0x00 写在前面
本文将接续第一篇文章,继续分析afl-gcc向程序中插入的关键代码。
0x01 afl-as源码分析(第二部分)
上一篇文章中说到,若桩代码计数器ins_lines不为0,afl-as会将main_payload_64/main_payload_32(取决于use_64bit标志位状态)插入整个汇编文件末尾。
main_payload_64代码分析
去除了对于MacOS以及OpenBSD的系统适配后,合并宏定义后代码整理结果如下:
/* --- AFL MAIN PAYLOAD (64-BIT) --- */
.text
.att_syntax
.code64
.align 8
__afl_maybe_log:
lahf
seto %al
/* Check if SHM region is already mapped. */
movq __afl_area_ptr(%rip), %rdx
testq %rdx, %rdx
je __afl_setup
__afl_store:
/* Calculate and store hit for the code location specified in rcx. */
#ifndef COVERAGE_ONLY
xorq __afl_prev_loc(%rip), %rcx
xorq %rcx, __afl_prev_loc(%rip)
shrq $1, __afl_prev_loc(%rip)
#endif /* ^!COVERAGE_ONLY */
#ifdef SKIP_COUNTS
orb $1, (%rdx, %rcx, 1)
#else
incb (%rdx, %rcx, 1)
#endif /* ^SKIP_COUNTS */
__afl_return:
addb $127, %al
sahf
ret
.align 8
__afl_setup:
/* Do not retry setup if we had previous failures. */
cmpb $0, __afl_setup_failure(%rip)
jne __afl_return
/* Check out if we have a global pointer on file. */
movq __afl_global_area_ptr(%rip), %rdx
testq %rdx, %rdx
je __afl_setup_first
movq %rdx, __afl_area_ptr(%rip)
jmp __afl_store
__afl_setup_first:
/* Save everything that is not yet saved and that may be touched by
getenv() and several other libcalls we'll be relying on. */
leaq -352(%rsp), %rsp
movq %rax, 0(%rsp)
movq %rcx, 8(%rsp)
movq %rdi, 16(%rsp)
movq %rsi, 32(%rsp)
movq %r8, 40(%rsp)
movq %r9, 48(%rsp)
movq %r10, 56(%rsp)
movq %r11, 64(%rsp)
movq %xmm0, 96(%rsp)
movq %xmm1, 112(%rsp)
movq %xmm2, 128(%rsp)
movq %xmm3, 144(%rsp)
movq %xmm4, 160(%rsp)
movq %xmm5, 176(%rsp)
movq %xmm6, 192(%rsp)
movq %xmm7, 208(%rsp)
movq %xmm8, 224(%rsp)
movq %xmm9, 240(%rsp)
movq %xmm10, 256(%rsp)
movq %xmm11, 272(%rsp)
movq %xmm12, 288(%rsp)
movq %xmm13, 304(%rsp)
movq %xmm14, 320(%rsp)
movq %xmm15, 336(%rsp)
/* Map SHM, jumping to __afl_setup_abort if something goes wrong. */
/* The 64-bit ABI requires 16-byte stack alignment. We'll keep the
original stack ptr in the callee-saved r12. */
pushq %r12
movq %rsp, %r12
subq $16, %rsp
andq $0xfffffffffffffff0, %rsp
leaq .AFL_SHM_ENV(%rip), %rdi
call getenv@PLT
testq %rax, %rax
je __afl_setup_abort
movq %rax, %rdi
call atoi@PLT
xorq %rdx, %rdx /* shmat flags */
xorq %rsi, %rsi /* requested addr */
movq %rax, %rdi /* SHM ID */
call shmat@PLT
cmpq $-1, %rax
je __afl_setup_abort
/* Store the address of the SHM region. */
movq %rax, %rdx
movq %rax, __afl_area_ptr(%rip)
movq __afl_global_area_ptr@GOTPCREL(%rip), %rdx
movq %rax, (%rdx)
movq %rax, %rdx
__afl_forkserver:
/* Enter the fork server mode to avoid the overhead of execve() calls. We
push rdx (area ptr) twice to keep stack alignment neat. */
pushq %rdx
pushq %rdx
/* Phone home and tell the parent that we're OK. (Note that signals with
no SA_RESTART will mess it up). If this fails, assume that the fd is
closed because we were execve()d from an instrumented binary, or because
the parent doesn't want to use the fork server. */
movq $4, %rdx /* length */
leaq __afl_temp(%rip), %rsi /* data */
movq $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) ", %rdi /* file desc */
call write@PLT
cmpq $4, %rax
jne __afl_fork_resume
__afl_fork_wait_loop:
/* Wait for parent by reading from the pipe. Abort if read fails. */
movq $4, %rdx /* length */
leaq __afl_temp(%rip), %rsi /* data */
movq $" STRINGIFY(FORKSRV_FD) ", %rdi /* file desc */
call read@PLT
cmpq $4, %rax
jne __afl_die
/* Once woken up, create a clone of our process. This is an excellent use
case for syscall(__NR_clone, 0, CLONE_PARENT), but glibc boneheadedly
