1 摘要
Dispatch(调度)负责字节码的调度,每条字节码执行完后由Dispatch负责调度下一条字节码执行,相当于寄存器EIP++、执行下一条字节码。Dispatch是V8维护的全局指令调度机制,它由调度表(dispatch table)、一个物理寄存器和调度函数Dispatch()组成,每条字节码处理程序(Bytecode handler)执行结束后不执行下一条字节码,而是执行函数Dispatch(),由它负责调用下一条字节码。本文讲解Dispatch机制的源码、数据结构和Dispatch()调度方法。
本文内容组织方式:讲解Dispatch机制具体实现(章节2);Dispatch()调度下一条字节码的源码分析(章节3)。
2 Dispatch机制
字节码处理程序的地址存储在Dispatch table中,使用物理寄存器维护。Dispatch table是指针数组,数组元素是Code类型指针,指向一个字节码处理程序。
1. class Code : public HeapObject {
2. public:
3. NEVER_READ_ONLY_SPACE
4. using Flags = uint32_t;
5. #define CODE_KIND_LIST(V) \
6. V(OPTIMIZED_FUNCTION) \
7. V(BYTECODE_HANDLER) \
8. V(STUB) \
9. V(BUILTIN) \
10. V(REGEXP) \
11. V(WASM_FUNCTION) \
12. V(WASM_TO_CAPI_FUNCTION) \
13. V(WASM_TO_JS_FUNCTION) \
14. V(JS_TO_WASM_FUNCTION) \
15. V(JS_TO_JS_FUNCTION) \
16. V(WASM_INTERPRETER_ENTRY) \
17. V(C_WASM_ENTRY)
18. enum Kind {
19. #define DEFINE_CODE_KIND_ENUM(name) name,
20. CODE_KIND_LIST(DEFINE_CODE_KIND_ENUM)
21. #undef DEFINE_CODE_KIND_ENUM
22. NUMBER_OF_KINDS
23. };
24. static const char* Kind2String(Kind kind);
25. #ifdef ENABLE_DISASSEMBLER
26. const char* GetName(Isolate* isolate) const;
27. V8_EXPORT_PRIVATE void Disassemble(const char* name, std::ostream& os,
28. Address current_pc = kNullAddress);
29. #endif
30. //.................省略很多代码....................
31. //.................省略很多代码....................
32. };
注意: 在Isolate中,还有另一个数据表,用于管理所有Builtin,表项也是Code类型。本文的Dispatch table数据表,只包含Code类型为BYTECODE_HANDLER的Builtin地址。
字节码调度由Builtin方法实现,其外层的入口函数为BuildWithMacroAssembler(),代码如下:
1. Code BuildWithMacroAssembler(Isolate* isolate, int32_t builtin_index,
2. MacroAssemblerGenerator generator,
3. const char* s_name) {
4. HandleScope scope(isolate);
5. // Canonicalize handles, so that we can share constant pool entries pointing
6. // to code targets without dereferencing their handles.
7. CanonicalHandleScope canonical(isolate);
8. constexpr int kBufferSize = 32 * KB;
9. byte buffer[kBufferSize];
10. MacroAssembler masm(isolate, BuiltinAssemblerOptions(isolate, builtin_index),
11. CodeObjectRequired::kYes,
12. ExternalAssemblerBuffer(buffer, kBufferSize));
13. masm.set_builtin_index(builtin_index);
14. DCHECK(!masm.has_frame());
15. generator(&masm);
16. int handler_table_offset = 0;
17. // JSEntry builtins are a special case and need to generate a handler table.
18. DCHECK_EQ(Builtins::KindOf(Builtins::kJSEntry), Builtins::ASM);
19. DCHECK_EQ(Builtins::KindOf(Builtins::kJSConstructEntry), Builtins::ASM);
20. DCHECK_EQ(Builtins::KindOf(Builtins::kJSRunMicrotasksEntry), Builtins::ASM);
21. if (Builtins::IsJSEntryVariant(builtin_index)) {
22. handler_table_offset = HandlerTable::EmitReturnTableStart(&masm);
23. HandlerTable::EmitReturnEntry(
24. &masm, 0, isolate->builtins()->js_entry_handler_offset());
25. }
26. //.....................................................
