykong.com/2020/06/06/etcd-3/
三、未授权访问利用
刚刚我们搭建好的etcd环境,没有经过特殊配置,默认是未经授权即可访问的。
使用官方提供的etcdctl直接用命令行即可访问etcd,无需去了解每个http api。
下载etcd:https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd/releases
解压后在命令行中进入etcd目录下。
etcdctl api版本切换:
export ETCDCTL_API=2
export ETCDCTL_API=3
切换版本后可以执行etcdctl -h命令查看帮助。
目前网上的公开文章大部分都是在讲v2版本api的利用,比如:
直接访问http://ip:2379/v2/keys/?recursive=true ,可以看到所有的key-value值。
或者使用etcdctl:
etcdctl --endpoints="http://ip:2379" ls
etcd v3版本的api和v2版本完全不同,所以访问上面的url不会看到任何数据。这里主要简单介绍一下v3版本api的使用。
搭建好上面的测试环境后,可以执行以下命令,向etcd中插入几条测试数据:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 put /testdir/testkey1 "Hello world1"
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 put /testdir/testkey2 "Hello world2"
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 put /testdir/testkey3 "Hello world3"
查看指定key的值:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 get /testdir/testkey1
执行下面命令即可读取etcd中存储的所有数据:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 get / --prefix
--prefix用来指定前缀,上述命令的意思就是获取所有“/”作为前缀的key value值
如果结果过多,还可以通过--limit选项限制数量:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 get / --prefix --limit=2
下面命令可用于列出当前目标所属同一集群的所有节点:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 member list
更多etcdctl使用示例可以在压缩包中的:README-etcdctl.md、READMEv2-etcdctl.md文档里查看,分别对应v3、v2版本api。
四、未授权访问可能产生的风险
kubernetes的master会安装etcd v3用来存储数据,如果管理员进行了错误的配置,导致etcd未授权访问的情况,那么攻击者就可以从etcd中拿到kubernetes的认证鉴权token,从而接管集群。
在真实的场景中,还有一些应用使用etcd来存储各种服务的账号密码、公私钥等敏感数据。而很多etcd服务的使用者完全没有考虑过其安全风险,这种情况和redis的使用情况差不多,在企业内网比较普遍,甚至也有少部分人会将其开放到公网。
更多关于etcd未授权访问风险的描述可参考:https://gcollazo.com/the-security-footgun-in-etcd/
五、如何安全的使用etcd(修复方案)
etcd目前支持两种安全方案,分别解决了不同问题。
1、basic认证(基于角色的访问控制)
这种安全方案解决了用户认证和权限管理的问题。
etcd在2.1版本之前,是一个完全开放的系统,任何人都可以通过rest api对etcd数据进行增删改查。2.1版本之后,引入了用户认证功能,并且支持权限管理。但为了向前兼容,默认并未开启,需要手动启用。
etcd 2.x版本开启basic认证的相关命令和etcd 3.x版本有所区别,可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/ucmir183/article/details/84454506
此处主要讲解etcd 3.x版本开启basic认证的过程。首先创建root用户:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 user add root
如图,输入密码,重复输入并确认密码后创建成功:
接下来执行下面命令启用认证:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 auth enable
启用认证后会自动为root账号创建一个root角色,该角色拥有全部etcd数据的读写权限。接下来访问etcd就必须要带着账号密码了。
例如:
查看所有角色:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 --user root:password role list
查看所有用户:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 --user root:password user list
创建一个新的角色:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 --user root:password role add staff
授予staff角色/testdir/testkey1只读权限:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 --user root:password role grant-permission staff read /testdir/testkey1
授予staff角色/pub/作为key前缀的所有数据读写权限:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 --user root:password role grant-permission staff --prefix=true readwrite /pub/
查看staff角色权限:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 --user root:password role get staff
结果如图:
创建一个新用户:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 --user root:password user add staffuser1
同样需要输入要创建用户的密码。
授予staffuser1用户staff角色权限:
etcdctl --endpoints=192.168.126.143:23791 --user root:password user grant-role staffuser1 staff
创建后的staffuser1用户将拥有我们之前配置的staff角色的数据访问权限。
更多访问控制相关命令可参考官方文档:https://etcd.io/docs/v3.4/op-guide/authentication/
2、基于TLS的身份验证和数据传输
互联网中所有明文传输数据的方式,都面临三个风险:窃听、篡改和冒充。SSL/TLS协议的出现解决了这三个问题。
基于TLS的身份验证方式既解决了传输安全的问题,也可以用来解决未授权访问的问题。
TLS协议的原理不在这里赘述,如果不了解可以自行查阅相关资料。接下来主要讲etcd如何使用TLS进行身份验证和数据传输的实践。