caches getpid() results and offers no way to update the value, breaking
abort(), raise(), and a bunch of other things :-( */
call fork@PLT
cmpq $0, %rax
jl __afl_die
je __afl_fork_resume
/* In parent process: write PID to pipe, then wait for child. */
movl %eax, __afl_fork_pid(%rip)
movq $4, %rdx /* length */
leaq __afl_fork_pid(%rip), %rsi /* data */
movq $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) ", %rdi /* file desc */
call write@PLT
movq $0, %rdx /* no flags */
leaq __afl_temp(%rip), %rsi /* status */
movq __afl_fork_pid(%rip), %rdi /* PID */
call waitpid@PLT
cmpq $0, %rax
jle __afl_die
/* Relay wait status to pipe, then loop back. */
movq $4, %rdx /* length */
leaq __afl_temp(%rip), %rsi /* data */
movq $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) ", %rdi /* file desc */
call write@PLT
jmp __afl_fork_wait_loop
__afl_fork_resume:
/* In child process: close fds, resume execution. */
movq $" STRINGIFY(FORKSRV_FD) ", %rdi
call close@PLT
movq $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) ", %rdi
call close@PLT
popq %rdx
popq %rdx
movq %r12, %rsp
popq %r12
movq 0(%rsp), %rax
movq 8(%rsp), %rcx
movq 16(%rsp), %rdi
movq 32(%rsp), %rsi
movq 40(%rsp), %r8
movq 48(%rsp), %r9
movq 56(%rsp), %r10
movq 64(%rsp), %r11
movq 96(%rsp), %xmm0
movq 112(%rsp), %xmm1
movq 128(%rsp), %xmm2
movq 144(%rsp), %xmm3
movq 160(%rsp), %xmm4
movq 176(%rsp), %xmm5
movq 192(%rsp), %xmm6
movq 208(%rsp), %xmm7
movq 224(%rsp), %xmm8
movq 240(%rsp), %xmm9
movq 256(%rsp), %xmm10
movq 272(%rsp), %xmm11
movq 288(%rsp), %xmm12
movq 304(%rsp), %xmm13
movq 320(%rsp), %xmm14
movq 336(%rsp), %xmm15
leaq 352(%rsp), %rsp
jmp __afl_store
__afl_die:
xorq %rax, %rax
call _exit@PLT
__afl_setup_abort:
/* Record setup failure so that we don't keep calling
shmget() / shmat() over and over again. */
incb __afl_setup_failure(%rip)
movq %r12, %rsp
popq %r12
movq 0(%rsp), %rax
movq 8(%rsp), %rcx
movq 16(%rsp), %rdi
movq 32(%rsp), %rsi
movq 40(%rsp), %r8
movq 48(%rsp), %r9
movq 56(%rsp), %r10
movq 64(%rsp), %r11
movq 96(%rsp), %xmm0
movq 112(%rsp), %xmm1
movq 128(%rsp), %xmm2
movq 144(%rsp), %xmm3
movq 160(%rsp), %xmm4
movq 176(%rsp), %xmm5
movq 192(%rsp), %xmm6
movq 208(%rsp), %xmm7
movq 224(%rsp), %xmm8
movq 240(%rsp), %xmm9
movq 256(%rsp), %xmm10
movq 272(%rsp), %xmm11
movq 288(%rsp), %xmm12
movq 304(%rsp), %xmm13
movq 320(%rsp), %xmm14
movq 336(%rsp), %xmm15
leaq 352(%rsp), %rsp
jmp __afl_return
.AFL_VARS:
.lcomm __afl_area_ptr, 8
#ifndef COVERAGE_ONLY
.lcomm __afl_prev_loc, 8
#endif /* !COVERAGE_ONLY */
.lcomm __afl_fork_pid, 4
.lcomm __afl_temp, 4
.lcomm __afl_setup_failure, 1
.comm __afl_global_area_ptr, 8, 8
.AFL_SHM_ENV:
.asciz "SHM_ENV_VAR"
接下来我们逐函数进行分析。
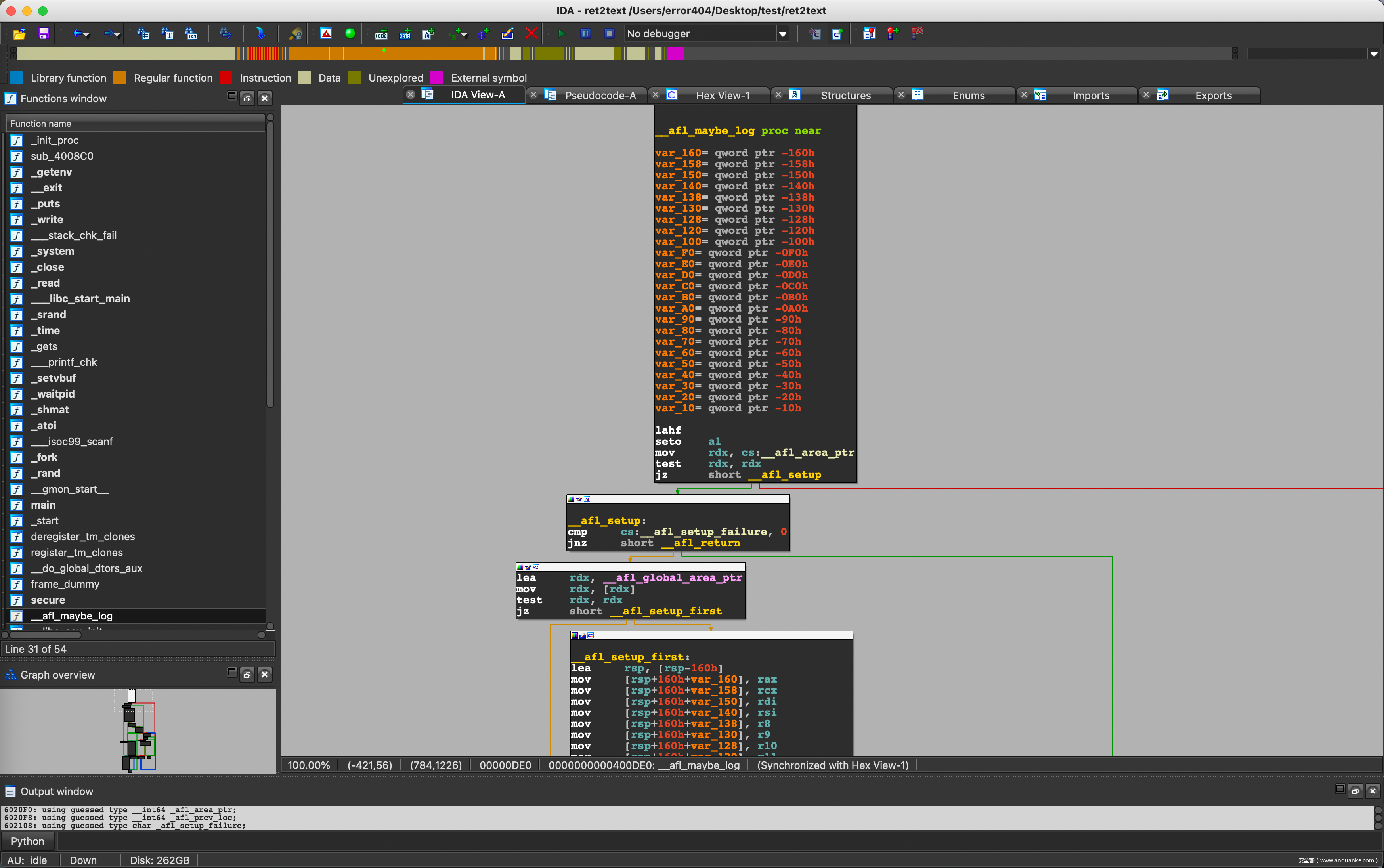
__afl_maybe_log函数
此函数主要负责保存现场并且检查共享内存是否已被分配。
__afl_maybe_log:
lahf
seto %al
/* Check if SHM region is already mapped. */
movq __afl_area_ptr(%rip), %rdx
testq %rdx, %rdx
je __afl_setup
- 使用
lahf(Load AH with Flags)指令将标志寄存器的低八位(CF-进位标志、PF-奇偶标志、AF-辅助进位标志、ZF-零标志、SF-符号标志)存储到AH寄存器中。- 进位标志:用于反映运算是否产生进位或借位。如果运算结果的最高位产生一个进位或借位,则
CF置1,否则置0。运算结果的最高位包括字操作的第15位和字节操作的第7位。移位指令也会将操作数的最高位或最低位移入CF。 - 奇偶标志:用于反映运算结果低
8位中“1”的个数。“1”的个数为偶数,则PF置1,否则置0。 - 辅助进位标志:算数操作结果的第三位(从
0开始计数)如果产生了进位或者借位则将其置为1,否则置为0,常在BCD(binary-codedecimal)算术运算中被使用。 - 零标志:用于判断结果是否为
0。运算结果0,ZF置1,否则置0。 - 符号标志:用于反映运算结果的符号,运算结果为负,
SF置1,否则置0。因为有符号数采用补码的形式表示,所以SF与运算结果的最高位相同。
- 进位标志:用于反映运算是否产生进位或借位。如果运算结果的最高位产生一个进位或借位,则
- 使用
seto %al记录此时OF(溢出标志)的状态,当标志寄存器中的此标志位置位时,将AL寄存器置位。- 溢出标志:反映有符号数加减运算是否溢出。如果运算结果超过了
8位或者16位有符号数的表示范围,则OF置1,否则置0。
- 溢出标志:反映有符号数加减运算是否溢出。如果运算结果超过了
- 使用