27. //................省略很多.............................
28. }
BuildWithMacroAssembler()的分析方法参见第九篇文章,直接给出它的重要参数:builtin_index值为65,是Builtin编号,generator为Generate_InterpreterEnterBytecodeDispatch,下面是源码:
1. static void Generate_InterpreterEnterBytecode(MacroAssembler* masm) {
2. // Set the return address to the correct point in the interpreter entry
3. // trampoline.
4. Label builtin_trampoline, trampoline_loaded;
5. Smi interpreter_entry_return_pc_offset(
6. masm->isolate()->heap()->interpreter_entry_return_pc_offset());
7. DCHECK_NE(interpreter_entry_return_pc_offset, Smi::kZero);
8. // If the SFI function_data is an InterpreterData, the function will have a
9. // custom copy of the interpreter entry trampoline for profiling. If so,
10. // get the custom trampoline, otherwise grab the entry address of the global
11. // trampoline.
12. __ movq(rbx, Operand(rbp, StandardFrameConstants::kFunctionOffset));
13. __ LoadTaggedPointerField(
14. rbx, FieldOperand(rbx, JSFunction::kSharedFunctionInfoOffset));
15. __ LoadTaggedPointerField(
16. rbx, FieldOperand(rbx, SharedFunctionInfo::kFunctionDataOffset));
17. __ CmpObjectType(rbx, INTERPRETER_DATA_TYPE, kScratchRegister);
18. __ j(not_equal, &builtin_trampoline, Label::kNear);
19. __ movq(rbx,
20. FieldOperand(rbx, InterpreterData::kInterpreterTrampolineOffset));
21. __ addq(rbx, Immediate(Code::kHeaderSize - kHeapObjectTag));
22. __ jmp(&trampoline_loaded, Label::kNear);
23. __ bind(&builtin_trampoline);
24. // TODO(jgruber): Replace this by a lookup in the builtin entry table.
25. __ movq(rbx,
26. __ ExternalReferenceAsOperand(
27. ExternalReference::
28. address_of_interpreter_entry_trampoline_instruction_start(
29. masm->isolate()),
30. kScratchRegister));
31. __ bind(&trampoline_loaded);
32. __ addq(rbx, Immediate(interpreter_entry_return_pc_offset.value()));
33. __ Push(rbx);
34. // Initialize dispatch table register.
35. __ Move(
36. kInterpreterDispatchTableRegister,
37. ExternalReference::interpreter_dispatch_table_address(masm->isolate()));
38. // Get the bytecode array pointer from the frame.
39. __ movq(kInterpreterBytecodeArrayRegister,
40. Operand(rbp, InterpreterFrameConstants::kBytecodeArrayFromFp));
41. if (FLAG_debug_code) {
42. // Check function data field is actually a BytecodeArray object.
43. __ AssertNotSmi(kInterpreterBytecodeArrayRegister);
44. __ CmpObjectType(kInterpreterBytecodeArrayRegister, BYTECODE_ARRAY_TYPE,
45. rbx);
46. __ Assert(
47. equal,
48. AbortReason::kFunctionDataShouldBeBytecodeArrayOnInterpreterEntry);
49. }
50. // Get the target bytecode offset from the frame.
51. __ movq(kInterpreterBytecodeOffsetRegister,
52. Operand(rbp, InterpreterFrameConstants::kBytecodeOffsetFromFp));
53. __ SmiUntag(kInterpreterBytecodeOffsetRegister,
54. kInterpreterBytecodeOffsetRegister);
55. // Dispatch to the target bytecode.