首先我们需要下载cfssl:https://github.com/cloudflare/cfssl/releases
cfssl 是 CloudFlare 的 PKI证书管理工具。
下载cfssl-certinfo_1.5.0_linux_amd64、cfssljson_1.5.0_linux_amd64、cfssl_1.5.0_linux_amd64这三个文件,下载后全部移动到/usr/local/bin/目录下。
[root@localhost Downloads]# mv cfssl_1.5.0_linux_amd64 /usr/local/bin/cfssl
[root@localhost Downloads]# mv cfssljson_1.5.0_linux_amd64 /usr/local/bin/cfssljson
[root@localhost Downloads]# mv cfssl-certinfo_1.5.0_linux_amd64 /usr/local/bin/cfssl-certinfo
[root@localhost Downloads]# ls /usr/local/bin/cfssl*
/usr/local/bin/cfssl /usr/local/bin/cfssl-certinfo /usr/local/bin/cfssljson
创建将要存放PKI配置和证书的目录,并进入目录下:
[root@localhost /]# mkdir /etc/etcd/pki -p
[root@localhost /]# cd /etc/etcd/pki/
2.1 创建CA根证书
[root@localhost pki]# vi ca-csr.json
填入下面内容:
{
"CN": "ETCD Root CA",
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "CN",
"L": "Shanghai",
"ST": "Shanghai"
}
]
}
生成根证书和key
[root@localhost pki]# cfssl gencert -initca ca-csr.json | cfssljson -bare ca
[root@localhost pki]# ls
ca.csr ca-csr.json ca-key.pem ca.pem
2.2 签发证书配置文件
我们需要签发三种证书,创建ca-config.json文件,定义三个profile:
{
"signing": {
"default": {
"expiry": "168h"
},
"profiles": {
"server": {
"expiry": "8760h",
"usages": [
"signing",
"key encipherment",
"server auth"
]
},
"client": {
"expiry": "8760h",
"usages": [
"signing",
"key encipherment",
"client auth"
]
},
"peer": {
"expiry": "8760h",
"usages": [
"signing",
"key encipherment",
"server auth",
"client auth"
]
}
}
}
}
其中,server作为服务端与客户端通信时的服务端证书,client作为服务端与客户端通信时的客户端证书,peer作为集群节点之间的通信证书。
2.3 生成服务端证书
创建etcd-server.json文件
{
"CN": "etcd server",
"hosts": [
"172.16.2.1",
"172.16.2.2",
"172.16.2.3",
"192.168.126.143"
],
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "CN",
"L": "Shanghai",
"ST": "Shanghai"
}
]
}
生成服务端证书:
[root@localhost pki]# cfssl gencert -ca=ca.pem -ca-key=ca-key.pem -config=ca-config.json -profile=server etcd-server.json | cfssljson -bare server
2021/03/31 07:24:58 [INFO] generate received request
2021/03/31 07:24:58 [INFO] received CSR
2021/03/31 07:24:58 [INFO] generating key: rsa-2048
2021/03/31 07:24:58 [INFO] encoded CSR
2021/03/31 07:24:58 [INFO] signed certificate with serial number 545742070794152469099370572346380711975550497369
[root@localhost pki]# ls
ca-config.json ca-csr.json ca.pem server.csr server.pem
ca.csr ca-key.pem etcd-server.json server-key.pem
上面这种方式,把所有节点的ip都写到了hosts中,集群成员使用统一的服务端证书。生产环境一般把hosts写成统一的对外域名。也可以分开创建三个配置文件,每个配置文件里面填写一个ip,不公用,这样方便后面扩容。
2.4 生成客户端证书
创建etcd-client.json文件,因为客户端证书仅用于签发验证客户端身份,因此不需要hosts字段。
{
"CN": "etcd client",
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "CN",
"L": "Shanghai",
"ST": "Shanghai"
}
]
}
生成客户端证书:
[root@localhost pki]# cfssl gencert -ca=ca.pem -ca-key=ca-key.pem -config=ca-config.json -profile=client etcd-client.json | cfssljson -bare client
由于没有填写hosts字段,因此会有“[WARNING] This certificate lacks a “hosts” field. ”的警告,忽略就好。
2.5 生成peer节点通信证书
创建etcd-peer.json文件:
{
"CN": "etcd peer",
"hosts": [
"172.16.2.1",
"172.16.2.2",
"172.16.2.3"
],
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "CN",
"L": "Shanghai",
"ST": "Shanghai"
}
]
}
生成peer节点通信证书:
[root@localhost pki]# cfssl gencert -ca=ca.pem -ca-key=ca-key.pem -config=ca-config.json -profile=peer etcd-peer.json | cfssljson -bare peer
2.6 重新创建带TLS传输认证的etcd集群
首先停止运行之前创建的etcd集群,并将其删除。
[root@localhost w4ter0]# docker stop $(docker ps -a -q)
9cc6afc100ad
56148a0ebae2
43ef4286ca34
[root@localhost w4ter0]# docker rm $(docker ps -a -q)
9cc6afc100ad
56148a0ebae2
43ef4286ca34
执行下面命令创建新的etcd集群。