movq __afl_area_ptr(%rip), %rdx将__afl_area_ptr(%rip)的值存入RDX寄存器中。此处__afl_area_ptr(%rip)是在BSS段中存储的一个一个指针,此指针指向共享内存。 - 使用
testq %rdx, %rdx检查RDX寄存器的值是否存在,若存在则代表共享内存已被分配,否则,应当认为此时共享内存未被分配。 - 如果
RDX为空,ZF置位,此时跳转进入__afl_setup;否则,按顺序执行__afl_store函数。
__afl_store函数
此函数主要负责记录命中桩代码的次数并计算其覆盖区域。
__afl_store:
/* Calculate and store hit for the code location specified in rcx. */
#ifndef COVERAGE_ONLY
xorq __afl_prev_loc(%rip), %rcx
xorq %rcx, __afl_prev_loc(%rip)
shrq $1, __afl_prev_loc(%rip)
#endif /* ^!COVERAGE_ONLY */
#ifdef SKIP_COUNTS
orb $1, (%rdx, %rcx, 1)
#else
incb (%rdx, %rcx, 1)
#endif /* ^SKIP_COUNTS */
- 首先,这里用到了
RCX寄存器的值,如果还记得上一篇文章中对于__afl_maybe_log的调用逻辑的分析的话,应该记得RCX的值是一个随机数,而这个随机数事实上是用于标记本次桩命中逻辑的。 - 当
COVERAGE_ONLY标志未被设置:- 将
__afl_prev_loc(旧值) ^ 随机数(RCX)的值存入RCX寄存器中。 - 将
__afl_prev_loc(旧值) ^ __afl_prev_loc(旧值) ^ 随机数(RCX)的值存储在__afl_prev_loc中,即将随机数存入__afl_prev_loc中。 - 将
__afl_prev_loc中的值逻辑右移1位。
- 将
- 当
SKIP_COUNTS标志被设置,将Byte[RDX + RCX * 1]的值与1进行或操作并将结果存回原处。- 此处的
(%rdx, %rcx, 1)是一种比例寻址的写法,语法为(基地址,偏移量,比例因子),最终取出基地址+偏移量*比例因子的值。
- 此处的
- 当
SKIP_COUNTS标志未被设置,将Byte[RDX + RCX * 1]的值增加1。此时RDX是共享内存的地址,RCX是__afl_prev_loc(旧值) ^ 随机数(RCX),而当程序进行到第二个桩时,事实上__afl_prev_loc(旧值)就是上一个桩标识 >> 1的值了。即,此步事实上就是share_mem[__afl_prev_loc(旧值) ^ 随机数(RCX)]++。实际上是存入一个64k大小的哈希表,存在碰撞几率,但是问题不大。而这个索引是通过异或得到的。
__afl_return函数
此函数主要负责AFL插入的桩代码返回。
__afl_return:
addb $127, %al
sahf
ret
- 使用
add命令将AL寄存器的值加上0x7F用以恢复OF标志的值。 - 从
AH寄存器中恢复标志寄存器的低八位。 - 函数返回。
__afl_setup函数
此函数主要用于检查文件全局指针是否存在。
__afl_setup:
/* Do not retry setup if we had previous failures. */
cmpb $0, __afl_setup_failure(%rip)
jne __afl_return
/* Check out if we have a global pointer on file. */
movq __afl_global_area_ptr(%rip), %rdx
testq %rdx, %rdx
je __afl_setup_first
movq %rdx, __afl_area_ptr(%rip)
jmp __afl_store
- 检查
AFL初始化失败计数器__afl_setup_failure(%rip)的值是否为0,若不为0,则跳转进入__afl_return函数。 - 将
__afl_global_area_ptr(%rip)这个BSS段变量(此变量表示一个文件全局指针)的值存入RDX寄存器,检查RDX寄存器是否为空,若为空,则跳转进入__afl_setup_first函数。 - 若
RDX寄存器不为空,则将RDX寄存器的值写入__afl_area_ptr随后跳入__afl_store函数。此时文件全局指针就是我们的共享内存指针。
__afl_setup_first函数
此函数主要用于获取共享内存。
__afl_setup_first:
/* Save everything that is not yet saved and that may be touched by
getenv() and several other libcalls we'll be relying on. */
leaq -352(%rsp), %rsp
movq %rax, 0(%rsp)
movq %rcx, 8(%rsp)
movq %rdi, 16(%rsp)
movq %rsi, 32(%rsp)
movq %r8, 40(%rsp)
movq %r9, 48(%rsp)
movq %r10, 56(%rsp)
movq %r11, 64(%rsp)
movq %xmm0, 96(%rsp)
movq %xmm1, 112(%rsp)
movq %xmm2, 128(%rsp)
movq %xmm3, 144(%rsp)
movq %xmm4, 160(%rsp)
movq %xmm5, 176(%rsp)
movq %xmm6, 192(%rsp)
movq %xmm7, 208(%rsp)
movq %xmm8, 224(%rsp)
movq %xmm9, 240(%rsp)
movq %xmm10, 256(%rsp)
movq %xmm11, 272(%rsp)
movq %xmm12, 288(%rsp)
movq %xmm13, 304(%rsp)
movq %xmm14, 320(%rsp)
movq %xmm15, 336(%rsp)
/* Map SHM, jumping to __afl_setup_abort if something goes wrong. */
/* The 64-bit ABI requires 16-byte stack alignment. We'll keep the
original stack ptr in the callee-saved r12. */
pushq %r12
movq %rsp, %r12
subq $16, %rsp
andq $0xfffffffffffffff0, %rsp
leaq .AFL_SHM_ENV(%rip), %rdi
call getenv@PLT
testq %rax, %rax
je __afl_setup_abort
movq %rax, %rdi
call atoi@PLT
xorq %rdx, %rdx /* shmat flags */
xorq %rsi, %rsi /* requested addr */
movq %rax, %rdi /* SHM ID */
call shmat@PLT
cmpq $-1, %rax
je __afl_setup_abort
/* Store the address of the SHM region. */
movq %rax, %rdx
movq %rax, __afl_area_ptr(%rip)
movq __afl_global_area_ptr@GOTPCREL(%rip), %rdx
movq %rax, (%rdx)
movq %rax, %rdx
- 开辟一块
0x160大小的栈空间,并保存RAX、RCX、RDI、RSI、R8、R9、R10、R11、Xmm0-Xmm15寄存器的值到栈上。 - 保存
R12寄存器到栈上,然后将RSP保存在R12寄存器内,再开辟一段0x10大小的栈空间,进行内存对齐。 - 调用