56. __ movzxbq(r11, Operand(kInterpreterBytecodeArrayRegister,
57. kInterpreterBytecodeOffsetRegister, times_1, 0));
58. __ movq(kJavaScriptCallCodeStartRegister,
59. Operand(kInterpreterDispatchTableRegister, r11,
60. times_system_pointer_size, 0));
61. __ jmp(kJavaScriptCallCodeStartRegister);
62. }
63. //================================分隔线=========================
64. //================================分隔线=========================
65. //================================分隔线=========================
66. void Builtins::Generate_InterpreterEnterBytecodeDispatch(MacroAssembler* masm) {
67. Generate_InterpreterEnterBytecode(masm);
68. }
上述代码由两部分组成,Generate_InterpreterEnterBytecodeDispatch()是字节码调度程序的入口,Generate_InterpreterEnterBytecode()是调度的具体实现,下面给出几点重要概念:
(1) Generate_InterpreterEnterBytecodeDispatch()是Builtin方法。它的index为65号(V8版本不同,index可能略有不同)。
(2) V8使用物理寄存器保存Dispatch table地址,寄存器名字为kInterpreterDispatchTableRegister,在实际运行时映射到物理寄存器。使用物理寄存器可以避免指令调度时的入栈出栈,简化指令设计,提高效率。
下面解释代码的重要语句:
(1) 代码35行把dispatch table地址移动到kInterpreterDispatchTableRegister寄存器,ExternalReference::interpreter_dispatch_table_address(masm->isolate())负责从isolate中取出基址,interpreter_dispatch_table_address的源码如下:
1. ExternalReference ExternalReference::interpreter_dispatch_table_address(
2. Isolate* isolate) {
3. return ExternalReference(isolate->interpreter()->dispatch_table_address());
4. }
5. //================================分隔线=========================
6. interpreter::Interpreter* interpreter() const {
7. return interpreter_;
8. }
9. //================================分隔线=========================
10. Address dispatch_table_address() {
11. return reinterpret_cast<Address>(&dispatch_table_[0]);
12. }
上述代码,可以看到dispatch_table_是数组,基址是&dispatch_table_[0],它的位置是isolate->interpreter_->dispatch_table_。
(2) 代码39行从堆栈中获取bytecode array的基址。
(3) 代码51行获取目标bytecode的偏移量(offset)。
(4) 代码56、58行,计算目标bytecode地址,存入kJavaScriptCallCodeStartRegister。
(5) 代码61行,跳转到kJavaScriptCallCodeStartRegister,调度完毕,图1为函数调用堆栈。
3 Dispatch()方法
Dispatch()是字节码处理程序最后调用的方法,故称之为尾部调用(TailCall)方法,下面给出几条字节码处理程序源码:
1. // StaGlobal <name_index> <slot>
2. //
3. // Store the value in the accumulator into the global with name in constant pool
4. // entry <name_index> using FeedBackVector slot <slot>.
5. IGNITION_HANDLER(StaGlobal, InterpreterAssembler) {
6. TNode<Context> context = GetContext();
7. // Store the global via the StoreGlobalIC.
8. TNode<Name> name = CAST(LoadConstantPoolEntryAtOperandIndex(0));
9. TNode<Object> value = GetAccumulator();
10. TNode<IntPtrT> raw_slot = Signed(BytecodeOperandIdx(1));
11. TNode<Smi> smi_slot = SmiTag(raw_slot);
12. TNode<HeapObject> maybe_vector = LoadFeedbackVector();
13. Label no_feedback(this, Label::kDeferred), end(this);
14. GotoIf(IsUndefined(maybe_vector), &no_feedback);
15. CallBuiltin(Builtins::kStoreGlobalIC, context, name, value, smi_slot,
16. maybe_vector);
17. Goto(&end);
18. Bind(&no_feedback);
19. CallRuntime(Runtime::kStoreGlobalICNoFeedback_Miss, context, value, name);
20. Goto(&end);
21. Bind(&end);
22. Dispatch();
23. }
24. // LdaContextSlot <context> <slot_index> <depth>
25. //
26. // Load the object in |slot_index| of the context at |depth| in the context
27. // chain starting at |context| into the accumulator.