节点1:
docker run -d -p 23791:2379 -p 23801:2380 \
-v /etc/etcd/pki:/pki \
--name etcdnode1 \
--network=mynet \
--ip 172.16.2.1 \
quay.io/coreos/etcd:v3.3.1 \
etcd -name etcdnode1 \
-advertise-client-urls https://172.16.2.1:2379 \
-initial-advertise-peer-urls https://172.16.2.1:2380 \
-listen-client-urls https://0.0.0.0:2379 \
-listen-peer-urls https://0.0.0.0:2380 \
-initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster \
-initial-cluster "etcdnode1=https://172.16.2.1:2380,etcdnode2=https://172.16.2.2:2380,etcdnode3=https://172.16.2.3:2380" \
-initial-cluster-state new \
-cert-file=/pki/server.pem \
-key-file=/pki/server-key.pem \
-client-cert-auth \
-trusted-ca-file=/pki/ca.pem \
-peer-client-cert-auth \
-peer-cert-file=/pki/peer.pem \
-peer-key-file=/pki/peer-key.pem \
-peer-trusted-ca-file=/pki/ca.pem
节点2:
docker run -d -p 23792:2379 -p 23802:2380 \
-v /etc/etcd/pki:/pki \
--name etcdnode2 \
--network=mynet \
--ip 172.16.2.2 \
quay.io/coreos/etcd:v3.3.1 \
etcd -name etcdnode2 \
-advertise-client-urls https://172.16.2.2:2379 \
-initial-advertise-peer-urls https://172.16.2.2:2380 \
-listen-client-urls https://0.0.0.0:2379 \
-listen-peer-urls https://0.0.0.0:2380 \
-initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster \
-initial-cluster "etcdnode1=https://172.16.2.1:2380,etcdnode2=https://172.16.2.2:2380,etcdnode3=https://172.16.2.3:2380" \
-initial-cluster-state new \
-cert-file=/pki/server.pem \
-key-file=/pki/server-key.pem \
-client-cert-auth \
-trusted-ca-file=/pki/ca.pem \
-peer-client-cert-auth \
-peer-cert-file=/pki/peer.pem \
-peer-key-file=/pki/peer-key.pem \
-peer-trusted-ca-file=/pki/ca.pem
节点3:
docker run -d -p 23793:2379 -p 23803:2380 \
-v /etc/etcd/pki:/pki \
--name etcdnode3 \
--network=mynet \
--ip 172.16.2.3 \
quay.io/coreos/etcd:v3.3.1 \
etcd -name etcdnode3 \
-advertise-client-urls https://172.16.2.3:2379 \
-initial-advertise-peer-urls https://172.16.2.3:2380 \
-listen-client-urls https://0.0.0.0:2379 \
-listen-peer-urls https://0.0.0.0:2380 \
-initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster \
-initial-cluster "etcdnode1=https://172.16.2.1:2380,etcdnode2=https://172.16.2.2:2380,etcdnode3=https://172.16.2.3:2380" \
-initial-cluster-state new \
-cert-file=/pki/server.pem \
-key-file=/pki/server-key.pem \
-client-cert-auth \
-trusted-ca-file=/pki/ca.pem \
-peer-client-cert-auth \
-peer-cert-file=/pki/peer.pem \
-peer-key-file=/pki/peer-key.pem \
-peer-trusted-ca-file=/pki/ca.pem
再次访问新创建的etcd集群,直接访问
etcdctl --endpoints="https://192.168.126.143:23791" member list
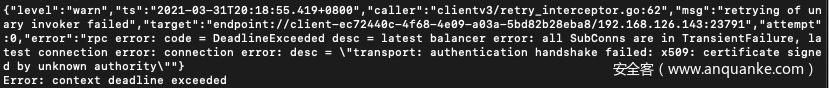
会报如下错误:
浏览器中访问报错如下:
需要携带客户端的证书和密钥访问。将签发的客户端证书、密钥和ca证书copy到本机etcdctl同级目录下,指定对应参数即可正常访问:
etcdctl --endpoints="https://192.168.126.143:23791" --cacert=ca.pem --cert=client.pem --key=client-key.pem member list
至此,我们完成了基于TLS的身份验证和数据传输配置。
虽然上面两个方案都能解决etcd未授权访问的问题,但是为保证安全,实际使用时强烈建议两种方案同时上,既实现了权限管控,又保障了传输安全。
参考资料:
https://etcd.io/docs/v3.4/op-guide/
https://blog.csdn.net/u011508407/article/details/108549703
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_30788731/article/details/97545042
https://www.jianshu.com/p/7bbef1ca9733
https://blog.csdn.net/ucmir183/article/details/84454506
https://juejin.cn/post/6844903678269210632
https://www.cnblogs.com/effortsing/p/10332492.html
http://blueskykong.com/categories/etcd/
https://gcollazo.com/the-security-footgun-in-etcd/
漏洞悬赏计划:涂鸦智能安全响应中心( https://src.tuya.com )欢迎白帽子来探索。
招聘内推计划:涵盖安全开发、安全测试、代码审计、安全合规等所有方面的岗位,简历投递sec#tuya.com,请注明来源。