getenv("SHM_ENV_VAR")获取共享内存标识符,若返回空,则跳入__afl_setup_abort函数 - 否则,将共享内存标识符存入
RDI,并调用atoi将其转换为数字。 - 调用
shmat(RAX,0,0),即调用shmat(atoi(getenv("SHM_ENV_VAR")),0,0)来连接共享内存标识符所示的共享内存,连接成功后把共享内存区对象映射到调用进程的地址空间,随后可像本地空间一样访问。-
shmat的函数原型为void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg),shmid表示共享内存标识符,shmaddr表示共享内存标识符指定共享内存出现在进程内存地址的什么位置,可以直接指定为NULL让内核自己决定一个合适的地址位置,shmflg表示标志位,未指定标志位时,共享内存默认为读-写权限,目前只定义了两个可用的标志位:-
#define SHM_RDONLY 010000(只读标志):当此标志被附加时,共享内存为只读权限。 -
#define SHM_RND 020000(SHMLBA标志):当此标志被设置时,共享内存被连接到SHMLBA所指向的内存区域。
-
-
- 检查
shmat()的返回值是否为-1,若为-1则表示共享内存分配失败,跳入__afl_setup_abort函数。 - 将附加好的共享内存地址存入
RDX寄存器以及__afl_area_ptr中 - 将
__afl_global_area_ptr的地址存入RDX中 - 将附加好的共享内存地址存入
[RDX]中 - 将附加好的共享内存地址存入
RDX寄存器中- 这里是一种寻址的写法,可以简单的认为
[__afl_global_area_ptr@GOTPCREL(%rip)]=__afl_global_area_ptr(%rip)
- 这里是一种寻址的写法,可以简单的认为
__afl_forkserver函数
此函数主要用于栈内存对齐以及向状态管道写入四字节以告知父进程已经准备好了。
__afl_forkserver:
/* Enter the fork server mode to avoid the overhead of execve() calls. We
push rdx (area ptr) twice to keep stack alignment neat. */
pushq %rdx
pushq %rdx
/* Phone home and tell the parent that we're OK. (Note that signals with
no SA_RESTART will mess it up). If this fails, assume that the fd is
closed because we were execve()d from an instrumented binary, or because
the parent doesn't want to use the fork server. */
movq $4, %rdx /* length */
leaq __afl_temp(%rip), %rsi /* data */
movq $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) ", %rdi /* file desc */
call write@PLT
cmpq $4, %rax
jne __afl_fork_resume
- 使用两次
pushq %rdx来使得占内存对齐。 - 调用
write(STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)),__afl_temp,4)来向指定文件描述符写4个字节,写入的内容是__afl_temp的值。- 此处,
FORKSRV_FD的值由config.h指定,语句为#define FORKSRV_FD 198。 - 这个文件描述符实际上是程序的状态管道,具体逻辑在
afl-fuzz.c中。
- 此处,
- 检查实际写入字节数是否为4字节,若不为四字节,则跳转至
__afl_fork_resume函数。
__afl_fork_wait_loop函数
此函数为AFL的桩代码主逻辑,且桩代码将在此处循环。
__afl_fork_wait_loop:
/* Wait for parent by reading from the pipe. Abort if read fails. */
movq $4, %rdx /* length */
leaq __afl_temp(%rip), %rsi /* data */
movq $" STRINGIFY(FORKSRV_FD) ", %rdi /* file desc */
call read@PLT
cmpq $4, %rax
jne __afl_die
/* Once woken up, create a clone of our process. This is an excellent use
case for syscall(__NR_clone, 0, CLONE_PARENT), but glibc boneheadedly
caches getpid() results and offers no way to update the value, breaking
abort(), raise(), and a bunch of other things :-( */
call fork@PLT
cmpq $0, %rax
jl __afl_die
je __afl_fork_resume
/* In parent process: write PID to pipe, then wait for child. */
movl %eax, __afl_fork_pid(%rip)
movq $4, %rdx /* length */
leaq __afl_fork_pid(%rip), %rsi /* data */
movq $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) ", %rdi /* file desc */
call write@PLT
movq $0, %rdx /* no flags */
leaq __afl_temp(%rip), %rsi /* status */
movq __afl_fork_pid(%rip), %rdi /* PID */
call waitpid@PLT
cmpq $0, %rax
jle __afl_die
/* Relay wait status to pipe, then loop back. */
movq $4, %rdx /* length */
leaq __afl_temp(%rip), %rsi /* data */
movq $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) ", %rdi /* file desc */
call write@PLT
jmp __afl_fork_wait_loop
- 调用
read(STRINGIFY(FORKSRV_FD),__afl_temp,4),即read(198,__afl_temp,4),用以从状态管道中读取四字节状态数据。 - 当读取的字节数不为4字节时,跳转
__afl_die函数。 - 一旦程序运行到此处,应当视为程序的流程命中了一次插桩,此时调用
fork()函数创建一个子进程。若fork()函数返回负值,表示子进程创建失败,跳转__afl_die函数。若fork()函数返回0,表示此进程为子进程,跳转__afl_fork_resume函数。 - 将子进程号存储在
__afl_fork_pid中。 - 调用
write(STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)),__afl_fork_pid,4),即write(199,__afl_fork_pid,4),用以将子进程号发送至状态管道。 - 调用