28. IGNITION_HANDLER(LdaContextSlot, InterpreterAssembler) {
29. TNode<Context> context = CAST(LoadRegisterAtOperandIndex(0));
30. TNode<IntPtrT> slot_index = Signed(BytecodeOperandIdx(1));
31. TNode<Uint32T> depth = BytecodeOperandUImm(2);
32. TNode<Context> slot_context = GetContextAtDepth(context, depth);
33. TNode<Object> result = LoadContextElement(slot_context, slot_index);
34. SetAccumulator(result);
35. Dispatch();
36. }
37. // LdaImmutableContextSlot <context> <slot_index> <depth>
38. //
39. // Load the object in |slot_index| of the context at |depth| in the context
40. // chain starting at |context| into the accumulator.
41. IGNITION_HANDLER(LdaImmutableContextSlot, InterpreterAssembler) {
42. TNode<Context> context = CAST(LoadRegisterAtOperandIndex(0));
43. TNode<IntPtrT> slot_index = Signed(BytecodeOperandIdx(1));
44. TNode<Uint32T> depth = BytecodeOperandUImm(2);
45. TNode<Context> slot_context = GetContextAtDepth(context, depth);
46. TNode<Object> result = LoadContextElement(slot_context, slot_index);
47. SetAccumulator(result);
48. Dispatch();
49. }
上述代码给出了三条字节码处理程序,它们的尾部都调用了Dispatch()方法。下面给出Dispatch()源码,并解释重要语句。
1. void InterpreterAssembler::Dispatch() {
2. Comment("========= Dispatch");
3. DCHECK_IMPLIES(Bytecodes::MakesCallAlongCriticalPath(bytecode_), made_call_);
4. TNode<IntPtrT> target_offset = Advance();
5. TNode<WordT> target_bytecode = LoadBytecode(target_offset);
6. if (Bytecodes::IsStarLookahead(bytecode_, operand_scale_)) {
7. target_bytecode = StarDispatchLookahead(target_bytecode);
8. }
9. DispatchToBytecode(target_bytecode, BytecodeOffset());
10. }
第2行代码是注释功能,调试代码时很有用;第4行Advance()是获取目标字节码在bytecode array中的偏移量,请读者自行分析;第5行读取目标字节码;第9行进入DispatchToBytecode(),该方法又进入DispatchToBytecodeHandlerEntry(),代码如下:
void InterpreterAssembler::DispatchToBytecodeHandlerEntry(
TNode<RawPtrT> handler_entry, TNode<IntPtrT> bytecode_offset) {
// Propagate speculation poisoning.
TNode<RawPtrT> poisoned_handler_entry =
UncheckedCast<RawPtrT>(WordPoisonOnSpeculation(handler_entry));
TailCallBytecodeDispatch(InterpreterDispatchDescriptor{},
poisoned_handler_entry, GetAccumulatorUnchecked(),
bytecode_offset, BytecodeArrayTaggedPointer(),
DispatchTablePointer());
}
该方法的参数1是目标字节码,它的作用是从dispatch table中索引对应的字节码处理程序;参数2是目标字节码的偏移量,它的作用是从bytecode array中读取操作数,下面进入TailCallBytecodeDispatch():
0. template <class... TArgs>
1. void CodeAssembler::TailCallBytecodeDispatch(
2. const CallInterfaceDescriptor& descriptor, TNode<RawPtrT> target,
3. TArgs... args) {
4. DCHECK_EQ(descriptor.GetParameterCount(), sizeof...(args));
5. auto call_descriptor = Linkage::GetBytecodeDispatchCallDescriptor(
6. zone(), descriptor, descriptor.GetStackParameterCount());
7. Node* nodes[] = {target, args...};
8. CHECK_EQ(descriptor.GetParameterCount() + 1, arraysize(nodes));
9. raw_assembler()->TailCallN(call_descriptor, arraysize(nodes), nodes);
10. }
代码第5行建立目标字节码的call discriptor,见下面代码:
0. CallDescriptor* Linkage::GetBytecodeDispatchCallDescriptor(
1. Zone* zone, const CallInterfaceDescriptor& descriptor,
2. int stack_parameter_count) {
3. const int register_parameter_count = descriptor.GetRegisterParameterCount();
4. const int parameter_count = register_parameter_count + stack_parameter_count;
5. DCHECK_EQ(descriptor.GetReturnCount(), 1);
6. LocationSignature::Builder locations(zone, 1, parameter_count);
7. locations.AddReturn(regloc(kReturnRegister0, descriptor.GetReturnType(0)));
8. for (int i = 0; i < parameter_count; i++) {
9. if (i < register_parameter_count) {
10. // The first parameters go in registers.
11. Register reg = descriptor.GetRegisterParameter(i);
12. MachineType type = descriptor.GetParameterType(i);
13. locations.AddParam(regloc(reg, type));
14. } else {
15. int stack_slot = i - register_parameter_count - stack_parameter_count;
16. locations.AddParam(LinkageLocation::ForCallerFrameSlot(
17. stack_slot, MachineType::AnyTagged()));
18. }
19. }
20. MachineType target_type = MachineType::Pointer();
21. LinkageLocation target_loc = LinkageLocation::ForAnyRegister(target_type);
22. const CallDescriptor::Flags kFlags =
23. CallDescriptor::kCanUseRoots | CallDescriptor::kFixedTargetRegister;
24. return new (zone) CallDescriptor( // --
25. CallDescriptor::kCallAddress, // kind
26. target_type, // target MachineType
27. target_loc, // target location
28. locations.Build(), // location_sig
29. stack_parameter_count, // stack_parameter_count
30. Operator::kNoProperties, // properties
31. kNoCalleeSaved, // callee-saved registers
32. kNoCalleeSaved, // callee-saved fp
33. kFlags, // flags
34. descriptor.DebugName());
35. }
这个函数的参数2是目标字节码,参数3是栈参数的数量,函数的作用是申请寄存器等资源、生成CallDescriptor。CallDescriptor描述了调用字节码时应该提供的参数类型、数量等,代码24行的注释给出了它的布局。
返回TailCallBytecodeDispatch(),第9行raw_assembler()->TailCallN()的第一个参数是CallDescriptor,源码下如:
1. void RawMachineAssembler::TailCallN(CallDescriptor* call_descriptor,
2. int input_count, Node* const* inputs) {
3. // +1 is for target.
4. DCHECK_EQ(input_count, call_descriptor->ParameterCount() + 1);
5. Node* tail_call =
6. MakeNode(common()->TailCall(call_descriptor), input_count, inputs);
7. schedule()->AddTailCall(CurrentBlock(), tail_call);
8. current_block_ = nullptr;
9. }
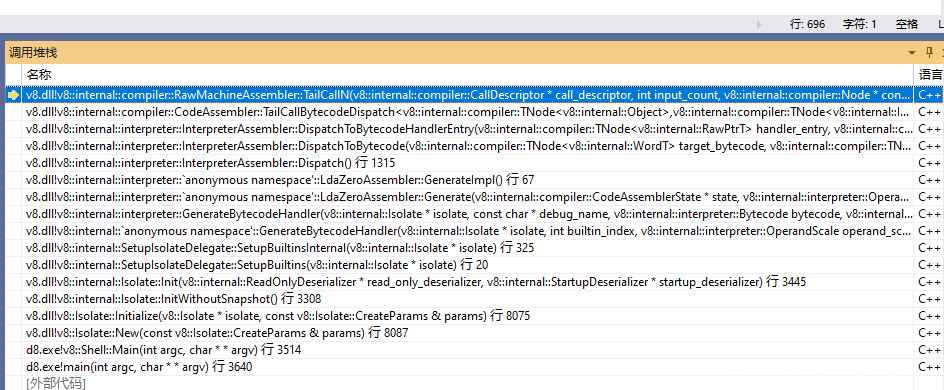
第5行生成Node节点,第7行由AddTailCall()把节点加到当前基本块(Basic Block)的尾部,完成字节码调度,AddTailCall()源码请读者自行分析,图2给出了上述过程的调用堆栈。
学习过程中,需要分析和调试汇编码,思路一旦中断就可能得从头再来,一定要多做笔记。
好了,今天到这里,下次见。
恳请读者批评指正、提出宝贵意见
微信:qq9123013 备注:v8交流 邮箱:v8blink@outlook.com