waitpid(__afl_fork_pid,__afl_temp,0),暂停当前进程,直到接收到子进程的信号或子进程退出为止。传入的__afl_temp将用于保存程序状态。 - 若
waitpid函数返回-1,则函数出错,跳转__afl_die函数。 - 调用
write(STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)),__afl_temp,4),即write(199,__afl_temp,4),用以将四字节任意数据发送至状态管道,以告知父进程,此时本进程处于等待状态。 - 跳回
__afl_fork_wait_loop,即,进入循环。
__afl_fork_resume函数
此函数用于恢复关闭两个状态管道并恢复现场。
__afl_fork_resume:
/* In child process: close fds, resume execution. */
movq $" STRINGIFY(FORKSRV_FD) ", %rdi
call close@PLT
movq $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) ", %rdi
call close@PLT
popq %rdx
popq %rdx
movq %r12, %rsp
popq %r12
movq 0(%rsp), %rax
movq 8(%rsp), %rcx
movq 16(%rsp), %rdi
movq 32(%rsp), %rsi
movq 40(%rsp), %r8
movq 48(%rsp), %r9
movq 56(%rsp), %r10
movq 64(%rsp), %r11
movq 96(%rsp), %xmm0
movq 112(%rsp), %xmm1
movq 128(%rsp), %xmm2
movq 144(%rsp), %xmm3
movq 160(%rsp), %xmm4
movq 176(%rsp), %xmm5
movq 192(%rsp), %xmm6
movq 208(%rsp), %xmm7
movq 224(%rsp), %xmm8
movq 240(%rsp), %xmm9
movq 256(%rsp), %xmm10
movq 272(%rsp), %xmm11
movq 288(%rsp), %xmm12
movq 304(%rsp), %xmm13
movq 320(%rsp), %xmm14
movq 336(%rsp), %xmm15
leaq 352(%rsp), %rsp
jmp __afl_store
- 调用
close(STRINGIFY(FORKSRV_FD))和close(STRINGIFY(FORKSRV_FD + 1)),即调用close(198)和close(199),关闭两个状态管道。 - 弹出栈中的两个用于对齐的无用数据。(此数据在
__afl_forkserver中被压栈) - 从
R12寄存器中恢复RSP寄存器的值。(此值在__afl_setup_first中被保存) - 从栈中恢复所有在
__afl_setup_first中被保存的寄存器值。 - 回收在
__afl_setup_first中被开辟的栈空间。 - 跳转
__afl_store函数。
__afl_die函数
__afl_die:
xorq %rax, %rax
call _exit@PLT
调用exit(0)退出。
__afl_setup_abort函数
__afl_setup_abort:
/* Record setup failure so that we don't keep calling
shmget() / shmat() over and over again. */
incb __afl_setup_failure(%rip)
movq %r12, %rsp
popq %r12
movq 0(%rsp), %rax
movq 8(%rsp), %rcx
movq 16(%rsp), %rdi
movq 32(%rsp), %rsi
movq 40(%rsp), %r8
movq 48(%rsp), %r9
movq 56(%rsp), %r10
movq 64(%rsp), %r11
movq 96(%rsp), %xmm0
movq 112(%rsp), %xmm1
movq 128(%rsp), %xmm2
movq 144(%rsp), %xmm3
movq 160(%rsp), %xmm4
movq 176(%rsp), %xmm5
movq 192(%rsp), %xmm6
movq 208(%rsp), %xmm7
movq 224(%rsp), %xmm8
movq 240(%rsp), %xmm9
movq 256(%rsp), %xmm10
movq 272(%rsp), %xmm11
movq 288(%rsp), %xmm12
movq 304(%rsp), %xmm13
movq 320(%rsp), %xmm14
movq 336(%rsp), %xmm15
leaq 352(%rsp), %rsp
jmp __afl_return
- 将
AFL初始化失败计数器__afl_setup_failure加1。 - 从
R12寄存器中恢复RSP寄存器的值。(此值在__afl_setup_first中被保存) - 从栈中恢复所有在
__afl_setup_first中被保存的寄存器值。 - 回收在
__afl_setup_first中被开辟的栈空间。 - 跳转
__afl_return函数。
main_payload_64代码总结
至此,main_payload_64的所有函数分析完毕,其流程图如下:
P.S:凡是线有交叉的均使用了不同颜色的线进行标注。
但事实上这只是afl-as对目标程序进行的插桩处理,正式进行fuzz时,还会有部分关键逻辑在afl-fuzz中,我将在日后对afl-fuzz进行分析时进行详述。
main_payload_32代码分析
去除了对于MacOS以及OpenBSD的系统适配后,合并宏定义后代码整理结果如下:
/* --- AFL MAIN PAYLOAD (32-BIT) --- */
.text
.att_syntax
.code32
.align 8
__afl_maybe_log:
lahf
seto %al
/* Check if SHM region is already mapped. */
movl __afl_area_ptr, %edx
testl %edx, %edx
je __afl_setup
__afl_store:
/* Calculate and store hit for the code location specified in ecx. There
is a double-XOR way of doing this without tainting another register,
and we use it on 64-bit systems; but it's slower for 32-bit ones. */
#ifndef COVERAGE_ONLY
movl __afl_prev_loc, %edi
xorl %ecx, %edi
shrl $1, %ecx
movl %ecx, __afl_prev_loc
#else
movl %ecx, %edi
#endif /* ^!COVERAGE_ONLY */
#ifdef SKIP_COUNTS
orb $1, (%edx, %edi, 1)
#else
incb (%edx, %edi, 1)
#endif /* ^SKIP_COUNTS */
__afl_return:
addb $127, %al
sahf
ret
.align 8
__afl_setup:
/* Do not retry setup if we had previous failures. */
cmpb $0, __afl_setup_failure
jne __afl_return
/* Map SHM, jumping to __afl_setup_abort if something goes wrong.
We do not save FPU/MMX/SSE registers here, but hopefully, nobody
will notice this early in the game. */
pushl %eax
pushl %ecx
pushl $.AFL_SHM_ENV
call getenv
addl $4, %esp
testl %eax, %eax
je __afl_setup_abort
pushl %eax
call atoi
addl $4, %esp
pushl $0 /* shmat flags */
pushl $0 /* requested addr */
pushl %eax /* SHM ID */
call shmat
addl $12, %esp
cmpl $-1, %eax
je __afl_setup_abort
/* Store the address of the SHM region. */
movl %eax, __afl_area_ptr
movl %eax, %edx
popl %ecx
popl %eax
__afl_forkserver:
/* Enter the fork server mode to avoid the overhead of execve() calls. */
pushl %eax
pushl %ecx
pushl %edx
/* Phone home and tell the parent that we're OK. (Note that signals with
no SA_RESTART will mess it up). If this fails, assume that the fd is
closed because we were execve()d from an instrumented binary, or because
the parent doesn't want to use the fork server. */
pushl $4 /* length */
pushl $__afl_temp /* data */
pushl $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) " /* file desc */
call write
addl $12, %esp
cmpl $4, %eax
jne __afl_fork_resume
__afl_fork_wait_loop:
/* Wait for parent by reading from the pipe. Abort if read fails. */
pushl $4 /* length */
pushl $__afl_temp /* data */
pushl $" STRINGIFY(FORKSRV_FD) " /* file desc */
call read
addl $12, %esp
cmpl $4, %eax
jne __afl_die
/* Once woken up, create a clone of our process. This is an excellent use
case for syscall(__NR_clone, 0, CLONE_PARENT), but glibc boneheadedly
caches getpid() results and offers no way to update the value, breaking
abort(), raise(), and a bunch of other things :-( */
call fork
cmpl $0, %eax
jl __afl_die
je __afl_fork_resume
/* In parent process: write PID to pipe, then wait for child. */
movl %eax, __afl_fork_pid
pushl $4 /* length */
pushl $__afl_fork_pid /* data */
pushl $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) " /* file desc */
call write
addl $12, %esp
pushl $0 /* no flags */
pushl $__afl_temp /* status */
pushl __afl_fork_pid /* PID */
call waitpid
addl $12, %esp
cmpl $0, %eax
jle __afl_die
/* Relay wait status to pipe, then loop back. */
pushl $4 /* length */
pushl $__afl_temp /* data */
pushl $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) " /* file desc */
call write
addl $12, %esp
jmp __afl_fork_wait_loop
__afl_fork_resume:
/* In child process: close fds, resume execution. */
pushl $" STRINGIFY(FORKSRV_FD)
call close
pushl $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1))
call close
addl $8, %esp
popl %edx
popl %ecx
popl %eax
jmp __afl_store
__afl_die:
xorl %eax, %eax
call _exit
__afl_setup_abort:
/* Record setup failure so that we don't keep calling
shmget() / shmat() over and over again. */
incb __afl_setup_failure
popl %ecx
popl %eax
jmp __afl_return
.AFL_VARS:
.comm __afl_area_ptr, 4, 32
.comm __afl_setup_failure, 1, 32
#ifndef COVERAGE_ONLY
.comm __afl_prev_loc, 4, 32
#endif /* !COVERAGE_ONLY */
.comm __afl_fork_pid, 4, 32
.comm __afl_temp, 4, 32
.AFL_SHM_ENV:
.asciz "SHM_ENV_VAR"
32位代码与64位代码大同小异,接下来进行分析
__afl_maybe_log函数
此函数主要负责保存现场并且检查共享内存是否已被分配。
__afl_maybe_log:
lahf
seto %al
/* Check if SHM region is already mapped. */
movl __afl_area_ptr, %edx
testl %edx, %edx
je __afl_setup
与64位代码完全相同,只不过保存共享内存指针的位置变成了edx
__afl_store函数
此函数主要负责记录命中桩代码的次数并计算其覆盖区域。
__afl_store:
/* Calculate and store hit for the code location specified in ecx. There
is a double-XOR way of doing this without tainting another register,
and we use it on 64-bit systems; but it's slower for 32-bit ones. */
#ifndef COVERAGE_ONLY
movl __afl_prev_loc, %edi
xorl %ecx, %edi
shrl $1, %ecx
movl %ecx, __afl_prev_loc
#else
movl %ecx, %edi
#endif /* ^!COVERAGE_ONLY */
#ifdef SKIP_COUNTS
orb $1, (%edx, %edi, 1)
#else
incb (%edx, %edi, 1)
#endif /* ^SKIP_COUNTS */
此处代码不再使用两次异或进行赋值,因为在32位下,异或的速度要慢于直接赋值。因此此处逻辑变为:
- 当
COVERAGE_ONLY标志未被设置:- 将
__afl_prev_loc(旧值)的值存入EDI寄存器中。 - 将
EDI ^ 随机数(ECX)即__afl_prev_loc(旧值) ^ 随机数(ECX)的值存入EDI寄存器中。 - 将
ECX(随机数)中的值逻辑右移1位并存入ECX。 - 将
ECX(右移过的随机数)存入__afl_prev_loc中。
- 将
- 若
COVERAGE_ONLY标志被设置,直接将ECX(随机数)中的值存入EDI寄存器中。 - 当
SKIP_COUNTS标志被设置,将[EDX + EDI * 1]的值与1进行或操作并将结果存回原处。 - 当
SKIP_COUNTS标志未被设置,将[EDX + EDI * 1]的值增加1。
__afl_return函数
此函数主要负责AFL插入的桩代码返回。
__afl_return:
addb $127, %al
sahf
ret
与64位版本的__afl_return函数完全相同。
__afl_setup函数
此函数主要用于分配共享内存。
__afl_setup:
/* Do not retry setup if we had previous failures. */
cmpb $0, __afl_setup_failure
jne __afl_return
/* Map SHM, jumping to __afl_setup_abort if something goes wrong.
We do not save FPU/MMX/SSE registers here, but hopefully, nobody
will notice this early in the game. */
pushl %eax
pushl %ecx
pushl $.AFL_SHM_ENV
call getenv
addl $4, %esp
testl %eax, %eax
je __afl_setup_abort
pushl %eax
call atoi
addl $4, %esp
pushl $0 /* shmat flags */
pushl $0 /* requested addr */
pushl %eax /* SHM ID */
call shmat
addl $12, %esp
cmpl $-1, %eax
je __afl_setup_abort
/* Store the address of the SHM region. */
movl %eax, __afl_area_ptr
movl %eax, %edx
popl %ecx
popl %eax
此处与64位代码不同,我们不再进行文件全局指针的检查并在此函数就进行共享内存的分配工作,不再经过__afl_setup_first函数。
- 检查
AFL初始化失败计数器__afl_setup_failure的值是否为0,若不为0,则跳转进入__afl_return函数。 - 保存
EAX和ECX的值,将它们依次入栈。- 此处我们没有保存
FPU/MMX/SSE寄存器,但是在期望状态下,此时这三类寄存器应当未被改变。-
FPU: 8个80位浮点寄存器(数据),16位状态寄存器,16位控制寄存器,16为标识寄存器。 -
MMX: 将8个FPU寄存器重命名为8个64位MMX寄存器,即mm0到mm7。[号称多媒体处理技术] -
SSE: 8个128位寄存器(从xmm0到xmm7),MXSCR寄存器,EFLAGS寄存器,专有指令。(复杂浮点运算)
-
- 此处我们没有保存
- 调用
getenv("SHM_ENV_VAR")获取共享内存标识符,若返回空,则跳入__afl_setup_abort函数。 - 否则,将共享内存标识符入栈,并调用
atoi将其转换为数字。 - 调用
shmat(EAX,0,0),即调用shmat(atoi(getenv("SHM_ENV_VAR")),0,0)来连接共享内存标识符所示的共享内存,连接成功后把共享内存区对象映射到调用进程的地址空间,随后可像本地空间一样访问。 - 检查
shmat()的返回值是否为-1,若为-1则表示共享内存分配失败,跳入__afl_setup_abort函数。 - 将附加好的共享内存地址存入
EDX寄存器以及__afl_area_ptr中 - 从栈中恢复
EAX和ECX的值。
__afl_forkserver函数
此函数主要用于栈内存对齐以及向状态管道写入四字节以告知父进程已经准备好了。
__afl_forkserver:
/* Enter the fork server mode to avoid the overhead of execve() calls. */
pushl %eax
pushl %ecx
pushl %edx
/* Phone home and tell the parent that we're OK. (Note that signals with
no SA_RESTART will mess it up). If this fails, assume that the fd is
closed because we were execve()d from an instrumented binary, or because
the parent doesn't want to use the fork server. */
pushl $4 /* length */
pushl $__afl_temp /* data */
pushl $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) " /* file desc */
call write
addl $12, %esp
cmpl $4, %eax
jne __afl_fork_resume
- 保存
EAX、ECX和EDX的值,将它们依次入栈。 - 调用
write(STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)),__afl_temp,4),即write(199,__afl_temp,4),用以将四字节任意数据发送至状态管道,以告知父进程,此时本进程处于就绪状态。 - 检查实际写入字节数是否为4字节,若不为四字节,则跳转至
__afl_fork_resume函数。
__afl_fork_wait_loop函数
此函数为AFL的桩代码主逻辑,且桩代码将在此处循环。
__afl_fork_wait_loop:
/* Wait for parent by reading from the pipe. Abort if read fails. */
pushl $4 /* length */
pushl $__afl_temp /* data */
pushl $" STRINGIFY(FORKSRV_FD) " /* file desc */
call read
addl $12, %esp
cmpl $4, %eax
jne __afl_die
/* Once woken up, create a clone of our process. This is an excellent use
case for syscall(__NR_clone, 0, CLONE_PARENT), but glibc boneheadedly
caches getpid() results and offers no way to update the value, breaking
abort(), raise(), and a bunch of other things :-( */
call fork
cmpl $0, %eax
jl __afl_die
je __afl_fork_resume
/* In parent process: write PID to pipe, then wait for child. */
movl %eax, __afl_fork_pid
pushl $4 /* length */
pushl $__afl_fork_pid /* data */
pushl $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) " /* file desc */
call write
addl $12, %esp
pushl $0 /* no flags */
pushl $__afl_temp /* status */
pushl __afl_fork_pid /* PID */
call waitpid
addl $12, %esp
cmpl $0, %eax
jle __afl_die
/* Relay wait status to pipe, then loop back. */
pushl $4 /* length */
pushl $__afl_temp /* data */
pushl $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) " /* file desc */
call write
addl $12, %esp
jmp __afl_fork_wait_loop
此函数除了因为函数调用约定导致的变化外,与64位__afl_fork_wait_loop函数逻辑相同,此处不再赘述。
__afl_fork_resume函数
此函数用于恢复关闭两个状态管道并恢复现场。
__afl_fork_resume:
/* In child process: close fds, resume execution. */
pushl $" STRINGIFY(FORKSRV_FD) "
call close
pushl $" STRINGIFY((FORKSRV_FD + 1)) "
call close
addl $8, %esp
popl %edx
popl %ecx
popl %eax
jmp __afl_store
- 调用
close(STRINGIFY(FORKSRV_FD))和close(STRINGIFY(FORKSRV_FD + 1)),即调用close(198)和close(199),关闭两个状态管道。 - 从栈中恢复
EDX、ECX、EAX的寄存器值。(在__afl_forkserver函数中被保存) - 跳转
__afl_store函数。
__afl_die函数
__afl_die:
xorl %eax, %eax
call _exit
调用exit(0)退出。
__afl_setup_abort函数
__afl_setup_abort:
/* Record setup failure so that we don't keep calling
shmget() / shmat() over and over again. */
incb __afl_setup_failure
popl %ecx
popl %eax
jmp __afl_return
- 将
AFL初始化失败计数器__afl_setup_failure加1。 - 从栈中恢复
ECX、EAX的寄存器值。(在__afl_setup函数中被保存) - 跳转
__afl_return函数。
main_payload_32代码总结
main_payload_32代码与64位代码相比,除了有部分因为调用约定导致的变化外,就是把桩代码初始化的过程完全移到了__afl_setup函数中,删除了__afl_setup_first函数。核心代码与逻辑并无区别。
afl-as中的add_instrumentation函数收尾
现在我们把目光移回afl-as中的add_instrumentation函数,在完成主代码插桩后,还有最后一点代码:
if (ins_lines)
fputs(use_64bit ? main_payload_64 : main_payload_32, outf);
if (input_file) fclose(inf);
fclose(outf);
if (!be_quiet) {
if (!ins_lines) WARNF("No instrumentation targets found%s.",
pass_thru ? " (pass-thru mode)" : "");
else OKF("Instrumented %u locations (%s-bit, %s mode, ratio %u%%).",
ins_lines, use_64bit ? "64" : "32",
getenv("AFL_HARDEN") ? "hardened" :
(sanitizer ? "ASAN/MSAN" : "non-hardened"),
inst_ratio);
}
- 主代码插桩结束后,检查待插桩文件的文件描述符是否已被关闭,若未被关闭,调用
fclose进行关闭。 - 调用
fclose关闭已插桩文件。 - 若
be_quiet标志被设置,则输出插桩详情,包括忽略了哪些代码,插入的桩代码数等等 - 返回主函数
afl-as主函数收尾
afl-as中主函数在add_instrumentation函数返回后也还有最后一点代码:
if (!just_version) add_instrumentation();
if (!(pid = fork())) {
execvp(as_params[0], (char**)as_params);
FATAL("Oops, failed to execute '%s' - check your PATH", as_params[0]);
}
if (pid < 0) PFATAL("fork() failed");
if (waitpid(pid, &status, 0) <= 0) PFATAL("waitpid() failed");
if (!getenv("AFL_KEEP_ASSEMBLY")) unlink(modified_file);
exit(WEXITSTATUS(status));
- 使用
fork创建一个子进程,随后在子进程中使用之前在edit_params函数中拼接好的as [args] <source.c>进行最终可执行文件的生成。 - 若
fork返回值为负数,引发致命错误"fork() failed",afl-as退出。 - 使用
waitpid阻塞主进程,等待子进程将可执行文件的生成过程运行结束,若返回值小于等于0,引发致命错误"waitpid() failed",afl-as退出。 - 若
"AFL_KEEP_ASSEMBLY"环境变量不存在,将插桩后的汇编文件删除。 -
afl-as退出。
0x03 关于__afl_store函数的进一步解释
此部分引用zoniony师傅在AFL源码分析笔记(一)中的表述。
__afl_store函数的内部是用来记录程序执行路径的,那么如何判断这条路径(代码)执行过,后面还要根据这些记录对后面变异有帮助。既要节约空间又要有效率,那单链表之类的肯定不能用,AFL用的是二元tuple(跳转的源地址和目标地址)来记录分支信息。
例如:
A->B->C->D->A-B
可以用[A,B] [B,C] [C,D] [D,A]四个二元组表示,只需要记录跳转的源地址和目标地址。并且[A,B]执行了两次,其余执行了一次,这里用hash映射在一张map中。具体流程如下:
- 为当前分支分配一个随机数$X_1$。
- 此时内存中保存了上一个分支的随机数$X_2$,那么$X_1 \otimes X_2$就代表这个二元
tuple的索引。那么share_mem[$X_1 \otimes X_2$]++就代表记录了此路径。 - 但是考虑一种特殊情况
A->B->A,此时,运算出的结果将为零。因此为了避免这个错误,需要在记录此路径后将此路径的随机数右移一位后再记录。即计算$X_1^{\prime} = X_1 >> 1$,然后记$X_1^{\prime}$为当前分支的随机数。
0x04 编译实例
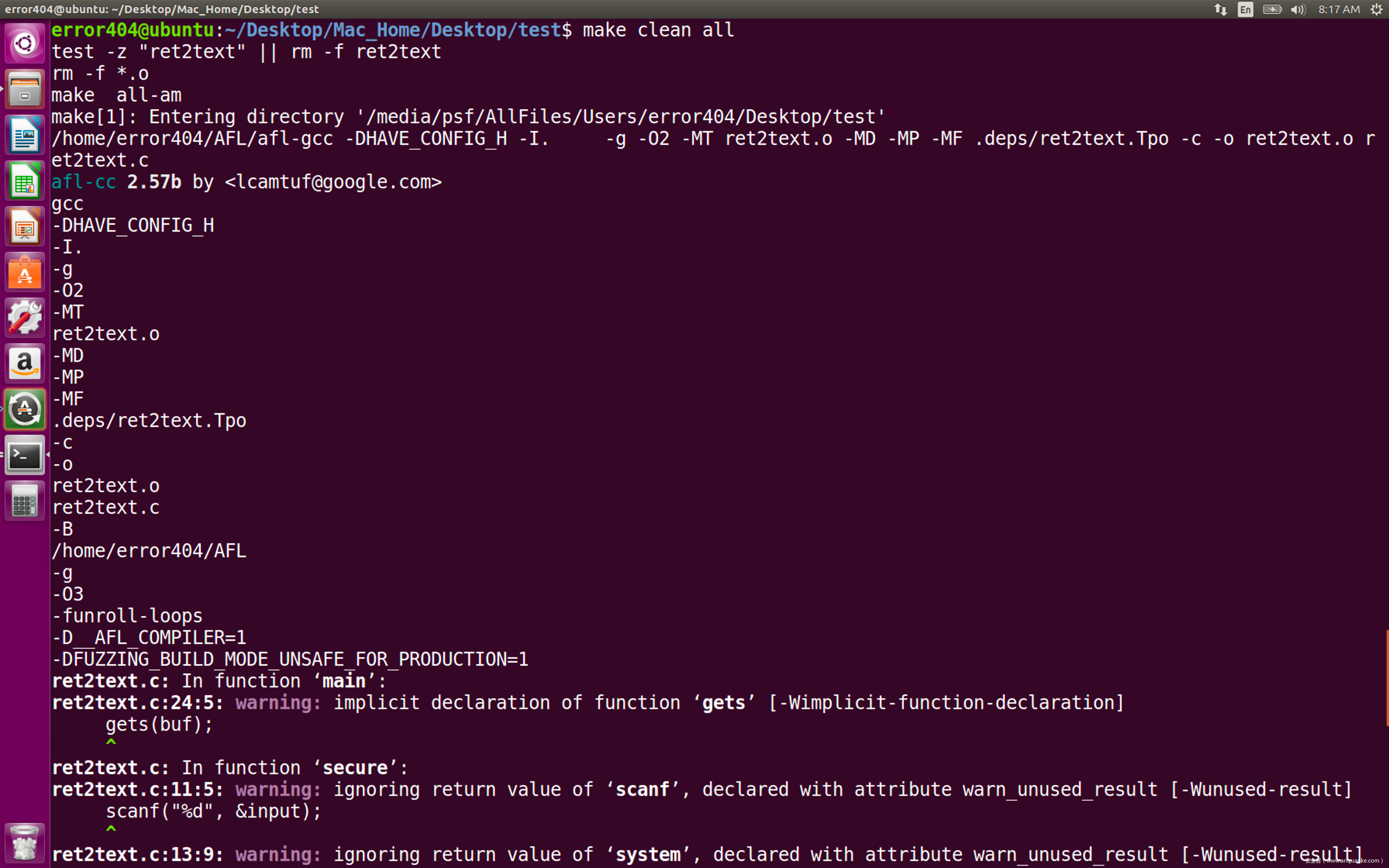
接下来使用
CC=/home/error404/AFL/afl-gcc ./configure --disable-shared
make clean all
进行编译,可以看到afl-gcc确实被执行了,并且编译出的程序存在AFL桩代码
PS:为了方便调试,我的afl-gcc添加了一些打印参数的语句,使用官方仓库时的回显可能与此处不同。
0x04 后记
虽然网上有很多关于AFL源码的分析,但是绝大多数文章都是抽取了部分代码进行分析的,本文则逐行对源码进行了分析,下一篇文章将针对afl-fuzz源码做分析。